Medication
When assessing a patient for Lyme disease, health care providers should consider:
- The signs and symptoms of Lyme disease
- The likelihood that the patient has been exposed to infected blacklegged ticks
- The possibility that other illnesses may cause similar symptoms
- Results of laboratory tests, when indicated
Nutrition
Untreated, Lyme disease can spread to other parts of your body for several months to years after infection, causing arthritis and nervous system problems. Ticks can also transmit other illnesses, such as babesiosis and Colorado tick fever. The deer tick (Ixodes scapularis) goes through three life stages.
What is the best way to treat chronic Lyme disease?
Will be discussed:
- Insight into the Borealis bacteria
- Determine your current condition
- Supplementing all deficiencies in the body
- Detoxify / detoxify the body
- Modulating the immune system
- Eliminate bacteria, viruses, fungi, toxins, heavy metals
- If the Viral and Bacterial Load becomes weaker than the immune system, recovery and healing begin
What happens if chronic Lyme disease is left untreated?
When people are diagnosed with Lyme disease in its early stages, a 10- to 20-day course of oral antibiotics—usually with a drug called doxycycline—will clear the infection and help them feel better fairly quickly. “This cures the vast majority of people, and they have a 100% recovery with no lasting effects,” says Dr. Zemel.
How I healed from chronic Lyme disease?
Can Lyme disease ever be truly cured?
See more
Can chronic Lyme disease be cured?
There is currently no cure for chronic Lyme disease. People with the condition typically get better with time, although it may take several months. In most cases, a doctor will focus the treatment plan on managing pain and other symptoms.
Can late stage Lyme disease be cured?
When treated early, Lyme disease can be cured and most patients will recover completely. Even when treated in later stages, most patients will respond well to antibiotics, though there may be some chronic damage to the nervous system or joints.
How serious is chronic Lyme?
Chronic Lyme disease can be linked to deadly symptoms, such as Lyme carditis (inflammation of the heart). According to Lymedisease.org, studies consistently show that chronic Lyme disease patients have poorer quality of life than those with other chronic diseases.
What is the best treatment for late stage Lyme disease?
Neurologic conditions associated with late Lyme disease are treated with intravenous antibiotics, usually ceftriaxone or cefotaxime, given daily for two to four weeks.
What is Stage 4 Lyme disease?
Late persistent Lyme disease If Lyme disease isn't promptly or effectively treated, damage to the joints, nerves, and brain may develop months or years after you become infected. It is the last and often the most serious stage of the disease.
How do you know if you have chronic Lyme disease?
Chronic Lyme disease is an ongoing Borrelia burgdorferi infection that can involve any body system or tissue. The infection produces a wide range of symptoms and signs, which can be debilitating for some patients. Common symptoms include severe fatigue, migratory musculoskeletal pain, headaches, and impaired memory.
How do you get chronic Lyme disease?
To contract Lyme disease, an infected deer tick must bite you. The bacteria enter your skin through the bite and eventually make their way into your bloodstream. In most cases, to transmit Lyme disease, a deer tick must be attached for 36 to 48 hours.
What does a Lyme flare up feel like?
The symptoms of a flare-up can include: an increase in fatigue. problems with memory and concentration, sometimes referred to as 'brain fog' extreme sensitivity to bright lights, heat, cold, and noise.
How do you test for late stage Lyme disease?
