
Explore
Treatment of First-Degree AV Block
- Medications. If the patient is symptomatic and does not have any immediately reversible causes and is demonstrating signs or symptoms of poor perfusion as a result of a bradyarrhythmia, the ...
- Pacing. ...
- Next Steps and Considerations. ...
What is the treatment for first degree AV block?
Drugs that most commonly cause first-degree AV block include the following: Class Ia antiarrhythmics (eg, quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide) Class Ic antiarrhythmics (eg, flecainide, encainide, propafenone)
What medications cause AV block?
Heart block, also called AV block, is when the electrical signal that controls your heartbeat is partially or completely blocked. This makes your heart beat slowly or skip beats and your heart can’t pump blood effectively. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, tiredness and shortness of breath. Pacemaker implantation is a common treatment.
Is AV block considered heart disease?
What Are ECG Characteristics of First-Degree AV Block?
- P wave for every QRS complex
- Prolonged PR interval that is greater than 0.20 seconds
- If the PR interval is greater than 0.30 seconds, a P wave may appear to be buried in the previous T wave
- If the PR interval is extended for more than 0.30 seconds, it is considered “marked”
- No beats are dropped in this rhythm
What are the symptoms of a 1st degree AV block?
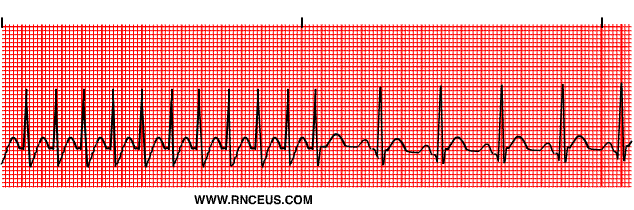
Can an AV block go away?
Some forms of heart block may go away on their own if the underlying condition that is causing the problem is treated or removed. For example, if your medication is causing heart block and you don't need it anymore, your condition might improve.
What is the treatment for a first-degree AV block?
In general, no treatment is required for first-degree AV block unless prolongation of the PR interval is extreme (>400 ms) or rapidly evolving, in which case pacing is indicated. Prophylactic antiarrhythmic drug therapy is best avoided in patients with marked first-degree AV block.
What medication is given for heart block?
Medications that may be used in the management of third-degree AV block (complete heart block) include sympathomimetic or vagolytic agents, catecholamines, and antidotes.
What causes an AV block?
The most common causes of AV block include: Fibrosis or sclerosis. Extra tissue can thicken, scar, and damage the pathways that send signals from the upper part to the lower part of your heart. Coronary artery disease.
How can I improve my AV block?
Carotid sinus massage increases vagal tone, which worsens the block at the AV node. In contrast, carotid sinus massage improves infranodal block due to slowing of atrial impulses conducted through the AV node. Exercise or atropine improves AV nodal conduction due to sympathetic stimulation.
Is 1st degree heart block serious?
Heart block is categorized as first-, second-, or third-degree: First-degree heart block is the least severe. The electrical signals slow down as they move from your atria to your ventricles. First-degree heart block might not require treatment of any kind.
Is AV block normal?
Some AV blocks are benign, or normal, in certain people, such as in athletes or children. Other blocks are pathologic, or abnormal, and have several causes, including ischemia, infarction, fibrosis, and drugs.
How long can you live with heart block?
The survival rate in the 68 cases of CHB was higher at one year (68%) as well as at 5 years (37%) than that reported by other investigators.
How common is AV block?
How common are heart blocks? First degree and Mobitz type 1 heart blocks are uncommon but not rare. It is estimated that 0.5-2% of otherwise healthy adults have these types of heart blocks.
How does an AV block work?
They team up to pump blood through your body. An electrical signal starts out in a spot called the sinoatrial (SA) node. It's known as your heart's natural pacemaker. The current heads down to a group of cells called the atrioventricular (AV) node.
What is the condition where the heart is blocked?
But sometimes this current gets delayed or stopped. The result: a condition called atrioventricular (AV) block or heart block. Certain health conditions, heart defects, and medicines can cause it.
What medications slow your heartbeat?
Medication. Certain drugs can slow your heartbeat. This includes blood pressure medicine like beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers.
Why does my heart block after a heart attack?
Extra tissue can thicken, scar, and damage the pathways that send signals from the upper part to the lower part of your heart. Coronary artery disease. This damages your heart's blood vessels. It may cause AV block before or after a heart attack. Some other causes are: Medication.
Can AV block be life threatening?
You might not have symptoms or need treatment. But if you do, a doctor can help you manage your condition. Without the right care, serious AV block can be life threatening.
Can you get AV block?
You can get mild AV block as your heart adapts to an intensive exercise routine. It's sometimes called "athlete's heart." But AV block is more likely to happen if you're older or there's something wrong with your heart.
What degree is a heart block?
Heart block can be first, second or third degree, depending on the extent of electrical signal impairment.
What is the name of the block that makes your heart beat?
