
Procedures
Sep 27, 2019 · The treatment for cardiac amyloidosis depends completely on which type you have, and in order to establish a diagnosis of amyloid you must first have what we call a tissue biopsy. So, some part of your body has been sampled and found to have amyloid deposits.
Therapy
2 rows · Jan 18, 2021 · Cardiac amyloidosis often shows a slight pericardial effusion, which, in most cases, is not ...
Nutrition
Mar 14, 2020 · Medications Chemotherapy. Many of the same types of medicines used to treat some forms of cancer are used in AL amyloidosis to stop... Heart medications. If your heart is affected, your doctor may suggest blood thinners to reduce the risk of clots and... Targeted therapies. For certain types of ...
What treatments are available for amyloidosis?
Management of cardiac amyloidosis involves treatment and prevention of complications, and halting or delaying amyloid deposition by specific treatments. Specific pharmacologic treatments available for ATTR amyloidosis include stabilizing molecules (tafamidis) and genetic silencers (patisiran and inotersen).
When to suspect a diagnosis of amyloidosis?
There’s a wide range of other treatments and medications that can help people with cardiac amyloidosis. These typically treat symptoms of this condition and usually involve the following: Heart transplant .
How to diagnose amyloidosis?
Oct 29, 2021 · The treatment for cardiac amyloidosis depends completely on which type you have, and in order to establish a diagnosis of amyloid you must first have what we call a tissue biopsy. So, some part of your body has been sampled and found to have amyloid deposits.
How does amyloidosis affect the heart?

What is the best treatment for cardiac amyloidosis?
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved tafamidis meglumine (Vyndaqel) and tafamidis (Vyndamax) for cardiomyopathy caused by transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (ATTR-CM) in adults in May 2019. These are the first FDA-approved treatments for ATTR-CM.Mar 25, 2020
How long can you live with cardiac amyloidosis?
Average life expectancy varies based on the type of cardiac amyloid (protein), how much the organs are involved and the stage at diagnosis. Based on these factors, the worst case scenario could be six months, while in some cases, life expectancy can be eight to 10 years after diagnosis.
What are the stages of cardiac amyloidosis?
Stage I (TnI <0.1 ng/mL and NT-proBNP <332 pg/mL), stage II (TnI >0.1 ng/mL and NT-proBNP >332 pg/mL), and stage III (TnI >0.1 ng/mL and NT-proBNP >332 pg/mL). Stage I (TnI <0.1 ng/mL and BNP <81 pg/mL), stage II (TnI >0.1 ng/mL or NT-proBNP >81 pg/mL), and stage III (TnI >0.1 ng/mL and NT-proBNP >81 pg/mL).Jan 17, 2019
How do you get cardiac amyloidosis?
The condition can be inherited. This is called familial cardiac amyloidosis. It can also develop as the result of another disease such as a type of bone and blood cancer, or as the result of another medical problem causing inflammation. Cardiac amyloidosis is more common in men than in women.Jun 25, 2020
What is the latest treatment for amyloidosis?
Diagnoses are often delayed, and approximately 30% of patients die within the first year of diagnosis. The new approval is for subcutaneous daratumumab (Darzalex Faspro), to be used in combination with bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone.Jan 20, 2021
Is exercise good for cardiac amyloidosis?
By exercising regularly, you can help fight pain and fatigue related to amyloidosis. The key, though, is to exercise safely. Finding a workout buddy can help.Aug 20, 2018
How serious is cardiac amyloidosis?
Patients who have the AL type of amyloid affecting the heart do have the worst prognosis, and in fact, for those patients, if they start to get heart failure symptoms, severe shortness of breath and fluid building up, a person generally will deteriorate quite rapidly unless they receive effective treatment.
Is amyloidosis a terminal of the heart?
Amyloid reduces your heart's ability to fill with blood between heartbeats. Less blood is pumped with each beat, and you may experience shortness of breath. If amyloidosis affects your heart's electrical system, your heart rhythm may be disturbed. Amyloid-related heart problems can become life-threatening.Mar 14, 2020
Is cardiac amyloidosis fatal?