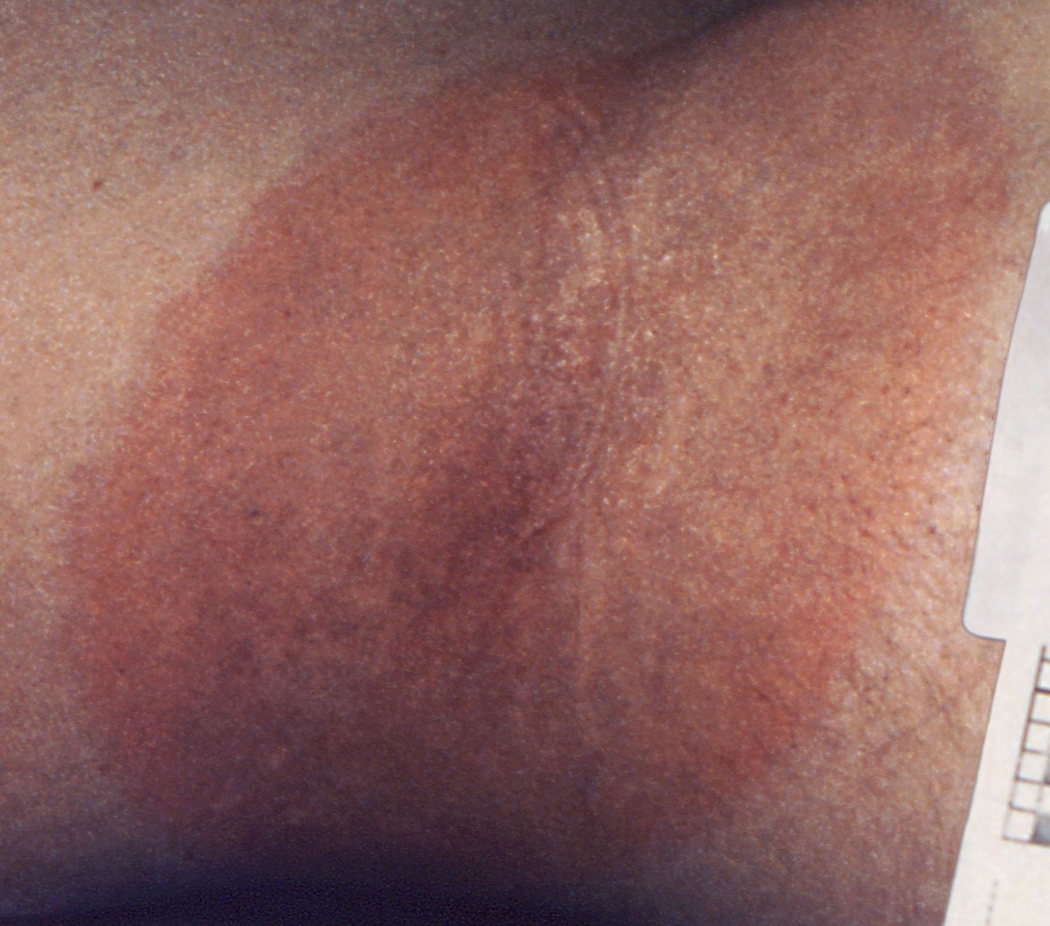
Diagnosis. The diagnosis of late-stage Lyme disease can be very difficult, and is usually made by a specialist in infectious diseases. The diagnosis can be confirmed if the affected person has had the characteristic 'bull's eye' rash and has lived or worked in areas where ticks are present, or with a blood test.
What is the best antibiotic for chronic Lyme disease?
Doxycycline is considered the first-line drug of choice for Lyme disease by most physicians.
Can stage 3 Lyme be treated?
Stage 3 (late disseminated) Lyme disease is also treated with various antibiotics: For Lyme disease that causes arthritis, 28 days of oral doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime is prescribed. Additional courses of antibiotics may be necessary, depending on the severity and persistence of your symptoms.
What is stage 3 Lyme disease?
Stage 3: Late disseminated Lyme disease This stage is characterized by: arthritis of one or more large joints. brain disorders, such as encephalopathy, which can cause short-term memory loss, difficulty concentrating, mental fogginess, problems with following conversations, and sleep disturbance.
What causes chronic lyme disease?
No one knows what causes chronic Lyme disease. One theory is the infection damages tissues or alters the immune system.
What is the best medicine for brain fog?
