
Everydayhealth.com
1. Get Your Fill of Water...
2. Load Up on Vitamin C for a Healthy Urinary Tract...
3. Soothe UTI Pain With Heat...
4. Cut Bladder Irritants From Your Diet...
5. Go Ahead, Empty Your Bladder Again...
6. Consider Herbal Remedies...
7. Change to Healthier Habits...
Learn More...Healthline.com
1. Drink Plenty of Fluids...
2. Increase Vitamin C Intake...
3. Drink Unsweetened Cranberry Juice...
4. Take a Probiotic...
5. Practice These Healthy Habits...
6. Try These Natural Supplements...
Learn More...Top10homeremedies.com
1. Apple Cider Vinegar...
2. Indian Gooseberry (Amla)...
3. Cranberry Juice...
4. Baking Soda...
5. Tea Tree Oil...
6. Blueberries...
7. Pineapple...
8. Uva Ursi...
Learn More...Tinyqualityhomes.org
1. Parsley Tea...
2.Cranberry Juice...
3.Apple Cider Vinegar...
4.Garlic...
5.Water...
6.Cucumbers...
7.Tea Tree Oil...
8.Marshmallow Root Tea...
Learn More...How to get rid of UTI in 24 hours?
Method 2 Method 2 of 3: Alleviating a UTI at Home
- Drink plenty of water. Antibiotics are the only way to really treat a UTI, but given that they often pass in a few days, there are things you can ...
- Try some cranberry juice. Drinking cranberry juice is often cited as a home remedy for a UTI. ...
- Take vitamin C supplements. ...
- Avoid consuming irritants. ...
What antibiotics are used to treat E coli?
coli?
- Drink clear fluids. Drink clear fluids throughout the day. ...
- Replace electrolytes. E.coli toxins cause the intestines to dump electrolytes as well as water, so drink broths and soups.
- Practice good hygiene. Remember that as long as the symptoms last, you are shedding E. ...
- Rest. Fighting infection wears out the body, so give the body plenty of bed rest. ...
How do you treat E coli UTI?
coli
- 5 Home Remedies for UTI with E. coli. When you’re suffering from E. ...
- Natural Supplements for UTI with E. coli. Swedish Bitter. Anoint your belly area with Swedish bitter or sea buckthorn cream, in the evening, before bedtime.
- Best Diet for UTI with E. coli. Avoid all dairy products except for fresh cow cheese (have 250 gr/week). ...
What drugs are used for UTI?
They’ll likely prescribe one of the following antibiotics to treat it before the culture comes back:
- Amoxicillin / augmentin
- Ceftriaxone ( Rocephin)
- Cephalexin ( Keflex)
- Ciprofloxacin ( Cipro)
- Fosfomycin ( Monurol)
- Levofloxacin ( Levaquin)
- Nitrofurantoin ( Macrodantin, Macrobid)
- Trimethoprim / sulfamethoxazole ( Bactrim, Septra)
See more

What is best antibiotic for E. coli UTI?
However, among bacteria causing UTIS, E. coli is considered as the most predominant cause of both community and nosocomial UTIs. Antibiotics commonly recommended for treatment of UTIs include co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole), nitrofurantoin, ciprofloxacin and ampicillin [3, 10].
How do you get rid of E. coli in the urinary tract?
After a positive urinalysis, your doctor might prescribe Bactrim or Cipro, two antibiotics often used to treat UTIs caused by E. coli. If you're not better after a few doses, the E. coli may be resistant to these drugs.
How serious is E. coli in the urinary tract?
E. coli normally lives harmlessly in the human intestinal tract, but it can cause serious infections if it gets into the urinary tract. In women, the trip from the anus to the urethra is a short one. This is the reason why "wiping front to back" after using the toilet is helpful in preventing UTI.
How long does E. coli last in UTI?
How long does it last? Symptoms usually last 5 to 10 days. People with mild symptoms usually recover on their own without treatment. Antibiotics are not helpful for treating E.
What are the symptoms of E. coli in urine?
Some common symptoms include:Strong, persistent urge to urinate.Painful and burning urination.Passing only minimal amounts of urine.Strong-smelling, cloudy urine.Red or pink-tinged urine, which indicates blood is present.Pain in the upper back and sides.Fever and chills.Nausea.More items...•
What are the first signs of E. coli?
