How long does it take to recover from a TIA?
This can cause sudden symptoms similar to a stroke, such as speech and visual disturbance, and numbness or weakness in the face, arms and legs. But a TIA does not last as long as a stroke. The effects last a few minutes to a few hours and fully resolve within 24 hours.
What can trigger a TIA?
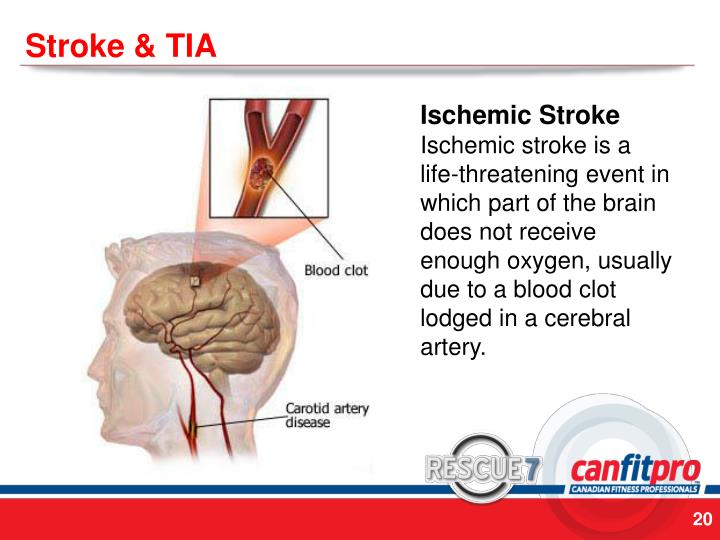
The blockage in the blood vessels responsible for most TIAs is usually caused by a blood clot that's formed elsewhere in your body and travelled to the blood vessels supplying the brain. It can also be caused by pieces of fatty material or air bubbles.
What should you do immediately after a TIA?
Streib recommends that all patients visit an emergency room during or immediately after a TIA to receive imaging of their brain and blood vessels. These scans can inform patients and providers of the cause of their TIA and their immediate stroke risk. Scans also help them decide upon a treatment plan.
Do TIAs need treatment?
Although the symptoms of a transient ischaemic attack (TIA) resolve in a few minutes or hours without any specific treatment, you'll need treatment to help prevent another TIA or a full stroke from happening in the future. A TIA is a warning sign that you're at increased risk of having a full stroke in the near future.
Are you hospitalized for a TIA?
If you have had a TIA within the last 48 hours, you will likely be admitted to the hospital so that doctors can search for the cause and observe you. High blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, high cholesterol, and blood disorders will be treated as needed.
Can a TIA be brought on by stress?
Conclusions. Higher levels of stress, hostility and depressive symptoms are associated with significantly increased risk of incident stroke or TIA in middle-aged and older adults.
Should I see a neurologist after a TIA?
Always treat a TIA as seriously as you would a stroke. "Even though the symptoms resolve, there might be damage to the brain, so you need to see a neurologist," Dr. Rost advises.
Can you live a normal life after TIA?
In the emergency room, you learned you'd had a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also known as a mini-stroke. While symptoms went away within several hours, your concern that it could happen again did not. The good news is you absolutely can live a full life after a mini-stroke.
How long can you live after TIA?
Results—At 1 year, 91.5% of hospitalized patients with TIA survived compared with 95.0% expected survival in the general population. After 5 years, observed survival was 13.2% lower than expected in relative terms. By 9 years, observed survival was 20% lower than expected.
What medication is first line therapy for TIA?
Antiplatelet agents, rather than oral anticoagulants, are recommended as initial therapy. Aspirin 50–325 mg/day, a combination of aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole, and clopidogrel are all reasonable first-line options (class I recommendation).
What is the major complication associated with a TIA?
Complications of TIA – also referred to as “mini-strokes” – may include: Blood clots (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism) Difficulty swallowing. Urinary tract infections, or UTI.
How serious is a TIA?
A Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) is often called a mini-stroke, but it's really a major warning. TIA is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain. Because most TIA symptoms last from only a few minutes up to 24 hours, they are often dismissed and not taken seriously.
How to reduce the chance of stroke after TIA?
These include: eating a healthy, balanced diet – a low-fat, reduced-salt, high-fibre diet is usually recommended, including plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables.
How do anticoagulants help with TIA?
Anticoagulant medicines can help to prevent blood clots by changing the chemical composition of your blood in a way that stops clots from forming. They're usually offered to people who had a TIA that was caused by a blood clot in their heart.
What is the procedure to remove the lining of the carotid arteries?
A carotid endarterectomy involves removing part of the lining of the carotid arteries – the main blood vessels that supply the head and neck – plus any blockage inside the carotid arteries.
How long does it take for a transient ischaemic attack to resolve?
Although the symptoms of a transient ischaemic attack (TIA) resolve in a few minutes or hours without any specific treatment, you'll need treatment to help prevent another TIA or a full stroke from happening in the future.
How to reduce risk of stroke?
Plus, strength exercises on 2 days every week. stopping smoking – if you smoke, stopping may significantly reduce your risk of having a stroke in the future. cutting down on alcohol – men and women are advised to limit alcohol intake to 14 units per week.
Can a carotid endarterectomy reduce the risk of a stroke?
By unblocking the carotid arteries when they have become moderately or severely narrowed, a carotid endarterectomy can significantly reduce the risk of having a stroke or another TIA. Find out more about a carotid endarterectomy.
Can a stroke be fatal?
A stroke is a serious health condition that can cause permanent disability and can be fatal in some cases, but appropriate treatment after a TIA can help to reduce your risk of having a stroke. Your treatment will depend on your individual circumstances, such as your age and medical history.
What drugs can cause a TIA?
Drugs like amphetamines, cocaine, and heroin can raise your chances of a TIA or stroke. In addition to other lifestyle changes, if you're a woman, you should take a few more steps to avoid a TIA or stroke. For instance, if you're over age 75, ask your doctor to check you for atrial fibrillation.
How to avoid stroke?
Make sure to limit saturated fats and sugar and avoid trans fats. Get a good night's sleep. Regular shut-eye can lower your risk of a stroke. Create a routine to relax at night and get to bed at a reasonable time. Limit alcohol. If you drink, keep it to one drink a day if you're a woman or two if you're a man.
What is the procedure called to open the carotid artery?
Another choice is a procedure called carotid angioplasty and stenting. Your doctor makes a small opening in your groin. They'll use a balloon-like device to widen your carotid artery, then put in a small wire tube, called a stent, to keep it open. They then remove the balloon.
What to do if your neck is blocked?
Surgery. If one of the carotid arteries in your neck is narrowed or blocked, you may need surgery to help clear it out and restore normal blood flow. One option is an operation called carotid endarterectomy, where your doctor opens up the carotid artery, scrapes out the plaque, and closes it back up.
What is the name of the drug that helps blood clots?
Anticoagulants change those proteins to make it harder for them to form clots. If you only need an anticoagulant for the short term, you might get one called heparin . For longer-term use, you might get one of these drugs:
Why do you need regular tests after a stroke?
You'll need regular tests to make sure you get just the right dose to prevent a stroke and limit side effects. Medicines for other conditions. When your doctor runs tests after a TIA, you might learn that you have another health problem that raises your stroke risk.
Can TIA cause heartburn?
You might get problems like heartburn, bloating, or an upset stomach. Anticoagulants. After your TIA, if you have atrial fibrillation ( AFib) -- a problem with your heart 's rhythm -- it could be because the clot that triggered your TIA started in your heart.
Make an Appointment
Our team of dedicated access representatives is here to help you make an appointment with the specialists that you need.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a TIA depend on the size and location of the blockage. Symptoms may include:
Diagnosis
There is no single test that can diagnose a TIA. A doctor will take as much information as possible from the patient and his or her family, or anyone who witnessed the TIA. The doctor will perform a thorough physical and neurological exam, looking for weakness, numbness, lack of coordination or trouble speaking or understanding.
Risk Factors
Two types of arteries supply blood to the brain, and a blockage in either type can result in a TIA. A blockage in one of the cerebral arteries prevents blood from reaching the portion of the brain ordinarily sustained by that artery. A blockage in one of the carotid arteries causes blood flow problems for the entire brain–not just a single section.
Treatments
The goal of treatment is to prevent a stroke. The foundation of stroke prevention is usually a combination of medication and lifestyle changes.
How many days after TIA can you get a stroke?
The risk of stroke within 90 days of a TIA may be as high as 17%, with the greatest risk during the first week. 6. That’s why it’s important to treat the underlying causes of stroke, including heart disease, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation (fast, irregular heartbeat), high cholesterol, and diabetes.
What do you need to do after a stroke?
After a stroke, you may need rehabilitation ( rehab) to help you recover. Before you are discharged from the hospital, social workers can help you find care services and caregiver support to continue your long-term recovery.
What is the best medicine for a stroke?
If you get to the hospital within 3 hours of the first symptoms of an ischemic stroke, you may get a type of medicine called a thrombolytic (a “clot-busting” drug) to break up blood clots. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a thrombolytic. tPA improves the chances of recovering from a stroke.
What is the best way to get to the hospital for a stroke?
Stroke Treatment. Calling 9-1-1 at the first symptom of stroke can help you get to the hospital in time for lifesaving stroke care. Your stroke treatment begins the moment emergency medical services (EMS) arrives to take you to the hospital. Once at the hospital, you may receive emergency care, treatment to prevent another stroke, ...
Why do people go to the hospital for stroke?
Stroke patients who are taken to the hospital in an ambulance may get diagnosed and treated more quickly than people who do not arrive in an ambulance. 1 This is because emergency treatment starts on the way to the hospital. The emergency workers may take you to a specialized stroke center to ensure that you receive the quickest possible diagnosis ...
What type of doctor treats strokes?
Brain scans will show what type of stroke you had. You may also work with a neurologist who treats brain disorders, a neurosurgeon that performs surgery on the brain, or a specialist in another area of medicine.
Do not drive to the hospital for a stroke?
Do not drive to the hospital or let someone else drive you. The key to stroke treatment and recovery is getting to the hospital quickly. Yet 1 in 3 stroke patients never calls 9-1-1. 1 Calling an ambulance means that medical staff can begin life-saving treatment on the way to the emergency room.
What is the difference between a stroke and a TIA?
The big difference between a TIA and a stroke is that a TIA resolves quickly before any permanent brain damage or neurological symptoms can occur. This happens because a TIA is a temporary interruption of blood flow to a part of the brain and sometimes, the blood supply can be restored quickly. A stroke, in contrast to a TIA, is an interruption ...
How to prevent secondary strokes?
People who exercise or engage in physically active leisure activities have a lower risk of stroke, and exercise may also help prevent secondary strokes in those who have already had a stroke. 3 Always talk to your doctor before you begin a new exercise regimen. 4. Be Proactive. Many stroke sufferers have known friends or family who have had TIAs.
How long before stroke do you remember symptoms?
Quite often a stroke survivor may recall unusual fleeting neurological symptoms in the days, weeks or months prior to the stroke. Patients usually say, 'I thought it would go away,' or 'I just brushed it off because it got better,' or even, 'I didn't know what to make of it, so I didn’t want to ask for trouble.'.
Can a stroke be small?
A stroke can be large or small. In fact, a stroke can be small enough or insignificant enough that it isn't even noticed, resulting in a silent stroke . In the first few minutes, it is almost impossible to predict whether a neurological event will turn out to be a stroke or a TIA. But there are a few ways to modify the outcome.
Can you get a stroke at age 60?
If you have any risk factors for stroke, including age over 60, heart disease, high blood pressure, blood problems, high cholesterol, diabetes or smoking, you should become familiar with the ways that you can recognize a stroke or a TIA . There are, in fact, a few things that you can do to reduce the chances that a TIA will progress to a stroke.
Can you get TPA for a stroke?
Some of the most powerful stroke treatments, such as TPA, must be administered within a short window of time. 5 If you receive emergency treatment, your symptoms can resolve, and you have a much better chance of avoiding the permanent effects of a stroke. This can essentially make the outcome of what might have been a serious stroke substantially better.
Is a stroke a TIA?
A stroke, in contrast to a TIA, is an interruption of blood flow to a region of the brain that lasts long enough for brain tissue damage to occur. This type of damage leaves brain cells unable to function normally. A stroke can be large or small. In fact, a stroke can be small enough or insignificant enough that it isn't even noticed, ...
How to reduce TIA?
Stopping smoking reduces your risk of a TIA or a stroke. Limit cholesterol and fat. Cutting back on cholesterol and fat, especially saturated fat and trans fat, in your diet may reduce buildup of plaques in your arteries. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
How to prevent TIA?
Limit sodium. If you have high blood pressure, avoiding salty foods and not adding salt to food may reduce your blood pressure.
What is a transient ischemic attack?
A transient ischemic attack has the same origins as that of an ischemic stroke, the most common type of stroke. In an ischemic stroke, a clot blocks the blood supply to part of your brain. In a transient ischemic attack, unlike a stroke, the blockage is brief, and there is no permanent damage. The underlying cause of a TIA often is a buildup ...
How many people have a stroke after a transient ischemic attack?
About 1 in 3 people who has a transient ischemic attack will eventually have a stroke, with about half occurring within a year after the transient ischemic attack. A transient ischemic attack can serve as both a warning of a future stroke and an opportunity to prevent it.
What is a TIA?
Overview. A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary period of symptoms similar to those of a stroke. A TIA usually lasts only a few minutes and doesn't cause permanent damage. Often called a ministroke, a transient ischemic attack may be a warning. About 1 in 3 people who has a transient ischemic attack will eventually have a stroke, ...
How long do TIA symptoms last?
Symptoms. Transient ischemic attacks usually last a few minutes. Most signs and symptoms disappear within an hour, though rarely symptoms may last up to 24 hours. The signs and symptoms of a TIA resemble those found early in a stroke and may include sudden onset of:
What causes TIA in the brain?
The underlying cause of a TIA often is a buildup of cholesterol-containing fatty deposits called plaques (atherosclerosis) in an artery or one of its branches that supplies oxygen and nutrients to your brain. Plaques can decrease the blood flow through an artery or lead to the development of a clot.
What Causes a Mini Stroke?
TIAs, or mini strokes, are caused by a loss of blood flow to certain areas of the brain. That accounts for the stroke-like symptoms characteristic of an attack, including weakness or numbness on one side of the body, trouble with speech or coordination, loss of vision or blurred vision and confusion. But those symptoms can have several causes.
Treatment Options for Mini Strokes
A mini stroke is an event, not a condition, so treatment for mini strokes typically focuses on preventing another event from happening. That can include making lifestyle changes, taking medications to manage contributing health conditions or surgery to clear blockages and enhance blood flow to the brain.
Lifestyle Management Reduces Risks
For many people, heart and artery disease are causes of a TIA. Lifestyle factors play a major role in the development of these diseases, so making healthy changes is the first step toward reducing the risk of future events.
Medication: The Next Step
In some instances, lifestyle modifications may be the only thing needed to prevent future mini strokes or strokes. But for some people, medication may also be necessary to support these healthy changes and reduce risk factors.
Surgery: A Third Option
When lifestyle and medication, or a combination of the two, aren’t enough to reduce the risk factors for TIA and stroke, surgery may be needed to restore healthy blood flow to the brain.
How long does it take for a stroke to happen after a TIA?
In one study, about 12 % of people who suffer a TIA die within one year . The risk of having a full-blown stroke is highest in the 90 days following a TIA. About 9 % to 17 % of patients who have a TIA have a stroke within 90 days. If you’re worried that you’re having a TIA, get medical help right away.
What causes a TIA?
TIAs are caused by a clot or blockage in the brain. The blockage is short term. The clot usually dissolves on its own or gets dislodged, and symptoms usually last for a short time. The statistics tell part of the story: A TIA happens before about 12 % of all strokes.
Can TIA be seen in hospital?
Some causes are only visible with hospital equipment. When a TIA occurs in a young person with no clear risk factors, the patient might be sent to a neurologist for testing to rule out vasculitis, carotid artery dissection and other types of injury or infection.
Can you call 911 if you have a TIA?
But it is not safe to assume you don’t need urgent medical care. In fact, you should call 911 right away. The warning signs for a TIA are the same as a stroke and sudden onset of the following: Weakness, numbness or paralysis on one side of your body.
Can you have a stroke with a TIA?
Anyone can have a TIA, but the risk increases with age. If you’ve previously had a stroke, pay careful attention to the signs of TIA, because they could signal a second stroke in your future. The risk factors are smoking, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and blood clots called embolisms.