Chinese medicine. Herbs may be used to tame reactions that trigger inflammation, and help symptoms such as joint pain and “ brain fog.”
Can a tick bite cause lyme disease?
A bite from a bacteria-infected tick causes Lyme disease. If you get the disease, you might have lingering symptoms. Some people have ongoing pain and fatigue, says Afton Hassett, PsyD, principal investigator at the Chronic Pain and Fatigue Research Center at University of Michigan.
Can stopping a prescription cause symptoms?
Some experts believe stopping the drugs before your prescription ends may cause symptoms to linger. Do find experts who can help your symptoms. Ask your doctor if it would be worth your while to visit naturopaths, traditional Chinese medicine doctors, psychologists, or other experts.
What is the most common manifestation of Lyme disease?
Treatment regimens listed in the following table are for the erythema migrans rash, the most common manifestation of early Lyme disease. These regimens may need to be adjusted depending on a person’s age, medical history, underlying health conditions, pregnancy status, or allergies. Consult an infectious disease specialist regarding individual patient treatment decisions.
What is the treatment for lyme disease?
People with other forms of disseminated Lyme disease may require longer courses of antibiotics or intravenous treatment with antibiotics such as ceftriaxone. For more information about treating other forms of Lyme disease, see: Neurologic Lyme disease. Lyme carditis.
How long does a lyme disease last?
In a small percentage of cases, symptoms such as fatigue (being tired) and myalgia (muscle aches) can last for more than 6 months. This condition is known as post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS), although it is also sometimes called chronic Lyme disease.
How long does it take to recover from lyme disease?
Lyme arthritis. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has funded several studies on the treatment of Lyme disease that show most people recover within a few weeks of completing a course of oral antibiotics when treated soon after symptom onset.
Can you get Lyme disease with antibiotics?
People treated with appropriate antibiotics in the early stages of Lyme disease usually recover rapidly and completely. Early diagnosis and proper antibiotic treatment of Lyme disease can help prevent late Lyme disease.
Can you take macrolide with azithromycin?
NOTE: For people intolerant of amoxicillin, doxycycline, and cefuroxime, the macrolide azithromycin may be used, although it is less effective. People treated with azithromycin should be closely monitored to ensure that symptoms resolve.
What is the test for B. burgdorferi?
If the ELISA test is positive, this test is usually done to confirm the diagnosis. In this two-step approach, the Western blot detects antibodies to several proteins of B. burgdorferi.
What to do if you don't have a lyme disease rash?
Lab tests to identify antibodies to the bacteria can help confirm or rule out the diagnosis. These tests are most reliable ...
What is the test used to detect lyme disease?
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test. The test used most often to detect Lyme disease, ELISA detects antibodies to B. burgdorferi. But because it can sometimes provide false-positive results, it's not used as the sole basis for diagnosis. This test might not be positive during the early stage of Lyme disease, ...
What happens after Lyme disease treatment?
After treatment, a small number of people still have some symptoms, such as muscle aches and fatigue. The cause of these continuing symptoms, known as post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome, is unknown, and treating with more antibiotics doesn't help.
How long does it take for a central nervous system infection to go away?
Intravenous antibiotics. If the disease involves the central nervous system, your doctor might recommend treatment with an intravenous antibiotic for 14 to 28 days. This is effective in eliminating infection, although it may take you some time to recover from your symptoms. Intravenous antibiotics can cause various side effects, ...
How long after an infection can you test for antibodies?
Lab tests to identify antibodies to the bacteria can help confirm or rule out the diagnosis. These tests are most reliable a few weeks after an infection, after your body has had time to develop antibodies. They include: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test.
What to do if you have been bitten by a tick?
Make a list of: Your symptoms, and when they began. All medications, vitamins and other supplements you take, including doses. Questions to ask your doctor.
What is the ILADS treatment plan?
ILADS recommends individualized treatment based on the severity of symptoms, the presence of tick-borne coinfections and patient response to treatment. LDo believes that patients and their doctors should make Lyme disease treatment decisions together. This requires that patients be given sufficient information about the risks and benefits ...
