Treatment for a blast injury Initial treatment options (as with sudden deafness) are hemorheologic infusion therapy with HAES (hydroxyethyl starch) and Procaine Procaine is a local anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is used primarily to reduce the pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin, and it is also used in dentistry. Owing to the ubiquity of the trade name Novocain, in some regions, procaine is referred to generically as novocaine. It acts mainl…Procaine
What is the best treatment for a blast injury?
Treatment for a blast injury Initial treatment options (as with sudden deafness) are hemorheologic infusion therapy with HAES (hydroxyethyl starch) and Procaine. Thereafter, cortisone can be administered. If both these treatments fail, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is another alternative.
What is the blast technique®?
The BLAST Technique® (Bi-Lateral Analysis and Stimulation Treatment) started it’s incarnation in 2008 with it’s creator, psychotherapist Nick Davies who managed to speed up the process and efficacy of PTSD and trauma treatment for an all-round better and more efficient experience for the client.
What are the treatment options for blast cells of leukemia?
A smaller number of patients have blast cells that act like cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). These cells are more sensitive to chemo drugs. Remissions can be induced in about half of these patients with drugs like vincristine, prednisone, and doxorubicin, along with imatinib, if that hasn't been given yet.
Which antibiotics are used in the treatment of blast wounds?
In patients with open wounds from blasts, consider broad-spectrum prophylactic antibiotics and provide tetanus toxoid if immunization is not up to date. Examine the lungs, abdomen, and tympanic membranes of all patients exposed to a significant explosion.
How is blast crisis treated?
Patients in BC should be treated with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor according to mutation profile, with or without chemotherapy, with the goal of achieving a second chronic phase and proceeding to allogeneic stem cell transplantation as quickly as possible.
How do you reduce blast cells?
Treatment aims to reduce the blast count in bone marrow to below 5%. Chemotherapy is the main treatment....Treatmentchemotherapy.targeted therapy.radiation therapy.stem cell therapy, also known as bone marrow transplantation.
What causes blood blasts?
Circulating blasts can be seen with severe infections, medications (e.g. granulocyte colony stimulating factor), bone marrow replacing processes and hematopoietic neoplasms. Acute leukemia is the most important hematopoietic neoplasm to recognize because it can rapidly lead to death.
Can blast cells be normal?
Many of the white blood cells may be myeloblasts (often just called blasts), which are very early forms of blood-forming cells that are not normally found in the blood. These cells don't work like normal, mature white blood cells.
How successful is leukemia treatment?
The cure rates and survival outcomes for patients with ALL have improved over the past few decades. Today, nearly 90 percent of adults diagnosed with ALL achieve a complete remission, which means that leukemia cells can no longer be seen in the bone marrow with a microscope.
What is end stage leukemia?
End stage leukemia has signs and symptoms that show the person is in the final days of life: Slow breathing with long pauses; noisy breathing with congestion. Cool skin that may turn a bluish, dusky color, especially in the hands and feet. Dryness of mouth and lips. Decreased amount of urine.
Can Leukaemia be cured?
As with other types of cancer, there's currently no cure for leukemia. People with leukemia sometimes experience remission, a state after diagnosis and treatment in which the cancer is no longer detected in the body. However, the cancer may recur due to cells that remain in your body.
Can CBC detect blasts?
A CBC test can find leukemic blood cells, which are called blasts. It can also detect changes in the amount of any type of blood cell. Finding any one of these changes in the blood can suggest the presence of leukemia.
How are blast cells detected?
Peripheral blood smear. In this test, a sample of your blood is examined under a microscope. It checks the number, shape, and size of white blood cells, and looks for immature white blood cells called blasts.
How many blasts is normal?
The number of immature cells (blasts) in the bone marrow is usually normal (less than 5%). A small percentage of the red blood cells in the bone marrow (less than 15%) may contain sideroblasts (iron granules that form a ring).
How long can a person live with AML without treatment?
Overall survival for AML Without treatment, survival is usually measured in days to weeks. With current treatment regimens, 65%–70% of people with AML reach a complete remission (which means that leukemia cells cannot be seen in the bone marrow) after induction therapy.
Does everyone have blasts in their blood?
We all have blasts. In fact, each of us started out as a blast or, more precisely, a blastocyst (a jumble of cells that divides enough times to become an embryo). However, when different types of blasts appear in unexpected areas, or when abnormal blasts develop, they can be an indicator of cancer or another disease.
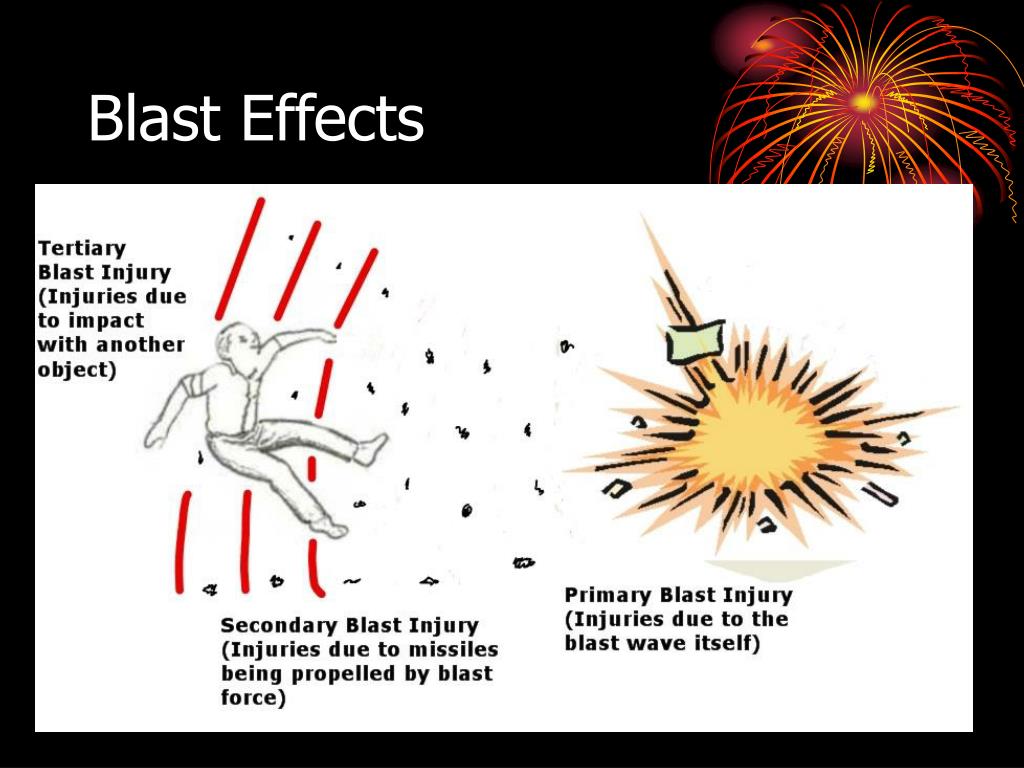
What is primary blast injury?
Primary blast injury is organ and tissue damage caused solely by the effect of transmitted blast waves associated with high-order explosives. The principle mechanism driving the extent of blast injuries is the amount of kinetic energy released over a short time by the explosion 1).
What is a blast eye?
Blast eye – rupture of the globe of the eye. Blast belly – injury causing abdominal hemorrhage and perforation (immediate and delayed). It can also cause injury to solid organs and testicular rupture. Primary blast injuries can be subtle and have a delayed presentation.
What is the impact of blast wave?
The blast wave causes damage to more extensively to air-filled organs. The resulting barotrauma can affect the lungs, auditory organs, the eye, brain, and gastrointestinal tract. Blast ear – tympanic membrane rupture and middle ear damage. Blast lung – injury to the lung parenchyma, can have delayed symptom presentation.
What happens if the pressure of a blast wave exceeds 40 psi?
If the pressure exceeds 40 psi, the victim could sustain a pulmonary contusion, pneumothorax, air embolism, interstitial parenchyma damage, and/or subcutaneous emphysema.
What is the most common cause of death in victims of an explosion?
Secondary blast injuries are the most common cause of mortality in victims of an explosion. Exposed areas of the victims’ body are at high risk for penetration of debris that is propelled by the explosion. Often areas of highest risk for injury are the head, neck, and extremities.
What happens when you explode?
An explosion creates a blast wave. An intense blast wave can tear tissue. A less intense blast can damage the eardrums, lungs, and abdomen. Blast waves also throw debris at very high speed that can injure any part of the body.
What is a high order explosive?
Explosives are categorized as high order explosives or low order explosives 3). High order explosives have a strong supersonic pressure wave, known as the blast wave or shock wave. Low order explosions have a subsonic explosion and lack the high order explosive blast wave. Examples of low order explosives include – pipe bombs, gun powder, petroleum-based bombs. In addition to the blast wave, an explosion can cause blast wind. Blast wind is the flow of superheated air that can interact with people and objects and cause injury or damage.
What is a blast crisis?
Blast crisis refers to the transformation of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) from the chronic or accelerated phase to blast phase. This is characterized by blast cells (≥20% by WHO criteria; ≥30% by MD Anderson Cancer Center and the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry criteria) in the peripheral blood smear or the bone marrow, or the presence of an extramedullary accumulation of blast cells, or large foci or clusters of blasts in the bone marrow biopsy. [1]#N#Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016 May 19;127 (20):2391-405. [Erratum in: Blood. 2016 Jul 21;128 (3):462.] http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/127/20/2391.long http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27069254?tool=bestpractice.com#N#[2]#N#National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Chronic myeloid leukemia. 2018 [internet publication]. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx#N#CML is characterized by the presence of the Philadelphia chromosome, which results from a reciprocal translocation of chromosomes 9 and 22, juxtaposing the proto-oncogene c-abl from chromosome 9 to the breakpoint cluster region in chromosome 22. [3]#N#Ghelani D, Sneed TB, Bueso-Ramos CE, et al. Chapter 4. Chronic myeloid leukemia. In: Kantarjian HM, Wolff RA, Koller CA, eds. MD Anderson manual of medical oncology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2006:57-74.
What is the blast phase of CML?