Symptoms of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) infection vary for each person, but often include severe stomach cramps, diarrhea (often bloody), and vomiting. Some people may have a fever, which usually is not very high (less than 101˚F/38.5˚C). Most people get better within 5 to 7 days.
How do you know if a UTI has spread to your kidneys?
A kidney infection is, in essence, a UTI that has spread into the kidneys. While this type of infection is rare, it's also very dangerous and if you're experiencing any of the following signs of a kidney infection, you should see a doctor immediately: Upper back or side pain. Fever, shaking or chills.
Can E. coli in urine cause sepsis?
Abstract. Background: Escherichia coli is a common cause of a broad spectrum of infections, from non-complicated urinary tract infection, to severe sepsis and septic shock, that are associated to high impact outcomes, such as ICU admission and mortality.
What happens if E. coli goes untreated?
Most cases of E. coli infections are mild and do not cause a serious health risk. Cases resolve on their own with rest and drinking plenty of fluids. However, some strains can cause severe symptoms and even life-threatening complications, such as hemolytic uremic syndrome, which can lead to kidney failure and death.
Why won't my UTI clear up with antibiotics?
There are three primary reasons that this may happen: an antibiotic-resistant strain of bacteria is causing your UTI. another type of bacteria, fungi, or virus may be causing your infection. your UTI may be another condition that has UTI-like symptoms.
What is the treatment for E. coli?
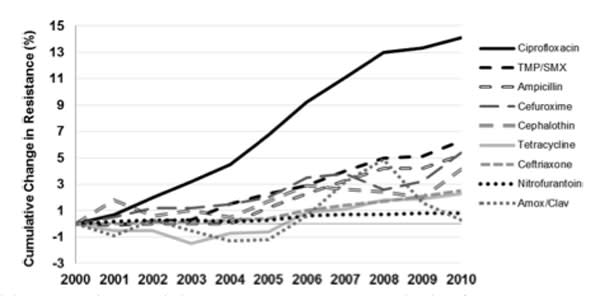
The standard treatment for most urinary tract infections is antibiotics. However, some E. coli strains are resistant to most antibiotic drugs. These strains are called extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli. Researchers found that UTIs caused by E. coli, which are resistant to ciprofloxacin, increased from 3-17 percent in 2000 up ...
What is the antibiotic for UTI?
Escherichia coli or better known as E. coli, is the bacterium responsible for over 80 percent of common UTI cases. The standard treatment for most urinary tract infections is antibiotics. However, some E. coli strains are resistant to most antibiotic drugs. These strains are called extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli.
What is the procedure to visualize bladder?
Cystoscopy: Doctors may recommend cystoscopy to individuals with recurrent urinary tract infections. This procedure involves the use of a cystoscope to visualize your bladder on the inside. A cystoscope (a thin tube with lens) is inserted into the urethra and through the bladder.
What is urine culture?
A urine culture involves growing bacteria in the laboratory. This test helps the doctor in identifying what type of bacteria is causing your UTI, and the type of antibiotic that would be most effective for your condition. Cystoscopy: Doctors may recommend cystoscopy to individuals with recurrent urinary tract infections.
What is the function of the urinary system?
The main function of the urinary system is to get rid of waste, maintain the body’s water balance, and regulate electrolytes. Its function starts with the kidneys, the organ that filter blood to produce urine, which is composed of extra fluid and wastes. Before leaving the body, urine travels through two thin tubes called ureters to reach ...
What test is used to diagnose a urinary tract infection?
There are multiple tests that can be used to diagnose urinary tract infections: Urine test: The doctor may ask you to collect a urine sample for a urinalysis. The test involves checking the presence and amount of red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), or bacteria.
What is the name of the tube that emptied the bladder when it is time to urinate?
Urine flows out of the body through When it is time to urinate, the bladder empties and urine flows out of the body through a tube called urethra. As you might expect, a urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, urinary bladder, ...
What is the treatment for E. coli?
Treatment includes IV fluids, blood transfusions and kidney dialysis.
How to diagnose E. coli infection?
To diagnose illness caused by E. coli infection, your doctor sends a sample of your stool to a laboratory to test for the presence of E. coli bacteria. The bacteria may be cultured to confirm the diagnosis and identify specific toxins, such as those produced by E. coli O157:H7.
How to prevent dehydration?
Follow these tips to prevent dehydration and reduce symptoms while you recover: Drink clear liquids. Drink plenty of clear liquids, including water, clear sodas and broths, gelatin, and juices. Avoid apple and pear juices, caffeine, and alcohol. Avoid certain foods.