What does LDo mean?
LDo endorses the ILADS guidelines, which allow greater exercise of clinical discretion by physicians and provide patients with more treatment options. It is the doctor’s responsibility to tell patients about the different treatment options so that patients can make an informed choice.
What is the ILADS approach?
These physicians use treatment approaches employed for persistent infections like tuberculosis , including a combination of drugs and longer treatment durations.
Can you take probiotics while taking antibiotics?
It is important to take probiotics while on antibiotics to maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. Furthermore, antibiotics may interact with other drugs, supplements or food. The National Institutes of Health’s MedLinePlus website gives information about drug interactions. « Previous Page Lyme Disease Diagnosis.
Can ILADS treat Lyme disease?
They may treat a Lyme rash for a longer period of time than the IDSA recommends, to ensure that the disease does not progress. They are unlikely to withhold treatment pending laboratory test results .
Can spirochetal infection persist?
IDSA claims that spirochetal infection cannot persist in the body after a short course of antibiotics. The group also denies the existence of chronic Lyme disease. In contrast, the International Lyme and Associated Diseases Society (ILADS), regards Lyme disease as often difficult to diagnose and treat, resulting in persistent infection in many ...
Can antibiotics be used for lyme disease?
The ideal antibiotics, route of administration and duration of treatment for persistent Lyme disease are not established. No single antibiotic or combination of antibiotics appears to be capable of completely eradicating the infection, and treatment failures or relapses are reported with all current regimens, although they are less common with early aggressive treatment.
What is the cause of Lyme disease?
In addition to Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacteria that causes Lyme disease, there are several other tick-borne co-infections that may also contribute to more prolonged and complicated illness.
What is a PTLD?
Post Treatment Lyme Disease (PTLD) represents a research subset of patients who remain significantly ill 6 months or more following standard antibiotic therapy for Lyme disease. PTLD is characterized by a constellation of symptoms that includes severe fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, sleep disturbance, depression, and cognitive problems such as difficulty with short-term memory, speed of thinking, or multi-tasking. In the absence of a direct diagnostic biomarker blood test, PTLD has been difficult to define by physicians, and its existence has been controversial. However, our clinical research shows that meticulous patient evaluation when used alongside appropriate diagnostic testing can reliably identify patients with a history of previously treated Lyme disease who display the typical symptom patterns of PTLD.
How common is PTLD after lyme disease?
The rates of Post Treatment Lyme Disease after neurologic involvement may be as high as 20% or even higher.
What are the risk factors for lyme disease?
Risk factors for Post Treatment Lyme Disease include: 1 Delay in diagnosis 2 Increased severity of initial illness 3 Presence of neurologic symptoms
How high is the risk of Lyme disease after treatment?
The rates of Post Treatment Lyme Disease after neurologic involvement may be as high as 20% or even higher. Other risk factors being investigated are genetic predispositions and immunologic variables.
What antibiotics are used for borrelia?
Other antibiotics that have activity against borrelia include the penicillin-like antibiotic, amoxicillin, and the second generation cep halosporin, Ceftin. The mainstay of treatment is with oral (pill) antibiotics, but intravenous antibiotics are sometimes indicated for more difficult to treat cases of neurologic-Lyme disease, such as meningitis, ...
Can antibiotics help with lyme disease?
The use of antibiotics is critical for treating Lyme disease. Without antibiotic treatment, the Lyme disease causing bacteria can evade the host immune system, disseminate through the blood stream, and persist in the body. Antibiotics go into the bacteria preferentially and either stop the multiplication of the bacteria (doxycycline) ...
How long does it take to cure lyme disease?
In more complicated cases, Lyme disease can usually be successfully treated with three to four weeks of antibiotic therapy.
How long does it take to get Lyme disease treatment?
Patients were treated with 30 days of an intravenous antibiotic followed by 60 days of treatment with an oral antibiotic.
What animal models have provided information on the transmission and pathogenesis of Lyme disease?
Animal models have provided considerable information on the transmission and pathogenesis of Lyme disease, as well as on the mechanisms involved in the development of protective immunity. Studies of the effects of antibiotic therapy in animals infected with B. burgdorferi have been conducted most often with mice but also with rats, hamsters, gerbils, dogs, and non-human primates.
How long does it take for ceftriaxone to improve?
In a statistical model, the ceftriaxone group showed a slightly greater improvement at 12 weeks, but at 24 weeks both the ceftriaxone and the placebo groups had improved similarly from baseline. In addition, adverse effects attributed to intravenous ceftriaxone occurred in 26 percent of patients.
Which bacteria causes Lyme disease?
The susceptibility of B. burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease, to specific antibiotics
Does prolonged antibiotic therapy help with PTLDS?
However, prolonged antibiotic therapy showed no benefit when compared with groups who received placebo.
Can bacteria survive after antibiotics?
In one study, NIAID-supported scientists found that remnants of B. burgdorferi remained in mice after antibiotic treatment. Another team of NIAID-supported investigators found that intact B. burgdorferi persist in nonhuman primates after antibiotic treatment. It was not possible to culture these bacteria and it is not clear whether they are infectious. More recent work by replicated the earlier finding of persisting DNA but non-cultivatable B. burgdorferi after antibiotic treatment using a mouse model. Additional research is needed and continues to be supported by NIAID to learn more about persistent infection in animal models and its potential implication for human disease.
What is a post treatment lyme disease?
This condition may be referred to as post-treatment Lyme disease (PTLD) or chronic Lyme disease (CLD). We don’t know exactly how many people who are diagnosed and treated remain ill. CDC estimates range from 10-20%.
What is a Lyme disease checklist?
LymeDisease.org has developed a Lyme disease symptom checklist to help you document your exposure to Lyme disease and common symptoms for your healthcare provider. You will receive a report that you can print out and take with you to your next doctor’s appointment.
How many people with lyme disease are unable to work?
Over 40% of patients with chronic Lyme disease reported that they currently are unable to work because of Lyme disease and 24% report that they have received disability at some point in their illness. « Previous Page Pets and Lyme disease. Next Page » Early Lyme Disease.
How many people died from lyme disease in 2014?
Although experts do not often attribute deaths to Lyme disease, studies have documented at least 23. In 2014, the CDC issued a warning regarding three sudden cardiac deaths related to Lyme carditis.
Can lyme disease be untreated?
To view Adult Lyme Symptoms, click here. Untreated or undertreated Lyme can cause some people to develop severe symptoms that are hard to resolve. This condition may be referred to as post-treatment Lyme disease (PTLD) or chronic Lyme disease (CLD).
Is lyme disease common in other diseases?
Many of the symptoms associated with Lyme disease are common in other diseases. The CDC surveillance criteria for confirmed cases specifically exclude most of the symptoms that patients report, including fatigue, sleep impairment, joint pain, muscle aches, other pain, depression, cognitive impairment, neuropathy, and headaches.
Is Lyme disease worse than congestive heart failure?
Investigators of the four NIH-sponsored retreatment trials documented that the patients’ quality of life was consistently worse than that of control populations and equivalent to that of patients with congestive heart failure.
How long does Lyme disease last?
However, a study by the CDC found that patients with Lyme disease generally reported longer treatment durations – with 60% of patients treated for five or more weeks and 36% treated for more than eight weeks (Hook 2015). Unfortunately, that study did not ask patients how long they had been ill.
Why is antibiotic use controversial?
The use and duration of antibiotics for chronic Lyme disease treatment is controversial because there is no biomarker that can determine whether the Lyme bacteria has been eradicated in CLD patients. Patients are often told that either chronic Lyme disease does not exist or that it is “incurable.”.
How many people have lyme disease?
As many as 3 million people have chronic Lyme disease in the US, and nobody knows the best way to treat them,” said Lorraine Johnson, CEO of LymeDisease.org. “The key finding here is that patients who are now well or who report substantial improvement have taken longer courses of antibiotics.”.
Why do physicians treat lyme disease?
Physicians who treat Lyme disease as their primary focus might be expected to have better results than physicians who don’t simply because volume of cases handled means a greater experience level . It is commonly recognized in medicine that volume of cases is associated with better treatment outcomes (Joynt 2013). Just as patients with cancer commonly seek out physicians who specialize in that area, perhaps patients with chronic Lyme disease should also.
How long does it take to get rid of lyme disease?
According to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2-4 weeks of antibiotic treatment is more than enough to knock out the illness.
What type of clinician oversees tick borne diseases?
Choices included: family physicians, internists, rheumatologists, infectious disease specialists, and clinicians whose practice focused on tick-borne diseases (often referred to as Lyme Literate MDs or LLMDs). Very few patients (11%) selected an infectious disease specialist. Seventy-five percent of high responders and well patients report having their care overseen by an LLMD.
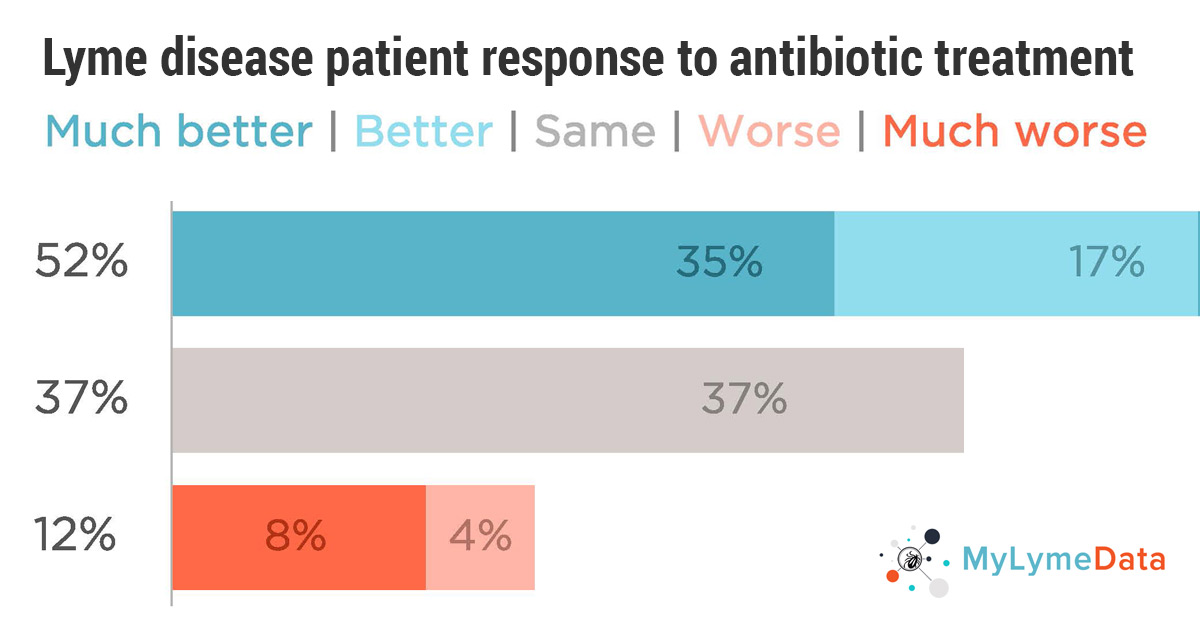
What is mylymedata viz?
MyLymeData Viz provides the community with results from MyLymeData . If you are enrolled in MyLymeData, we thank you for providing the data that will accelerate the pace of research in Lyme disease. If you are not enrolled, please enroll today.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment