
- The main treatments for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer include surgery, BCG (immunotherapy) and intravesical chemotherapy. You may have surgery alone or a combination of these treatments.
- Most people have a transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT) operation. This is done during a cystoscopy under general anaesthetic.
- In a TURBT, a slender tube is passed through the urethra and into the bladder, and the doctor uses a wire loop to remove the cancer.
- TURBT can be repeated if the cancer comes back.
- Immunotherapy uses a vaccine known as Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), which causes the body's immune system to try to destroy the cancer. It is inserted directly into the bladder. ...
- BCG may cause flu-like side effects. Because it is a live vaccine, you will need to take some safety precautions at home.
- Chemotherapy drugs may be put directly into the bladder through a flexible tube called a catheter. This is called intravesical chemotherapy.
- Each time the chemotherapy drugs are inserted, it is called an instillation.
- The most common side effect of intravesical chemotherapy is bladder inflammation (cystitis).
What are the treatments for non-invasive bladder cancer?
Since bladder cancer tends to recur, patients diagnosed with non-invasive bladder cancer need to be scrupulous about maintaining their prescribed checkups. The treatments for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer are different from more advanced disease. Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer is often treated by removal of the tumor.
What chemotherapy is used for bladder radiation therapy?
This is also known as the bladder preservation approach or trimodal therapy. The type of chemotherapy used for patients undergoing bladder radiation therapy can include cisplatin alone or a combination of a drug called mitomycin-C (available as a generic drug) and fluorouracil (5-FU).
What is neoadjuvant therapy for bladder cancer?
Neoadjuvant therapy is treatment that is given before surgery, such as chemotherapy. The treatments your doctor recommends mainly depend on the stage of bladder cancer. Treatment for cancer in the renal pelvis and/or ureter follow the same treatment plans based on the stage of the disease.
Is there a cure for Stage 4 bladder cancer?
Metastatic bladder cancer (stage IV) A combination of treatments may be used to help manage the cancer. There are no methods to permanently cure metastatic bladder cancer for most people. The goals of treatment are to slow the spread of cancer, shrink the tumor (called remission), and extend life for as long as possible.
What is the first treatment for bladder cancer?
What is stage 0 bladder cancer?
What is the treatment for T3 tumors?
What to do if you have cancer that hasn't been removed?
How to get rid of stage IV cancer?
What is the treatment for cancer that recurs in distant parts of the body?
Can you get a partial cystectomy for bladder cancer?
See more
About this website
What is the best treatment for superficial bladder cancer?
The main treatment for superficial bladder cancer is TURBT or TUR (transurethral resection), which is used to remove the entire tumor. That may be all you need at this time. The tumor grade will help determine if you need further treatment. In some cases, you may need chemotherapy.
What is the main treatment objective with non invasive bladder carcinoma?
If cancer cells are found only in the inner layers of the bladder (non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer or NMIBC), the main treatment is surgery to remove the cancer. Surgery is commonly combined with chemotherapy or immunotherapy, which is delivered directly into the bladder (intravesical).
Can low grade non invasive bladder cancer be cured?
People with low-grade noninvasive bladder cancer (stage 0a) are treated with transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) first. Low-grade noninvasive bladder cancer rarely turns into aggressive, invasive, or metastatic disease, but patients are at risk for developing more low-grade cancers throughout their life.
Does non invasive bladder cancer spread?
Over time, the cancer may grow outside the bladder into tissues close by. Bladder cancer may spread to lymph nodes nearby and others farther away. The cancer may reach the bones, the lungs, or the liver and other parts of the body.
How long does it take for your bladder to heal after TURBT?
How fast you recover varies from person to person, but generally the lining of the bladder will heal in about 10 days. You can usually get back to most normal activities by two weeks (but don't do anything too strenuous). Ask your surgeon when you can go back to work.
Is a 5 cm bladder tumor large?
CONCLUSIONS: Larger tumor size (>5 cm) is associated with greater length of stay, reoperation, readmission, and death following TURBT. Patients should be counseled appropriately and likely warrant vigilant observation prior to and following hospital discharge.
What is the survival rate for non invasive bladder cancer?
Survival by stageStage5-year relative survivalcancer is only in the inner lining of the bladder (non-invasive or stage 0)95%cancer is only in the deeper layers of the bladder wall (invasive and localized)69%cancer has spread to nearby areas, such as lymph nodes (regional)35%1 more row
How often does low grade bladder cancer come back?
In our population of initially diagnosed low grade Ta bladder tumors, the recurrence rate and WP rate were 43.2% and 11.1%, respectively.
