
The conventional Stage 1 cervical cancer treatment options include:
- Surgery: Surgical procedures like Simple/Radical Hysterectomy to remove uterus and cervix (and pelvic lymph nodes) with cancer.
- Radiation: Can be given by using External Beam
- Radiation therapy, or Brachytherapy by placing a device filled with radioactive material inside vagina.
What is the life expectancy of someone with cervical cancer?
Jan 15, 2022 · Patients in Stage 1B1 cervical cancer are recommended chemoradiation. The primary treatment for cervical cancer with stage 1B1 or above is chemoradiation. During this, patients undergo chemotherapy and radiation therapy simultaneously. It also helps remove other cancer cells left in the lymph nodes, blood vessels or tissue after the surgery.
What is the best treatment for cervical cancer?
Mar 21, 2022 · Stage 1 cervical cancer treatments vary, based on your desire to maintain fertility. Treatment will also be determined by any spread of cancerous cells into the blood, lymphatic vessels, or nearby tissues. At this stage, localized cancer is usually treated with a cone biopsy (conization) in people who wish to preserve fertility.
How do you cure cervical cancer?
Immunotherapy for Cervical Cancer Common treatment approaches Depending on the type and stage of your cancer, you may need more than one type of treatment. For the earliest stages of cervical cancer, either surgery or radiation combined with chemo may be used. For later stages, radiation combined with chemo is usually the main treatment.
What are survival rates for cervical cancer?
Jun 17, 2021 · Most early-stage cervical cancers are treated with a radical hysterectomy operation, which involves removing the cervix, uterus, part of the vagina and nearby lymph nodes. A hysterectomy can cure early-stage cervical cancer and prevent recurrence. But removing the uterus makes it impossible to become pregnant.
Can Stage 1 cervical cancer be cured?
Stage I cervical cancer is curable for the majority of patients if surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy are appropriately used. A variety of factors ultimately influence a patient's decision to receive treatment of cancer.
What is the first line of treatment for cervical cancer?
Palliative platinum-based chemotherapy (CT) is the standard first-line treatment for metastatic/recurrent cervical cancer. The prognosis remains poor and effective second line options are urgently needed.
How long can you live with Stage 1 cervical cancer?
The prognosis for invasive cervical cancer depends on the stage. More than 90% of women with stage 0 survive at least 5 years after diagnosis. Stage I cervical cancer patients have a 5-year survival rate of 80% to 93%. Women with stage II cervical cancer have a 5-year survival rate of 58% to 63%.Sep 30, 2021
What is the best treatment for cervical cancer?
For the earliest stages of cervical cancer, either surgery or radiation combined with chemo may be used. For later stages, radiation combined with chemo is usually the main treatment. Chemo (by itself) is often used to treat advanced cervical cancer.
Do you need chemo for Stage 1 cervical cancer?
Stage 1 cervical cancer is usually treated with: surgery. combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy (chemoradiotherapy)
What are the symptoms of Stage 1 cervical cancer?
Signs and symptoms of stage 1 cervical cancer can include:Watery or bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and can have a foul odor.Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between menstrual periods or after menopause.Menstrual periods may be heavier and last longer than normal.Feb 17, 2022
Does a hysterectomy cure cervical cancer?
Nearly half of cervical cancers are diagnosed at an early stage, meaning the tumors are small and have not spread beyond the cervix. Although there are other treatment options, radical hysterectomy is the most common treatment for early-stage disease, and cure rates for the disease are around 80%.May 25, 2021
Does cervical cancer spread quickly?
Usually, cervical cancer grows slowly, but sometimes it can develop and spread quickly. Cervical cancer is one of the cancers that can occur in young women.
What are the warning signs of cervical cancer?
Once the cancer is more advanced, women may start to experience the following warning signs of cervical cancer:Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding. ... Fatigue. ... Loss of Appetite or Unexplained Weight Loss. ... Foul Smelling Vaginal Discharge. ... Pain During Sexual Intercourse. ... Lower Back, Pelvic or Appendix Pain. ... Leg Pain.
How do you remove cervical cancer?
Most early-stage cervical cancers are treated with a radical hysterectomy operation, which involves removing the cervix, uterus, part of the vagina and nearby lymph nodes. A hysterectomy can cure early-stage cervical cancer and prevent recurrence.Jun 17, 2021
Is cervical cancer treatable?
Cervical cancer is generally viewed as treatable and curable, particularly if it is diagnosed when the cancer is in an early stage. This disease occurs in the cervix, or the passageway that joins the lower section of the uterus to the vagina.
What is the main cause of cervical cancer?
It occurs most often in women over age 30. Long-lasting infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of cervical cancer. HPV is a common virus that is passed from one person to another during sex.
What is the treatment for stage 1 cervical cancer?
other health conditions that you have. Stage 1 cervical cancer is usually treated with: surgery. combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy (chemoradiotherapy) Read more about how your doctor decides which treatment you need.
What is the stage of cervical cancer?
Stage 1. Stage 1 means that the cancer is only in the neck of the womb (cervix). The main treatment is surgery. You might also have combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy (chemoradiotherapy) if you have stage 1B cervical cancer.
How long does radiotherapy last for stage 1B cervical cancer?
With this treatment, you have chemotherapy during your course of radiotherapy. You have daily external radiotherapy for 5 days every week, for around 5 weeks.
How big is stage 1B1?
In stage 1B1 the cancer is deeper than 5mm but no more than 2cm in size. In stage 1B2 the cancer is at least 2cm but not bigger than 4cm in size. In stage 1B3 the cancer is at least 4cm but is still only in the cervix.
How often do you get chemo after a radiotherapy course?
During your course of radiotherapy, you also have chemotherapy once a week or once every 2 or 3 weeks.
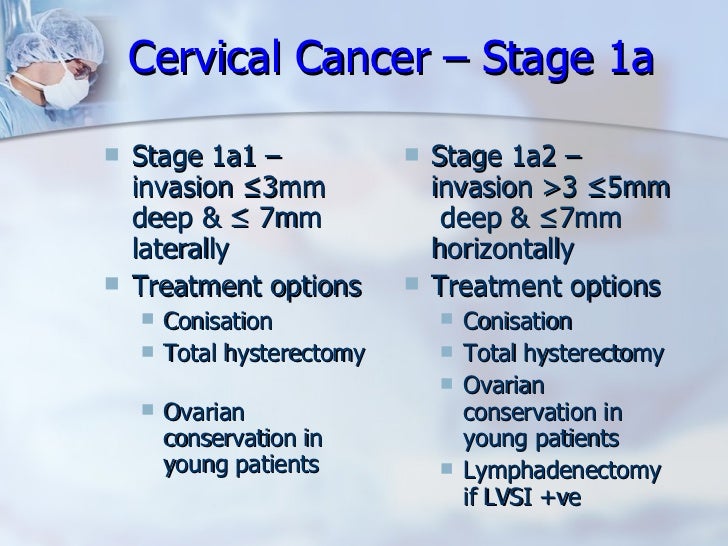
What is stage 1A?
Stage 1A. In stage 1A the growth is so small that it can only be seen with a microscope or colposcope. It can be divided into 2 smaller groups: stage 1A1. stage 1A2. Stage 1A1 means the cancer has grown less than 3 millimetres (mm) into the tissues of the cervix.
Can you have a baby after cervical cancer surgery?
Surgery for early cervical cancer usually involves removing your cervix and womb (hysterectomy). For some very early cer vical cancers, it might be possible to just remove most of the cervix, but leave enough behind so that you might be able to become pregnant and have a baby afterwards .
Surgery
Surgery is a main treatment for stage 1 cervical cancer. The type of surgery you are offered will depend on many factors, including your age, the stage and if you want to become pregnant.
Radiation therapy
You may be offered radiation therapy for stage 1 cervical cancer. It is used as the main treatment if you can’t have surgery or choose not to have surgery.
Chemoradiation
You may be offered chemoradiation for stage 1B1 cervical cancer. It is often a main treatment for stage 1B2 or higher cervical cancer. It is used if you can’t have surgery or choose not to have surgery.
Clinical trials
Talk to your doctor about clinical trials open to women with cervical cancer in Canada. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, find and treat cancer. Find out more about clinical trials.
What are the treatments for cervical cancer?
Common types of treatments for cervical cancer include: Surgery for Cervical Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Cervical Cancer. Chemotherapy for Cervical Cancer. Targeted Therapy for Cervical Cancer. Immunotherapy for Cervical Cancer.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What are the best doctors for cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team may include: 1 A gynecologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the female reproductive system 2 A gynecologic oncologist: a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system who can perform surgery and prescribe chemotherapy and other medicines 3 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer 4 A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team may include: A gynecologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the female reproductive system. A gynecologic on cologist: a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system who can perform surgery and prescribe chemotherapy and other medicines. A radiation on cologist: a doctor who uses radiation ...
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
Who are the specialists involved in cancer care?
Many other specialists may be involved in your care as well, including nurse practitioners, nurses, psychologists, social workers, rehabilitation specialists, and other health professionals. Health Professionals Associated with Cancer Care.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What is the test for cervical cancer?
A Pap test can detect abnormal cells in the cervix, including cancer cells and cells that show changes that increase the risk of cervical cancer. HPV DNA test.
What tests are done to determine if you have cervical cancer?
Your cancer's stage is a key factor in deciding on your treatment. Staging exams include: Imaging tests.
What is palliative care?
Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. Palliative care specialists work with you, your family and your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support that complements your ongoing care.
What tests can be done to check if you have cancer?
Tests such as X-ray, CT, MRI and positron emission tomography (PET) help your doctor determine whether your cancer has spread beyond your cervix. Visual examination of your bladder and rectum. Your doctor may use special scopes to see inside your bladder and rectum.
Can you remove cancer from a small cervix?
Surgery to cut away the cancer only. For a very small cervical cancer, it might be possible to remove the cancer entirely with a cone biopsy. This procedure involves cutting away a cone-shaped piece of cervical tissue, but leaving the rest of the cervix intact.
Can you use chemotherapy for cervical cancer?
Sometimes both methods are used. For locally advanced cervical cancer, low doses of chemotherapy are often combined with radiation therapy, since chemotherapy may enhance the effects of the radiation . Higher doses of chemotherapy might be recommended to help control symptoms of very advanced cancer.
Can you be prepared for cancer?
No one can be prepared for a cancer diagnosis. You can, however, try to manage the shock and fear you're feeling by taking steps to control what you can about your situation.
What is the most local stage of cervical cancer?
Stage 1 cervical cancer is the most local stage of cervical cancer. In stage 1, cancer cells: Grow from the surface of the cervix into deeper tissues of the cervix. Have not spread to nearby lymph nodes. Have not spread to distant sites. Stage 1 is split into A and B, which are further divided.
How to stay healthy with cervical cancer?
The best way to stay healthy is to see your healthcare provider regularly for routine screening. Many of the symptoms of cervical cancer can also be caused by other conditions. If you experience any signs and symptoms of cervical cancer, see a healthcare professional right away.
How many women will have cervical cancer in 2020?
Cervical cancer is one of the most common forms of gynecologic cancers, with 6 in 1,000 women receiving a cervical cancer diagnosis at some point in their lifetime. In 2020, American Cancer Society’s estimates there were an estimated 14,000 new cases of invasive cervical cancer diagnosed in the United States.
What happens when cervix cancer grows?
Cervical cancer occurs when previously healthy cells in the cervix become abnormal. As they grow, they crowd healthy cells. If the abnormal cells spread to other areas of the body, it makes it harder for the body to function correctly. Cervical cancer used to be one of the most common causes of cancer death for American women.
What is stage 2 cancer?
Stage 2 is split into A and B, but 2A is additionally divided. 2A: Cancer has grown beyond the cervix and uterus, but not into the parametrium. 2A1: The cancer is smaller than 4 cm (1 ⅗ inch). 2A2: The cancer is larger than 4 cm. 2B: The cancer extends beyond the cervix and uterus and has spread into the parametrium.
What is a radical hysterectomy?
A radical hysterectomy is a total hysterectomy, however, it includes the uppermost part of the vagina near the cervix (parametrium) and the pelvic ligaments that support the uterus.
Where does stage 2 cervical cancer spread?
Stage 2 cancer spreads to the parametrium and past the uterus to the upper vagina. Because the tumor is growing into nearby tissue, noticeable symptoms are more likely to occur at this stage. Symptoms of stage 2 cervical cancer include: Abnormal uterine bleeding.
What are the stages of cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer stages. Stage 1: The cancer is limited to the cervix and hasn’t grown any farther. This stage is further separated into subcategories. Stage 1A: The cancer is still so small that only a microscope can see it. Stage 1A1: There is a tiny amount of cancer. The tumor has grown 3 mm or less into the tissue of the cervix.
How does cervical cancer recur?
A metastatic recurrence occurs when the cancer has spread to other organs, such as the kidney, bladder or lymph nodes. This recurrence happens when the cervical cancer cells break off from the original tumor and travel to other parts of the body through the lymphatic or circulatory system. The cells then reattach at a new location. When the disease appears in another part of the body, it may be referred to as regional or distant recurrence. Symptoms of recurrent cervical cancer vary from patient to patient.
What is metastatic recurrence?
A metastatic recurrence occurs when the cancer has spread to other organs, such as the kidney, bladder or lymph nodes. This recurrence happens when the cervical cancer cells break off from the original tumor and travel to other parts of the body through the lymphatic or circulatory system.
How do you know if you have cervical cancer?
Signs and symptoms of local cervical cancer recurrence may include: Bleeding between periods, after sexual intercourse or after menopause. Periods that are heavier and last longer than usual. Unusual vaginal discharge that may be watery, pink or foul-smelling. Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse.
What is stage 3 cancer?
Stage 3: The cancer has reached the lower portion of the vagina and/or the muscles that surround the pelvic area (pelvic walls). The tumor may be large enough to cause kidney problems by blocking the tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder (the ureters). It may have reached nearby lymph nodes.
What is the stage of cancer in the pelvis?
Stage 3C1: The cancer has grown into lymph nodes in the pelvis. Stage 3C2: The cancer has reached lymph nodes around the aorta. Stage 4: The cancer has spread into the bladder, rectum, or beyond the pelvic area to distant parts of the body.
What percentage of cervical cancer patients have relapsed?
A number of treatment options are available for cancer that has relapsed, especially when it’s detected early. About 35 percent of patients with invasive cervical cancer develop persistent or recurrent disease following treatment. The recurrent cervical cancer rate is lower for those with early-stage disease.
What Is Stage 1 Cervical Cancer?
- The stage of a cancer tells you how big it is and whether it has spread. It helps your doctor decide which treatment you need. Doctors use the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging system for cervical cancer. There are 4 stages, numbered 1 to 4. Stage 1 means that your cancer is within the neck of the womb (cervix). It hasn’t spread to nearby tissues or oth…
Stage 1A
- In stage 1A the growth is so small that it can only be seen with a microscope or colposcope. It can be divided into 2 smaller groups: 1. stage 1A1 2. stage 1A2 Stage 1A1 means the cancer has grown less than 3 millimetres (mm) into the tissues of the cervix. Stage 1A2 means the cancer has grown between 3 and 5 mm into the cervical tissues.
Stage 1B
- In stage 1B the cancerous areas are larger, but the cancer is still only in the tissues of the cervix and has not spread. It can usually be seen without a microscope, but not always. It can be divided into 3 groups: 1. stage 1B1 2. stage 1B2 3. stage 1B3 In stage 1B1 the cancer is deeper than 5mm but no more than 2cm in size. In stage 1B2 the cancer is at least 2cm but not bigger than 4cm i…
Treatment
- The stage of your cancer helps your doctor to decide which treatment you need. Treatment also depends on: 1. your type of cancer (the type of cells the cancer started in) 2. where the cancer is 3. other health conditions that you have Stage 1 cervical cancer is usually treated with: 1. surgery 2. combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy (chemoradioth...
Surgery
- Surgery for early cervical cancer usually involves removing your cervix and womb (hysterectomy). For some very early cervical cancers, it might be possible to just remove most of the cervix, but leave enough behind so that you might be able to become pregnant and have a baby afterwards. This is called a radical trachelectomy. For some stage 1A1 cancers, it might be possible to remo…
Combined Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
- You might have chemoradiotherapy for stage 1B cervical cancers. With this treatment, you have chemotherapy during your course of radiotherapy. You have daily external radiotherapy for 5 days every week, for around 5 weeks. You also have a boost of internal radiotherapy (brachytherapy) at the end of your course. During your course of radiotherapy, you also have chemotherapy once a …
Other Stages