Amyloidosis can affect the heart, kidneys, liver, spleen, nervous system, stomach or intestines. The condition is rare (affecting fewer than 4,000 people in the United States each year), but it can be fatal.
Can you survive cardiac amyloidosis?
Amyloidosis has a poor prognosis, and the median survival without treatment is only 13 months. Cardiac involvement has the worst prognosis and results in death in about 6 months after onset of congestive heart failure. Only 5% of the patients with primary amyloidosis survive beyond 10 years.Mar 25, 2020
When should you suspect cardiac amyloidosis?
The most common clinical scenarios that should elicit suspicion for amyloidosis are non-diabetic nephrotic range proteinuria, cardiac failure with left ventricular hypertrophy in the absence of aortic stenosis or hypertension, peripheral or autonomic neuropathy without an obvious cause, chronic inflammatory ...
What are warning signs of amyloidosis?
Signs and symptoms of amyloidosis include:Feeling very weak or tired.Losing weight without trying.Swelling in the belly, legs, ankles or feet.Numbness, pain or tingling in hands or feet.Skin that bruises easily.Purple spots (purpura) or bruised-looking areas of skin around the eyes.More items...
What is the best treatment for high tumor burden?
Bortezomib-based regimens. Patients with high tumor burden or who are ineligible for SCT achieved favorable results with combinations including proteasome inhibitors such as cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (CyBorD) or bortezomib, melphalan, and dexamethasone, rather than melphalan plus dexamethasone.
What is Daratumumab used for?
Daratumumab is an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody used for multiple myeloma. A case report and a retrospective study have described the safety and efficacy of daratumumab in patients with relapsed or refractory AL amyloidosis [75].
What is CA in medical terms?
Cardiac amyloidosis (CA) is a systemic disease caused by the extracellular deposition of insoluble amyloid fibrils in the heart [1]. The clinical outcome depends on the extent of tissue involvement and the type of deposited amyloid fibrils.
Is pomalidomide a derivative of thalidomide?
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide with structural similarity to both thalidomide and lenalidomide. A study of patients previously treated with melphalan, bortezomib, and SCT showed promising results. All patients were evaluable for a hematologic response, with a response rate of 38% [74]. Monoclonal antibodies.
Is ixazomib a proteasome inhibitor?
Ixazomib is a new oral proteasome inhibitor; relapse-refractory AL produces a hematologic response in 52% of patients and an organ response in 56% of patients at a dosage of 4 mg by mouth weekly [70]. The immunomodulatory derivatives.
Is beta blocker effective for HF?
Therefore, traditional HF treatment, including beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin-receptor blockers, appears to be less effective in these patients [33]. In patients with atrial fibrillation and CA, beta-blockers may play a role in rate control, but caution is advised.
Is lenalidomide used in amyloidosis?
Lenalidomide has also been tested in amyloidosis. In a trial of lenalidomide, melphalan, and dexamethasone with 22 of 25 patients having stage II or III cardiac amyloidoses, the 1-year survival rate was 58%. Organ responses were seen in 8%.
What are the different forms of amyloidosis?
Systemic forms of amyloidosis affecting the heart, are mainly AL, ATTRwt, and some forms of ATTRv amyloidosis.
What is the pathophysiology of AL amyloidosis?
The underlying cause of AL amyloidosis is usually a small clonal B cell or plasma cell population, whereas only about 10% of patients have overt multiple myeloma or, in rare cases, a secretory active B-cell lymphoma.
What is ATTR amyloidosis?
ATTR amyloidosis is the most common familial form of amyloidosis and is caused mainly by non-synonymous mutations in the transthyretingene (TTR; Chr. 18q12.1; 147 amino acids), which lead to instability of the protein's tetrameric structure.
What is CMR imaging?
In recent years, cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) has gained considerable importance in the diagnosis of amyloidosis and its distinction from other cardiomyopathies. The following three strengths of the method are particularly important: 1 the exact analysis of heart function and anatomy, 2 the recording of myocardial infiltration using contrast-enhanced images (“late gadolinium enhancement” [LGE]), 3 the recognition of diffuse changes in the myocardial extracellular space with specific mapping techniques.