Heart Block. Heart block, also called AV block, is when the electrical signal that controls your heartbeat is partially or completely blocked. This makes your heart beat slowly or skip beats and your heart can’t pump blood effectively. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, tiredness and shortness of breath. Pacemaker implantation is ...
What medications slow the heart's electrical impulses?
You take medications that slow the conduction of the heart’s electrical impulses including some heart medications (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin), high blood pressure drugs, antiarrhythmics; muscle relaxants and sedatives; antidepressants and antipsychotics; diuretics; lithium.
Is a heart block a first degree or second degree?
First-degree heart block: May not have any symptoms. May be found during a routine electrocardiogram (ECG) although heart rate and rhythm are usually normal. First-degree block is common in athletes, teenagers, young adults and those with a highly active vagus nerve. Second-degree heart block symptoms:
Can heart block be prevented?
Some cases of heart block may be congenital (present at birth). But most heart block develops after birth. Some causes can’t be prevented. We also know that the risk of heart block increases with age and so does heart disease. Some causes of heart disease are preventable.
Do you need treatment for a heart block?
First-degree block: If you have first-degree heart block, you probably won’t need treatment.
Can you get heart block if your mother has autoimmune disease?
You may be at increased risk of a heart block if: Your mother has an autoimmune disease, such as lupus. You are of older age. Risk of heart block increases with age. You have other heart conditions including coronary artery disease, heart valve disease. You have birth defects of the heart.
What is AV block?
AV block, or atrioventricular block, is a major cause of significant bradyarrhythmias. To diagnose and manage AV block, it is important to have a basic understanding of the anatomy of the conduction system of the heart.
What causes AV block?
Acquired AV block is most commonly caused by idiopathic fibrosis, acute myocardial infarction, or drug effects. AV block can also be congenital. If AV block is symptomatic, and determined to be permanent, pacing is the only effective long-term therapy. Conduction Terminology.
What is the most common abnormality of the intraventricular conduction system?
Left anterior fascicular block, or hemiblock, is the most commonly seen conduction abnormality of the intraventricular system with up to a 6% prevalence in the normal population. After left anterior hemiblock, the next most common abnormality of the intraventricular conduction system is right bundle branch block, followed by left bundle branch block and left posterior fascicular block, or hemiblock.
How many P to P intervals are there in a premature atrial complex?
The P to P intervals remain constant and the pause, including the blocked P wave, equals two P to P intervals. In the case of a nonconducted premature atrial complex, the nonconducted P wave will be premature.
How long can you keep anticoagulant for atrial fibrillation?
Patients on anticoagulants who need temporary or permanent pacemaker placement are at increased risk of bleeding complications. If the procedure is not emergent, and the patient is on warfarin for atrial fibrillation, the drug can be withheld for 3 to 5 days, and restarted postprocedure when the risk of bleeding is acceptable.
Why is my heart block reversible?
Reversible causes of complete heart block can be due to metabolic abnormalities, drug effects, Lyme disease, or vasovagal episodes. In these cases, the complete heart block resolves once the abnormality has been treated. In true complete heart block, the sinus rate is faster than the ventricular rate.
Where does blood come from in the AV node?
The blood supply to the AV node is from the AV nodal artery, a branch of the right coronary artery in 90% of hearts, with the remaining 10% arising from the left circumflex coronary artery. The His-bundle has a dual blood supply from branches of the anterior and posterior descending coronary arteries.
What is the benefit of AV block?
Patients with asymptomatic, intermittent second-degree Mobitz II, high-degree, or third-degree AV block benefit from long-term event monitoring to assess for symptoms, bradycardia, or periods of asystole, as this would affect the timing of pacemaker implantation.
What is a 2:1 AV block?
A constant PP interval and normal PR interval in conducted beats is present. This progresses to 2:1 atrioventricular (AV) block. A 2:1 AV block can be present with conduction delay in the AV node or His-Purkinje system, but it is more likely to be in the AV node for all patients (with a greater chance of AV block in the His-Purkinje system if there is a bundle branch block). Review extended monitoring strips because Mobitz I or Mobitz II may be present at other times, and this might help to determine the level of the block.
What is the conduction ratio of a high degree atrioventricular block?
High-degree atrioventricular block is demonstrated with a 4:1 atrial-to-ventricular conduction ratio. Note the P wave prior to the QRS conducts whereas the others do not. Courtesy of Life in the Fast Lane (https://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/basics/high-grade-block/), Edward J Burns, MD, Sydney, Australia.
What is the PR interval of atrioventricular block?
This rhythm strip shows first-degree atrioventricular block block with a PR interval of 0.360 sec. Note the fixed prolonged PR interval.
Does CRT help with AV block?
The BLOCK-HF (Biventricular Versus Right Ventricular Pacing in Patients With Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Atrioventricular Block) randomized trial evaluated the effect of CRT in heart failure patients with AV block and found that CRT caused LV reverse remodeling and improved ejection fraction. [ 21] In addition, CRT pacing reduced mortality and heart failure admissions compared to RV pacing. [ 21] Based on these findings, for patients with high-degree AV block, CRT pacing therapy could be considered for patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class I, II, or III symptoms, an ejection fraction below 50%, and when chronic RV pacing is required. However, this study was published after the 2008 pacemaker guidelines [ 1, 2] and is not currently incorporated into any guidelines.
Should patients with AV block have their activities restricted?
Patients with AV block should have their activities restricted to reduce the risk of injury until they have been properly evaluated and treated.
Is atrioventricular block faster than ventricular block?
Third-degree atrioventricular block (complete heart block). The atrial rate is faster than the ventricular rate, and no association exists between the atrial and ventricular activity.
What is the goal of AV block therapy?
The goals of therapy are to treat symptoms and to prevent syncope and sudden cardiac death due to very slow or absent ventricular rates. Patients with advanced AV block (usually type II second-degree, third-degree, or infranodal AV block) of irreversible cause should undergo permanent pacemaker placement.
What is an AV block?
Atrioventricular (AV) block is a cardiac electrical disorder defined as impaired (delayed or absent) conduction from the atria to the ventricles. The severity of the conduction abnormality is described in degrees: first-degree; second-degree, type I (Wenckebach or Mobitz I) or type II (Mobitz II); and third-degree (complete) AV block. This classification scheme should be applied only during sinus rhythm and not during rapid atrial arrhythmias or to premature atrial beats. [1]#N#Josephson ME. Clinical cardiac electrophysiology: techniques and interpretations. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2008.
What is an AV block?
AV Heart Block is partial or complete block of electrical impulses originating in the atrium or sinus node, preventing them from reaching the AV node and ventricles.
What is a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision?
There is a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision. 2. Has a high potential for abuse. Has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States or a currently accepted medical use with severe restrictions. Abuse may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence.
Is abuse a low potential for abuse relative to those in Schedule 4?
Has a low potential for abuse relative to those in schedule 4. Has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States. Abuse may lead to limited physical dependence or psychological dependence relative to those in schedule 4.
What is the PR interval for a first degree atrioventricular block?
First-degree atrioventricular block. The PR interval is 0.24 seconds (240 ms) in a patient with asymptomatic first-degree atrioventricular block.
Can you discontinue AV block?
In patients with symptomatic first-degree AV block, discontinue medications with potential for AV block, if possible. Electrophysiology consultation may be indicated for patients with first-degree AV block and symptoms of syncope or heart failure.
Is a permanent pacemaker implantation indicated for asymptomatic first degree AV block?
Permanent pacemaker implantation is not indicated for asymptomatic first-degree AV block (class III recommendation; level of evidence, B).
Is a pacemaker a first degree block?
According to guidelines from the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), permanent pacemaker implantation is reasonable for first-degree AV block with symptoms similar to those of pacemaker syndrome or hemodynamic compromise (class IIa recommendation; level of evidence, B). [ 28] Additional ACC/AHA/HRS recommendations have been formulated for other patients with first-degree AV block, as follows.
Can you be hospitalized for AV block?
In general, hospitalization specifically for first-degree AV block is not indicated. However, admission may be indicated for associated conditions (eg, MI). Patients with a marked first-degree AV block can present with symptoms similar to the pacemaker syndrome. [ 3] In these individuals, admission may be indicated.
Can you treat AV block?
In general, no treatment is indicated for asymptomatic isolated first-degree atrioventricular (AV) heart block.

Clinical significance
- In people with heart block, also called AV block, the electrical signal that controls the heartbeat is partially or completely blocked from reaching the ventricles.
Classification
- Heart block is classified as first-, second- or third-degree, depending on the extent of electrical signal impairment.
Overview
- Type I heart block (also called Mobitz Type I or Wenckebach's AV block) is the less serious form of second-degree heart block. In this condition, the electrical signal goes slower and slower until the heart actually skips a beat.
Symptoms
- In patients with Type II heart block (also called Mobitz Type II), some of the electrical signals do not reach the ventricles, and the pattern is irregular. Individuals with this type of heart block may have a heartbeat that is slower than normal. The area that is blocked is lower in the conduction system and is often associated with more severe conduction disease. Symptoms of second- an…
Mechanism
- In patients with third-degree (complete) heart block, the electrical signal is not sent from the atria to the ventricles. The heart compensates by producing electrical signals from a specialized pacemaker area in the ventricles. These signals make the heart contract and pump blood, but at a rate that is much slower than normal.
Signs and symptoms
- First-degree heart block often does not cause symptoms. It may be detected during a routine electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), but the patients heart rate and rhythm are usually normal.
Causes
- Acquired heart block has many possible causes, including heart attack (the most common cause), heart disease, an enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy), heart failure and rheumatic fever. Sometimes heart block occurs as a result of injury to the heart during open heart surgery, as a side effect of some drugs, or after exposure to a toxin.