Medication
The frontal lobe dementia life expectancy can be as long as seventeen years, but some patients only live two years as they soon succumb to complications of the disease. Frontal lobe dementia is distinguished from other types of dementia by the presence of abnormalities in the nerve cells of the brain — known as Pick bodies.
Therapy
Methylphenidate (‘Ritalin’) can Ameliorate Abnormal Risk-Taking Behavior in the Frontal Variant of Frontotemporal Dementia. Shibley Rahman 1, Trevor W Robbins 2, John R Hodges 3,4, Mitul A ...
How long does a person live with frontal lobe dementia?
Variables Impacting Life Expectancy Calculations
- Gender. Men don’t live as long with Alzheimer’s as women. ...
- Age. Someone diagnosed at 65 lives an average of about eight years, while someone over 90 who gets a diagnosis typically lives about three-and-a-half more years.
- Strength of Symptoms at Diagnosis. ...
- Other Health Problems. ...
Can Ritalin help against frontotemporal dementia?
Top 27 Natural Home Remedies For Dementia Patients
- Water. Adults should drink 2-3 liters of water (about 8 glasses of water) every day. ...
- Walking. Among home remedies for dementia, walking is one of the most effective. ...
- Diet Changes. ...
- Get Enough Sleep. ...
- Take Note. ...
- Read Books Regularly. ...
- Avoid Mental Stress. ...
- Learn New Things. ...
- Play Game. ...
- Chew Gum. ...
What is the life expectancy for someone with dementia?
What are the best remedies for dementia?
See more

How long does a person live with frontal lobe dementia?
Duration and Treatment The length of FTD varies, with some patients declining rapidly over two to three years, and others showing only minimal changes over a decade. Studies have shown persons with FTD to live with the disease an average of eight years, with a range from three years to 17 years.
How quickly does frontal lobe dementia progress?
Disease duration in frontotemporal dementia is approximately 7–9 years on average from onset of clinical symptoms.
Does frontotemporal dementia have a cure?
There is currently no cure for FTD, and no treatments slow or stop the progression of the disease, but there are ways to help manage the symptoms.
How do you improve frontotemporal dementia?
Treatments for frontotemporal dementiamedicines – to control some of the behavioural problems.therapies – such as physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and speech and language therapy for problems with movement, everyday tasks and communication.More items...
What are 5 extreme behavior changes found with FTD?
Lack of interest (apathy), which can be mistaken for depression. Repetitive compulsive behavior, such as tapping, clapping or smacking lips. A decline in personal hygiene. Changes in eating habits, usually overeating or developing a preference for sweets and carbohydrates.
What are the main symptoms of frontotemporal lobe dementia?
What are the symptoms of frontotemporal dementia?Behavior and/or dramatic personality changes, such as swearing, stealing, increased interest in sex, or a deterioration in personal hygiene habits.Socially inappropriate, impulsive, or repetitive behaviors.Impaired judgment.Apathy.Lack of empathy.Decreased self awareness.More items...
What I can do to improve my temporal lobe?
Listen to a lot of great music. Music, from country to jazz, from rock to classical, is one of the true joys of life. Music has healing properties. Listening to it can activate and stimulate the temporal lobes and bring peace or excitement to your mind.
Does frontotemporal dementia show up on MRI?
Atrophy or shrinkage of specific regions of the brain that might be suggestive of FTD can be identified by MRI.
Is there a test for frontotemporal dementia?
Genetic testing A specialist may recommend that a person with FTD symptoms has a genetic test. This can show if the person's condition is caused by a specific faulty gene. Knowing this can help the specialist to make a more precise diagnosis and to better understand the changes that are happening in the person's brain.
Is frontal lobe dementia the same as frontotemporal dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is one of the less common types of dementia. It is sometimes called Pick's disease or frontal lobe dementia. The first noticeable FTD symptoms are changes to personality and behaviour and/or difficulties with language.
How to help someone with FTD?
Physical exercise, music or other activities that the person enjoys or finds useful are also very helpful. These activities are often the most effective way of helping a person with FTD to maintain a good quality of life. It is important to try this before considering any drug treatments, such as antipsychotics.
What to do if you have a FTD?
If drugs are being considered, the person with FTD should be referred to a specialist who can advise on the risks and benefits. Remember carers need support too. Changes in behaviour can be very distressing for anyone caring for someone with FTD and it’s important that carers are supported as well.
What can a speech therapist do for a person with FTD?