Which amyloidosis is mainly the light chain?
Systemic forms of amyloidosis, which affect the heart, are mainly the light chain (AL) and ATTR amyloidoses, resulting from the deposition of misfolded transthyretin (either as the wild-type [ATTRwt] or mutated [ATTRv] form).
How many patients have CTS before cardiac manifestation?
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) occurs in up to 70% of patients with ATTRwt amyloidosis 5–10 years before cardiac manifestation. Furthermore, spinal canal stenosis may occur. An atraumatic biceps tendon rupture occurs in about 33% of patients.
How many proteins are involved in amyloidosis?
So far, more than 30 different proteins have been described to cause, when misfolded, amyloidosis.
What are the two types of amyloidosis that are most likely to damage the heart?
The two kinds most likely to damage the heart are light chain amyloidosis (AL) and transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR). Treatment depends on the specific subtype of amyloidosis. It may involve medication, chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation.
How to diagnose amyloidosis?
To confirm a diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis, you will need either a cardiac biopsy or technetium pyrophosphate scan. A cardiac biopsy involves taking a small sample of heart tissue that the doctor examines under the microscope.
What is a technetium pyrophosphate scan?
A technetium pyrophosphate scan is similar to an MRI in that it gives a picture of the heart. A dye is injected before the scan and will cause transthyretin amyloidosis to “light up.”. If either test indicates TTR amyloidosis, genetic testing is recommended to confirm the subtype. Other tests that might be recommended:
How to treat TTR?
Treatment depends on the subtype and may involve a combination of these approaches: 1 Medication to stabilize the TTR protein (for ATTR, not AL) 2 Medication to “silence” the TTR gene and prevent the body from producing the TTR protein (for ATTR, not AL) 3 Medications to reduce swelling or control irregular heartbeat 4 A pacemaker to regulate the heartbeat 5 Chemotherapy (for AL, not for ATTR) 6 Auto stem cell transplant (for AL, not for ATTR) 7 Clinical trial participation to test new therapies.
Can amyloidosis be reversed?
Cardiac amyloidosis is a serious condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach. Though the condition cannot be reversed, treatment may be able to slow the progression of the amyloid deposits and address damage to the heart.
What is the most important principle of treatment for cardiac amyloidosis?
The most important principle of treatment for cardiac amyloidosis is strict fluid balance control. Specialist heart failure nurse involvement may help patients to achieve this. When there is cardiac amyloidosis, the heart may be too stiff to pump the blood efficiently around the body.
What is the treatment for AL amyloidosis?
Treatment of AL amyloidosis is directed towards the abnormal plasma cells. Some of the drugs must be used cautiously when there are AL amyloid deposits in the heart. Doctors take into account the presence of amyloid deposits in the heart when choosing treatment regimens.
What is ATTR amyloid?
ATTR amyloid in the heart. In 2019 two new genetic therapies, patisiran and inotersen, were approved by the regulatory authorities in the EU and the US, and subsequently by NHS England, for treating neuropathy in patients with hereditary ATTR amyloidosis.
What happens to amyloid precursor protein in SAP scan?
SAP scans in thousands of patients with various forms of amyloidosis have shown that when amyloid precursor protein supply is controlled: existing amyloid deposits often regress (become smaller) new amyloid deposits stop appearing. organ function is often preserved and may also recover.
How to treat amyloidosis?
Treatment of cardiac amyloidosis, as in all types of amyloidosis, is currently based on the following principles: 1 Reducing the supply of amyloid forming precursor proteins. 2 Supporting the function of organs containing amyloid.
What is the best treatment for a swollen ankle?
Diuretics : Doctors will often prescribe diuretics (water tablets) which increase the amount of urine produced and help the body to lose excess salt and water in the urine. This can help to reduce ankle swelling and breathlessness. Diuretics prescribed may include furosemide and spironolactone.
Why is it important to tell your doctor about your medications?
It is very important that patients tell their doctors about any drugs they may be taking, including complementary or alternative medications or supplements. Some drugs may interact inside the body and lead either to toxicity due to raised drug levels, or lack of effect due to reduced drug levels.
What is used to treat AL amyloidosis?
