
What is the drug of choice for atrial flutter?
Initial treatment of atrial flutter targets the rate control (which is frequently ~150 BPM). Drugs of choice include beta blockers such as esmolol (0.5 mg/kg IV bolus followed by 50-300 ucg/kg/min) and propranolol, or calcium channel blockers such as verapamil (5-10 mg IV) or diltiazem.
What is the fastest way to cure atrial flutter?
Heart rate medicines: The most common way to treat atrial fibrillation is with drugs that control your heartbeat. These slow your rapid heart rate so your heart can pump more effectively. Most people take a medication called digoxin (Lanoxin). You may require additional drugs.May 29, 2020
Can atrial flutter go away by itself?
Sometimes, atrial flutter goes away by itself and no further action is needed. If it persists, your doctor may pursue any of the following treatments: Treatment of any underlying conditions. Catheter ablation — procedure to destroy the errant electrical pathways; performed together with an electrophysiological study.
How do you calm atrial flutter?
You may be able to keep your heart pumping smoothly for a long time if you:manage your blood pressure.manage your cholesterol levels.eat a heart-healthy diet.exercise for 20 minutes most days of the week.quit smoking if you smoke.maintain a healthy weight.get enough sleep.drink alcohol in moderation.More items...
Can you live a long life with atrial flutter?
The good news is that although AF is a long-term condition, if managed correctly, you can continue to lead a long and active life. There are a number of steps you can take that will help you manage your condition, lower your risk of stroke and relieve any worries you may have.
What is the major cause of atrial flutter?
Atrial flutter is one of the more common abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). It's caused by an abnormal electrical circuit in the upper chambers of the heart (atria) that makes the atria beat quickly and flutter instead of fully squeezing.
What happens if atrial flutter is not treated?
When untreated, atrial flutter often leads to a rapid heart beat. During atrial flutter, the atrium can beat up to 300 times a minute, and every second beat gets through to the ventricle, resulting in a pulse rate in the range of 150 beats per minute (the normal heart beat is 60 to 90 beats per minute).Nov 29, 2005
How successful is ablation for atrial flutter?
If it does not, you may need a second catheter ablation procedure to eliminate the flutter. In these cases, the overall success rate is approximately 75-85 percent.
How fast is atrial flutter?
Atrial flutter occurs when a “reentrant” circuit is present, causing a repeated loop of electrical activity to depolarize the atrium at a rate of about 250 to 350 beats per minute; the atrial rate in atrial fibrillation is 400 to 600 bpm.
Which is more serious AFib or atrial flutter?
Both heart diseases have the potential of becoming serious. However, many doctors and other health care professionals consider atrial flutter to be less serious than atrial fibrillation because flutter symptoms tend to be less severe and flutter waves have a less risk of embolization (clot formation).
What is catheter ablation for atrial flutter?
Catheter ablation is an emerging technique that is used to treat atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. This procedure involves the use of energy, either through heat or freezing, to eliminate (ablate) the areas of heart muscle that are causing the heart to beat irregularly.
How to cure atrial flutter?
Currently, atrial flutter is successfully "cured" by radiofrequency catheter ablation; but treatment to restore atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm has been the traditional use of medications and external cardioversion.
What is radiofrequency ablation?
A technique pioneered at UCSF, radiofrequency catheter ablation destroys or disrupts parts of the electrical pathways causing the arrhythmias, providing relief for patients who may not have responded well to medications, or who would rather not or can't take medications.
How do pacemakers work?
They are small devices that are implanted beneath the skin below the collarbone and connected to a pace wire (s) positioned inside the heart via a vein; this delivers a small electrical impulse to stimulate the heart to beat when it is going too slow.
What is the purpose of a pacemaker?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the first of a new type of pacemaker that paces both ventricles of the heart to coordinate their contractions and improve their pumping ability. According to the test results presented to the FDA, cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT):
Where is the implantable cardioverter defibrillator located?
It is slightly larger than a pacemaker and usually is implanted beneath the skin below the collarbone. It is connected to a defibrillation/pace wire (s) positioned inside the heart via a vein.
Can you convert atrial fibrillation to normal?
The less time a patient is in atrial fibrillation, the easier it is to cardiovert back to a normal rhythm, but even patients with long-standing chronic atrial fibrillation can be converted successfully to a normal rhythm through internal cardioversion.
What is the treatment for atrial flutter?
Catheter ablation treatment. Two types of catheter ablation are available for the treatment of chronic or recurrent atrial flutter, one curative and one palliative. Appropriate application of radiofrequency energy via an electrode catheter can be used to cure atrial flutter.
When does atrial flutter occur?
