- Antibiotics: treat bacterial pneumonia. Antibiotics may be prescribed orally or intravenously at a clinic or hospital for more serious bacterial lung infections. ...
- Antifungals: treat fungal lung infections caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, Aspergillus fungus, or other fungal spores. Medications include ketoconazole, itraconazole, amphotericin B, voriconazole, and others.
- Corticosteroids: reduce inflammation and tamp down your body’s immune response to help manage various symptoms. Examples include cortisone, prednisone, fluticasone (Flonase). They’re available in different forms (oral, injection, inhaler).
- Bronchodilators: help relax airway muscles to improve breathing for asthma or COPD. Examples include albuterol (ProAir HFA, Ventolin HFA) and salmeterol (Serevent Diskus). ...
- Leukotriene modifiers: either limit or block the effects of leukotrienes, which helps improve breathing and wheezing in asthma. Examples include montelukast (Singulair), zileuton (Zyflo, Zyflo CR), and zafirlukast (Accolate).
- Biologic medications: made from living cells. They work to reduce your body’s inflammatory response by helping with chronic symptoms such as shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing. ...
- Roflumilast (Daliresp): relieves inflammation and helps with airflow to the lungs
- Anti-inflammatories and pain relievers: available over the counter to help with mild symptoms of lung inflammation, such as fever, body aches, and pain. ...
Full Answer
What are home remedies for fungal infections?
Oct 20, 2021 · Biopsies can be done through bronchoscopy —a procedure that involves inserting a narrow tube or scope with a light and camera on the end through the nose or mouth and guiding it down the windpipe to get an internal view of the lungs. 1 Blastomycosis Blastomycosis is caused by the fungus Blastomyces dermatitidis .
What is the cure for lung fungus?
Symptoms include fever, coughing up blood, shortness of breath, and chest pains. To treat this fungal lung infection, physicians prescribe anti-fungal medicines. Early diagnosis and immediate treatment are crucial.
Can I survive lung cancer without treatment?
Jun 04, 2021 · Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for bacterial lung infections, with different antibiotics recommended depending on the particular type of infection and suspected organism. The choice of using oral antibiotics versus intravenous treatment will depend on the severity of the infection.
Which ointment is best for fungal infection?
Jul 03, 2019 · Natural killer cells control the fungal expansion in the lung via the direct and indirect killing of invading organisms. Adaptive immune cells including Th1 and Th17 cells confer anti-fungal activity by producing their signature cytokines, interferon-γ, and IL-17.
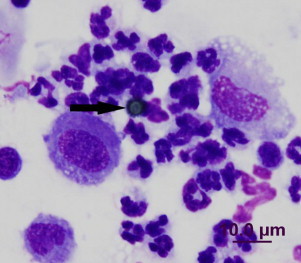
Can fungal infection in lungs be cured?
Fungus balls in the lungs (aspergillomas) usually do not require treatment with drugs and do not usually respond to drugs. If these balls cause bleeding (causing people to cough up blood) or other symptoms, they may need to be removed surgically.
What antibiotics treat lung fungal infections?
Amphotericin or caspofungin is used for the empirical treatment of serious fungal infections. Aspergillosis: voriconazole is the treatment of choice; liposomal amphotericin is an alternative first-line treatment when voriconazole cannot be used.Mar 23, 2022
What are the symptoms of a fungal infection in the lungs?
However, the symptoms of invasive aspergillosis in the lungs include:Fever.Chest pain.Cough.Coughing up blood.Shortness of breath.Other symptoms can develop if the infection spreads from the lungs to other parts of the body.
What happens if you have fungus in your lungs?
Breathing in tiny bits of fungus (called spores) irritates the lungs and can cause something called allergic alveolitis: a bit like asthma. It can make you breathless and give you a cough that just won't go away. Some people who live in damp, mouldy accommodation can develop this.Sep 28, 2017
How do you get fungus in your lungs?
When mold spores are inhaled, immune system cells surround and destroy them. But people who have a weakened immune system from illness or immunosuppressant medications have fewer infection-fighting cells. This allows aspergillus to take hold, invading the lungs and, in the most serious cases, other parts of the body.Jan 6, 2022
How long does it take to recover from fungal pneumonia?