How often does low grade bladder cancer become high grade?
70% of patients experience recurrent low-grade tumors, with low rates of progression, 5–15%, to a higher grade or stage [2, 22].
What does non invasive cancer mean?
(NON-in-VAY-siv) In medicine, it describes a procedure that does not require inserting an instrument through the skin or into a body opening. In cancer, it describes disease that has not spread outside the tissue in which it began.
Is superficial bladder cancer curable?
Bladder cancer is related to a history of smoking, but other factors including job-related and environmental exposures can cause the cancer. Fortunately, superficial bladder cancer is highly treatable.
What is the life expectancy of someone with bladder cancer?
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time (usually 5 years) after they were diagnosed....5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer.SEER Stage5-year Relative Survival RateAll SEER stages combined77%3 more rows•Mar 1, 2022
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
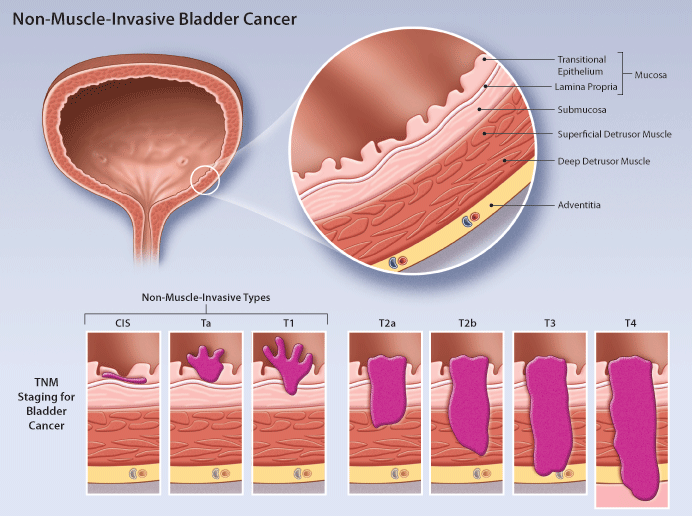
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis). In either case, the cancer has not inv...
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall but have not reached the muscle layer.Transurethral resecti...
Treating Stage II Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall. Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typically the first treatment for these cancers...
Treating Stage III Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs.Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typical...
Treating Stage IV Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the abdominal or pelvic wall (T4b tumors) or have spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. Stage IV ca...
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment (progresses) or comes back (recurs), your treatment options will depend on where and how much the canc...
Bladder Cancer: Stages and Grades
ON THIS PAGE: You will learn about how doctors describe a cancer’s growth or spread, as well as the way the tumor cells look when viewed under a microscope. This is called the stage and grade. Use the menu to see other pages.What is cancer staging?Staging is a way of describing where the cancer is located, if or where it has invaded or spread, and whether it is affecting other parts of the body.
Staging and grading of bladder cancer - Macmillan Cancer Support
Your cancer doctor needs certain information about the cancer to advise you on the best treatment for you. This includes the stage of the bladder cancer and its grade. They get this information from the tests you have.
BCG Treatment for Bladder Cancer: What You Need to Know
Jennifer Welsh is a Connecticut-based science writer and editor with over ten years of experience under her belt. She’s previously worked and written for WIRED Science, The Scientist, Discover Magazine, LiveScience, and Business Insider.
What is the next step to confirm bladder cancer?
If any of these tests suggest that you have bladder cancer, the next step to confirm the diagnosis is a transurethral resection of a bladder tumor (TUR BT) described below. You will likely be put to sleep for this procedure. During a TURBT the doctor will both try to remove all visible tumors and take tissue.
What is bladder cancer?
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) is cancer found in the tissue that lines the inner surface of the bladder. The bladder muscle is not involved. Bladder cancer is the 6th most common cancer in the United States. Nearly 84,000 people will be diagnosed in the United States with bladder cancer in 2021.
How is a TURBT done?
Transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) is usually done under anesthesia. The surgery is done through the urethra using a cystoscope, so there is no cutting into the abdomen. You will be given general or spinal anesthesia.
What is the tube that a doctor uses to see the bladder?
Cystoscopy : A doctor will use a thin tube that has a light and camera at the end of it (cystoscope) to pass through the urethra into the bladder. It allows your doctor to see inside the bladder cavity. Usually your doctor will use a flexible cystoscope and a local anesthetic for your exam in the office.
How to tell the stage of bladder cancer?
The tumor stage tells how much of the tissue has the cancer. Doctors can tell the grade and stage of bladder cancer by taking a small sample of the tumor. This is called a biopsy. A pathologist in a lab examines the sample under a microscope and determines the grade and stage of the cancer.
How many people will have bladder cancer in 2021?
Nearly 84,000 people will be diagnosed in the United States with bladder cancer in 2021. Bladder cancer is more common in males than females. Three times more men than women tend to get this disease. Bladder cancer is more common as a person grows older. It is found most often in the age group of 75-84.
How many patients with low grade T1 cancer will have a tumor recurrence?
Over half of patients with low-grade Ta cancers will have a tumor recurrence. About 6% will progress to a higher stage. High-grade T1 cancers recur at a rate of about 45% and 17% of these will probably progress to a higher stage.
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Immunotherapy is a cancer treatment approach that uses drugs and vaccines to harness the immune system’s natural ability to fight cancer, in the same way it fights off infections. The approach is still being researched and there is a lot left to learn, but clinical studies have shown that immunotherapy holds a lot of promise in its ability to treat a wide range of malignancies, including some types of bladder cancer.
What is the procedure to remove a bladder tumor?
Cystectomy (Bladder Removal) Surgery. When bladder cancer tumors completely invade the bladder’s muscular wall, the standard of care is to perform bladder removal surgery. Typically, complete removal of the bladder ( radical cystectomy) is required. Partial cystectomy is rare because the requirements are that the tumor is easily accessible ...
What is the procedure called when a camera is passed through the urethra?
Cystoscopy is an outpatient procedure during which a thin, lighted tube with a camera is passed through the urethra into the bladder, allowing your doctor to see the inside of the bladder.
What percentage of bladder cancer is superficial?
Bladder Cancer Liver Gallbladder and Pancreas Urological Conditions Cancer. Over 75 percent of bladder cancers remain confined to the lining of the bladder and do not invade the bladder wall. These are called nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer, or superficial bladder cancer, and when managed well, they are associated with excellent prognoses.
Why is partial cystectomy rare?
Partial cystectomy is rare because the requirements are that the tumor is easily accessible and small in size, and that there are no tumors in the rest of the bladder. This approach is usually used only if the cancer has not left its site of origin.
What is a TUR procedure?
Transurethral resection (TUR) is an endoscopic or scope procedure that does not involve making an incision in the body. Drug therapy after TUR is commonly prescribed for patients with large, multiple or high-grade tumors.
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy, used to treat cancer, is a special high-energy X-ray that is more powerful than the X-rays used for imaging studies. Radiation therapy is planned and executed in a way to kill cancer cells or alter their ability to reproduce, while the surrounding healthy cells are minimally affected.
How long does it take to remove bladder cancer?
This is done during a cystoscopy under a general anaesthetic. It takes 15–40 minutes, and does not involve any external cuts to the body.
How to remove cancer cells from the urethra?
The surgeon may use a wire loop on the cystoscope to remove the tumour through the urethra. Other methods for destroying cancer cells include burning the base of the tumour with the cystoscope (fulguration), or using a high-energy laser.
What is the name of the tube that is put into the bladder to administer chemo?
Chemotherapy drugs may be put directly into the bladder through a flexible tube called a catheter. This is called intravesical chemotherapy. Each time the chemotherapy drugs are inserted, it is called an instillation. The most common side effect of intravesical chemotherapy is bladder inflammation (cystitis).
What is the tube that drains urine into a bag called?
You may have a thin tube (catheter) in your bladder to drain your urine into a bag. The catheter may be connected to a system that washes the blood and blood clots out of your bladder. This is known as bladder irrigation.
How long does it take for a BCG to be put in the bladder?
You may be asked to change position every 15 minutes so the vaccine washes over the entire bladder. Each treatment session takes up to two hours. For most people, the initial course of weekly BCG treatments is followed by what is known as maintenance BCG.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with anti-cancer (cytotoxic) drugs. It aims to kill cancer cells while doing the least possible damage to healthy cells. Although the drugs are usually given as tablets or injected into a vein (systemic chemotherapy), in intravesical chemotherapy the drugs are put directly into the bladder using a flexible tube called a catheter, which has been inserted through the urethra.
Can bladder cancer be treated with intravenous chemo?
Intravesical chemotherapy is used only for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. It helps keep the cancer from coming back (recurrence). This form of chemotherapy can't reach cancer cells outside of the bladder lining or other parts of the body, so it's not suitable for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Each treatment is called an instillation.
How to treat stage 0A bladder cancer?
But to help keep these cancers from coming back, you may also need intravesical therapy—a treatment that is put directly into the bladder using a catheter.
What is non-muscle invasive bladder cancer?
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer is when the tumor (s) have not spread into the bladder muscle. These tumors are Stage 0 (which can be further divided into stage 0a and stage 0is/Tis) or Stage I (1) bladder cancer. Learn more about staging. Ask your health care team about the short- and long-term side effects your treatment may cause ...
How often should I have my bladder removed?
If your cancer doesn’t come back, follow-up visits can be spaced longer apart, such as every 6 months or once a year. If you are at high risk for recurrence or you have many recurrences, your doctor may recommend that you have your bladder removed. This is called a cystectomy.
How often do you have to see a urologist for a TURBT?
If you have Stage 0is or Stage I (1), your urologist may have you come back about 4 to 6 weeks for another TURBT. Then, you will have additional cystoscopies and other tests every three months.
Can bladder cancer be treated with clinical trials?
Patients with non-muscle and muscle-invasive bladder cancer, may want to consider clinical trials as treatment options. These research studies might be investigating new drugs, new drug combinations, or new surgical or radiation techniques. Or, they might be looking at ways to help cancer survivors. Learn more about clinical trials.
Can bladder cancer come back?
Bladder cancer has a high risk of coming back. You will need to have routine follow-up tests and exams to find a recurrence as early as possible. If you have a Stage 0a noninvasive papillary tumor, the TURB-T that removes the tumor will be the only treatment you need. However, you will need to see your urologist regularly for cystoscopies ...
What is the best treatment for bladder cancer?
In general, the main treatment options for bladder cancer are: Surgery. Chemotherapy. Immunotherapy (local and systemic) Targeted therapy. Radiation therapy. To learn more about the basics of each type of treatment, read this guide’s Types of Treatment section.
What is the first line of treatment for urothelial cancer?
The first treatment a person is given for advanced urothelial cancer is called first-line therapy . If that treatment stops working, then a person receives second-line therapy.
What is stage IV bladder cancer?
Metastatic urothelial cancer (stage IV) If bladder cancer has spread to another part of the body, doctors call it metastatic bladder cancer. If this happens, it is a good idea to talk with doctors, usually medical oncologists, who have experience in treating it.
What is stage 0A in TURBT?
People with low-grade noninvasive bladder cancer (stage 0a) are treated with TURBT first. Low-grade noninvasive bladder cancer rarely turns into aggressive, invasive, or metastatic disease, but patients are at risk for developing more low-grade cancers throughout their life.
What is neoadjuvant therapy?
Neoadjuvant therapy is treatment that is given before surgery, such as cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The treatments your doctor recommends mainly depend on the stage of bladder cancer. Treatment for cancer in the renal pelvis and/or ureter follow the same treatment plans based on the stage of the disease.
Can you get a TURBT before surgery?
Sometimes, people with muscle-invasive bladder cancer receive systemic chemotherapy first, before surgery.
Can pembrolizumab be used for bladder cancer?
Pembrolizumab is approved by the FDA to treat bladder cancer that has not been stopped by, or responded to, BCG treatment (also called “BCG-unresponsive”) and radical cystectomy to remove the bladder cannot be done because of other medical reasons or the patient chooses not to have that surgery.
What should a clinician do when diagnosing bladder cancer?
(Clinical Principle) A clinician should perform upper urinary tract imaging as a component of the initial evaluation of a patient with bladder cancer.
Is MIBC a surrogate endpoint?
The survival rate for the majority of patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) is favorable; however, the rates of recurrence and progression to muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) are important surrogate endpoints for overall prognosis, as these are major determinants of long-term outcome.
With Dr. Amy Luckenbaugh
You can read the entire Understanding Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer webinar transcript at the bottom of this page.
Full Transcript
Welcome to understanding non muscle invasive bladder cancer, a patient insight webinar from the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network.
What is the first treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemo (with or without radiation) is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (M1). After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it's gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done.
What is stage 0 bladder cancer?
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis or carcinoma in situ). In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded (spread deeper into) the bladder wall.
What is the treatment for T3 tumors?
An option for some patients with single, small tumors (some T3) might be treatment with a second (and more extensive) transurethral resection (TURBT) followed by a combination of chemo and radiation. If cancer is still found when cystoscopy is repeated, cystectomy might be needed.
What to do if you have cancer that hasn't been removed?
(Less often, close follow-up alone might be an option.) If all of the cancer wasn't removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy (removal of part or all of the bladder).
How to get rid of stage IV cancer?
The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options.
What is the treatment for cancer that recurs in distant parts of the body?
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy , might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
Can you get a partial cystectomy for bladder cancer?
Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients . Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo.
