What are the side effects of treatment with corticosteroids?
- Blindness (sudden, when injected in the head or neck area)
- burning, numbness, pain, or tingling at or near place of injection
- confusion
- excitement
- false sense of well-being
- hallucinations (seeing, hearing, or feeling things that are not there)
- mental depression
- mistaken feelings of self-importance or being mistreated
- mood swings (sudden and wide)
What are the most common alternatives to corticosteroids?
Benefits of Oxymetholone
- Increases body strength. Oxymetholone steroid doubles your strength due to its ability to uplift body weight and produce hormones making it easier for you to weight lift.
- Enhance joint functionality. ...
- Quick weight gain. ...
- Muscle growth. ...
- Burn calories. ...
How do topical corticosteroids thin out the skin?
- Inhibitory effect on keratinocyte proliferation in the epidermis
- Inhibition of collagen 1 and 3 synthesis in the dermis
- Inhibition of fibroblasts and hyaluronan synthase 3 enzyme resulting in the reduction of hyaluronic acid in the extracellular matrix leading to dermal atrophy.[1,4]
Are corticosteroids safe for long-term use?
Treatment for less than one month is considered short-term treatment. Corticosteroids for a few days or weeks are relatively safe when prescribed for acute dermatitis. Treatment continuing for more than 3 months is regarded as long-term, and results in the majority of undesirable side effects.

What type of medication is a corticosteroid?
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone and cortisone, are a class of drugs that can effectively reduce inflammation. However, they also cause a range of side effects that limit their use. Corticosteroids are different than the performance-enhancing drugs that some athletes and bodybuilders use.
What is long term corticosteroid treatment?
While corticosteroids have many uses, they also come with several long-term side effects. These medications are known to lead to problems like osteoporosis (thin bones), a weakened immune system, cataracts, thin skin with topical products, and fungal infections of the mouth or throat with inhalers.
What are 5 common side effects of steroids?
What are the possible side effects of steroids?Increased appetite.Weight gain.Changes in mood.Muscle weakness.Blurred vision.Increased growth of body hair.Easy bruising.Lower resistance to infection.More items...•
What are the side effects of long term corticosteroid use?
Long-term corticosteroid use may be associated with more serious sequel, including osteoporosis, aseptic joint necrosis, adrenal insufficiency, gastrointestinal, hepatic, and ophthalmologic effects, hyperlipidemia, growth suppression, and possible congenital malformations.
What Are Corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids are man-made drugs that closely resemble cortisol, a hormone that your adrenal glands produce naturally. Corticosteroids are often...
What Are Some Types of Steroids?
Some corticosteroid medicines include cortisone, prednisone, and methylprednisolone. Prednisone is the most commonly used type of steroid to treat...
How Are Steroids Beneficial?
When inflammation threatens to damage critical body organs, steroids can be organ-saving and in many instances, life-saving. For example, steroids...
How Will My Doctor Decide If Steroids Are The Right Treatment?
The decision to prescribe steroids is always made on an individual basis. Your doctor will consider your age, physical activity, and other medicine...
What Are The Possible Side Effects of Steroids?
The chance of side effects depends on the dose, type of steroid, and length of treatment. Some side effects are more serious than others. Common si...
Does Everyone Have Side Effects?
Not all patients will develop side effects. How often any side effect occurs varies from patient to patient.If steroid use is brief (from a few day...
How Can The Side Effects of Steroids Be minimized?
To minimize the side effects of steroids, doctors follow several guidelines: 1. Use steroids only when necessary. 2. Watch the patient closely to d...
What are corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids are man-made drugs that closely resemble cortisol, a hormone that your adrenal glands produce naturally. Corticosteroids are often referred to by the shortened term "steroids." Corticosteroids are different from the male hormone-related steroid compounds that some athletes abuse.
What are some examples of local steroid treatments?