A speech and language therapist with the right skills and experience can support someone with FTD who is losing their language or speaking abilities. They can help the person get the most out of their existing skills and find new ways for them to communicate.
What are the best professionals to help with FTD?
Supporting a person with FTD often involves a team of professionals that can include a: GP. community nurse. psychiatrist. speech and language therapist. neurologist. social worker. When someone has problems with movement or co-ordination, support from a physiotherapist or occupational therapist can also help.
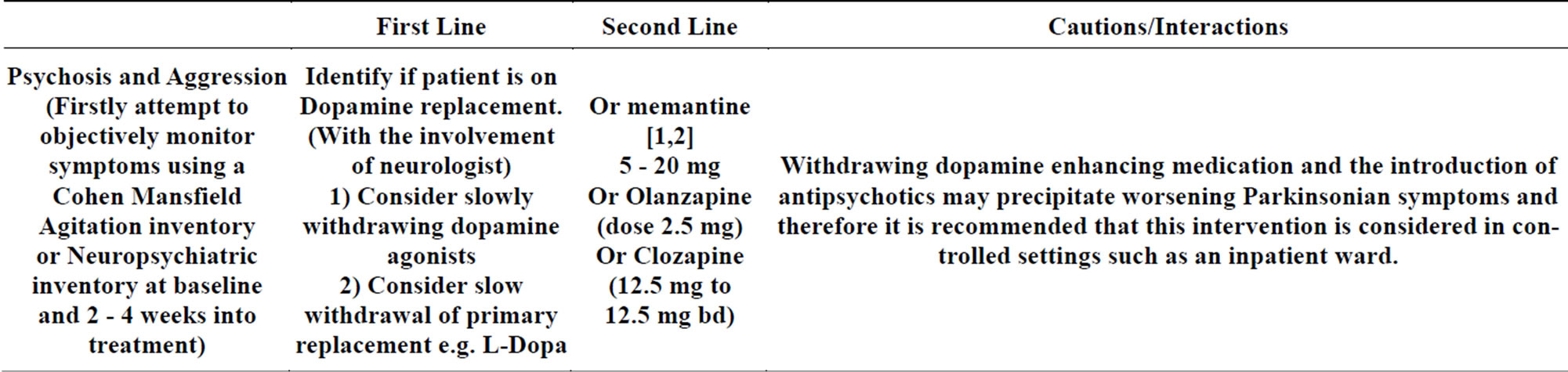
Does donepezil make FTD worse?
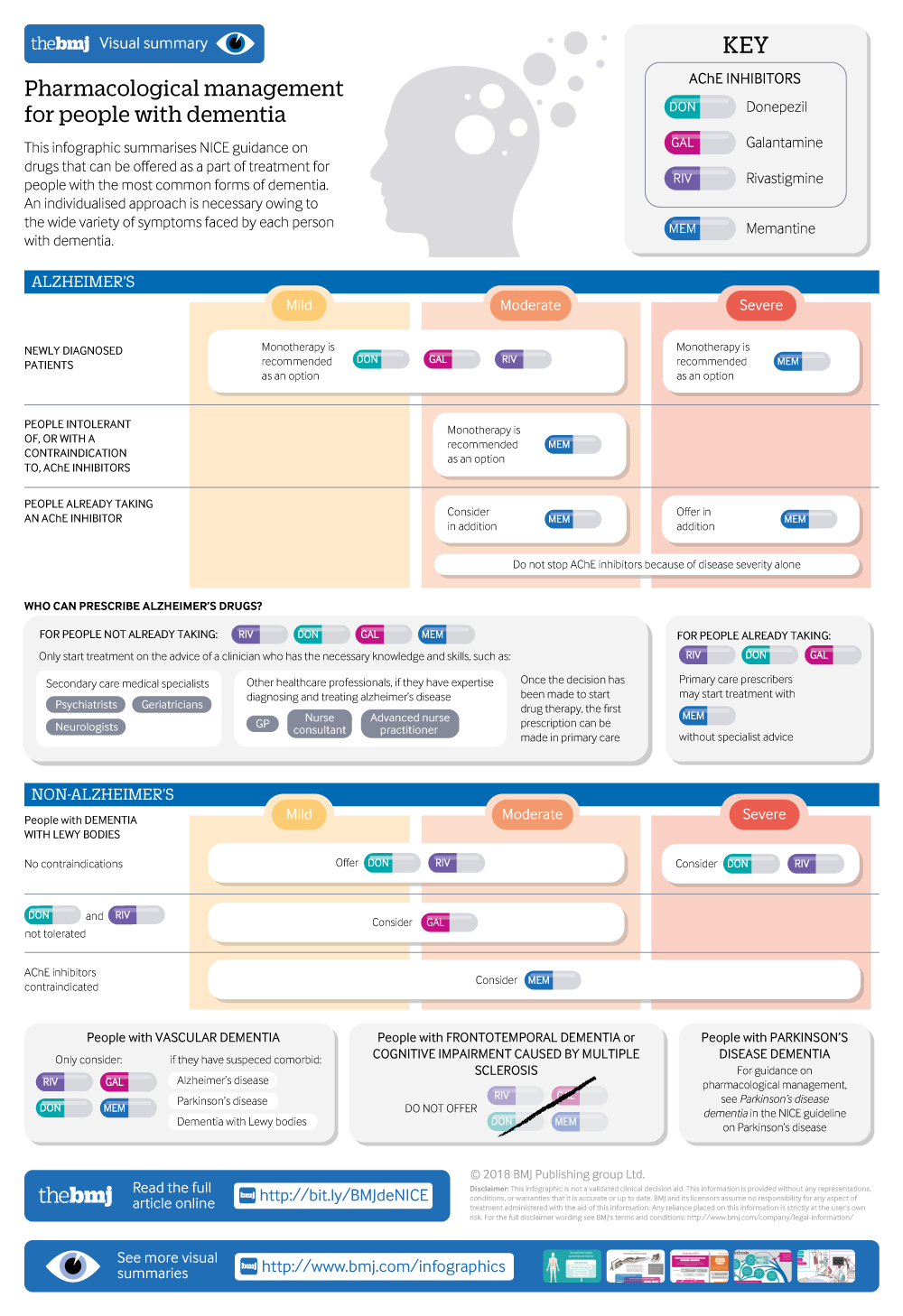
These drugs, known as cholinesterase inhibitors (for example, donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine) can actually make the symptoms of FTD worse. However, there are many other ways to help someone with the condition to live well. Find out more below.
Is there a cure for FTD?
There is currently no cure for frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and the progression of the disease cannot be slowed. However there are many ways to help a person with FTD live well. Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
Can you treat frontotemporal dementia?
There is currently no cure for frontotemporal dementia and the progression of the disease cannot be slowed down. Drugs that are commonly used to treat other types of dementia are not recommended for people with FTD. These drugs, known as cholinesterase inhibitors (for example, donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine) can actually make the symptoms ...
How long does FTD last?
The condition may last from three to 17 years before death, with an average duration of eight years after diagnosis.
Does therapy help with frontotemporal dementia?
Therapy is designed to relieve the symptoms or behaviors caused by frontotemporal dementia, but there is no treatment to stop or reverse the underlying brain deterioration.
Can a FTD patient be a caregiver?
