Antidote
| Agent | Description |
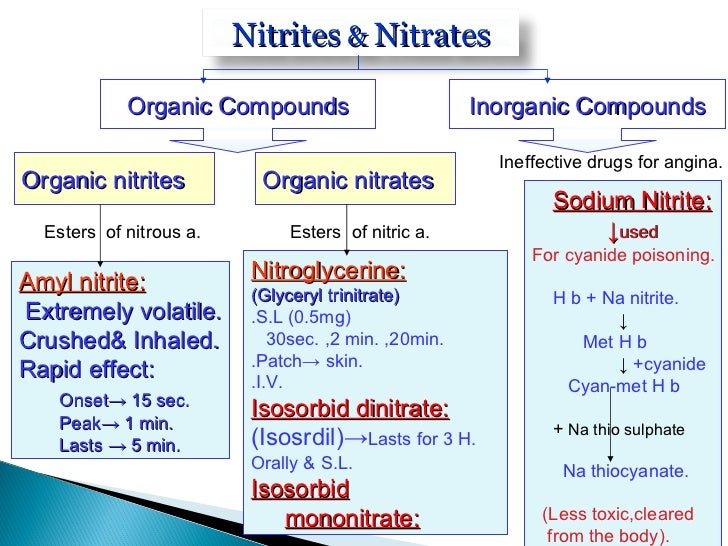
| Nitrites | The nitrites oxidize some of the hemoglo ... |
| Thiosulfate | The evidence for sodium thiosulfate 's u ... |
| Hydroxocobalamin | Hydroxocobalamin, a form (or vitamer) of ... |
| 4-Dimethylaminophenol | 4-Dimethylaminophenol (4-DMAP) has been ... |
Full Answer
How do you treat a person for cyanide poisoning?
What should I do if I am exposed to cyanide?
- Do not make yourself vomit if you have swallowed cyanide. Cyanide in your vomit could contaminate others, or damage your airway.
- Remove and bag all items on your body, including clothes, contacts or glasses, and jewelry. ...
- Wash your hair and body for 20 minutes with soap and water, and rinse thoroughly. ...
How can you reverse the effects of cyanide?
You can:
- Take proper precautions against a home fire. Install and maintain smoke detectors. ...
- Childproof your home. If you have young children, childproofing your home is essential — especially if you’re at risk of occupational exposure. ...
- Follow work safety regulations. If you work with cyanide, use removable absorbent paper to line work surfaces. ...
What is the antidote for cyanide poisoning?
What to do in Case of Cyanide Poisoning
- As first aid, initiate inhalation of oxygen immediately while preparing for IV administration.
- Administer amyl nitrate simultaneously with oxygen. To do this, break the PVC Durule tube and let the patient inhale the amyl nitrate for 15 to 20 seconds every 2 ...
- Discontinue the amyl nitrate and Inject 300 mg (10 ml) of sodium nitrate IV. ...
Why is sudden death in cyanide poisoning?
INTRODUCTION Cyanide is a deadly poison, utilized in some pharmaceutical and chemical industries, and is rarely available to the public. It gets rapidly absorbed into the circulation and tissues, and arrests aerobic metabolism which leads to sudden deterioration of organ function and death.
See more

How do you treat cyanide?
The only treatment for cyanide toxicity approved for use in the United States is a kit consisting of amyl nitrite, sodium nitrite, and sodium thiosulfate (Cyanide Antidote Kit; Acorn Inc., Buffalo Grove, IL). It was formerly known as the Pasadena or Lilly Kit.
Which drug can be used in cyanide poisoning?
Lorazepam is the drug of choice; midazolam and phenobarbital are second-line agents. Cyanide antidotes are the key medications for hydrogen cyanide (HCN) poisoning. Hydroxocobalamin (HCO, vitamin B-12) is the first-line therapy for cyanide toxicity.
Can the effects of cyanide poisoning be reversed?
doses of either of these drugs survived the lethal dose of cyanide. Results of these studies indicate that intravenous sodium nitrite, DMAP, and hydroxylamine hydrochloride, and amyl nitrite by inhalation, are all effective in reversing the lethal effects of cyanide poisoning.
Is B12 an antidote to cyanide?
The Vitamin B12 Analog Cobinamide Is an Effective Antidote for Oral Cyanide Poisoning - PMC. The .
How does oxygen help cyanide poisoning?
A high tension of oxygen can block the respiratory gasp reaction to intravenous cyanide in man; it can partially reverse electrocardiographic anoxic changes of a dog poisoned by cyanide; it can protect goldfish from lethal doses of this histotoxic agent.
Is Sugar an antidote to cyanide?
One study found a reduction in cyanide toxicity in mice when the cyanide was first mixed with glucose. However, as yet glucose on its own is not an officially acknowledged antidote to cyanide poisoning.
Can cyanide be detected in autopsy?
Cyanide was identified and confirmed in biological samples from autopsies and articles left by the deceased in other 163 cases. Concentrations of cyanide in heart blood and peripheral blood. The concentrations of cyanide were determined in biological samples, such as heart blood and peripheral blood (femoral vein).
Does artificial respiration help cyanide poisoning?
Patients usually recover spontaneously from poisoning due to cyanide gas inhalation if they can be brought into open air before respiration ceases. Artificial respiration is imperative if there is interruption of breathing.
How to treat cyanide exposure?
2. Treat Skin Exposure. Avoid touching a person whose skin has been exposed to cyanide; only emergency personnel with special protective clothing should have direct contact with the victim, as secondary contamination is possible. 3.
What to do if you are exposed to cyanide?
Treat the person as follows, depending on whether cyanide was inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin: 1. Treat Inhalation or Ingestion. Get the person to fresh air immediately.
What to do if you can't get away from cyanide gas?
If you can't get away from the area where cyanide gas is, stay low to the ground. If the person has difficulty breathing or has stopped breathing, do hands-only CPR: For a child, start CPR for children. For an adult, start adult CPR. Do not do mouth-to- mouth resuscitation.
What is potassium cyanide used for?
Potassium cyanide is used in gold and silver extraction , chemical analysis, to make other chemicals, and as an insecticide. Plants: Mostly from the family Rosaceae, seeds and pits from plants such as apricot, bitter almond, cherry laurel, plum, peach, pear, and apple contain cyanogenic glycosides.
Why is cyanide poisoning so toxic?
The mechanism of toxicity occurs because cyanide stops the cells of the body from being able to use oxygen, which all cells need to survive. The symptoms of cyanide poisoning are similar to those experienced when hiking or climbing at high altitudes, and include: General weakness. Confusion. Bizarre behavior.
What are the sources of cyanide poisoning?
Common sources of cyanide poisoning include. smoke inhalation from fires, industries that use cyanide (photography, chemical research, synthetic plastics, metal processing, and electroplating), plants (such as apricot pits and a type of potato called cassava), the cancer treatment laetrile, and. cigarette smoke.
How long does it take to detect cyanide?
The diagnostic test to detect cyanide takes hours to days to perform.
What is the most common source of cyanide?
Cigarette smoke is the most common source of cyanide exposure for most people. Cyanide is naturally found in tobacco, and smokers can have more than 2.5 times the mean whole blood cyanide level of nonsmokers, though this is generally not enough to cause poisoning.
What to do if someone is unconscious and short of breath?
In most cases, calling 911 and waiting for the ambulance to arrive is the best thing to do.
Can cyanide cause a seizure?
Abdominal pain. Seizures. Typically, acute cyanide ingestion will have a dramatic, rapid onset, immediately affecting the heart and causing sudden collapse. It also can immediately affect the brain and cause a seizure or coma.
What is cyanide poisoning?
Cyanide poisoning is a condition that develops when you inhale, touch, or swallow cyanide. Cyanide is a poisonous chemical gas that prevents your body from absorbing oxygen. The lack of oxygen can damage your organs and be life-threatening.
Can you vomit if you swallowed cyanide?
Do not make yourself vomit if you have swallowed cyanide. Cyanide in your vomit could contaminate others, or damage your airway. Remove and bag all items on your body, including clothes, contacts or glasses, and jewelry. Try not to touch affected items with bare hands, or try to touch only a small part of each item.
What are the symptoms of cyanide poisoning?
Early symptoms include headache, dizziness, fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and vomiting.
What is the cause of hydrogen cyanide poisoning?
Acute hydrogen cyanide poisoning can result from inhalation of fumes from burning polymer products that use nitriles in their production, such as polyurethane, or vinyl. It can also be caused by breakdown of nitroprusside into nitric oxide and cyanide. Nitroprusside may be used during treatment of hypertensive crisis.
How much cyanide is in blood?
Blood levels of cyanide can be measured but take time. Levels of 0.5–1 mg/L are mild, 1–2 mg/L are moderate, 2–3 mg/L are severe, and greater than 3 mg/L generally result in death. If exposure is suspected, the person should be removed from the source of exposure and decontaminated.
What happens if you have cyanide ions?
Cyanide ions interfere with cellular respiration, resulting in the body's tissues being unable to use oxygen. Diagnosis is often difficult. It may be suspected in a person following a house fire who has a decreased level of consciousness, low blood pressure, or high lactic acid.
How long does it take for a cyanide to start to show symptoms?
Onset of symptoms usually occurs within a few minutes. Some survivors have long-term neurological problems. Toxic cyanide-containing compounds include hydrogen cyanide gas and a number of cyanide salts. Poisoning is relatively common following breathing in smoke from a house fire.
Which is better, cobinamide or cyanide?
Cobinamide is the final compound in the biosynthesis of cobalamin. It has greater affinity for the cyanide than cobalamin itself, which suggests that it could be a better option for emergency treatment.
Can hydrogen cyanide cause a coma?
Acute exposure. If hydrogen cyanide is inhaled it can cause a coma with seizures, apnea, and cardiac arrest, with death following in a matter of seconds. At lower doses, loss of consciousness may be preceded by general weakness, dizziness, headaches, vertigo, confusion, and perceived difficulty in breathing.
Drugs used to treat Cyanide Poisoning
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.