Examples of local steroid treatments include joint injections, eye drops, ear drops and skin creams. Systemic steroid treatments include oral medicines (given by mouth) or medicine that is delivered directly into a vein (intravenously or IV) or muscle (intramuscularly). Systemic steroids circulate through the bloodstream to various body sites.
What are some types of steroids?
Some corticosteroid medicines include cortisone, prednisone and methylprednisolone. Prednisone is the most commonly used type of steroid to treat certain rheumatologic diseases (like r heumatoid arthritis or lupus ).
How do steroids work?
Steroids work by decreasing inflammation and reducing the activity of the immune system. Inflammation is a process in which the body's white blood cells and chemicals can protect against infection and foreign substances such as bacteria and viruses. In certain diseases, however, the body's defense system (immune system) doesn't function properly. This might cause inflammation to work against the body's tissues and cause damage. Signs of inflammation include:
When are steroids given?
Steroids may be the main therapy for certain diseases. For other conditions, steroids might only be used sparingly or when other measures have not been successful.
How are steroids beneficial?
When inflammation threatens to damage critical body organs, steroids can be organ-saving and in many instances, life-saving. For example, steroids may prevent the worsening of kidney inflammation, which could lead to kidney failure in people who have lupus or vasculitis. For these patients, steroid therapy might eliminate the need for kidney dialysis or transplantation.
How will my doctor decide if steroids are the right treatment?
Your healthcare provider will consider your age, physical activity, and other medicines you are taking. Your provider will also make sure you understand the potential benefits and risks of steroids before you start taking them.
How effective are corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids are effective in suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation. They are useful for a variety of conditions, particularly when prompt treatment is necessary. Both long-term and short-term use of corticosteroids can have side effects, some of which are serious.
Why do you take lower corticosteroids?
Taking lower dosages over shorter periods will reduce the risk of side effects from corticosteroids. Doctors will always try to prescribe the lowest dosage that will still provide effective treatment.
How do corticosteroids help the body?
They can reduce inflammation, suppress overactive immune system responses, and help with hormonal imbalances. Corticosteroids are fast-acting in the body, which makes them useful for treating sudden, severe symptoms.
Why do you use retinoid cream at the same time as corticosteroid creams?
applying a retinoid cream at the same time as corticosteroid creams, gels, or lotions to reduce the risk of thin skin
How to avoid interactions with other medications?
avoiding interactions by making sure that the doctor is aware of all other medications and supplements
Why are corticosteroids good for you?
Corticosteroids are fast-acting in the body, which makes them useful for treating sudden, severe symptoms. For example, they can effectively manage allergic responses.
What are the different forms of corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids can come in the form of: tablets. capsules. eye drops. lotions, creams, ointments, or gels. nasal or mouth sprays. injections. A doctor will prescribe different forms of corticosteroids, depending on the problem. For example, they may prescribe a cream, lotion, ointment, or gel to treat skin conditions.
Why were the corticosteroids stopped early?
16-20 Some of these trials were stopped early due to under enrollment following the release of the results from the RECOVERY trial. Given that the sample size of many these ...
What are some other corticosteroids than dexamethasone?
Corticosteroids Other Than Dexamethasone. If dexamethasone is not available, alternative glucocorticoids such as prednisone, methylprednisolone, or hydrocortisone can be used. Half-life, duration of action, and frequency of administration vary among corticosteroids.
How long does dexamethasone last?
Long-acting corticosteroid: dexamethasone; half-life: 36 to 72 hours, administer once daily. Intermediate-acting corticosteroids: prednisone and methylprednisolone; half-life: 12 to 36 hours, administer once daily or in two divided doses daily.
How long does hydrocortisone last?
Short-acting corticosteroid: hydrocortisone; half-life: 8 to 12 hours, administer in two to four divided doses daily. Hydrocortisone is commonly used to manage septic shock in patients with COVID-19; see Care of Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 for more information.
What is the purpose of a short course of betamethasone?