Many FTD patients remain at home and others require nursing home care. Being a caregiver of an FTD patient can be physically and emotionally exhausting. If you are a caregiver, you should seek as much help as possible to carry out your day-to-day tasks.
What is the best treatment for dementia?
physiotherapy – to help with movement difficulties. relaxation techniques – such as massage, and music or dance therapy. social interaction, leisure activities and other dementia activities – such as memory cafes, which are drop-in sessions for people with memory problems and their carers to get support and advice.
Is there a cure for frontotemporal dementia?
There's currently no cure for frontotemporal dementia, but there are treatments that can help manage some of the symptoms.
What is frontotemporal dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia is a group of disorders characterized by the loss of nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, which causes these lobes to shrink. The cause of FTD is unknown. Symptoms typically first occur between the ages of 40 and 65 and can include changes in personality and behavior, ...
What is the cause of dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), a common cause of dementia, is a group of disorders that occur when nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are lost. This causes the lobes to shrink. FTD can affect behavior, personality, language, and movement.
What is the cause of FTD?
The cause of FTD is unknown. Researchers have linked certain subtypes of FTD to mutations on several genes. Some people with FTD have tiny structures, called Pick bodies, in their brain cells. Pick bodies contain an abnormal amount or type of protein.
What is the most common type of FTD?
FTD affects men and women equally. The most common types of FTD are: Frontal variant. This form of FTD affects behavior and personality. Primary progressive aphasia. Aphasia means difficulty communicating. This form has two subtypes: Progressive nonfluent aphasia, which affects the ability to speak. Semantic dementia, which affects the ability ...
When does FTD start?