It can occur in patients with ostensibly normal atria or with abnormal atria. Atrial flutter occurs commonly in patients in the first week after open heart surgery. Patients with atrial flutter not uncommonly demonstrate sinus bradycardia or other manifestations of sinus node dysfunction.
How to restore sinus rhythm?
When atrial flutter is diagnosed , three options are available to restore sinus rhythm: (1) administer an antiarrhythmic drug; (2) initiate DC cardioversion; or (3) initiate rapid atrial pacing to terminate the atrial flutter (fig 4 ). Selection of acute treatment for atrial flutter with either DC cardioversion, atrial pacing or antiarrhythmic drug therapy will depend on the clinical presentation of the patient and both the clinical availability and ease of using these techniques. Since DC cardioversion requires administration of an anaesthetic agent, this may be undesirable in the patient who presents with atrial flutter having recently eaten or the patient who has severe chronic obstructive lung disease. Such patients are best treated with either antiarrhythmic drug therapy or rapid atrial pacing to terminate the atrial flutter, or with an AV nodal blocking drug to slow the ventricular response rate. When atrial flutter is associated with a situation requiring urgent restoration of sinus rhythm—for example, 1:1 AV conduction or hypotension—prompt DC cardioversion is the treatment of choice. For the patient who develops atrial flutter following open heart surgery, use of the temporary atrial epicardial wire electrodes to perform rapid atrial pacing to restore sinus rhythm is the treatment of choice (fig 4 ).
How long does atrial flutter last?
Atrial flutter typically is paroxysmal, usually lasting seconds to hours, but on occasion lasting longer. Occasionally, it is a persistent rhythm. Atrial flutter as a stable, chronic rhythm is unusual, as it usually reverts either to sinus rhythm or to atrial fibrillation, either spontaneously or as a result of treatment. However, atrial flutter has been reported to be present for up to 20 years or more. It can occur in patients with ostensibly normal atria or with abnormal atria. Atrial flutter occurs commonly in patients in the first week after open heart surgery. Patients with atrial flutter not uncommonly demonstrate sinus bradycardia or other manifestations of sinus node dysfunction. Atrial flutter is also associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, mitral or tricuspid valve disease, thyrotoxicosis, and surgical repair of certain congenital cardiac lesions which involve large incisions or suture lines in the atria. 10 It is also associated with enlargement of the atria for any reason, especially the right atrium.
What is the most common atrial tachyarrhythmia?
Treatment of atrial flutter. After atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter is the most important and most common atrial tachyarrhythmia. Although it was first described 80 years ago, techniques for its diagnosis and management have changed little for decades.
What is the INR for atrial fibrillation?
In short, in patients with atrial flutter, daily warfarin treatment to achieve an international normalised ratio (INR) of 2 to 3 is recommended using the same criteria as for atrial fibrillation. Also, the same criteria apply for cardioversion.
Is atrial flutter a long term treatment?
This is among the reasons why this form of therapy is no longer the long term treatment of choice in most patients with atrial flutter. For patients in whom drug treatment is selected, an important measure of efficacy should be the frequency of recurrence of atrial flutter rather than a single recurrent episode.
How to get rid of atrial flutter?
Often, getting rid of the atrial flutter altogether with an ablation procedure is the preferable course of action. In any case, however, chronic anticoagulation therapy may be recommended to prevent stroke based on a person's unique risk factors, just as with atrial fibrillation. 6.
How to stop a flutter?
In people who are having an acute episode, atrial flutter can be stopped quite readily with electrical cardioversion or by acutely administering antiarrhythmic drugs (usually, ibutilide or dofetilide).
How much success does ablating atrial fibrillation have?
Fortunately, ablating atrial flutter is usually a relatively straightforward procedure with a very favorable rate of success (well over 90% ). However, there is a 10% to 33% chance of the flutter returning or atrial fibrillation occurring after ablation of the most common type of atrial flutter.
What is flutter wave?
Flutter waves are signals appearing on an ECG that represent the electrical impulse that is spinning around the atrial reentrant circuit. 4.
What is the cause of a fast heart rate?
Atrial flutter is a cardiac arrhythmia —a condition defined by an abnormal heart rhythm. More specifically, it is an arrhythmia that typically causes tachycardia (a fast heart rate) and palpitations . Atrial flutter is caused by the formation of extremely rapid, abnormal electrical impulses arising in the atria of the heart.
How many beats per minute is a heartbeat?
Typically, about half of these impulses are transmitted to the ventricles, producing a heart rate that is usually around 150 beats per minute. Ariel Skelley/Blend Images/Getty Images. The condition is related in many ways to atrial fibrillation, the more well-known arrhythmia.
Can antiarrhythmics help with atrial flutter?