5 In general, the duration of treatment for fungal pneumonia can last up to year. In very advanced cases of cryptococcus, valley fever, and aspergillosis, fungal growths called mycetomas can form in the lungs and need to be surgically removed.May 4, 2021
How do you get rid of lung fungus?
These drugs are the standard treatment for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. The most effective treatment is a newer antifungal drug, voriconazole (Vfend). Amphotericin B is another option. All antifungal drugs can have serious side effects, including kidney and liver damage.Jan 6, 2022
Which are the 3 most common respiratory diseases caused by fungi?
In North America, three major endemic mycoses including coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and blastomycosis could present as community acquired pneumonias (CAP) (27).Jul 3, 2019
Can Covid cause fungus in lungs?
The novel coronavirus has recently been linked to two serious fungal infections: COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) and COVID-19 associated mucormycosis (CAM). The resurgence of these rare fungal infections has medical personnel concerned.
How do you test for lung fungus?
Imaging tests such as a chest X-ray or CT scan can help with diagnosis because your doctor may be able to spot a nodule or fungal mass on your lung, caused by the mold, that would prompt your doctor to do further testing. If they are still unsure, a tissue biopsy may be the best way to get a clear diagnosis.Jan 25, 2021
What are 5 diseases caused by fungi?
Other diseases and health problems caused by fungiAspergillosis. About. Symptoms. ... Blastomycosis. About. Symptoms. ... Candidiasis. Candida infections of the mouth, throat, and esophagus. Vaginal candidiasis. ... Candida auris.Coccidioidomycosis. About. Symptoms. ... C. neoformans Infection. About. ... C. gattii Infection. ... Fungal Eye Infections. About.More items...
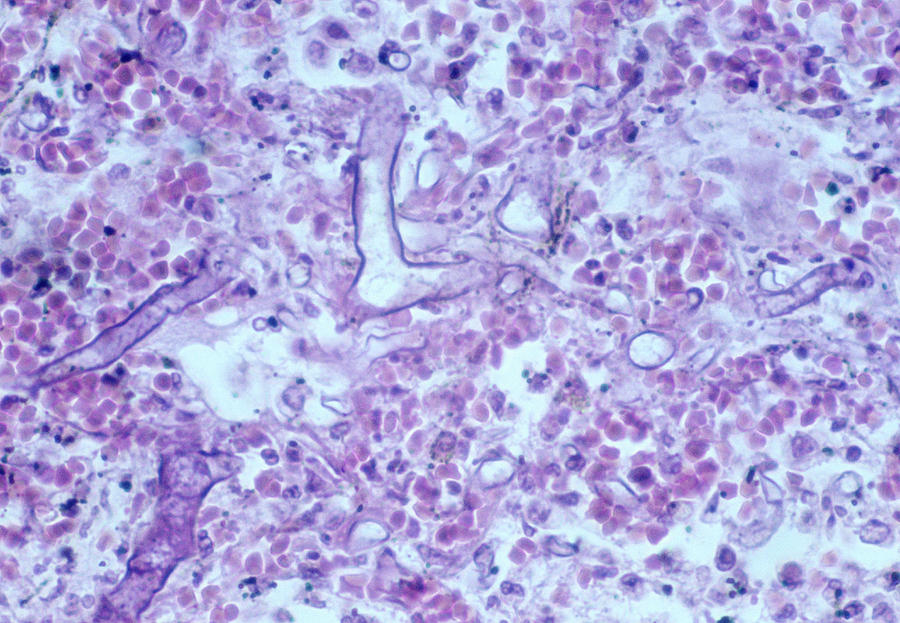
Fungal Infections in Lungs
There are multiple fungi that can cause an infection in the lungs. The following are the most common infections. Learn their symptoms, how they are diagnosed, and how they are treated.
Primary Lung Cancer
When cancer starts in the lungs, it is referred to as primary lung cancer. It is further classified into types of lung cancer based upon the cells in which the cancer originated. Types of primary lung cancer include: 8
Fungal Infections in Lungs and Cancer: Common Symptoms
When an individual suddenly develops symptoms such as fever, chest pain, and cough, the healthcare provider may initially prescribe antibiotics. However, if symptoms do not improve after a course of antibiotics, they may undergo further imaging tests to determine the source of the symptoms.
A Word From Verywell
It's important to notify your healthcare team if you develop symptoms that could potentially be related to a fungal infection. Getting an infection treated promptly is essential to preventing it from spreading to other areas of the body and causing additional complications.
How does fungus enter the body?
The fungus enters the body by inhalation where most people’s immune system is strong enough to fight infection. However, people with a weakened immune system may contract fungal lung disease. This includes people suffering from cancer, autoimmune disease, or any other serious condition.
Where is fungus most common?
Up until now, fungal infections were most common in certain geographical areas such as South and Central America and Africa, where the fungus is more prevalent.
Can fungus in the lungs be life threatening?
Final Thoughts. Fungus in your lungs can be life-threatening, if you fall into the at-risk group. Symptoms include fever, coughing up blood, shortness of breath, and chest pains. To treat this fungal lung infection, physicians prescribe anti-fungal medicines. Early diagnosis and immediate treatment are crucial.
Can fungus cause lung disease?
Aspergillosis – The Most Common Fungal Lung Infection. Fungus in your lungs can cause Aspergillosis, the most common fungal lung disease. As this fungus exists everywhere, you cannot avoid it. For most people, it poses no risks, however, people with suppressed immune systems can get seriously ill when suffering from this fungal lung disease.
What is the best treatment for bacterial lung infection?
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for bacterial lung infections, with different antibiotics recommended depending on the particular type of infection and suspected organism. The choice of using oral antibiotics versus intravenous treatment will depend on the severity of the infection.
What causes a lung infection?
Lung infections may be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or rarely in the United States, parasites.
What is the name of the disease that affects the airways between the bronchi and the alveoli?
Bronchiolitis is an infection that affects the smaller airways ( bronchioles) between the larger bronchi, and the tiny alveoli where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. Most common in children under two years old, it is the leading cause of hospitalizations of infants during the first year of life.
What causes a cough and a runny nose?
It is caused most often by a number of viruses, including common cold viruses and respiratory syncytial virus, but occasionally due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms often begin with a low-grade fever and runny nose, followed by the characteristic barking cough which worsens at night. 7.
What is the smallest airway in the body?
Pneumonia is a lung infection that affects the smallest of airways, the alveoli, where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. The severity can range from a mild disease that can be treated at home, to life-threatening infections requiring intensive care.
What are the symptoms of a cough?
There are also symptoms that are less common but no less important. Cough: A cough may be dry or “wet” (productive of mucus) and may be mild or severe. Mucus production: Mucus may be clear, yellow, green, brown, or rust colored and may have no odor or a foul odor.
What is croup in lungs?
Croup is an infection that involves structures above the lungs (the larynx and trachea) but can also involve the bronchi. It is caused most often by a number of viruses, including common cold viruses and respiratory syncytial virus, but occasionally due to a bacterial infection.
What are the conditions that can cause fungus to invade the lung?
Leukemia, diabetes and HIV are some of the conditions where the immune system may be weak to the point that fungi can invade the lung tissue. Fungal pneumonia can progress to disseminated disease where it affects other organs like the brain, liver, kidneys and heart and result in life threatening complications.
How do fungi cause respiratory diseases?
Fungi can cause respiratory diseases by either directly invading the lung tissue or triggering an immune reaction when the it enters the air passages . Fungal pneumonia usually refers to infections where the fungi invade lung tissue. These infections arise when the fungi or parts of it like spores enter the airways through inhalation.
Why do fungal infections not cause infection?
It does not cause any infection because the fungal population is limited by a variety of factors and the immune system prevents these fungi from invading living tissue. Other fungal species may only be found in certain parts of the world.
Why is my fever persistent?
Fever which may be persistent. The fever may not always be due to fungal pneumonia particularly in people who are immune compromised. Cough which is usually dry although mucus (sometimes blood stained) may be seen in a productive cough that can develop later.
What is the best antifungal for aspergillosis?
Antifungal Drugs. Amphotericin B is the mainstay of treatment, particularly in acutely ill patients. Voriconazole and other azoles are preferred over amphotericin B these days especially for aspergillosis. Echinocandins like anidulafungin, caspofungin and micafungin are used for Candida infections.
What is disseminated disease?
Disseminated Disease. In people who are immune compromised the infection can spread beyond the respiratory system. This is known as disseminated disease. It may even spread throughout most of the body (systemic). As a result there may be other signs and symptoms depending on the organ that is affected.
Can fungi cause pneumonia?
When it affects a person with a normal functioning immune system (immune competent) it is usually self-limiting and may not even need to be treated in some instances. There are many different species of fungi that can cause pneumonia. Many are not commonly heard of because it is so rare in human diseases.
What are the pulmonary fungal infections?
Respiratory fungal infection is a severe clinical problem, especially in patients with compromised immune functions. Aspergillus, Cryptococcus, Pneumocystis, and endemic fungi are major pulmonary fungal pathogens that are able to result in life-threatening invasive diseases. Growing data being reported have indicated that multiple cells and molecules orchestrate the host's response to a fungal infection in the lung. Upon fungal challenge, innate myeloid cells including macrophages, dendritic cells (DC), and recruited neutrophils establish the first line of defense through the phagocytosis and secretion of cytokines. Natural killer cells control the fungal expansion in the lung via the direct and indirect killing of invading organisms. Adaptive immune cells including Th1 and Th17 cells confer anti-fungal activity by producing their signature cytokines, interferon-γ, and IL-17. In addition, lung epithelial cells (LEC) also participate in the resistance against fungal infection by internalization, inflammatory cytokine production, or antimicrobial peptide secretion. In the host cells mentioned above, various molecules with distinct functions modulate the immune defense signaling: Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as dectin-1 expressed on the cell surface are involved in fungal recognition; adaptor proteins such as MyD88 and TRAF6 are required for transduction of signals to the nucleus for transcriptional regulation; inflammasomes also play crucial roles in the host's defense against a fungal infection in the lung. Furthermore, transcriptional factors modulate the transcriptions of a series of genes, especially those encoding cytokines and chemokines, which are predominant regulators in the infectious microenvironment, mediating the cellular and molecular immune responses against a fungal infection in the lung.
What are the pathogenic fungi that cause pulmonary infection?
The pathogenic fungi including Cryptococcus neoformans (Cn), Aspergillus (Ap), Pneumocystis (Pc), and Endemic fungi (Ef) can cause pulmonary infection in human and in murine models. Fungal pathogens could trigger host immune response upon inhalation, and lung tissue is the major infectious target of these pathogens.
What is calcineurin in A. fumigatus?
Calcineurin and related pathways are implicated in the controls of hyphal synthesis, morphological character , and virulence in A. fumigatus. Calcineurin is a heterodimer consisting of catalytic subunit A and Ca 2+ /calmodulin binding unit, a mutant of A. fumigatus with depleted calcineurin A catalytic subunit displayed deficiency in morphology and decreased filamentation ( 181 – 183 ). Meanwhile, calcineurin mutant with decreased beta-glucan amounts promoted the fungicidal activity of cell wall inhibitors, implying that targeting calcineurin can be a potential synergistic therapy with other fungicides against A. fumigatus ( 184 ). The growth of C. neoformans was sensitive to CsA and FK506 which mediates the signal transduction on Ca 2+ -regulated protein phosphatase calcineurin and the Calcineurin mutant strains failed to be infectious in an animal model of cryptococcosis in the brain, suggesting that calcineurin is necessary for pathogenicity of C. neoformans ( 185) ( Figure 4B ). In addition, host calcineurin signaling is also important for host immune responses to fungal infection, for instance, the intervention of neutrophils ability on Aspergillus species germination was inhibited in hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) individuals and this impairment was partly attributed to the administration of calcineurin inhibitors ( 186 ), suggesting that calcineurin signaling might affect neutrophils activity against Aspergillus, especially in immunocompromised hosts. Besides the neutrophils, calcineurin signaling has also been associated with macrophages. It was reported that calcineurin inhibitor tacrolimus impaired macrophage immune responses and the clearance of the major mold pathogen A. fumigatus from the airway, possibly due to the inhibition on A. fumigatus -induced phagosomal TLR9-BTK-Calcineurin-NFAT cascades independent of MyD88, and NFAT collaborating with NF-κB contributed to TNF-α production in primary alveolar macrophages ( 187 ). By targeting host and pathogen calcineurin signaling, cyclosporine (CsA) can be used as both an immunosuppressive drug and antimicrobial agent, which inhibits the protein phosphatase calcineurin. However, inhibition on host calcineurin or its downstream calcineurin-NFAT pathway by CsA, can protect transplant recipients from severe transplant rejection, and it might at the same time increase host immune defects leading to organ transplant-related invasive aspergillosis. Interestingly, the diversity of immunosuppressants determined different outcomes in transplant patients but the death rate appeared to be lower in individuals who received the calcineurin-inhibitors ( 188 ), the precise mechanisms on the host calcineurin signaling in cryptococcosis remains to be investigated.