A short course of betamethasone or dexamethasone, which are known to cross the placenta, is routinely used to decrease neonatal complications of prematurity in women with threatened preterm delivery. 40,41
Is Budesonide a glucocorticoid?
Budesonide is a synth etic, inhaled corticosteroid with potent glucocorticoid activity and weak mineralocorticoid activity. It has broad anti-inflammatory properties and has Food and Drug Administration-labeled indications for the management of chronic respiratory diseases including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Certain inhaled corticosteroids have been shown to impair viral replication of SARS-CoV-2 25 and downregulate expression of the receptors used for cell entry. 26,27 These mechanisms support the potential of inhaled corticosteroids as therapeutic agents for COVID-19. However, observational studies have found that long-term use of inhaled corticosteroids prescribed for non-COVID-19 respiratory diseases either had no effect on COVID-19 outcomes or increased the risk of hospitalization. 28,29 More recently, two open-label randomized controlled trials provided additional insights regarding the role of inhaled budesonide in outpatients with COVID-19, as described below and in Table 4b.
Can corticosteroids cause secondary infections?
Combining systemic corticosteroids with other immunosuppressants, such as tocilizumab or baricitinib, could theoretically increase the risk of secondary infections. However, this adverse effect has not been reported in clinical trials to date.
What are corticosteroids used for?
Corticosteroids belonging to the glucocorticoid class influence the body system in several ways, but they are used mostly for their strong anti-inflammatory effects and in conditions that are related to the immune system function such as:
What are some examples of corticosteroids?
Examples of these include the naturally occurring hydrocortisone (Cortef) and cortisone, and the synthetic corticosteroids including:
What are the side effects of systemic corticosteroids?
These side effects are more apparent when corticosteroids are used at higher doses or for extended periods of time. This section lists only some of these side effects of corticosteroids.
What are corticosteroids? What is the mechanism of action (how do they work)?
Corticosteroids are steroid hormones that are either produced by the body or are man-made.
What are the differences between the types of systemic corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids differ in their relative amount of anti-inflammatory and mineralocorticoid potency and they are used according to these effects. Among the systemic (oral and injectable) corticosteroids, fludrocortisone (Florinef) has the most significant mineralocorticoid (salt retaining) actions and is best used for this effect despite it's strong anti-inflammatory action.
What drugs interact (contraindications) with corticosteroids?
Certain drugs such as troleandomycin (TAO), erythromycin ( Ery-Tab, EryPed 200), and clarithromycin ( Biaxin) and ketoconazole ( Nizoral) can reduce the ability of the liver to metabolize (breakdown) corticosteroids and this may lead to an increase in the levels and side effects of corticosteroids in the body. On the other hand, phenobarbital, ephedrine, phenytoin ( Dilantin ), and rifampin ( Rifadin, Rimactane) may reduce the blood levels of corticosteroids by increasing the breakdown of corticosteroids by the liver. This may necessitate an increase of corticosteroid dose when they are used in combination with these drugs.
Which glucocorticoids have salt retaining properties?
Some glucocorticoids also in addition to their anti-inflammatory actions have salt retaining properties but they are used mostly for their anti-inflammatory effects. Fludrocortisone ( Florinef ), a synthetic mineralocorticoid has strong salt retaining effects with significant anti-inflammatory actions, and is used mostly for it's salt retaining capabilities.
How are corticosteroids used?
Corticosteroid drugs are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), asthma, allergies and many other conditions. These drugs also help suppress the immune system in order to prevent organ rejection in transplant recipients. Corticosteroids also treat Addison's disease, a relatively rare condition where the adrenal glands aren't able to produce even the minimum amount of corticosteroid that the body needs.
What to wear when taking corticosteroids?
Wear a medical alert bracelet. This or similar identification is recommended if you've been using corticosteroids for a long time. See your doctor regularly. If you're taking long-term corticosteroid therapy, see your doctor regularly to check for side effects.
What side effects can corticosteroids cause?
Corticosteroids carry a risk of side effects, some of which can cause serious health problems . When you know what side effects are possible, you can take steps to control their impact.
What is the best medicine for rheumatoid arthritis?
Tablets, capsules or syrups help treat the inflammation and pain associated with certain chronic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. By inhaler and intranasal spray. These forms help control inflammation associated with asthma and nasal allergies. In the form of eyedrops.
Can corticosteroids cause pain?
Side effects of injected corticosteroids. Injected corticosteroids can cause temporary side effects near the site of the injection, including skin thinning, loss of color in the skin, and intense pain — also known as post-injection flare. Other signs and symptoms may include facial flushing, insomnia and high blood sugar.
Can corticosteroids cause side effects?
Side effects of oral corticosteroids. Because oral corticosteroids affect your entire body instead of just a particular area, this route of administration is the most likely to cause significant side effects. Side effects depend on the dose of medication you receive and may include:
Do corticosteroids cause inflammation?
When prescribed in doses that exceed your body's usual levels , corticosteroids suppress inflammation. This can reduce the signs and symptoms of inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis, asthma or skin rashes.
What is the purpose of injectable corticosteroids?
Injectable Corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are potent drugs used to reduce inflammation in the body's tissues. They are different from anabolic steroids. These are illegally used by some athletes to increase muscle tone. Corticosteroids can come in several forms: pills, liquids, creams, ointments, medicines sprayed into the nose, ...
What are the different forms of corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids can come in several forms: pills, liquids, creams, ointments, medicines sprayed into the nose, and injectable medicines.
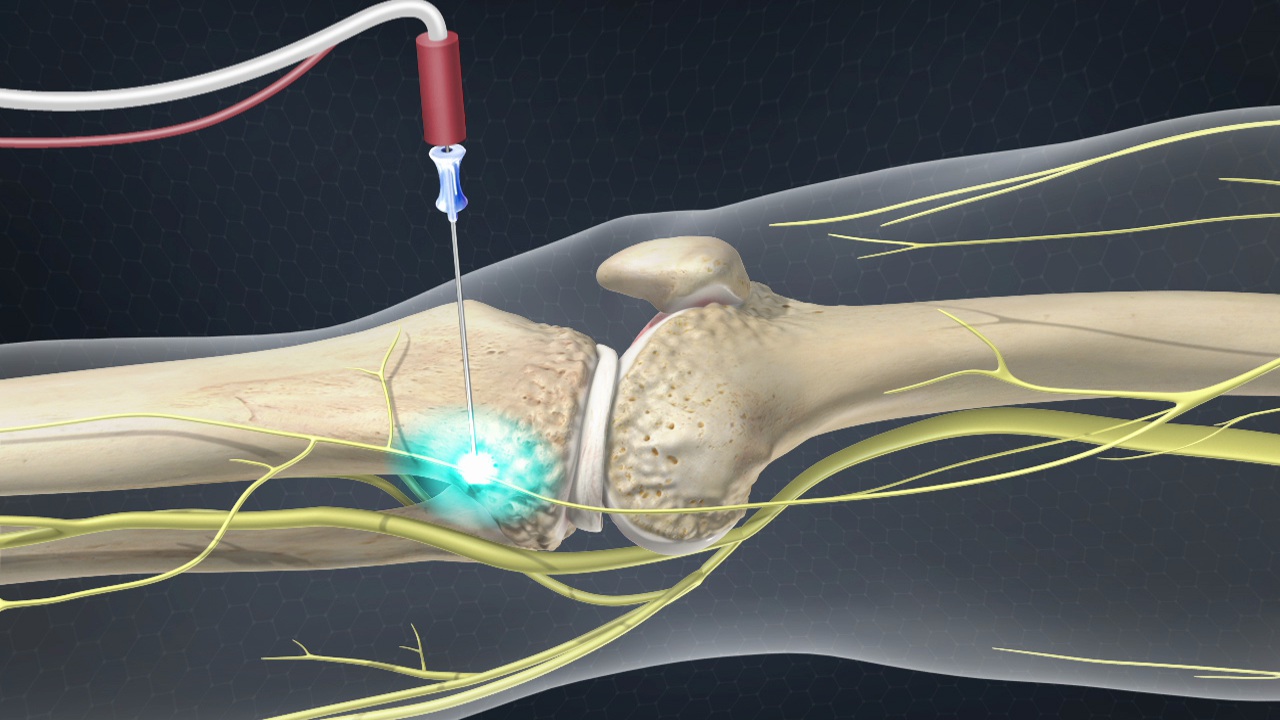
What is the best treatment for carpal tunnel?
