- Immobilization of the joint. The joint will typically be immobilized in a cast or boot for 2-4 weeks to give the area time to heal. ...
- Manipulation. In some cases, the doctor can manipulate the joint using his or her hands to place the bones back into their correct position. ...
- Surgery. For severe growth plate fractures, a surgical correction (open reduction) may be required. ...
How do you treat a growth plate injury at the ankle?
Treatment for Growth Plate Injury at Ankle Depends on Location of the Break. A walking boot may be an option in this situation. But, depending on how significant the break is, a child could need a short leg cast (from toes to just below the knee) and may not be able to put weight on the leg for several weeks.
What are the treatment options for growth plate fractures?
Treatment for growth plate fractures depends on the severity of the fracture. The least serious fractures usually require only a cast or a splint. If the fracture crosses the growth plate or goes into the joint and is not well-aligned, surgery may be necessary.
What is a growth plate fracture of the ankle?
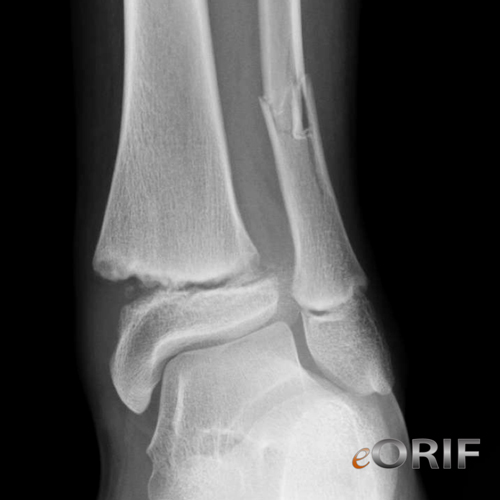
Ankle growth plate injuries most commonly either occur at the end of the fibula or tibia, two of the three bones that compose the ankle joint. Growth plate fractures in the ankle that occur at the end of the fibula, commonly associated with a typical ankle sprain, may not present on an X-ray.
What is the average recovery time for an ankle growth plate fracture?
Ankle growth plate injuries most commonly either occur at the end of the fibula or tibia, two of the three bones that compose the ankle joint. Growth plate fractures in the ankle that occur at the end of the fibula, commonly associated with a typical ankle sprain, may not present on an X-ray. These often require about four to six weeks of recovery.
What is the treatment for a fractured growth plate?
Growth Plate Fracture Treatment Growth plate fractures are generally treated with splints or casts. Sometimes, the bone may need to be put back in place to allow it to heal in the correct position. This may be done before or after the cast is placed and is called a closed reduction.
How long does a fracture in the growth plate take to heal?
Your child will have to wear a cast until the bones heal. This can take from a few weeks to 2 months or more.
Do you need surgery for a fractured growth plate?
Although most growth plate injuries respond to immobilizing the affected area for a few weeks, surgery may be needed if the injury is more severe or has the potential to affect a child's or teen's growth and development.
Can you walk on a fractured growth plate in ankle?
But, depending on how significant the break is, a child could need a short leg cast (from toes to just below the knee) and may not be able to put weight on the leg for several weeks. The risk for long-term problems related to a growth plate injury of the fibula is typically low.
How serious is a growth plate fracture?
Growth plate fractures often need immediate treatment because they can affect how the bone will grow. An improperly treated growth plate fracture could result in a fractured bone ending up more crooked or shorter than its opposite limb. With proper treatment, most growth plate fractures heal without complications.
Do growth plate fractures show up on xray?
Because growth plates haven't hardened into solid bone, they are difficult to interpret on X-rays. Doctors may ask for X-rays of both the injured limb and the opposite limb so that they can be compared. Sometimes a growth plate fracture cannot be seen on X-ray.
How long does growth plate surgery?
Typically, the child/adolescent is placed under general anesthesia for about an hour for this minimally invasive surgery. A 1-inch (2.5-cm) incision is made and the growth plate is fused.
What age do growth plates close?
Growth plates usually close near the end of puberty. For girls, this usually is when they're 13–15; for boys, it's when they're 15–17.
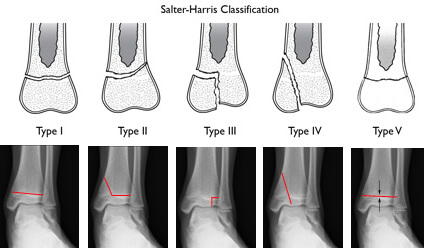
What are the five types of growth plate fractures?
Types of growth plate fracturesTransverse fractures through the growth plate (Salter 1)Fractures through the metaphysis and growth plate (Salter 2)Fractures through the epiphysis and growth plate (Salter 3)Fractures through the epiphysis, metaphysis and growth plate (Salter 4)More items...
Can a growth plate be mistaken for a fracture?
The symptoms of a growth plate injury may be similar to those of a sprain, a pulled muscle, or a broken bone, and so doctors usually recommend an X-ray to get a better sense of the cause of your child's symptoms.
What happens if you break the growth plate in your foot?
Most growth plate fractures heal and do not affect future bone growth. However, sometimes changes in the growth plate from the fracture can cause problems later. For example, the bone could end up a little crooked or slightly longer or shorter than expected.
Can growth plates be reopened?
No. Such thing is absolutely not possible. There is a surgery based on distraction osteogenesis that increases the lenght of long bones (aka leg lenghtening surgery).
What is the treatment for a growth plate fracture?
Treatment for growth plate fractures depends on the severity of the fracture. The least serious fractures usually require only a cast or a splint. If the fracture crosses the growth plate or goes into the joint and is not well-aligned, surgery may be necessary. Growth plates that are surgically realigned may have a better chance ...
Why are growth plates difficult to interpret?
Because growth plates haven't hardened into solid bone, they are difficult to interpret on X-rays. Doctors may ask for X-rays of both the injured limb and the opposite limb so that they can be compared.
How long after a fracture can you check X-rays?
Your doctor may recommend checking X-rays for several years after the fracture to make sure the growth plate is growing appropriately. Depending on the location and severity of the fracture, your child may need follow-up visits until his or her bones have finished growing.
Can a growth plate fracture be seen on an X-ray?
Sometimes a growth plate fracture cannot be seen on X-ray. If the child is tender over the area of the growth plate, your doctor may recommend a cast or a splint to protect the limb. X-rays are taken again in three to four weeks and, if there was a fracture, new bone healing will typically be seen at that time.
How long does it take for a growth plate fracture to heal?
Although everyone is different, the healing process for a growth plate fracture typically takes several weeks. The doctor may also request a year of follow-up appointments to monitor the child and make sure the bones are continuing to heal and grow normally. X-rays are usually taken at the follow-up appointments.
What causes a growth plate to fracture?
The main causes of growth plate fractures are falls, accidents, or other types of trauma to the body. Repetitive or constant use of a joint—for instance, when a child is overworking the limb or joint when practicing sports such as pitching or gymnastics—can also cause growth plate fractures. Other issues may cause a fracture ...
What happens if a growth plate is crushed?
If the growth plate is crushed, or severely injured, it may close and harden too early , before growth has been completed. If this happens, the patient is left with a hardened section of bone over the fracture line that may need to be repaired with surgery.
What are the different types of growth plate fractures?
Growth plate fractures are usually categorized according to the Salter-Harris classification: 1 Type I fracture: The bottom portion of the growth plate separates completely from the end of the bone. The bone remains in position. 2 Type II fracture: This is a break that affects the growth plate and also part of the bone. It is the type most often seen in children. 3 Type III fracture: This fracture is rare, and usually happens in older children. It occurs when the fracture goes through the growth plate and breaks off an end piece of the bone. This type of fracture often occurs in the lower leg. 4 Type IV fracture: This affects the growth plate, the end of the bone, and a portion of the bone shaft. These fractures are most common in the upper arm bone near the elbow. 5 Type V fracture: This fracture occurs when the growth plate is squeezed together and the end of the bone is crushed. This type of fracture is rare, and most often affects the bones of the ankle or knee.
Why do growth plates need to be treated?
A growth plate fracture must be treated quickly because it may interfere with proper bone growth. Treatment varies depending on how badly the growth plate and attached bone are fractured. This is how the various types of growth plate fractures are treated:
What is the difference between a type 1 and type 2 fracture?
Type I fracture: The bottom portion of the growth plate separates completely from the end of the bone. The bone remains in position. Type II fracture: This is a break that affects the growth plate and also part of the bone. It is the type most often seen in children.
How many growth plates are there in a child?
There are two growth plates, one at each end of each long bone in the body. The growth plates determine the shape and length of the child’s bone as he or she grows. Once a child has stopped growing, the growth plates will harden into solid bone.
What age do you have to be to get ankle growth plate?
For children whose bones have yet to reach skeletal maturity, around age 14 to 15 for girls and 16 to 17 for boys, injury to the ankle growth plate or a fractured growth plate in the ankle is a common occurrence. If left untreated, this can result in poor healing and negative long-term effects.
How long does it take to recover from a growth plate fracture?
These often require about four to six weeks of recovery.
How to tell if ankle is sprained?
Because ankle growth plates can be difficult interpret on an X-ray, the difference between a simple ankle sprain and a fractured ankle growth plate can be challenging to diagnose. Often an pediatric orthopedic specialist may need to assist with diagnosis. Common symptoms include: 1 Pain, swelling and tenderness 2 Bruising and misshaped appearance 3 Inability to bear weight 4 Tears or open skin wound
Can ankle sprains be left untreated?
When approaching adulthood, the cartilage that composes ankle growth plate fuses. Therefore, for older teenagers and adults, an injury to the ankle may mean only an ankle sprain.
Can a growth plate injury affect a child's ankle?
While all ankle growth plate injuries will require your child to limit the amount of weight he or she bears on the injured ankle, the severity and location of the injury can dictate the length of treatment.
Can an ankle growth plate be interpreted on an X-ray?
Because ankle growth plates can be difficult interpret on an X-ray, the difference between a simple ankle sprain and a fractured ankle growth plate can be challenging to diagnose. Often an pediatric orthopedic specialist may need to assist with diagnosis. Common symptoms include:
Why do growth plate fractures need immediate treatment?
Growth plate fractures often need immediate treatment because they can affect how the bone will grow. An improperly treated growth plate fracture could result in a fractured bone ending up more crooked or shorter than its opposite limb. With proper treatment, most growth plate fractures heal without complications.
What is a growth plate fracture?
A growth plate fracture affects the layer of growing tissue near the ends of a child's bones. Growth plates are the softest and weakest sections of the skeleton — sometimes even weaker than surrounding ligaments and tendons. An injury that might cause a joint sprain for an adult can cause a growth plate fracture in a child.
What to do if your child has a fracture?
If you suspect a fracture, take your child to be examined by a doctor. Also have your child evaluated if you notice a visible deformity in your child's arms or legs, or if your child is having trouble playing sports because of persistent pain.
What is the pain of a growth plate?
Pain and tenderness, particularly in response to pressure on the growth plate. Inability to move the affected area or to put weight or pressure on the limb. Warmth and swelling at the end of a bone, near a joint.
What factors increase the risk of crooked, accelerated or stunted bone growth?
But the following factors can increase the risk of crooked, accelerated or stunted bone growth. Severity of the injury. If the growth plate has been shifted, shattered or crushed, the risk of limb deformity is greater. Age of the child.
What is the best treatment for a growth plate fracture?
Casting and splinting are common ways to treat growth plate fractures, but surgery may also be required in certain cases.
How to treat growth plate closure?
Treatment options include: Surgically shutting down the growth plate on the opposite side. Surgical lengthening of the injured bone. Shortening of the normal bone.
What is the name of the area of the bone that is damaged by a growth plate?
Areas of the bone immediately above and below the growth plate may fracture. They are called the epiphysis (the tip of the bone) and metaphysis (the “neck” of the bone). The most common growth plate fracture runs through the metaphysis. For example, a tibial metaphyseal fracture is a growth plate fracture in the biggest of the leg bones below the knee.
Why do long bones have one growth plate?
Most long bones have one growth plate at each end. When a child is done growing because his or her growth plates have closed and are no longer creating new bone. Growth plates are vulnerable and may fracture — a similar injury would lead to a sprain in an adult.
Why does my child's growth plate break?
A child continues to grow while the plates are “open.”. A growth plate may fracture (break) due to a fall or another cause. A physical exam and X-rays are most often used to diagnose a growth plate fracture. Fractures of the growth plate can interrupt normal growth if not treated properly.
What are some examples of growth plate fractures?
An example is growth plate fractures that may occur in Little League pitchers because of excessive throwing. Your child should be treated at your local emergency room or urgent care clinic immediately after the injury. The medical staff will be able to tell you whether surgery is needed.
Can a fractured bone be put back in place?
Sometimes , the bone may need to be put back in place to allow it to heal in the correct position. This may be done before or after the cast is placed and is called a closed reduction. The length of time your child needs to be in a cast or splint depends on the location and severity of the fracture.
What to do if your child has a fractured bone?
If the fracture isn't severe and the broken parts of the bone still line up right, your child's doctor might just put on a cast, splint, or brace. Your child won't be able to move their limb that way, which gives the growth plate time and space to heal. Immobilizing the fracture will also help control pain.
How long does it take for a fractured bone to heal?
This can take from a few weeks to 2 months or more . If a ridge forms at the fracture line, your child's doctor may recommend surgery to remove the ridge. They can then pad the area with fat or another material to keep it from growing back.
What to do after a child's injury?
After the injury has healed, your child's doctor may suggest exercises to strengthen the injured area and make sure their limb moves like it's supposed to. Some children need another operation, such as reconstructive surgery, if the injury is serious enough.
What is it called when a child's leg stops growing?
One problem is something your child's doctor may call "growth arrest." This is when the injury causes their bone to stop growing. They could end up with one leg or arm shorter than the other.
Where are growth plates found?
Growth plates are areas of soft tissue at the ends of your child's long bones. They are found in many places, including the thigh, forearm, and hand. As the name suggests, growth plates help your child's bones grow. Adults don't have them -- only young kids or teens do.
Do younger bones heal better?
But one benefit is that younger bones tend to heal better. Treatment. To come up with a treatment plan, the doctor will take into account your child's age, general health, and if there are any related injuries.
Can you reduce bone density without surgery?
This is called a "reduction" and can be done either with or without surgery. If it's done without surgery, the doctor usually just moves the bones back in line with their hands without cutting into the skin. This is called "manipulation" and can be done in the emergency room or an operating room.