Blast phase of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), which can be discovered incidentally on CBC or in assessment of patients with symptoms and signs such as fever, fatigue, weight loss, anemia, thrombocytopenia, or splenomegaly. Diagnosis of CML requires presence of a Philadelphia chromosome gene mutation.
What is a blast injury?
Blast injuries. are characterized by anatomical and. physiological changes from the direct or reflective over-pressurization force impacting the body’s surface. The HE “blast wave” (over-pressure component) should be distinguished from “blast wind” (forced super-heated air.
What are some examples of blast injuries?
Examples include burns, angina, crush injuries, asthma or COPD exacerbations due to dust, smoke or toxic fumes. HE explosives can cause all four primary categories of injury, but their unique ability to cause primary blast injury makes them most fearsome.
Why are explosive devices important to first responders?
For these and many other reasons, first responders will continue to be called upon to mitigate the effects of bombings and other incidents invol ving the use of explosive devices or weapons.
What is a tertiary blast injury?
Tertiary blast injuries: Tertiary blast injury results from the human body actually being thrown by the blast wind and may manifest as fractures, traumatic amputations and brain injuries. 4. Quaternary blast injuries: Quaternary blast injury is everything else not caused by primary, secondary or tertiary mechanisms.
What happens when a blast over pressure wave hits a body surface?
When this blast over-pressure wave strikes body surfaces, it can cause pulmonary barotrauma, rupture of the eardrum, perforation of gas-filled structures like the intestines or gallbladder, ocular rupture and concussion – even in the absence of obvious physical head injury. 2.
Who is likely to assist in triage and moving patients to a casualty collection point?
EMS providers, as well as police officers and firefighters who are likely to assist in triage and moving patients to a casualty collection point, should have a basic understanding of the four types of blast injury.
What is blast injury?
What is a Blast Injury? A blast injury is caused by a complex pressure wave generated by an explosion. During an explosion, a compression of air forms in front of a blast wave, which heats and accelerates the movement of air molecules.
What are the mechanisms of blast injuries?
There are four basic mechanisms of blast injuries that a person can experience: Primary blast injuries. This refers to the explosion itself, where a pressure wave hits the victim and pushes on their organs. Organs surrounded by fluid such as the brain and spinal cord are especially susceptible to a pressure wave.
Why is the brain vulnerable to blasts?
The brain is particularly vulnerable to blast injuries because of its delicate composition. The severity of a blast injury depends on several factors, including the type of explosive used, the distance between the victim and the explosion, and the mechanism of the blast injury. In the following section, we’ll discuss the various ways individuals ...
What is secondary blast?
Secondary blast injuries. These are the result of fragments flying through the air after an explosion. They often cause penetrating brain injuries. Tertiary blast injuries. This can occur if the victim is thrown through the air into something solid, such as a wall.
Is a blast a traumatic brain injury?
Understanding Blast-Induced Traumatic Brain Injury: Mechanism, Symptoms, and Treatment. Blast- induced traumatic brain injuries can be more complicated than other TBIs. It can cause more complex and dangerous symptoms than brain injuries caused by car accidents and sports injuries. However, treatment for brain injuries caused by explosions remains ...
Is blast injury more complex than other TBIs?
In many ways, blast injuries are more complex than other TBIs. But when it comes to treatment, the principles remain the same. Even though the symptoms of blast-induced brain injury can be debilitating, the brain is a remarkably adaptive organ. By activating neuroplasticity through therapy, you can give yourself the best chance at making ...
What happens in the blast phase of CML?
In the blast phase of CML, the leukemia cells become more abnormal. The disease acts like an acute leukemia, with blood counts getting higher and symptoms appearing or getting worse. For people with blast phase CML who haven't been treated before, high-dose imatinib may be helpful.
What to do if leukemia doesn't respond to first treatment?
If the first treatment doesn’t work. If the leukemia doesn’t respond well to the first treatment, there are several options. Increasing the dose of the drug. This helps some people, although the higher dose often has worse side effects.
What is the treatment for CML?
The standard treatment for chronic phase CML is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) like imatinib (Gleevec), nilotinib (Tasigna), dasatinib (Sprycel), or bosutinib (Bosulif). If the first drug stops working or it never really worked well at all, the dose may be increased or another TKI might be tried.
What is the test to check for BCR-ABL?
Blood counts are checked often. The blood is also checked with a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test to measure the amount of the BCR-ABL gene. The bone marrow is checked, too, to see if the Philadelphia chromosome is there.
Can accelerated CML be treated?
The treatment options for accelerated phase CML depend on what treatments the patient has already had. In general, the options are a lot like those for patients with chronic phase CML. But patients with accelerated phase CML are less likely to have a long-term response to any treatment.
Is radiation therapy effective for CML?
Allogeneic SCT is less successful for blast phase CML than for earlier phases, and the long-term survival rate is less than 20%. Still, it's the only known option that may cure the disease.
Can stem cells be used for leukemia?
An allogeneic stem cell transplant may be the best option for most patients who are young and healthy enough to have this treatment . Most doctors prefer that the leukemia be controlled, preferably in remission, before starting the transplant procedure. To achieve this, chemo will often be used.