This condition happens when a nerve in the wrist becomes compressed or pinched, causing pain, numbness, tingling, and possibly weakness in the hand. Injecting a corticosteroid into the wrist can give immediate, though temporary, relief. An anesthetic like lidocaine may also be given with the steroid.
Can you take corticosteroids for a long time?
Using injectable corticosteroids for a long period of time is not suggested because of additional side effects. These include osteoporosis, cataracts, delayed growth, stomach ulcers, skin atrophy and depigmentation, and high blood pressure.
Can corticosteroids cause high blood sugar?
Corticosteroids can have a number of side effects, including high blood sugar levels. For this reason, people with diabetes are advised to tell their health care providers about their condition before taking any steroid medicines.
Can corticosteroids help with lower back pain?
Low back pain. Lower back pain from ruptured disks, spinal stenosis, and some other conditions may be treated with injectable corticosteroids to provide some relief. Lumbar radiculopathy is pain in the buttocks, hips, or legs that comes from a pinched nerve in the lower back. This type of pain can often be treated with corticosteroid injections near the pinched nerve. Sometimes other drugs like local anesthetics are given with the corticosteroid.
When to use corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids are used to quiet down the symptoms and provide immediate relief for patients .
How do Corticosteroids Work?
The human body naturally produces cortisol (and other hormones) from the adrenal glands which reside above the kidneys. Corticosteroids mimic these hormones’ effects on the body, and when prescribed in a high enough dosage, they suppress the immune system, resulting in decreased overall inflammation levels in the patient.
How are Corticosteroids for RA Administered?
Corticosteroids treatments are available in several formats. These formats include:
What are the side effects of corticosteroids?
Side effects of corticosteroids in RA patients may include: 1 Increased risk of viral or bacterial infection 2 Sudden withdrawal symptoms like weakness and fatigue 3 High blood pressure 4 Increased blood sugar 5 Swelling in legs 6 Risk of cataracts 7 Weight gain 8 Mood disruption including depression and anxiety 9 Insomnia
Why do people take corticosteroids in the morning?
Most types of corticosteroids are taken when the patient wakes up in the morning. This is because the steroids mimic the body’s own natural hormone production. Patients also take corticosteroids upon wakening to alleviate symptoms of morning stiffness.
How many corticosteroid injections are given per year?
Corticosteroid injections are typically delivered several months apart. Doctors may recommend that patients only receive a maximum of three or four corticosteroid injections per year.
What is bridge therapy?
As an interim treatment, or “bridge therapy” while waiting for DMARDs to take effect. During painful flare-ups when inflammation becomes active. As short-term inflammation and pain relief. Over longer periods of time in low doses for patients not responding to DMARDs.
What are corticosteroid hormones?
Corticosteroid hormones are naturally occurring hormones produced by the adrenal glands within the body. Topical corticosteroids are synthetic (man-made) corticosteroid medications used for treating skin conditions such as rash, dermatitis, itching, eczema, and psoriasis. Topical corticosteroids have potent anti-inflammatory actions and also suppress the immune response. Topical corticosteroids are used based on their potency, the area of the body to which they will be applied, and type of skin condition being treated.
What are the side effects of corticosteroids?
What are the side effects of topical corticosteroids? Common side effects of topical corticosteroids are: itching, burning, irritation, redness, and. dryness. Long-term use can lead to loss of skin tone, deterioration of skin cells, and risk of infections.
What are the different types of psoriasis?
Explore the different types of psoriasis such as plaque psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, and scalp psoriasis. Discover what causes...
How to report side effects of prescription drugs?
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Can you take topical corticosteroids while pregnant?
There is no evidence of safe and effective use of topic al corticosteroids in pregnant mothers. Therefore, they should be used only if clearly needed. Long term use and large applications of topical corticosteroids may cause birth defects in the unborn. It is not known whether topical corticosteroids enter breast milk.
Can topical corticosteroids interact with other drugs?
The risk of topical corticosteroids interacting with other drugs is low, and they do not have significant interactions with other drugs. Administration of other topical medications should be separated from administration of topical corticosteroid to avoid any potential interaction and diminished effect.
Can corticosteroids be used in breast milk?
It is not known whether topical corticosteroids enter breast milk. Therefore, caution must be exercised before using it in nursing mothers. Topical corticosteroids should not be applied to the breasts of nursing mothers unless the mothers instructed to do so by the physician.
Recommendations
- For nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19: 1. See Therapeutic Management of Nonhospitalized Adults with COVID-19for the Panel’s recommendations on the use of dexamethasone or other systemic corticosteroids in certain nonhospitalized patients. 2. There is insufficient evidence for the Panel to recommend either for or against the use of inhaled budesonide for the treatment of …
Rationale
- The Panel’s recommendations on the use of corticosteroids for COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients reflect a lack of data regarding their use in this population. In the RECOVERY trial (described below), dexamethasone was shown to reduce mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who required supplemental oxygen; however, treatment with dexamethasone was sto…
Systemic Corticosteroids Other Than Dexamethasone
- If dexamethasone is not available, alternative glucocorticoids (e.g., prednisone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone) can be used.
- For these drugs, the total daily dose equivalencies to dexamethasone 6 mg (oral or intravenous [IV])24 are:
- Half-life, duration of action, and frequency of administration vary among corticosteroids.
- If dexamethasone is not available, alternative glucocorticoids (e.g., prednisone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone) can be used.
- For these drugs, the total daily dose equivalencies to dexamethasone 6 mg (oral or intravenous [IV])24 are:
- Half-life, duration of action, and frequency of administration vary among corticosteroids.
- Hydrocortisone is commonly used to manage septic shock in patients with COVID-19; see Hemodynamics for more information. Unlike other corticosteroids previously studied in patients with ARDS, dexam...
Inhaled Corticosteroids
- Budesonide is a synthetic, inhaled corticosteroid with potent glucocorticoid activity and weak mineralocorticoid activity. It has broad anti-inflammatory properties and has Food and Drug Administration-labeled indications for the management of chronic respiratory diseases including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Certain inhaled corticosteroids have been s…
Considerations in Pregnancy
- A short course of betamethasone or dexamethasone, which are known to cross the placenta, is routinely used to decrease neonatal complications of prematurity in women with threatened preterm delivery.40,41 Given the potential benefit of decreased maternal mortality and the low risk of fetal adverse effects for a short course of dexamethasone therapy, the Panel recommends us…
Considerations in Children
- The safety and effectiveness of dexamethasone or other corticosteroids for COVID-19 treatment have not been sufficiently evaluated in pediatric patients and caution is warranted when extrapolating recommendations for adults to patients aged <18 years. The Panel recommends using dexamethasone for children with COVID-19 who require high-flow oxygen, noninvasive ven…
Clinical Trials
- Several clinical trials evaluating corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19 are currently underway or in development. Please see ClinicalTrials.govfor the latest information.