
Medication
Mar 15, 2022 · Masitinib is an orally administered tyrosine kinase inhibitor that can target mast cells and microglia, immune cells of the central nervous system. It can protect both the central and peripheral nervous systems by blocking the function of immune cells that are involved in …
Therapy
The discovery is significant because, to date, there is no cure or effective treatment for ALS, a progressive neuromuscular disease caused by deterioration of motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord. Individuals living with the disease experience progressive paralysis, including the muscles involved in breathing and swallowing.
Nutrition
Dec 20, 2021 · The primary goal of treatment for Lou Gehrig's disease, or ALS, is to improve life expectancy or quality of life. This can involve medication, non-invasive ventilation (assisted breathing using a mask), a feeding tube, physical therapy, and using assistive devices such as braces or a wheelchair.
How close are we to curing ALS?
Sep 02, 2020 · The drug is not a cure, but it may help slow the inexorable disability caused by ALS, which rapidly destroys the nerve cells that control the muscles that allow us to move, speak, eat and even...
What is ALS and how is it treated?
A wealth of new scientific understanding about the physiology ALS has occurred in recent years. There are currently four drugs approved by the U.S. FDA to treat ALS: Riluzole, Nuedexta, Radicava and Tiglutik. Studies to develop more treatments and a cure for ALS, many funded by The ALS Association, are ongoing around the world.
What medications are used for ALS?
How is ALS diagnosed and treated?

What is the most common treatment for ALS?
Although there is no known cure for ALS, the drug riluzole has been approved for treatment and may slow progression of the disease. It is expensive, however, and appears modestly effective. Generally, treatment is designed to help control symptoms. Drugs such as baclofen or diazepam may help control spasticity.
How long do you live after being diagnosed with ALS?
Symptoms and Diagnosis The rate at which ALS progresses can be quite variable, as well. Although the mean survival time with ALS is two to five years, some people live five years, 10 years or even longer. Symptoms can begin in the muscles that control speech and swallowing or in the hands, arms, legs or feet.
What are the chances of surviving ALS?
Approximately 50% of people diagnosed with ALS live at least three or more years after diagnosis. About 25% live five years or more and up to 10% live more than 10 years.
How does a person get ALS?
Familial (Genetic) ALS About 5 to 10 percent of all ALS cases are familial, which means that an individual inherits the disease from a parent. The familial form of ALS usually only requires one parent to carry the disease-causing gene. Mutations in more than a dozen genes have been found to cause familial ALS.
Is ALS a painful death?
Pain. There is no reason that people with ALS have to live in pain. Although only a limited number of people with ALS experience pain, the thought of living with constant pain can be frightening. The disease itself does not cause pain.
What are usually the first signs of ALS?
What is usually the first sign of ALS?Muscle twitches or fasciculations in the arm, leg, shoulder or tongue.Muscle tightness or stiffness (spasticity)Muscle cramps.Weakness of muscles affecting an arm, a leg, neck or diaphragm (the muscular partition separating the chest from the abdomen).Slurred speech.Nasal voice.More items...
How fast is ALS progression?
In general, the ALSFRS and FVC scores decrease by about 20% per year. If the decline in ALSFRS is more than 0.5 points per month, progression may be faster than average. Breathing declining at more than 3% per month also suggests a faster rate of progression.
Where does ALS usually start?
ALS often starts in the hands, feet or limbs, and then spreads to other parts of your body. As the disease advances and nerve cells are destroyed, your muscles get weaker. This eventually affects chewing, swallowing, speaking and breathing.Feb 22, 2022
How is the family of a person with ALS affected?
Family caregivers of ALS patients are deeply affected by the illness and often experience burden due to physical strain, emotional tension, personal and social limitations (Rabkin et al., 2000), anxiety and depression (Chiò et al., 2005; Pagnini et al., 2012).Mar 17, 2015
What are the 4 stages of ALS?
The 4 Stages of ALS- Lou Gehrig 's DiseaseStage 1- The Beginning. There are several changes which happen in the muscles as well as the physical appearance and effects as well. ... Stage 2- The Middle. ... Stage 3- The Late Stage. ... Stage 4- The Ending.May 15, 2015
Does ALS come on suddenly?
As I have mentioned before, ALS does not start abruptly. Consider Lou Gehrig. At first he never dreamed he had a disease.
Who is most commonly diagnosed with ALS?
It affects as many as 30,000 in the United States, with 5,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Estimates suggest that ALS is responsible for as many as five of every 100,000 deaths in people aged 20 or older. ALS is most common among persons over age 60.
How to treat ALS?
Currently there is no cure for ALS, yet patients suffering from the disease can be made more comfortable with the following options: 1 medications to relieve painful muscle cramps, excessive salivation and other symptoms. 2 heat or whirlpool therapy to relieve muscle cramping. 3 exercise, although recommended in moderation, may help maintain muscle strength and function. physical therapy to maintain mobility and ease the discomfort of muscle stiffness, cramps and fluid retention. 4 nutritional counseling to promote good nutrition and offer other dietary options when swallowing becomes difficult. 5 speech therapy and communication training to maintain as many verbal communication skills as possible. Communication training also indicates non-verbal techniques. 6 devices such as splints, corrective braces, grab bars, reach-extenders, etc. to help with daily activities such as dressing, eating, using the toilet and bathing. 7 special equipment such as wheelchairs, electric beds or mattresses to maximize functional independence.
What is the best way to help swallowing?
nutritional counseling to promote good nutrition and offer other dietary options when swallowing becomes difficult. speech therapy and communication training to maintain as many verbal communication skills as possible. Communication training also indicates non-verbal techniques.
How to help muscle cramps?
heat or whirlpool therapy to relieve muscle cramping. exercise, although recommended in moderation, may help maintain muscle strength and function. physical therapy to maintain mobility and ease the discomfort of muscle stiffness, cramps and fluid retention.
What is communication training?
Communication training also indicates non-verbal techniques. devices such as splints, corrective braces, grab bars, reach-extenders, etc. to help with daily activities such as dressing, eating, using the toilet and bathing.
Does Rilutek help with ALS?
Recently, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Rilutek®, the first drug that has reliably prolonged the survival of persons with ALS. Patients, however, will not get stronger nor regain lost strength with this drug.
How long do ALS patients live?
ALS patients gradually lose the ability to function and care for themselves. They may survive from two to 10 years after the onset of the disease, with about 20 percent of ALS patients living more than five years after diagnosis. UCSF Health medical specialists have reviewed this information.
Is there a cure for ALS?
ALS. Treatments. Although there is no known cure for ALS, the drug riluzole has been approved for treatment and may slow progression of the disease . It is expensive, however, and appears modestly effective. Generally, treatment is designed to help control symptoms.
How to treat ALS?
Fatigue. Therapies. Most treatments for ALS involve managing the symptoms of the disease as it worsens. Some of them include: Physical therapy and exercise: These keep your muscles strong and working as long as possible. Hot tub and whirlpool baths: These can ease your muscle spasms or cramps.
What are the symptoms of ALS?
Doctors may prescribe drugs to help ease other symptoms of ALS, which may include: 1 Constipation 2 Depression 3 Outbursts of laughter or crying 4 Lack of sleep 5 Fatigue
What is Lou Gehrig's disease?
It’s commonly known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, after the baseball player whose diagnosis and eventual death brought wide public attention to the illness. This condition kills the nerves that control motion in your body. As those nerves die, you lose control of your muscles.
How long can you live with ALS?
About 1 person in 25,000 will be diagnosed with ALS. Most of them die within 2 to 5 years of being diagnosed, usually because of respiratory failure. However, a small group, about 5% of those with ALS, have been able to survive for 20 years or more.
What are the side effects of a syringe?
The most common side effects include gastric distress, dizziness and bruising. Medication for Symptoms. Pain relievers or muscle relaxants such as baclofen (Gablofen, Kemstro, Lioresal) or diazepam ( Diastat, Valium) can help ease cramps. A variety of medications can lower how much saliva you make.
Is there a cure for ALS?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, is a disease that attacks the nerve cells in your brain and spinal cord. There is no known cure. But doctors do have treatments and therapies that can slow down or ease symptoms in you or a loved one. Researchers continue to study ALS, hoping to learn more about its causes and possible new treatments.