What is the most severe outcome of Cryptococcus infection?
The most severe outcome of Cryptococcus infection is cryptococcal meningitis.
What are the functions of collectins?
The functions of collectins encompass opsonization, inflammation regulation, and the direct clearance of pathogens ( 169 ). A previous study has demonstrated the protective effect of MBL in a mouse model of aspergillosis ( 170 ). In the airways, surfactant proteins render immune protection against fungal accumulation and then clearance by phagocytosis ( 171 ). Among them, SP-A in respiratory tract binds to C. neoformans without enhancing phagocytosis, while SP-D may play an essential role at the early stage of infection with an increased rate of uptake and phagocytosis. Thus, a greater number of phagocytosed C. neoformans cells in wild-type mice than in SP-D KO mice were observed. However, SP-D enhances fungal survival in macrophages in vitro, and mice lacking SP-D are protected in vivo ( 171, 172 ). The reason for these opposing findings awaits further investigation. Collectins, ficolins, and pentraxins are circulating proteins which could serve as opsonins ( 173 ). Type II alveolar epithelial cells could secrete H-Ficolin as innate immune opsonin to involve in pulmonary defenses against fungal infection. Silke Schelenz1s' group found that H-ficolin was involved in A. fumigatus defense through the activation of the lectin complement pathway, highlighting the interaction between host and fungus and the modulation of the immune response by ficolin ( 174 ). In addition, another human serum opsonin, L-ficolin was detected in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from patients with a fungal infection. L-ficolin opsonization increased IL-8 production from A549 cells and enhanced conidial uptake and the killing of A. fumigatus by macrophages and neutrophils, with a reduced release of inflammatory cytokines ( 175 ).
What is the role of TRAF6 in the immune system?
Besides MyD88, TRAF family proteins especially TRAF3 and TRAF6 play a crucial role in regulating innate and adaptive immune responses . In TLR signaling, TRAF6 is dependent on MyD88 instead of TRIF, and TRAF6 differently modulates MyD88- and IRAK-1-induced activation of NF-κB ( 109, 110 ). Although TRAF6 and TAK1 are implicated in candida infection ( 111 ), the roles of these molecules in CLRs initiated signaling have not been studied. In canonical CLR signaling, both TRAF6-TAK1 interaction and spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) phosphorylation are initial events involved for CARD9-Bcl10-MALT1 complex and downstream MAPK and NF-κB activation, adaptor Syk-coupled CLRs including Dectin1/2 and Mincle mediate innate immunity against fungal infection ( 92, 93, 112 ). Another study proved that Dectin-1-Syk and autophagy contributed to maturation of the A. fumigatus phagosome ( 113 ).
What are the roles of hematopoietic cells in fungi?
Multiple hematopoietic cells such as macrophages and DCs play crucial roles in anti-fungal immune resistance and tolerance to fungi, by keeping a balance of immunopathology/protective immunity. However, growing evidence implies that the epithelial cells play an essential role in infection and inflammation by releasing surfactant proteins and antimicrobial peptides ( 87 ). First, internalization of A. fumigatus conidia could also be performed by epithelial and endothelial cells ( 88 ). Lung epithelial cells (LEC) often play crucial roles in the crosstalk between fungal infection and mucosal immunity at pulmonary mucosa by linking the innate immunity and adaptive immunity. It is reported that the protective tolerance on LECs to A. fumigatus is achieved through indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) signaling ( 89 ).
What is the best treatment for a fungal lung infection?
A fungal lung infection will require treatment with an antifungal medication, such as ketoconazole or voriconazole. Antibiotics won’t work on viral infections.
What are the symptoms of a lung infection?
severe chest pain. a high fever. cough with mucus that is getting worse. People older than 65, children under the age of 2, and people with chronic health conditions or a compromised immune system should seek medical treatment right away if they experience any symptoms of a lung infection.
How do you know if you have a lung infection?
If you have a lung infection, here are the most common symptoms to expect: 1. Cough that produces thick mucus. Coughing helps to rid your body of the mucus produced from inflammation of the airways and lungs.
What causes a person to have a lung infection?
A lung infection can be caused by a virus, bacteria, and sometimes even a fungus. One of the most common types of lung infections is called pneumonia. Pneumonia, which affects the smaller air sacs of the lungs, is most often caused by contagious bacteria, but can also be caused by a virus. A person becomes infected by breathing in ...
What is it called when you have a virus in your lungs?
When the large bronchial tubes that carry air to and from your lungs become infected, it’s referred to as bronchitis. Bronchitis is more likely to be caused by a virus than by bacteria. Viruses can also attack the lungs or the air passages that lead to the lungs. This is called bronchiolitis.
What do doctors do to check for crackling?
The doctor will measure your temperature and listen to your chest with a stethoscope to check for crackling sounds.
What causes bronchitis?
They are typically caused by a virus or bacteria. The most common microorganisms responsible for bronchitis include: viruses such as the influenza virus or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV ) bacteria such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Bordetella pertussis.
Can I buy medication over the counter?
Yes, some medications to help manage mild symptoms are available over the counter. These include acetaminophen, NSAIDs, common cough and cold products, soothing teas, and more. Be sure to speak with a doctor before taking any OTC products, including supplements, herbs, or vitamins.
How effective are medications?
Medications to treat causes of lung inflammation are effective depending on your specific condition and how soon you receive treatment. For types of chronic lung inflammation, it’s important to take your medication regularly.
Is lung inflammation contagious?
Yes, some causes of lung inflammation are contagious. Infectious causes of lung inflammation from bacteria (pneumonia, tuberculosis) or viruses (influenza, COVID-19) are contagious. Other forms caused by autoimmune or genetic causes of lung inflammation aren’t contagious.
What is MAC lung disease?
MAC lung disease is an infection caused a group of bacteria called Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). MAC includes two closely related species, Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare, and may also be referred to as MAI.
What is the disease that spreads through the body?
In addition to lung disease, MAC can also cause an infection that spreads throughout the body, usually in people with advanced AIDS, called disseminated MAC disease, as well as a swelling in the lymph nodes called lymphadenitis that is most common in young children.
Can bronchitis cause infection?
Most of the time they cause no harm, but they can cause infection in groups with certain risk factors. These groups include people living with lung disease such as bronchiectasis and COPD, and people with a weakened immune system because of an autoimmune disorder or medical treatment such as drugs that compromise immunity.

Overview
Causes
Habitat
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms
Prognosis
- Certain species are naturally occurring on human skin and within certain cavities. It does not cause any infection because the fungal population is limited by a variety of factors and the immune system prevents these fungi from invading living tissue. Other fungal species may only be found in certain parts of the world. It may be found in the soil or in the droppings of certain an…
Treatment
- The signs and symptoms of fungal pneumonia are largely the same as that of viral and bacterial pneumonia. Since fungal pneumonia is not common, often other infectious lung conditions are suspected once the symptoms become apparent. The seriousness and prevalence of tuberculosis (TB), especially in people living with HIV/AIDS, means that it should first be excluded as a possib…