Chemotherapy. Many of the same types of medicines used to treat some forms of cancer are used in AL amyloidosis to stop the growth of abnormal cells that produce the protein leading to formation of amyloid.
What tests can be done to determine if you have amyloidosis?
Laboratory tests . Your blood and urine may be analyzed for abnormal protein that can indicate amyloidosis. Depending on your signs and symptoms, you may also have thyroid and liver function tests.
What drugs can cause amyloidosis?
For certain types of amyloidosis, drugs such as patisiran (Onpattro) and inotersen (Tegsedi) can interfere with the commands sent by faulty genes that create amyloid. Other drugs, such as tafamidis (Vyndamax, Vyndaqel) and diflunisal, can stabilize bits of protein in the bloodstream and prevent them from getting transformed into amyloid deposits.
Why is it important to know early diagnosis of amyloidosis?
Amyloidosis is often overlooked because the signs and symptoms can mimic those of more-common diseases. Early diagnosis can help prevent further organ damage. Precise diagnosis is important because treatment varies greatly, depending on your specific condition.
What to do if your heart is affected?
If your heart is affected, your doctor may suggest blood thinners to reduce the risk of clots and medications to control your heart rate. You may also need to restrict your salt intake and take drugs that increase urination, which can reduce the strain on your heart and kidneys. Targeted therapies.
How do you get stem cells from your blood?
Surgical and other procedures. Autologous blood stem cell transplant. This procedure involves collecting your own stem cells from your blood through a vein and storing them for a short time while you have high-dose chemotherapy. The stem cells are then returned to your body via a vein.
What is the difference between MRI and nuclear imaging?
These can be used to assess the structure and function of your heart. Nuclear imaging. In this test, tiny amounts of radioactive material (tracers) are injected into a vein.
What is the treatment for cardiac amyloidosis?
Specific pharmacologic treatments available for ATTR amyloidosis include stabilizing molecules (tafamidis) and genetic silencers (patisiran and inotersen).
What is the cause of amyloidosis?
Cardiac amyloidosis is a serious and progressive infiltrative disease that is caused by the deposition of amyloid fibrils at the cardiac level. It can be due to rare genetic variants in the hereditary forms or as a consequence of acquired conditions.
What is the pathognomonic histological property of green birefringence?
Cardiac amyloidosis is characterized by the extracellular deposition of mis-folded proteins in the heart with the pathognomonic histological property of green birefringence when viewed under cross polarized light after staining with Congo red. 1
What are the two critical phases of amyloidosis?
Diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis includes two critical phases: (i) suspicious phase and (ii) definite diagnosis phase. The latter phase also includes appropriate typing of the amyloid, which is critical to guide specific treatment.
What does grade 0 mean?
Grade 0: absence of tracer myocardial uptake and normal bone uptake; Grade 1: myocardial uptake in a lower degree than at bone level; Grade 2: similar myocardial and bone uptake; and Grade 3: myocardial uptake greater than bone with reduced/absent bone uptake. Figure 2. Open in new tab Download slide.
How many amyloids are in the myocardium?
While more than 30 proteins are known to be capable of aggregating as amyloid in vivo, only nine amyloidogenic proteins accumulate in the myocardium to cause significant cardiac disease. 3
Is cardiac uptake grade 1?
In the case that cardiac uptake is Grade 1, non-invasive diagnosis is not possible and histological confirmation of amyloid deposits (could be extracardiac) is required. Scintigraphy does not show cardiac uptake and at least one of the monoclonal protein tests is abnormal.
What is the best treatment for amyloids?
A bone marrow transplant (autologous peripheral blood transplant), which treats the source of the abnormal proteins and allows the heart to improve. Chemotherapy.
What is the cardiac amyloidosis clinic?
At the Cardiac Amyloidosis Clinic, doctors who specialize in blood conditions (hematologists), the heart (cardiologists ), imaging (radiologists) and other specialties work with you to provide excellent, comprehensive care. The team's seamless collaborative approach means you get an accurate diagnosis and treatment based on the exact type of abnormal protein affecting your heart.
What is the worst prognosis for an AL patient?