Medications used in managing ALS
There are two medications that have been FDA approved for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or motor neuron disease:
ALS therapies
Physical therapy – This kind of treatment involves a physical therapist who is able to address and assist with the pain associated with mobility and walking and provide the individual with equipment to aid them in staying somewhat independent. Walkers, wheelchairs and braces can be adjusted for the patient.
Clinical studies on ALS
There have been a number of clinical studies that have promising results regarding future treatment and medication options for ALS. A patient’s eligibility for joining one of these studies will depend on a number of aspects related to their condition. Bear in mind that although some studies have positive results, their outcomes are not guaranteed.
What is ALS in the US?
What is ALS? Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) or Lou Gherig’s Disease is a rapidly progressive neurological disease which attacks the neurons involved with voluntary movement, called motor neurons. It is estimated that ALS affects 2 in 100,000 people every year in Europe and the US.
When does ALS start?
Usually, the onset of the disease starts around the age of 60 and in inherited cases around the age of 50. The cause of ALS is not known, and scientists do not yet know why ALS strikes some people and not others.
What is Masitinib used for?
Masitinib is an orally administered tyrosine kinase inhibitor that can target mast cells and microglia, immune cells of the central nervous system. It can protect both the central and peripheral nervous systems by blocking the function of immune cells that are involved in ALS progression.
How many people in the world have ALS?
It is estimated that ALS affects 2 in 100,000 people every year in Europe and the US. The worldwide annual incidence of ALS is estimated to be about 1.9 per 100,000. ALS is characterized by stiff muscles, muscle twitching, and gradually worsening weakness due to muscle loss.
Where are MSCs collected?
MSCs are collected from the bone marrow, after which they are expanded and matured into cell s that produce high levels of neurotrophic factors compounds that promote nervous tissue growth and survival. The mature cells are then infused back into the patient through an injection into the spinal canal.
What is Tofersen used for?
inhibits the Superoxide Dismutase 1 (SOD1) gene, the second most common genetic form of ALS. Tofersen is an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) that is designed to reduce the production of SOD1 protein production.
What is the purpose of arimoclomol?
Arimoclomol is an orally or naso/gastrically-administered small molecule that can cross the blood-brain barrier. It can amplify the production of heat-shock proteins (HSPs), which can reduce protein misfolding and aggregation and improve lysosomal function.
What is Lou Gehrig's disease?
Canadians researchers have made a significant discovery regarding ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, opening the door to novel approaches to the treatment of the disease.
What is the SOD1 protein?
The study demonstrates that the SOD1 protein (superoxide dismutase 1) , which has been shown to be implicated in the ALS disease process, exhibits prion-like properties. The research found that SOD1 participates in a process called template-directed misfolding.
What is a prions?
Prions are “misfolded” proteins – the infectious, aggregating agents in diseases such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) in humans, chronic wasting disease (CWD) in deer and elk and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), also known as “mad cow” disease in cattle.
Is there a cure for ALS?
The discovery is significant because, to date, there is no cure or effective treatment for ALS, a progressive neuromuscular disease caused by deterioration of motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord. Individuals living with the disease experience progressive paralysis, including the muscles involved in breathing and swallowing.
What are the advances in ALS?
Advances have been made in recent years in the support and treatment for ALS. Researchers have also made advances in understanding the disease process of ALS , which will hopefully lead to new treatments.
How can a physical therapist help ALS patients?
Physical therapists can help a person with ALS to do physical exercise and stretching that strengthens functioning muscles, decreases spasticity, and doesn't overwork their muscles, with the goal of preserving the strength and flexibility they still have.
What are the different types of ALS?
ALS is medically classified by which motor neurons are impacted: 3 1 Classical ALS is characterized by a deterioration of upper and lower motor neurons. This type of ALS affects more than two-thirds of those with the disease. 2 Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) is characterized by deterioration of the upper motor neurons. If the lower motor neurons are not impacted within two years, the disease usually remains a pure upper motor neuron disease. This is the rarest form of ALS. 3 Progressive bulbar palsy (PBP) starts with difficulties in speaking, chewing, and swallowing due to lower motor neuron deterioration. This disorder affects about 25% of those with ALS. 4 Progressive muscular atrophy (PMA) is characterized by deterioration of the lower motor neurons. If the upper motor neurons are unaffected within two years, the disease usually remains a purely lower motor neuron disease.
What is Lou Gehrig's disease?
Treatments. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also called "Lou Gehrig's disease," is a progressive and ultimately fatal neurodegenerative disease that affects the nerves that control movement. ALS leads to people becoming so weak that they are paralyzed, and half of the people impacted will die within two ...
What is the difference between ALS and PLS?
Classical ALS is characterized by a deterioration of upper and lower motor neurons. This type of ALS affects more than two-thirds of those with the disease. Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) is characterized by deterioration of the upper motor neurons. If the lower motor neurons are not impacted within two years, ...
What is the disease that affects the motor neurons?
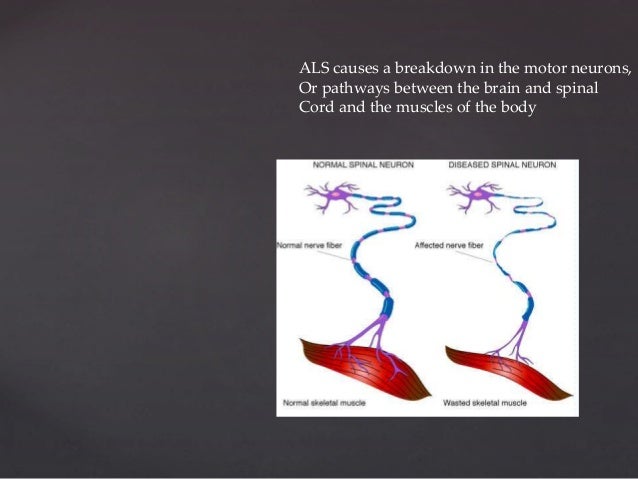
ALS is a neurodegenerative disease that affects motor neurons, which are the nerve cells that control the movement of muscles. "Upper motor neurons" originate in the brain. "Lower motor neurons" originate in the spinal cord. ALS destroys both upper and lower motor neurons, but a person often starts with symptoms of either upper or lower motor ...
How long do people with ALS live?
According to the ALS Association, the average life expectancy of a person with ALS is three years. However, it varies greatly: 6. 20% live five years or more. 10% live 10 or more years. 5% will live for more than 20 years.
How many people have ALS?
About 20,000 people in the U.S. have ALS at any given time, according to the ALS Association. It usually strikes between the ages of 40 and 70. Once symptoms set in, life expectancy is two to six years, on average.
Who is Linda Carroll?
Follow NBC HEALTH on Twitter & Facebook. Linda Carroll. Linda Carroll is a regular health contributor to NBC News and Reuters Health. She is coauthor of "The Concussion Crisis: Anatomy of a Silent Epidemic" and "Out of the Clouds: The Unlikely Horseman and the Unwanted Colt Who Conquered the Sport of Kings.".
Does experimental medication slow the progression of ALS?
An experimental medication may slow the progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, researchers reported Wednesday. The research was supported in part by donations from the Ice Bucket Challenge, the social media sensation that raised more than $200 million worldwide.
How many drugs are there for ALS?
Recent years have brought a wealth of new scientific understanding regarding the physiology of this disease. There are currently four drugs approved by the U.S. FDA to treat ALS (Riluzole, Nuedexta, Radicava, and Tiglutik).
What is ALS in the brain?
What is ALS? ALS, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord. A-myo-trophic comes from the Greek language. "A" means no. "Myo" refers to muscle, and "Trophic" means nourishment – "No muscle nourishment.".
What happens when motor neurons die?
When the motor neurons die, the ability of the brain to initiate and control muscle movement is lost. With voluntary muscle action progressively affected, people may lose the ability to speak, eat, move and breathe.
What are some examples of voluntary movements?
These actions are controlled by the muscles in the arms and legs. There are two different types of ALS , sporadic and familial. Sporadic, which is the most common form of the disease in the U.S., accounts for 90 to 95 percent of all cases.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment