What doctor treats erythromelalgia?
- Information Clearinghouse
- One AMS Circle
- Bethesda, MD 20892-3675 USA
- Phone: (301) 495-4484
- Toll-free: (877) 226-4267
- Email: [email protected]
- Website: http://www.niams.nih.gov/
Is there any natural treatment for erythromelalgia?
Treatments for eM There is no cure for EM. While it is true that treating an underlying disease may sometimes bring complete relief from EM symptoms, most cases of EM cannot be fully treated. In such cases, treatment focuses on relieving symptoms with medications and other techniques. It frequently takes a period of trial and error
What type of doctors treat erythromelalgia?
- What is the difference between primary and secondary erythromelalgia?
- How do doctors test for erythromelalgia? I have flare ups on my hands, feet, and face.
- Why are my feet/hands sometimes burning hot and other times painfully cold?
- Can certain foods cause flare-ups of erythromelalgia?
- Do symptoms of primary erythromelalgia worsen overtime?
Can erythromelalgia be cured?
Erythromelalgia can't be cured, but it sometimes gets better by itself. Many people find gently cooling the area helps. Raising the affected area can also help. If you have erythromelalgia, wearing loose clothing and not letting yourself get too hot can help prevent or reduce attacks. Keeping the room at a steady temperature can be helpful.

Is erythromelalgia serious?
Erythromelalgia can be mild, but it can also be very severe. It can be worse in warm weather, or when the hands and feet get hot (for example, wearing socks and shoes). Severe erythromelalgia can cause ongoing pain and affect your quality of life. It can also interfere with walking and other activities.
What medications can cause erythromelalgia?
Other causes associated with erythromelalgia include drugs such as verapamil, nicardipine, bromocryptine, pergolide, and mercury poisoning, and diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Raynaud's disease, pernicious anemia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, infectious mononucleosis and diabetic neuropathy.
What helps with erythromelalgia?
Erythromelalgia treatment may also include:Lidocaine infusions, a pain medication you receive through a vein in your arm.Nutritional supplements, such as magnesium and alpha-lipoic acid.Pain management therapies, including nerve blocks.Topical medications, such as creams you apply to your skin.
Is there a test for erythromelalgia?
Diagnosis of erythromelalgia is based on the symptoms and the increase in skin temperature. Tests, such as blood cell counts, are usually done to help identify a cause. Genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of hereditary erythromelalgia in a person who has onset of symptoms in childhood.
What causes erythromelalgia flare ups?
Some people with erythromelalgia have a faulty gene that causes the condition. Erythromelalgia can run in families when the faulty gene is passed down (inherited) from a parent to their child. The faulty gene causes changes in the way pain signals are delivered to the brain, increasing or strengthening them.
What vitamins help erythromelalgia?
Some nutritional supplements may be used to treat EM symptoms. For example, magnesium is a calcium-channel blocker and vasodilator that has been helpful for many EM patients. [43] Another supplement, alpha lipoic acid, has been used for decades for nerve injuries like those present in some people with EM.
Do steroids help with erythromelalgia?
“Perhaps any erythromelalgia patient could benefit from a trial of oral or intravenous corticosteroids. However, high doses may be required for efficacy,” Dr. Pagani-Estévez said. “ Those who received at least 200 mg prednisone cumulatively tended to respond better.
Does erythromelalgia have a cure?
There is no single “cure” for EM. While it is true that treating an underlying disease may sometimes bring complete relief, most cases of EM cannot be fully treated. In such cases, treatment must focus on relieving symptoms with medications and other techniques.
Can magnesium cure erythromelalgia?
Magnesium is one of the most important elements in the human body. A vast literature on magnesium suggests that it may be useful in a variety of vascular disorders including not only erythromelalgia, but also hypertension, migraine headaches, and Raynaud's phenomenon.
How much aspirin should I take for erythromelalgia?
The standard treatment is from 325 mg to 650 mg of aspirin per day. Aspirin prevents platelet aggravation through an irreversible inhibition of cyclooxygenase; the effect of a single dose of 500 mg aspirin usually lasts for about three days.