Symptoms typically first occur between the ages of 40 and 65 and can include changes in personality and behavior, progressive loss of speech and language skills, and sometimes physical symptoms such as tremors or spasms. FTD tends to progress over time.
Is FTD life threatening?
FTD is not life-threatening ─ people may live with it for years. But it can lead to an increased risk for other illnesses that can be more serious. Pneumonia is the most common cause of death, with FTD. People are also at increased risk for infections and fall-related injuries.
Can family members take FTD personally?
Coping with FTD can be frightening, frustrating, and embarrassing for the patient and family members. Since some symptoms can’t be controlled, family members should n't take their loved one’s behaviors personally . Families need to maintain their own well-being, while ensuring that their loved one is treated with dignity and respect.
What are the symptoms of frontotemporal dementia?
Many possible symptoms can result, including unusual behaviors, emotional problems, trouble communicating, difficulty with work, or difficulty with walking. Frontotemporal disorders are forms of dementia caused by a family of brain diseases known as frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). Dementia is a severe loss of thinking abilities ...
How is frontotemporal disorder diagnosed?
Frontotemporal disorders are diagnosed by physicians and psychologists based on a person’s symptoms and results of brain scans and genetic tests. With the exception of known genetic causes, FTLD can be identified definitively only by brain autopsy after death.
How long can a person live with FTLD?
Roughly 60 percent of people with FTLD are 45 to 64 years old. People can live with frontotemporal disorders for up to 10 years, sometimes longer, but it is difficult to predict the time course for an individual patient. The disorders are progressive, meaning symptoms get worse over time.
What is frontotemporal disorder?
What Are Frontotemporal Disorders? Damage to the brain’s frontal and temporal lobes causes forms of dementia called frontotemporal disorders. Frontotemporal disorders are the result of damage to neurons (nerve cells) in parts of the brain called the frontal and temporal lobes. As neurons die in the frontal and temporal regions, these lobes atrophy, ...
What did Brian's counselor recommend?
Three years after Brian’s symptoms began, his counselor recommended a neurological evaluation.
How to contact the NIA about Alzheimer's?
800-438-4380 (toll-free) [email protected]. www.nia.nih.gov/alzheimers. The National Institute on Aging’s ADEAR Center offers information and free print publications about Alzheimer’s and related dementias for families, caregivers, and health professionals.
Why are temporal lobes important?
They allow people to recognize objects and to relate appropriate emotions to objects and events. When the temporal lobes are dysfunctional, people may have difficulty recognizing emotions and responding appropriately to them.
What is frontotemporal dementia?
More Resources on Frontotemporal Dementia. Frontotemporal dementia is caused by a group of disorders that gradually damage the brain’s frontal and temporal lobes. These damages cause changes in thinking and behaviors. Symptoms can include unusual behaviors, emotional problems, trouble communicating, challenges with work, and difficulty with walking.
Why is frontotemporal dementia so hard to diagnose?
Frontotemporal dementia can be hard to diagnose because symptoms are similar to other conditions. Also, because these disorders are rare, physicians may be unfamiliar with the signs and symptoms. Talking with patients, family members, and caregivers can help doctors make a diagnosis.
What are the other movement disorders?
Other movement-related disorders include frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism and frontotemporal dementia with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (FTD-ALS). Symptoms can vary among these movement disorders.
What are the two types of movement disorders associated with FTD?
There are two types of rare movement disorders associated with FTD: corticobasal syndrome and progressive supranuclear palsy. Other movement-related disorders include frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism and frontotemporal dementia with amyotrophic ...
How long does it take for FTD to get worse?
FTD is progressive, meaning symptoms get worse over time. It can take less than two years to progress in some people, whereas in others it can take more than 10 years. High levels of care, such as 24-hour care, may be needed over time.
What is the difference between PPA and dementia?
This dementia involves changes in personality, behavior, emotions, and judgment. Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) involves changes in the ability to communicate — to speak, read, write, and understand what others are saying. Movement disorders happen when the parts of the brain that control movement are affected.
Can mutations cause FTD?
In some cases, mutations or changes in genes can be identified as the cause of FTD. For example, about 10% to 30% of bvFTD cases can be attributed to genetic causes. People with a family history of frontotemporal dementias are more likely to have a genetic form of the disease.
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- There's no single test for frontotemporal dementia. Doctors look for signs and symptoms of the disease and try to exclude other possible causes. The disorder can be especially challenging to diagnose early because symptoms of frontotemporal dementia often overlap with those of othe…