Medication
very recently, three novel drugs have been approved for patients who can be intensively treated: a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (midostaurin) for patients with flt3 mutations, a liposomal formulation of chemotherapy (cpx) for patients with features of secondary aml, and a cd33 antibody-drug conjugate (gemtuzumab-ozogamicin) for aml with cd33 …
Procedures
Feb 22, 2021 · Low-intensity HMA therapy with decitabine and azacitidine-based regimens is now the most common form of treatment among older (or unfit for intensive chemotherapy) patients with AML26,28. A third possible example is the non-submission of vosaroxin for FDA approval for the therapy of AML first salvage29.
Self-care
American Cancer Society: "Chemotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia," "Other Drugs for Acute Myeloid Leukemia," "Radiation Therapy for Acute Myeloid …
Nutrition
Dec 10, 2021 · Treatments for AML include chemotherapy, which may be followed by a stem cell transplant or, in some cases, surgery or radiation. The better your AML reacts to treatment, the better your outcome is likely to be, such as: 5
What drugs are used to treat leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia treatment depends on the subtype, as well as your overall health and other factors. AML is not divided into stages, which describe the extent of many other forms of cancers. In most cases, doctors use chemotherapy (drugs that destroy cancer cells) to treat AML.
Does AML have stages?
Can CLL be cured?
How is AML diagnosed?
See more

What is the survival rate of acute myeloid leukemia?
The 5-year overall survival rate for AML is 29.5 percent , according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI). This means that an estimated 29.5 percent of people in America living with AML are still living 5 years after their diagnosis.
Can you recover from acute myeloid leukemia?
Most often, the numbers used refer to the 5-year survival rate. That's how many people live at least 5 years after being diagnosed. People whose AML doesn't come back (relapse) in 5 years are usually cured. People who had AML that relapsed but then went into a second remission for 5 years are likely to be cured.
How long does it take to treat acute myeloid leukemia?
Treatment for AML is a long-term process. Chemotherapy and other treatment for the disease may take 6 to 12 months to complete. Some, but not all, patients are eligible for induction therapy.
What is the latest treatment for acute myeloid leukemia?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved two new treatments for some adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML): enasidenib (Idhifa®), a drug that targets aberrant forms of the IDH2 protein; and liposomal cytarabine-daunorubicin CPX-351 (Vyxeos™), a two-drug chemotherapy combination encapsulated ...Aug 28, 2017
Is AML the worst leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. It is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated.Mar 4, 2022
How fast does acute myeloid leukemia progress?
Acute leukemias — which are incredibly rare — are the most rapidly progressing cancer we know of. The white cells in the blood grow very quickly, over a matter of days to weeks. Sometimes a patient with acute leukemia has no symptoms or has normal blood work even a few weeks or months before the diagnosis.Oct 4, 2018
How many rounds of chemo is normal for AML?
Most people have 2 rounds of induction chemotherapy. The treatment will be carried out in hospital or in a specialist centre, as you'll need very close medical and nursing supervision. You may be able to go home between treatment rounds.
Does chemo work for acute myeloid leukemia?
Chemotherapy is the main treatment for most people with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Intense chemo might not be recommended for patients in poor health, but advanced age by itself is not a barrier to getting chemo.Sep 3, 2020
How aggressive is AML leukemia?
AML is an aggressive type of cancer that can develop rapidly, so treatment usually needs to begin soon after a diagnosis is confirmed. Chemotherapy is the main treatment for AML. It's used to kill as many leukaemia cells in your body as possible and reduce the risk of the condition coming back (relapsing).
Which type of leukemia is most fatal?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most fatal type of leukemia. The five-year survival rate (how many people will be alive five years after diagnosis) for AML is 29.5%. Leukemia is a cancer that usually affects white blood cells, though it can start in other types of blood cells.Feb 23, 2022
What cause acute myeloid leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is caused by a DNA mutation in the stem cells in your bone marrow that produce red blood cells, platelets and infection-fighting white blood cells. The mutation causes the stem cells to produce many more white blood cells than are needed.
What are the end stage symptoms of AML?
What are the symptoms of the final stages of AML?cool, dry skin.slow or labored breathing.blurry vision.decreased urination or incontinence.restlessness or involuntary muscle movements.decreased movements or weakness.loss of appetite and decreased fluid intake.increased drowsiness and sleepiness.More items...•Nov 23, 2021
What is the treatment for AML?
The main treatment for most types of AML is chemotherapy, sometimes along with a targeted therapy drug. This might be followed by a stem cell transplant. Other drugs (besides standard chemotherapy drugs) may be used to treat people with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Surgery and radiation therapy are not major treatments for AML, ...
Why is it important to discuss all of your treatment options?
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options and their goals and possible side effects, with your treatment team to help make the decision that best fits your needs. Some important things to consider include:
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you may have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: 1 A hematologist: a doctor who treats disorders of the blood 2 A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines
What is a medical oncologist?
A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, including physician assistants, nurse practitioners, nurses, nutrition specialists, social workers, and other health professionals. Health Professionals Associated with Cancer Care.
Why are clinical trials important?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
How old do you have to be to get chemo?
How intense the treatment is can depend on a person’s age and health. Doctors often give the most intensive chemo to people under the age of 60, but some older patients in good health may benefit from similar or slightly less intensive treatment.
What is cytarabine ara C?
Cytarabine (ara-C) An anthracycline drug such as daunorubicin (daunomycin) or idarubicin. This is sometimes called a 7 + 3 regimen, because it consists of getting cytarabine continuously for 7 days, along with short infusions of an anthracycline on each of the first 3 days.
Can leukemia be lower with chemo?
Some people with AML have very high numbers of leukemia cells in their blood when they are first diagnosed, which can cause problems with normal blood circulation. This is called leukostasis. Chemo can take a few days to lower the number of leukemia cells in the blood. In the meantime, leukapheresis (sometimes just called pheresis) might be used before chemo.
Can radiation therapy be used for leukemia?
Radiation therapy might be used as well. Patients typically need to stay in the hospital during induction (and possibly for some time afterward). Induction destroys most of the normal bone marrow cells as well as the leukemia cells, so most patients develop dangerously low blood counts, and may be very ill.
Can older people tolerate intensive consolidation?
Older patients or those in poor health may not be able to tolerate intensive consolidation treatment. Often, giving them more intensive therapy raises the risk of serious side effects (including treatment-related death) without providing much more of a benefit. These patients may be treated with:
Can AML be treated with chemo?
The acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) subtype of AML is treated differently. Treatment for AML usually needs to start as quickly as possible after it is diagnosed because it can progress very quickly. Sometimes another type of treatment needs to be started even before the chemo has had a chance to work.
Abstract
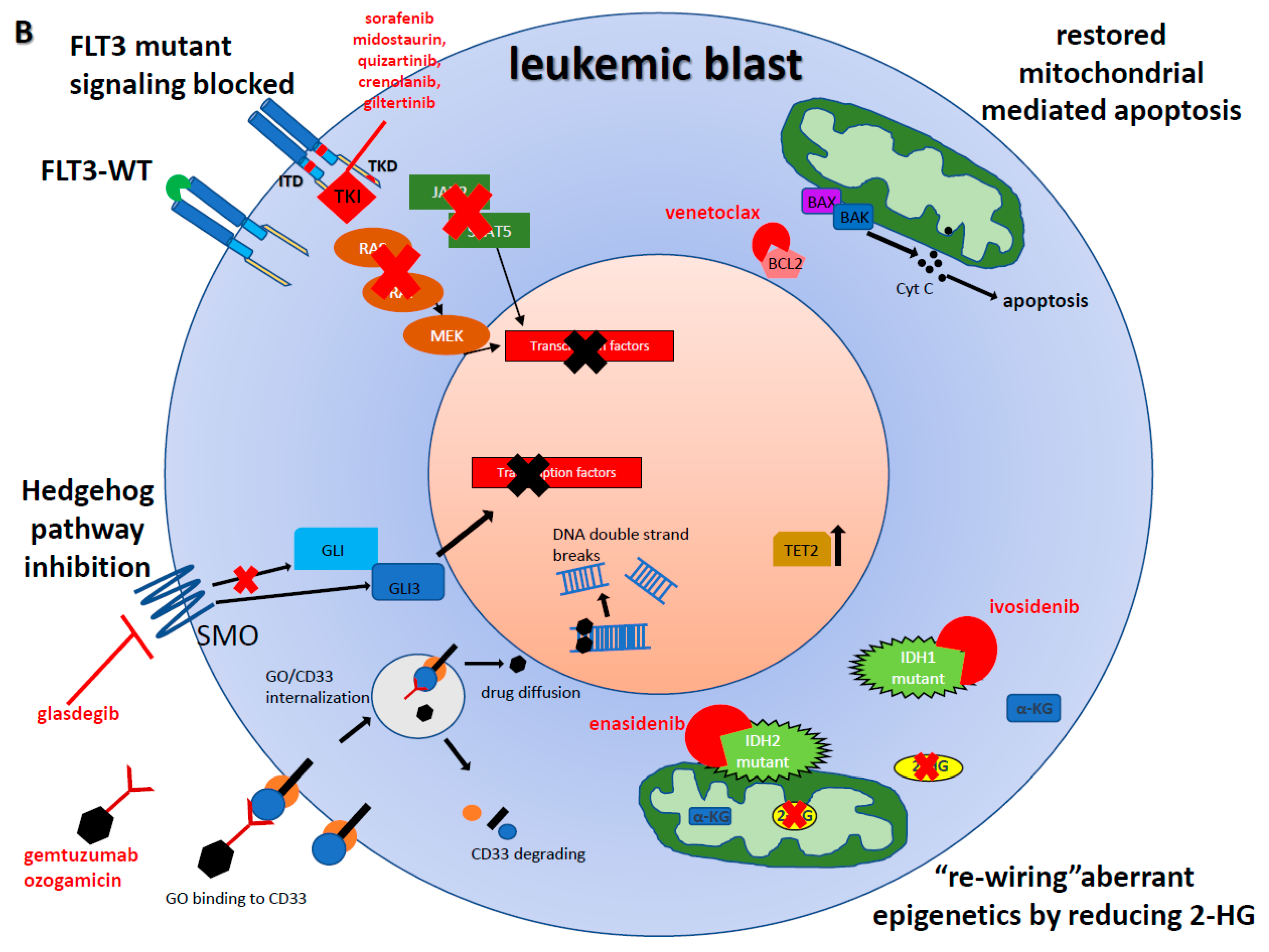
Progress in the understanding of the biology and therapy of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is occurring rapidly. Since 2017, nine agents have been approved for various indications in AML. These included several targeted therapies like venetoclax, FLT3 inhibitors, IDH inhibitors, and others.
Introduction
Progress in understanding the pathophysiology and improving the therapy of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is now occurring at a rapid pace.
Cytogenetic and molecular abnormalities
Acute myeloid leukemia has diverged from being considered as one acute leukemia entity to become a heterogeneous constellation of AML subentities characterized by diverse pathophysiologic, clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular profiles that benefit from individualized selective therapies and have vastly different outcomes.
Measurable residual disease in complete remission
Measuring residual disease in AML in complete remission (CR) is now part of the standard of care in AML 56 – 62. The detection of measurable residual disease (MRD) at the time of morphologic CR is associated with a higher relapse rate and with worse survival in AML.
Treatment of AML
The heterogeneous group of AML disorders requires different selective therapies.
Acute promyelocytic leukemia
Acute promyelocytic leukemia represents 5–10% of AML and is defined by the cytogenetic abnormality t (15; 17), which results in the PML-RAR alpha fusion oncogene and its encoded oncoprotein. The PML-RAR α oncoprotein acts as a dominant negative inhibitor of wild-type RAR α, causing a maturation block and the clinical-pathologic picture of APL.
Core-binding factor acute myeloid leukemia
The CBF AMLs include the subsets with chromosomal abnormalities involving inversion 16/t (16; 16) or t (8; 21). These constitute 10–15% of adult AML cases.
What is the treatment for AML?
Several different treatments work on AML: Chemotherapy. Stem cell transplant. Radiation. Targeted therapy. Your treatment will have two phases: Phase 1: Remission induction therapy. You'll get high doses of chemotherapy to destroy as many leukemia blast cells as possible. There are targeted therapy drugs as well.
What is the purpose of AML?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) pushes your bone marrow to make large numbers of abnormal and underdeveloped blood cells called blast cells. These cells crowd out healthy mature red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The goal of AML treatments is to destroy unhealthy immature blood cells in your bone marrow and blood.
What are the stages of chemo?
Phase 2: Post-remission therapy (Consolidation). Post-remission therapy uses more treatments to wipe out any cancer cells that might have been left behind after chemotherapy. This is called a complete remission. You have three options: 1 Chemotherapy. You may get several cycles of high-dose chemotherapy once a month. 2 Allogeneic (from a donor) stem cell transplant 3 Autologous (from yourself) stem cell transplant
Can chemotherapy cause blood clots?
Chemotherapy damages the leukemia cells and releases this protein, which can cause dangerous blood clots or severe bleeding. If you have APL, you'll get medicine to make your leukemia cells change into mature, healthy blood cells so they don't burst open and release their protein.
What is APL in cancer?
Another cancer years later. Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Treatment. Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a subtype of AML that doctors treat a little differently. In APL, the leukemia cells contain special proteins that change the way your blood clots.
What is the most common type of stem cell transplant?
There are two types of stem cell transplant: An allogeneic stem cell transplant uses stem cells taken from a donor. This is the most common type of stem cell transplant. A close relative like a parent, brother, or sister will be the best match. One risk of an allogenic transplant is graft-versus-host disease.
How does chemo kill cancer?
Chemotherapy uses strong drugs to kill cancer cells all over your body. You get these drugs by mouth, through an IV, or via an injection under your skin. If the cancer has spread to your brain or spinal cord, you'll get chemotherapy into the fluid around your brain and spinal cord.
Treating Leukostasis
Induction
Consolidation
Treating Frail Or Older Adults