Why is anti-diarrhea not recommended?
Antibiotics generally aren't recommended because they can increase the risk of serious complications and they don't appear to help treat the infection.
Can you take anti-diarrheal medication for E. coli?
What you can do in the meantime. If you or your child has an E. coli infection, it may be tempting to use an anti-diarrheal medication, but don't. Diarrhea is one way the body rids itself of toxins. Preventing diarrhea slows that process down.
How to get rid of E. coli in urine?
Drinking water (especially after intercourse) helps dilute urine and spur more frequent urination, which flushes E. coli from the urinary tract. Avoid diaphragms or spermicides. These can contribute to bacterial growth and kill the good bacteria that work to protects against UTIs.
Where is E. coli high risk?
Preventing E. coli–Related Traveler’s Diarrhea. Many areas of Central and South America, Mexico, Africa, the Middle East, and most of Asia are considered high-risk destinations for traveler's diarrhea. (There is some risk when traveling to Eastern Europe and a few Caribbean islands as well.)
What is the name of the bacteria that causes diarrhea?
Usually, traveler’s diarrhea occurs when an individual ventures to a developing country and is then exposed to bacteria (most often a strain of E . coli dubbed enterotoxigenic E. coli, or ETEC) via food or water to which their body has little to no familiarity.
How to stop vomiting from a syringe?
These include apple and pear juices, caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, dairy, fatty foods, and high-fiber foods. Gradually add bland food into your diet. Start with items like soda crackers, toast, eggs, and rice.
Can E. coli cause UTI?
Some strains of E. coli are a normal part of microbial communities in the gut, but can cause a urinary tract infection (UTI) if they make their way into the urinary system.
Does E. coli require antibiotics?
coli infections caused by Shiga toxin–producing E. coli, or STEC — which spurs an estimated 265,000 foodborne infections each year in the United States — does not require antibiotic treatment. ( 1)
Does hand sanitizer prevent E. coli?
While opting for a hand sanitizer may seem like a smart choice when no running water is close by, know that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved any products claiming to prevent E. coli infection. ( 9) It’s also very important to follow certain food preparation and cooking rules.
How to get rid of E. coli in feces?
Make sure that you don’t use the same bathroom as other family members. If you must, always clean bathroom surfaces with disinfectant after use. Wash your hands regularly throughout the day, especially after using the restroom. Finally, do not prepare food for other people or touch any utensils other people may use for eating.
What is E. coli?
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) invades intestinal cells and causes watery diarrhea and fever. Enteroinvasive E. coli is a rare form of E. coli that does not produce toxins. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) are bacteria that both attach to the intestinal lining and invade intestinal cells.
What causes death from E. coli?
Death caused by E. coli infections is usually due to hemolytic uremic syndrome. The Shiga toxin is absorbed by the intestines and enters the bloodstream. There, the toxin kills off red blood cells, causing anemia, and platelets, the blood cells responsible for clotting.
How long does E. coli last?
An infection with E. coli usually produces symptoms in about three days following the exposure to the bacteria. Symptoms can last for five to ten days. E. coli that produce Shiga or Shiga-like toxins will usually cause watery diarrhea for two or three days followed by bloody diarrhea for another seven days.
How many Escherichia coli infections are spread from person to person?
Person-to-person contact. Although animals are the main source of Escherichia coli infections, anywhere from 10% to 15% of infections are spread from person to person. The most common cause of person-to-person spread is poor hygiene.
What is the nastiest E. coli bug?
Still, the nastiest E. coli bugs are the strains found in the colon that can cause serious and even fatal intestinal infections. When the news covers stories about E. coli outbreaks sending people to the hospital, or resulting in death, it’s these more infectious E. coli strains they’re reporting on.
How is E. coli spread?
The infectious strains of E. coli normally live in animals but are spread to humans through the ingestion of animal feces in contaminated food or water.
How long should you take antibiotics for a recurrent UTI?
For recurrent UTIs, there are several antibiotic options for prevention: A shorter course (3 days) of antibiotics at the first sign of UTI symptoms; a prescription may be given to you to keep at home, but testing should be done at least once to confirm you have a UTI and not another problem.
How much does a UTI cost?
Roughly 40% of women experience a UTI at some time, and in women, it is the most common infection. Healthcare costs related to UTIs exceed $1.6 billion per year. A urinary tract infection (UTI) can happen anywhere along your urinary tract, which includes the kidneys (the organ that filters the blood to make urine), ...
What causes most UTIs in women?
Most UTIs in women (roughly 85%) are caused by a bacteria known as Escherichia coli (E. coli). Other types of bacteria, such as Staphylococcus saprophyticus may infrequently be present. UTI symptoms in women and men are similar. However, urinary tract infections occur more frequently in women than in men.
What is it called when bacteria get into the bladder?
A lower urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria gets into the urethra and is deposited up into the bladder -- this is called cystitis . Infections that get past the bladder and up into the kidneys are called pyelonephritis.
Why do women get UTIs?
Women are also more likely to get an infection after sexual activity or when using a diaphragm and spermicide for birth control. Other risk factors for the development of UTIs include catheter use, urinary tract structural abnormalities, diabetes, and a suppressed immune system.
How long does it take to get rid of cystitis?
Length of treatment for cystitis can range from a single, one-time dose, to a course of medication over 5 to 7 days. Kidney infections may require injectable treatment, hospitalization, as well as a longer course of antibiotic, depending upon severity of the infection.
What is the first line of antibiotics?
First-line options are usually selected from nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. Amoxicillin/clavulanate ( Augmentin) and certain cephalosporins, for example cefpodoxime, cefdinir, or cefaclor may be appropriate options when first-line options cannot be used.
How to treat E. coli in urine?
When there is E. coli in urine culture, it is important to identify the best treatment option. Antibiotics usually work well to treat urinary tract infections. If you have a simple infection, your doctor may prescribe Trimethoprim, Nitrofurantoin, Fosfomycin, Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline, and Ceftriaxone. Your symptoms will go away after taking these drugs for some time, but you may have to continue taking these for another week or so to complete the entire course. It is usually enough to take antibiotics for a couple of days only to treat an uncomplicated UTI. Your doctor may also give you a pain medication to numb your bladder and urethra. This will help relieve the burning sensation while urinating. You will notice your urine turn red or orange when using urinary tract analgesics.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for a UTI?
Your doctor may adapt a different approach when you have frequent UTIs. They may prescribe low dose antibiotics that you have to take for six months or longer . They may prescribe specific antibiotics that you have to take after a sexual encounter – this is usually the case when your UTI is related to sexual activity.
Why is my urine count 100?
If there are bacteria in your sample but the count is between 100 and 100,000, this may be due to infection or contamination of the sample in which you will need another urine culture. The infection isn't present usually when the count is 100 or less. Also, if different types of bacteria grow in a culture, it usually happens due to contamination.
What causes E. coli in the urinary tract?
Urine Culture with E. Coli: Meaning, Results and Treatment. Different microbes such as viruses, fungi, and bacteria can cause a urinary tract infection. Bacteria are the most common culprits even though your body has a natural defense system to throw these bacteria out of your body when they enter your urinary tract.
What is the purpose of a urine culture test?
They will then analyze your urine and if they find something specific, they will proceed with a urine culture test to confirm an infection . This test will help confirm the types of bacteria causing infection in your case – this will also help identify the best medicine for the infection.
What test do you need to confirm if you have a urinary tract infection?
To confirm your symptoms are due to a urinary tract infection, your doctor will ask for a urine test in which they will look for E. coli.
How long does it take to get a urine culture?
As mentioned already, a urine culture is a test that helps detect and identify the type of organism that's causing a UTI. It usually takes a couple of days to get your urine culture results, but some organisms don't grow that quickly in the culture, so you will have to wait longer for your result. Normal.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- For illness caused by E. coli, no current treatments can cure the infection, relieve symptoms or prevent complications. For most people, treatment includes: 1. Rest 2. Fluids to help prevent dehydration and fatigue Avoid taking an anti-diarrheal medication — this slows your digestive system down, preventing your body from getting rid of the toxins....
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Follow these tips to prevent dehydration and reduce symptoms while you recover: 1. Drink clear liquids.Drink plenty of clear liquids, including water, clear sodas and broths, gelatin, and juices. Avoid apple and pear juices, caffeine, and alcohol. 2. Avoid certain foods.Dairy products, fatty foods, high-fiber foods or highly seasoned foods can make symptoms worse. 3. Eat meals.Whe…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Most people don't seek medical attention for E. coliinfections. If your symptoms are particularly severe, you may want to visit your primary care doctor or seek immediate care. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment and know what to expect from your doctor.