Do Antihistamines help erythromelalgia?
A survey of the members of The Erythromelalgia Association reported marked improvement in 40% of patients with antihistamine, but not in 60%. This includes use of desloratadine, chlorpheniramine, and diphenhydramine.
Is erythromelalgia an autoimmune disease?
These findings suggest an underlying autoimmune component to the development of erythermalgia. Erythermalgia is a rare condition comprising a triad of symptoms including red, hot, painful distal extremities in the setting of a trigger, such as exercise or warmth.
Is there a medication for erythromelalgia?
Keep in mind the studies are case reports or small series as there are no medications approved for erythromelalgia.
Is erythromelalgia rare?
Erythromelalgia is a rare conditions (incidence of 0.6-2/100,000) without a clearly defined pathogenesis, creating challenges in defining an effective therapy. The association with myeloproliferative diseases, autoimmune diseases, neuropathies and infections would argue that these diseases or conditions should be treated but the impact on ...
Why is erythromelalgia so difficult to treat?
Treatment. Erythromelalgia can be challenging to treat because no two cases are the same. The response to different treatment options varies among individuals, and it can be a case of trial and error before a person , with the help of their doctor, finds what works for them.
What causes secondary erythromelalgia?
The most common causes include: nerve damage due to injuries or other conditions, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, sciatica, and frostbite. autoimmune diseases, including lupus, vasculitis, and rheumatoid arthritis. multiple sclerosis.
What causes burning pain in the extremities?
Management. Summary. Erythromelalgia is a rare condition that causes episodes of burning pain in the extremities. It mostly affects the feet, but people can also experience symptoms in the arms, hands, ears, legs, and face. According to the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD), erythromelalgia ...
How do you know if you have erythromelalgia?
According to The Erythromelalgia Association (TEA), other symptoms can include: swelling of the affected area. sweating more or less than the person usually would, but only in the affected area. purple discoloration when they are not experiencing an episode.
What is the best way to relieve heat pain?
Topical medications. These can come in the form of creams, gels, sprays, or patches. They include lidocaine, a local anesthetic to help numb the pain, and capsaicin creams or patches, which make the heat receptors in the skin less sensitive.
Is erythromelalgia rare?
According to the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD), erythromelalgia (EM) is rare and can affect either one or both sides of the body. In this article, we discuss the symptoms and causes of EM, as well as how to treat it and when to seek help.
What causes erythromelalgia?
About 15% of cases of erythromelalgia are caused by mutations in the SCN9A gene. The SCN9A gene gives instructions for making part of a sodium channel which carries sodium into cells and helps them make and transmit electrical signals. These sodium channels are found in nerve cells that transmit pain signals to the spine and brain. Mutations that cause erythromelalgia cause increased transmission of pain signals, leading to the signs and symptoms of the condition. In some of these cases, an affected individual inherits the mutation from an affected parent. In other cases, a new mutation occurs for the first time in an individual with no history of the condition in the family. [2]
What is the name of the condition where the hands and feet are red and burning?
Erythromelalgia (EM) is a rare condition characterized by episodes of burning pain, warmth, swelling and redness in parts of the body, particularly the hands and feet. This condition may occur spontaneously (primary EM) or secondary to neurological diseases, autoimmune diseases, or myeloproliferative disorders (secondary EM).
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
What causes SCN9A mutations?
About 15% of cases are caused by mutations in the SCN9A gene and are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Other cases may be caused by unidentified genes or by non-genetic factors. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include topical and/ or oral medications.
What is the TEA guide?
The Erythromelalgia Association (TEA) has a Patient Guide which includes helpful information about diagnosing EM. This guide can be used as an educational and awareness tool for patients, family and friends, and health care providers.
What is an orphanet?
Orphanet is a European reference portal for information on rare diseases and orphan drugs. Access to this database is free of charge. PubMed is a searchable database of medical literature and lists journal articles that discuss Erythromelalgia. Click on the link to view a sample search on this topic.
What is support and advocacy?
Support and advocacy groups can help you connect with other patients and families, and they can provide valuable services. Many develop patient-centered information and are the driving force behind research for better treatments and possible cures. They can direct you to research, resources, and services.
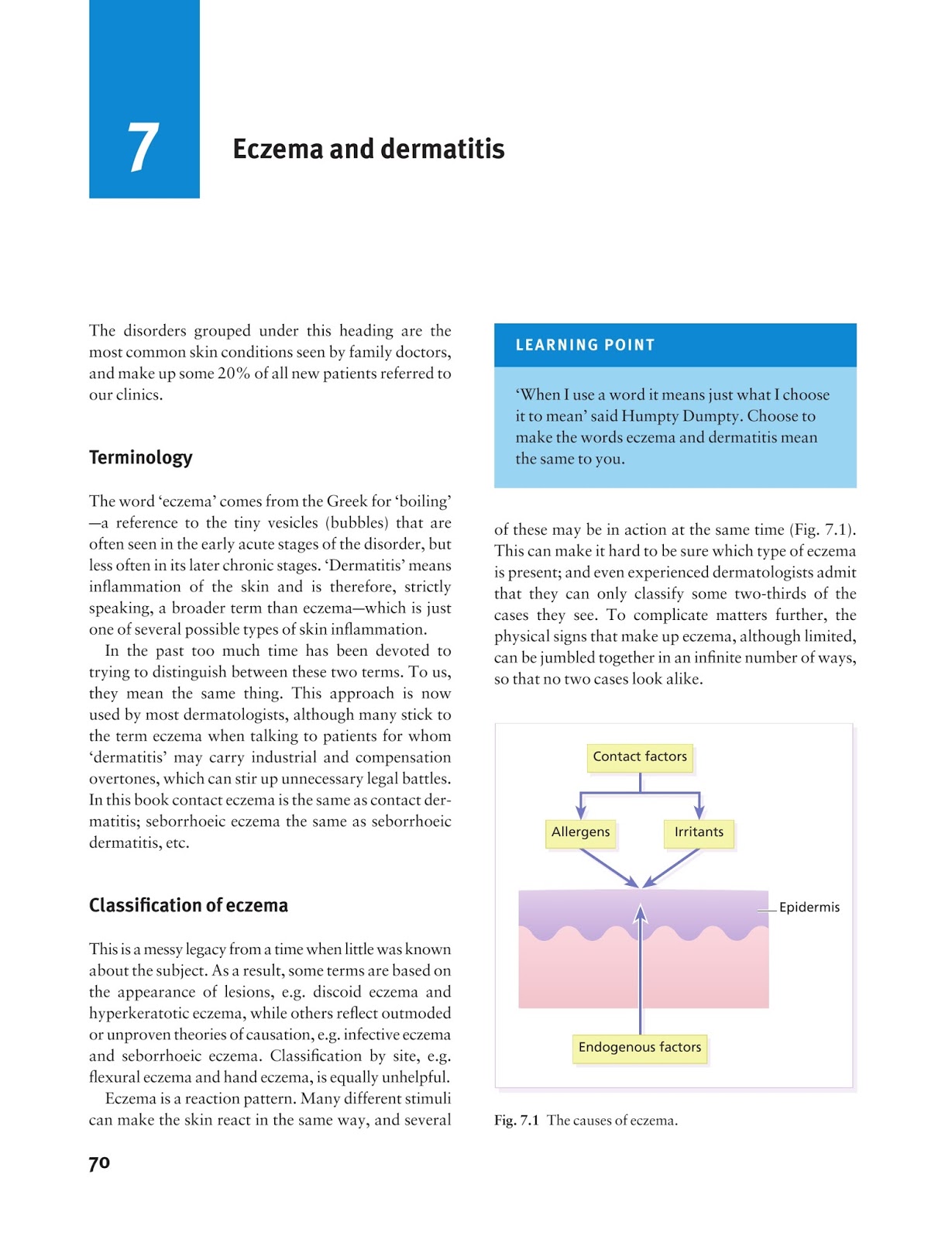
What causes erythromelalgia?
Causes of Erythromelalgia. Although erythromelalgia is usually caused by extreme heat or friction many times there is no identifiable cause. Most of the patients who have idiopathic erythromelalgia are over the age of sixty, which means there is no known cause.
How long does erythromelalgia last?
There are some that will only have tingling sensations and slight itching that will only last for several minutes. Others are not so lucky and will have severe skin discoloration and pain that is intense and can last for weeks, even months, at a time.
What causes redness on hands and feet?
This is a rare neurovascular peripheral pain disorder that affects your skin. It will cause the skin on your feet and hands to become red and have painful burning sensation. Early onset erythromelalgia can develop before a person turns twenty-five and late onset erythromelalgia will usually develop between the ages of forty and sixty.
How long does it take to diagnose erythromelalgia?
To get the proper diagnosis it can take several months and you may have to consult many different specialists to find out what the problem is. Erythromelalgia Treatment.
Can erythromelalgia be passed down to a child?
Although it could happen it is rare that it can run in families and have a parent be a carrier of a specific gene mutation and passing it down to a child. Some of the possible causes can include: Heavy metal poisoning.
Can erythromelalgia cause redness?
Although it is rare it is possible for you to have erythromelalgia symptoms of redness and burning to affect other parts of your body, especially the ears and scalp. When a person has erythromelalgia it can affect one or both side of your body. Other symptoms or signs can include:
Drugs used to treat Erythromelalgia
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What is the best treatment for EM?
Anticonvulsants, such as gabapentin (Neurontin)[33] and pregabalin (Lyrica),[34] may help relieve EM symptoms by reducing nerve activity and altering the way the body perceives pain. These medications are often used as a first-line treatment for EM, as well as for neuropathy (nerve damage), a condition often associated with EM.
What is the best medication for EM?
Antidepressants are also used to treat symptoms of EM and neuropathy, though it is not fully understood how they work. The most common antidepressants used for treating EM include duloxetine (Cymbalta), venlafaxine (Effexor),[35] amitriptyline (Elavil),[36] and nortriptyline (Pamelor). Doctors may also prescribe sertraline (Zoloft),[37] fluoxetine (Prozac), or paroxetine (Paxil). It is important to note that your doctor is not prescribing antidepressants because he thinks you are depressed—even though these drugs were originally developed to treat depression—but because they have been shown to actually reduce EM symptoms in some patients. These medications can also help with sleep, which can be difficult for people suffering from EM pain.
What supplements can help with EM?
Some nutritional supplements may be used to treat EM symptoms. For example, magnesium is a calcium-channel blocker and vasodilator that has been helpful for many EM patients.[43] Another supplement, alpha lipoic acid, has been used for decades for nerve injuries like those present in some people with EM.[44] Those whose EM benefits from antidepressant medications may find improvement with 5HTP, an amino acid that increases production of serotonin.[45] Any supplement should be treated like a prescription medication and discussed with your doctor before adding it to your treatment.
What tests can be done to diagnose EM?
Autoimmune diseases may be identified by blood tests for the presence of autoantibodies or by skin biopsies. Neurologists may perform electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction velocity (NCV) testing to identify nerve damage.
How to cope with EM?
In addition to relieving painful symptoms, coping with EM also involves taking measures to prevent flares from occurring. To do this, you must first identify what triggers an EM flare for you, and then limit or modify those activities or situations. By recognizing your triggers and learning methods of adapting, it is possible for you to continue many of your normal activities.
What is the first step to a diagnosis of EM?
The first step to diagnosing EM is seeing your primary care doctor. Your doctor may conduct tests for some of the common causes of EM, and she may refer you to a specialist to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Specialists that diagnose and treat EM include neurologists, dermatologists, rheumatologists, and vascular physicians or surgeons.
Does Tea research EM?
In addition to providing information and support to people with EM, TEA continues to encourage and fund research into effective treatments for all types of EM. Though EM is rare and has not been extensively studied, research into its causes, mechanisms, and treatments continues in both academic and commercial settings. At present, there is a growing interest in developing EM treatments, due in part to the belief that a drug designed to treat EM pain could work for many other kinds of pain as well. For the most up-to-date information on advances in EM research and treatments, visit TEA’s website at http://www.erythromelalgia.org.