Patients who have the AL type of amyloid affecting the heart do have the worst prognosis, and in fact, for those patients, if they start to get heart failure symptoms, severe shortness of breath and fluid building up, a person generally will deteriorate quite rapidly unless they receive effective treatment.
What is the name of the condition where abnormal proteins bind together to form a substance called?
Cardiac amyloidosis is a type of amyloidosis, which occurs when the body produces abnormal proteins that bind together to form a substance called amyloid. Amyloids can deposit in any tissue or organ, including the heart, kidneys, liver and nerves.
What is a biopsy?
Biopsy — examining a sample of tissue. MRI of the heart, though this can't be used in people with kidney disease as it uses an injected contrast agent. Mayo Clinic has led the way in developing innovative treatments for many heart disorders, including cardiac amyloidosis.
What is the Mayo Clinic team approach?
The team approach used at Mayo Clinic means efficient, effective care focused on you. Your care team partners with you to prevent or manage complications of your condition. You'll also receive a follow-up care plan that you can take with you for your home doctor.
Does amyloidosis cause shortness of breath?
It reduces your heart's ability to fill with blood between heartbeats, resulting in less blood being pumped with each beat. This can result in shortness of breath. Cardiac amyloidosis can also affect your heart's electrical system, resulting in a disturbed heart rhythm.
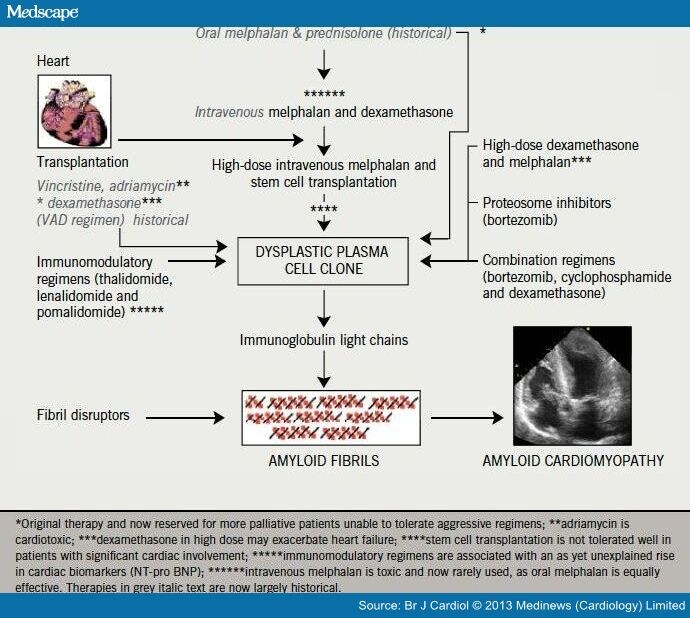
Amyloid Specific Treatment
Treatment of Cardiac Amyloidosis Symptoms
Blood Pressure
Special Medication Considerations
Specialist to consult
Drug Interactions
- AL amyloid in the heart
Treatment of AL amyloidosis is directed towards the abnormal plasma cells. Some of the drugs must be used cautiously when there are AL amyloid deposits in the heart. Doctors take into account the presence of amyloid deposits in the heart when choosing treatment regimens. - ATTR amyloid in the heart
New drugs In 2019 two new genetic therapies, patisiran and inotersen, were approved by the regulatory authorities in the EU and the US, and subsequently by NHS England, for treating neuropathy in patients with hereditary ATTR amyloidosis. Since then, the NAC doctors have bee…
Surgery and Anaesthesia
- All types of amyloid deposits in the heart (AL, ATTR and other rare hereditary types) cause the heart to stiffen which can lead to symptoms of heart failure. Patients can benefit from supportive treatment measures for heart failure, as described below. However many standard medications used for heart failure are not helpful for patients with cardiac amyloidosis.
Pregnancy and Fertility
- Careful control of high blood pressure is important in patients with amyloid deposits affecting the kidneys. However, certain blood pressure lowering drugs should be avoided if there is amyloid affecting the heart. The drugs which are most commonly used in heart failure due to other causes may actually lead to a worsening of heart failure due to amyloidosis. In patients with low blood p…