Sludge produced by a water treatment plant has three main uses: recycling: mainly agriculture, with or without supplements but also for reinstating eroded sites (quarries, roadway excavations, replanting landfill sites…), in forestry and urban landscaping applications.
What is sludge and how it is treated?
Mixed sludge received from secondary wastewater treatment is passed through a dissolved-air flotation tank, where solids rise to the surface and are skimmed off. The thickened sludge is pulped with steam, then passed to thermal hydrolysis, where large molecules such as proteins and lipids are broken down under heat and pressure.
What happens to sludge from a wastewater treatment facility?
· The 44 million gallons of residuals collected from the treatment processes are managed through a three-step process: 1) anaerobic digestion stabilization 2) belt filter press dewatering 3) biosolids application to farm fields as a soil amenity. All sludge is tested first to ensure it meets (and exceeds) EPA guidelines.
What is the best water treatment?
· Sludge flows into the thickening tank, and eventually, it removes excess water from the solids collecting at the bottom. A gravity thickener has a similar process to the tanks, but it has a sloped design so that solids collect at the base. Dissolved-air flotation is another type of sludge-thickening process. Small air particles attach to the suspended solid material.
What is the sludge thickening process in water treatment?
Sludge produced by a water treatment plant has three main uses: recycling, elimination or destruction of OM with recycled energy using thermal processes, disposal at a landfill site
How is sludge useful after its treatment?
The final destination of treated sewage sludge usually is the land. Dewatered sludge can be buried underground in a sanitary landfill. It also may be spread on agricultural land in order to make use of its value as a soil conditioner and fertilizer.
What happens to the waste sludge after the wastewater treatment process?
In the United States, sewage sludge is also called wastewater solids. After any form of treatment, sludge is often referred to as “biosolids”. In line with this, we can say that sludge treatment turns sludge into biosolids. "Biosolids" are usually either applied on land, incinerated, or landfilled.
How is sludge from wastewater treatment disposed?
Incineration disposal Most trace metals in the sewage sludge become concentrated in the ash (a five- to tenfold increase in concentration). This material most commonly is landfilled, although it potentially could be used in construction materials.
What do wastewater treatment plants do with sludge?
Sewage sludge treatment is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater. Sewage sludge is produced from the treatment of wastewater in sewage treatment plants and consists of two basic forms — raw primary sludge and secondary sludge, also known as activated sludge in the case of the activated sludge process.
Why is it so expensive to dispose of sewage sludge?
This “biosolid” sludge is expensive to dispose of because it must be landfilled, but the waste management industry is increasingly using a money-making alternative – repackaging the sludge as fertilizer and injecting it into the nation's food chain. Now the practice is behind a growing number of public health problems.
What happens to waste water drainage?
sewage treatment, disposal and reuse Treated wastewater (domestic sewage) can be reclaimed and reused for a variety of purposes, including golf course and landscape irrigation. With achievement of appropriate (secondary) treatment levels, it may be reused for the irrigation of certain agricultural crops.
What are the modes of disposal of treated sludge?
Methods of Removing SludgeThickening. It is usually the first step in treating sludge as it is not possible to handle thin sludge as it is a slurry of solids suspended in water. ... Sludge Digestion. ... Dewatering. ... Disposal. ... Anaerobic digestion.
Is sewage sludge biodegradable?
Sewage sludge not enough stabilized incorporates pathogens and can cause rapid and uncontrolled biodegradation with the release of toxic substances. However, the high organic content makes these wastes suitable for treatment by biological techniques.
What happens to sludge in septic tank?
Bacteria that lives in the tank helps to break down the sludge, turning it into a liquid. Near the top of the septic tank is a pipe that leads to a part of the yard called the drain field. When the waste water in the septic tank reaches this pipe, the water flows into the drain field and is filtered through the soil.
Where does the sludge from water treatment plants go?
Once treated, sewage sludge is then dried and added to a landfill, applied to agricultural cropland as fertilizer, or bagged with other materials and marketed as “biosolid compost” for use in agriculture and landscaping.
Can sludge be incinerated?
Bio-solids like municipal sludge, industrial sludge and fine solids can be incinerated with the advantage of eliminating the sludge. Energy from the incineration process can be recovered as green energy source.
What is dried sludge used as?
Dried sludge is used as manure, returning organic matter and nutrients to the soil.
What is sewage sludge incineration?
Sewage sludge incineration reduces the volume of the material to be disposed of, completely destroys pathogens, decomposes most organic chemicals, and recovers the small amount of heat value contained in sewage sludge. The residual ash is a stable, relatively inert, inorganic material that has just 10 to 20% of the original sludge's volume. Most trace metals in the sewage sludge become concentrated in the ash (a five- to tenfold increase in concentration). This material most commonly is landfilled, although it potentially could be used in construction materials.
What is sludge dewatering?
Sludge is dewatered to increase solids content to around 20%, then mixed with a high-carbon organic material such as sawdust. The mix is composted under aerobic conditions at temperatures of at least 131°F for several days during the composting process. Volume reduction of sludge. Reduces odors.
How is sludge concentrated?
Sludge solids are concentrated either by settling due to gravity or by introducing air, which causes sludge solids to float. Sludge retains the properties of a liquid, but solids content is increased to 5 to 6%. Dewatering. Several processes are used: air drying on sand beds.
How long does sludge stay in the air?
One of the most widely used methods for sludge treatment. Sludge is held in the absence of air for 15 to 60 days at temperatures of 68 to 131°F. Anaerobic bacteria feed on the sludge, producing methane and carbon dioxide. In some treatment plants, the methane is collected and burned to maintain the treatment temperature.
What is biosolids in wastewater treatment?
The industry defines biosolids as sewage sludge that has undergone sufficient treatment for stabilization and pathogen reduction, and that is of sufficiently high quality to be land applied. The term is intended to distinguish high-quality, treated sewage sludge from raw sewage sludge and from sewage sludge that contains large quantities of environmental pollutants. The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process. The term has been criticized by some as an attempt to disguise the real nature of sewage sludge, thereby making land application of this material less objectionable to the general public. Although "biosolids" undoubtedly does not conjure up the same negative images as does "sewage sludge" or simply "sludge," it is a legitimate and functional term when correctly used to make the distinction described above. In this document, "sewage sludge" will be used to refer to wastewater treatment solids generally, and "biosolids" will be used to refer specifically to material that is suitable for land application.
What is biosolids in sewage?
The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process.
What is municipal sewage?
Municipal wastewater, or sewage, refers to water that has been used in urban and suburban area homes or businesses for washing, bathing, and flushing toilets. Municipal wastewater also may include water from industrial sources.
Outstanding in the field
At the Kline’s Island Wastewater Treatment Plant, we rely on land application. The 44 million gallons of residuals collected from the treatment processes are managed through a three-step process: 1) anaerobic digestion stabilization 2) belt filter press dewatering 3) biosolids application to farm fields as a soil amenity.
Creating Energy
Another benefit of this process: A significant part of the energy needed to run the treatment plant is supplied by firing the methane generated by the anaerobic digesters during the conversion of sewage sludge to biosolids.
Why is sludge thickening important?
Generally, it contains biosolids removed from liquid sewage. Sludge thickening is important because it is the process used in wastewater treatment centers to increase the solids concentration and decrease the free water. This step minimizes the load on the downstream processes, such as sludge dewatering and digestion.
What is rotary drum thickener?
Rotary-drum thickeners are stainless-steel drums with spirals and a flow system used to treat solids. The drum mixes sludge to reduce the water content, leaving a solid concentration behind. Water flows out of the drum for reuse.
What is gravity thickening?
Gravity thickening involves using specially designed circular tanks that concentrate thin sludges to a more-dense sludge product.
What is sludge treatment?
before being used in agricultural spreading applications, sludge must have undergone a treatment (physical, biological, chemical, thermal, long-term storage or other as appropriate) intended to reduce its ability to ferment as well as the health risks associated with its use;
What is sludge used for?
sludge end uses. Sludge produced by a water treatment plant has three main uses: recycling: mainly agriculture, with or without supplements but also for reinstating eroded sites (quarries, roadway excavations, replanting landfill sites…), in forestry and urban landscaping applications. Recycling means that the main elements making up sludge ...
What is recycling in agriculture?
recycling: mainly agriculture, with or without supplements but also for reinstating eroded sites (quarries, roadway excavations, replanting landfill sites…), in forestry and urban landscaping applications. Recycling means that the main elements making up sludge (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus) can be re-incorporated via the soil into ...
Does the Order of the 8th January 1998 ban the spread of non-sanitised sludge?
The order of the 8 th January 1998 does not ban the spreading of non-sanitised sludge. However, it does impose restrictions on the use of non-sanitised residual sludge (distances to be implemented from dwellings, water outlets, waterways, waiting times to be implemented prior to market garden crops, animal pastures…
When was Directive 75/442/CEE issued?
Directive 75/442/CEE of the 15 th July 1975 on waste (obligation and responsibility incumbent on the producer and keeper of waste, obligation of information, penalties applicable if these obligations are not performed).
Why is sewage sludge treated?
Treatment is important because sludge emanates toxic gases and it can act as a health hazard. There are several treatment methods used to treat sewage sludge. The thickening method is used where sludge solids volume is reduced to less than half of its current volume.
How to manage sewage sludge?
Composting is one of the other ways to manage sewage sludge in treatment plants. In this method, dewatering is done which is followed by mixing the mostly solid sludge with high carbon organic material. The mix is laid for composting under aerobic conditions for a duration of time. ...
What is wastewater treatment?
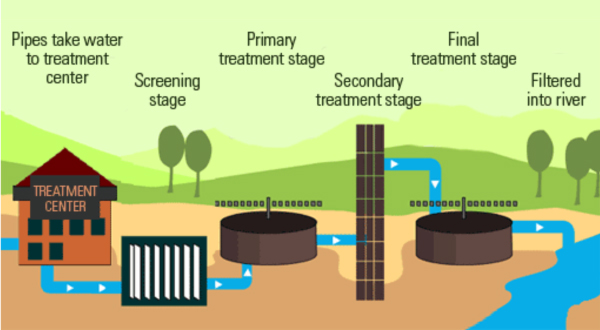
Wastewater treatment plants collect a large amount of domestic waste, industrial waste, agricultural waste, and waste from commercial spaces and provide treatment. This involves primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment of wastewater which uses physical, biological, and chemical means to purify the wastewater.
What is sewage sludge?
Sludge or sewage sludge can be defined as the residue or the by-product which is left after the wastewater treatment processes are carried out in the wastewater treatment plants. The solid, semi-solid, and slurry residue is a combination of various components like organic and inorganic materials, plant nutrients, chemicals, ...
What is the primary treatment of wastewater?
The primary treatment of wastewater plants involves various processes like filtering of solid particles like wood, paper, plastic, vegetable matter, etc. Also, oil and grease are removed during this process. Gravity sedimentation, flotation processes, chemical precipitation, sedimentation leads to the generation of primary sludge which is settled ...
Why is wastewater treatment important?
Treatment is important because sludge emanates toxic gases and it can act as a health hazard. There are several treatment methods used to treat sewage sludge.
What is the process of sludge?
In the aerobic process, the sludge is supplied with oxygen which produces carbon dioxide. The biological processes ably reduce sludge volume, eliminates pathogens, and even makes it easy to dry the sludge. It converts organic sludge into liquids and gases.
What are the consequences of poor sludge management?
Poorly designed sludge treatment and management systems can lead to undesirable consequences, such as plant shutdowns, financial loss, penalties and operational problems. Familiarity with the basic sludge management and treatment components outlined here will help operators ensure these systems are not overlooked. WT
What is dewatering equipment?
Dewatering equipment is needed to reduce the volume of liquid in produced sludge. Sludge dewatering can be carried out by different systems such as a filter press, decanter centrifuge and others. Most often a filter press system is used, although other options for dewatering are available.
What is a positive displacement pump?
Positive displacement pumps have been used in sludge and dense liquid services. Some positive displacement pumps have presented poor performance and low reliability. Therefore, special care is needed to select the proper positive displacement pumps for sludge services.
What is double disc pump?
A double disc pump is a positive displacement pump that uses a trunnion (elastomer), a disc and a connecting rod to force sludge from the suction side to the discharge side of the pump by creating a vacuum inside the pump body. The suction and discharge valve chambers (with the check valves) help to manage higher-than-normal concentrations of grit and solids in pumped sludge.
What is the concentration of alum sludge?
The solids in the sludge are mainly flocs, excess coagulant, such as alum. Alum sludge has a solids concentration of only about 1 % when automatically removed from the basin, or about 2% if manually removed. Many options exist for disposal of sedimentation sludge such as disposal in streams, lagoons and landfills.
What is terminal velocity?
The terminal velocity has great significance in the design of settling tanks. It is called design overflow rate or surface loading rate or hydraulic loading (m3 / m2/d). It shall be used for designing the surface area of the sedimentation basin.
How are sludges treated?
Mainly many sludges are treated using a variety of digestion techniques, the purpose of which is to reduce the bulk amount of organic matter and the number of disease-causing microorganisms present in the solids. see more. Show more replies. −.
Why is it important to treat sludge?
Therefore, it is extremely important to properly treat such sludge in order to minimize its environmental repercussions.
What is sewage sludge?
What is in sewage sludge? Sewage sludge is a byproduct of treated wastewater. It is composed of both organic and inorganic materials, a large concentration of plant nutrients, organic chemicals, as well as pathogens. Therefore, it is extremely important to properly treat such sludge in order to minimize its environmental repercussions.
How does sewage sludge digest?
After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. This is a biological process in which the organic solids present in the sludge are decomposed into stable substances. This process also helps reduce the total mass of solids, while destroying any present pathogens to enable easy dewatering. The sludge digestion process is a two-phase process. In the first stage, the dry solid sludge is heated and mixed in a closed tank to enable anaerobic digestion by acid-forming bacteria. These bacteria hydrolyze the large molecules of proteins and lipids present in the sludge and break them down into smaller water-soluble molecules, which they then ferment into various fatty acids. The sludge then flows into the second tank where it is converted by other bacteria to produce a mixture of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and methane, after which the methane is collected and reused to power the digestion tank and generate power (depending on the quantity retrieved).
What is the process of sludge digestion?
The sludge digestion process is a two-phase process. In the first stage, the dry solid sludge is heated and mixed in a closed tank to enable anaerobic digestion by acid-forming bacteria.
How much water is in dewatered sludge?
In most cases, dewatered sludge usually contains a significant amount of water, as much as 70 percent, in spite of its solidified state. Therefore, it is important to dry and dewater the sludge beforehand.
How long does it take to dry sludge?
While using sludge-drying beds is the most common way to carry out this process, it is extremely time-consuming and may take weeks before the process is complete . In order to quicken these processes, waste management plans are also employing solid-liquid separation devices to carry out this process.

Introduction
- Before 1950, most communities in the United States discharged their wastewater, or sewage, into streams and rivers with little if any treatment. As urban populations increased, the natural ability of streams and rivers to handle the wastewater was overwhelmed and caused water quality to deteriorate in many regions. In response to concerns about water quality degradation, thousand…
Production of Municipal Sewage Sludge
- Municipal wastewater, or sewage, refers to water that has been used in urban and suburban area homes or businesses for washing, bathing, and flushing toilets. Municipal wastewater also may include water from industrial sources. To remove chemicals or pollutants resulting from industrial processes, industrial contributors to municipal wastewater systems must pretreat their wastew…
Options For Dealing with Sewage Sludge
- Sewage sludge can be viewed either as an organic and nutrient resource to be used beneficially or as a waste material to be disposed of. Before 1991, large amounts of sewage sludge, including some from Pennsylvania, were disposed of by ocean dumping. Concerns about excess nutrient loading of ocean waters led to the banning of this practice. At pres...
Regulation of Land-Applied Biosolids
- The current regulations for land application of biosolids were established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (E.P.A.) in 1993. In 1997, Pennsylvania revised its regulations for land application of biosolids by largely adopting the technical aspects of the Federal regulations and by adding several requirements specific to Pennsylvania. The underlying premis…
What Does This Mean For Pennsylvania?
- The question that confronts municipalities, farmers, and rural communities in Pennsylvania is whether or not biosolids can be applied to land without creating undue risk to human health and the environment. When considering this question, it is helpful to separate short-term and long-term risk. In the short term, the risk from land application of biosolids can be maintained at very …