Antiarrhythmic drugs have a poor success rate with atrial flutter, but the opposite is true for ablation (rhythm control). For this reason, and because of the many toxicities common with antiarrhythmic drug therapy, ablation therapy is by far the treatment of choice for most people who have atrial flutter. Fortunately, ablating atrial flutter is ...
What to do if you think you have atrial fibrillation?
If you think you may have atrial fibrillation, it is critical that you make an appointment with your family doctor. If atrial fibrillation is found early, your treatment may be easier and more effective. However, you may be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist).
What is the best medication for atrial fibrillation?
These medications include dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban. They are shorter acting than warfarin and usually don't require regular blood tests or monitoring by your doctor.
How does catheter ablation help with atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is often caused by rapidly discharging triggers, or "hot spots." In catheter ablation to treat atrial fibrillation, a doctor inserts long, thin tubes (catheters) into your groin and guides them through blood vessels to your heart. The electrodes at the tips of the catheters help your doctor determine where these triggers are located. Electrodes at the catheter tips can use radiofrequency energy, extreme cold (cryotherapy) or heat to destroy these triggers, scarring the tissue so that the erratic signals are normalized.
What is the procedure called when a catheter is placed in the left atrium?
Left atrial appendage closure. Your doctor may also consider a procedure called left atrial appendage closure. In this procedure, doctors insert a catheter through a vein in the leg and eventually guide it to the upper left heart chamber (left atrium).
How to diagnose atrial fibrillation?
To diagnose atrial fibrillation, your doctor may review your signs and symptoms, review your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition, including:
What is the best medication to slow your heart rate?
Digoxin. This medication may control the heart rate at rest, but not as well during activity. Most people need additional or alternative medications, such as calcium channel blockers or beta blockers. Beta blockers. These medications can help to slow the heart rate at rest and during activity.
What is a transducer in a heart?
Usually, a wandlike device (transducer) is held on your chest. Sometimes, a flexible tube with the transducer is guided down your throat through to your esophagus. Your doctor may use an echocardiogram to diagnose structural heart disease or blood clots in the heart. Blood tests.
What are the treatments for atrial flutter?
There are effective treatments for atrial flutter, including medication or procedures designed to scar small areas of heart tissue (ablation).
What causes a heart to beat so fast?
In atrial flutter, your heart's upper chambers (atria) beat too quickly. This causes the heart to beat in a fast, but usually regular, rhythm. Atrial flutter is a type of heart rhythm disorder ( arrhythmia) caused by problems in your heart's electrical system.
Is atrial flutter a disorder?
Atrial flutter is similar to atrial fibrillation, a common disorder that causes the heart to beat in abnormal patterns. People with atrial flutter have a heart rhythm that's more organized and less chaotic than that of atrial fibrillation. Sometimes you may have episodes of both atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation.
What is atrial flutter?
An atrial flutter is a type of abnormal heart rhythm, or arrhythmia. The human heart has four chambers. Two of these chambers, the left atrium and right atrium, make up the upper part of the heart. An atrial flutter occurs in either or both of these upper chambers.
What are the symptoms of atrial flutter?
Not everyone with an atrial flutter has symptoms and the condition may never be detected unless found accidently through tests for other issues.
What causes atrial flutter?
Atrial flutter is usually related to age and is rarely found in people younger than 50 years old. It is related to damage to the heart. The arrhythmia may occur after heart surgery or damage to the heart muscle.
What are the risk factors for atrial flutter?
Age is the most common risk factor for atrial flutter, but there are some other risk factors as well that could increase the risk. Not all people with risk factors will get atrial flutter.
What are some conditions related to atrial flutter?
Atrial fibrillation, the most common heart arrhythmia, is similar to atrial flutter, but more dangerous. Both conditions cause a rapid heartbeat, but with atrial flutter, the heartbeat is fast and regular. With afib, the heartbeat is fast and irregular.
How do doctors diagnose atrial flutter?
It can be difficult to diagnose atrial flutter in people who have occasional episodes because the only way to detect the arrhythmia is by seeing the electrical impulses during a flutter incident.
What are the treatments for atrial flutter?
Treating atrial flutter depends on the frequency and severity of symptoms. Some people do not need treatment, but for those who do, options include:
How are atrial flutter symptoms similar?
If symptoms do occur, they are similar: The major difference in symptoms is in the regularity of the pulse rate. Overall, the symptoms of atrial flutter tend to be less severe. There is also less chance of clot formation and stroke.
What is the pulse rate of an atrial flutter?
Only every second beat gets through to the ventricles. The resulting pulse rate is around 150 bpm.
What is the difference between AFIB and AFIB?
Atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation (AFib) are both types of arrhythmias. They both occur when there are problems with the electrical signals that make your heart chambers contract. When your heart beats, you’re feeling those chambers contracting. Atrial flutter and AFib are both caused when the electrical signals occur faster than normal.
What is the treatment for AFIB?
Treatment for AFib and atrial flutter has the same goals: Restore the normal rhythm of the heart and prevent blood clots. Treatment for both conditions may involve: Medications, including: calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers to regulate the heart rate. amiodarone, propafenone, and flecainide to convert the rhythm back to normal.
What is the procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to destroy the area inside your heart that’s causing the abnormal heart
Electrical cardioversion: This procedure uses an electrical shock to reset the rhythm of your heart. Catheter ablation : Catheter ablation uses radiofrequency energy to destroy the area inside your heart that’s causing the abnormal heart rhythm.
What is the normal heart rate for AFIB?
This leads to a rapid and irregular heart rhythm. A normal heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute (bpm). In AFib, the heart rate ranges from 100 to 175 bpm.
Does chest pain cause a flutter?
yes. chest pain or tightness. yes. yes. increased chance of blood clots and stroke. yes. yes. The major difference in symptoms is in the regularity of the pulse rate. Overall, the symptoms of atrial flutter tend to be less severe.
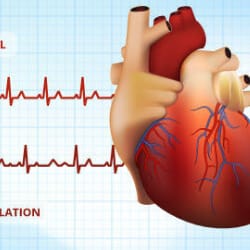
Mechanism
Classification
- All these types of atrial flutter fall under the category of type I atrial flutter as described by Wells and colleagues.11They are distinguished by the fact that they can always be interrupted by rapid atrial pacing, and have a rate range between 240340 beats/min (bpm).11 Type II atrial flutter11is a more rapid atrial flutter (rates >340 bpm) which is still being characterised. It is presently though…
Signs and symptoms
- Atrial flutter typically is paroxysmal, usually lasting seconds to hours, but on occasion lasting longer. Occasionally, it is a persistent rhythm. Atrial flutter as a stable, chronic rhythm is unusual, as it usually reverts either to sinus rhythm or to atrial fibrillation, either spontaneously or as a result of treatment. However, atrial flutter has been reported to be present for up to 20 years or …
Treatment
- When atrial flutter is diagnosed, three options are available to restore sinus rhythm: (1) administer an antiarrhythmic drug; (2) initiate DC cardioversion; or (3) initiate rapid atrial pacing to terminate the atrial flutter (fig 4). Selection of acute treatment for atrial flutter with either DC cardioversion, atrial pacing or antiarrhythmic drug t...
Diagnosis
- Similarly, when incisional re-entrant atrial flutter is identified by electrophysiological mapping techniques, a vulnerable isthmus usually can be identified and successfully ablated using radiofrequency catheter ablation techniques.9 There is insufficient information available to discuss the likely efficacy of successful radiofrequency ablation techniques to cure left atrial flu…
Prognosis
- Atrial flutter is quite difficult to suppress completely with drug treatment. In fact, based on available long term data, drug treatment offers a limited ability to maintain sinus rhythm without occasional to frequent recurrences of atrial flutter, even when multiple agents are used. This is among the reasons why this form of therapy is no longer the long term treatment of choice in m…
Medical uses
- In the past, standard antiarrhythmic drug treatment consisted of administration of a class IA agent (quinidine, procainamide, or disopyramide) in an effort to prevent recurrence. However, recent studies indicate that the type IC antiarrhythmic agents flecainide and propafenone are as effective, if not more effective, are generally better tolerated, and have less organ toxicity than cl…
Prevention
- Although one study found neither atrial clot formation nor stroke associated with atrial flutter in a relatively small cohort of patients after open heart surgery, the association of the potential risk of stroke with atrial flutter has now been established.14 15Other data support this association. Thus, atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation often co-exist in patients. Additionally, using transoesophageal …
Funding
- Supported in part by grant RO1 HL38408 from the National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, Maryland, USA.
Overview
Atrial Flutter Symptoms
Relevance
Risk Factors
Diagnosis
Treatment
- The goals of treatment for atrial flutter are to regulate your heart rate, reduce the risk of heart failure or stroke, and relieve any symptoms you may be experiencing. The right treatment option for you depends on several factors, including:5 1. Whether or not your atrial flutter is caused by an underlying condition 2. What symptoms you are experi...
A Word from Verywell
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment for atrial fibrillation depends on how long you've had A-fib, your symptoms and the underlying cause of the heartbeat problem. The goals of treatment are to: 1. Reset the heart rhythm 2. Control the heart rate 3. Prevent blood clots that can lead to stroke Atrial fibrillation treatment may involve: 1. Medications 2. Therapy to reset the h...
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment