How to treat hemangioma?
Stereotactically-assisted craniotomy, a surgical procedure in which a small hole is drilled into the skull and instruments are guided to the hemangioma using three-dimensional CT or MRI scans.
What is the cavernous sinus?
Cavernous hemangioma symptoms & treatment. The cavernous sinus is a hollow area that lies behind your eyes. A cavernous hemangioma happens when capillaries – small blood vessels that connect arteries and veins – swell and form a noncancerous mass called an angioma. These masses often occur in multiples in your brain, ...
Can hemangioma cause permanent blindness?
Treatment options for a cavernous hemangioma. Untreated angiomas can create serious problems, including permanent blindness. Treatment options depend on the location of the tumor, as well as whether it’s bleeding or causing seizures.
How to treat brain cavernous hemangioma?
In the treatment of a brain cavernous hemangioma, neurosurgery is usually the treatment chosen . Research needs to be conducted on the efficacy of treatment with stereotactic radiation therapy, especially on the long-term. However, radiotherapy is still being studied as a form of treatment if neurosurgery is too dangerous due to the location of the cavernoma. Genetic researchers are still working on determining the cause of the illness and the mechanism behind blood vessel formation. Clinical trials are being conducted to better assess when it is appropriate to treat a patient with this malformation and with what treatment method. Additionally, long-term studies are being conducted because there is no information related to the long-term outlook of patients with cavernoma. An existing registry known as The International Cavernous Angioma Patient Registry collects information from patients diagnosed with cavernoma in order to facilitate discovery of non-invasive treatments.
When do cavernous hemangiomas occur?
Cavernous hemangiomas of the brain and spinal cord (cerebral cavernous hemangiomas (malformations) (CCM)), can appear at all ages but usually occur in the third to fourth decade of a person's life with no sexual preference. In fact, CCM is present in 0.5% of the population.
What are the causes of cerebral cavernous malformations?
Genetic studies show that specific gene mutations or deletions are causes for the disease. The genes identified for cerebral cavernous hemangiomas (or malformations), are CCM1 (also KRIT1), CCM2 (also MGC4607, malcavernin) and CCM3 (also PDCD10). The loss of function of these genes is believed to be responsible for cerebral cavernous malformations. Furthermore, it is also believed that a "second hit mutation" is necessary for the onset of the disease. This means that having a mutation in one of the two genes present on a chromosome is not enough to cause the cavernous malformation, but mutation of both alleles would cause the malformation. Additionally, research on hemangiomas in general has shown that loss of heterozygosity is common in tissue where hemangioma develops. This would confirm that more than a single allele mutation is needed for the abnormal cell proliferation. KRIT1 has been shown to act as a transcription factor in the development of arterial blood vessels in mice. CCM2 has overlapping structure with CCM1 (KRIT1) and acts as a scaffolding protein when expressed. Both genes are involved with MAP3K3 and thus appear to be a part of the same pathway.
Why are capillary hemangiomas called raspberries?
They are sometimes described as resembling raspberries because of the appearance of bubble-like caverns. Unlike capillary hemangiomas, cavernous ones can be life-threatening and do not tend to regress.
What is a cavernous liver hemangioma?
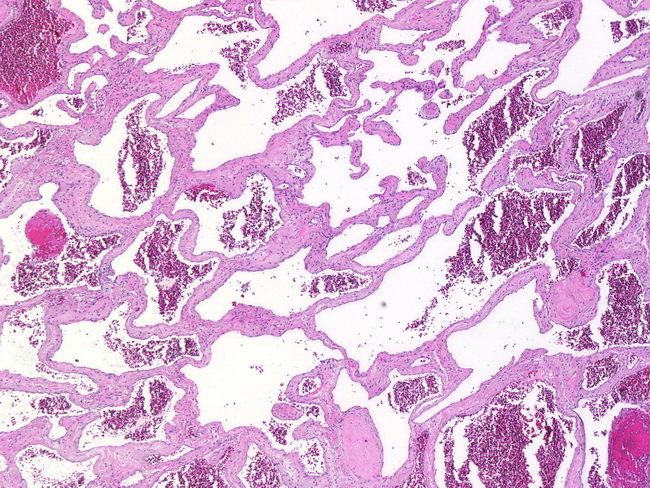
H&E stain. Cavernous hemangioma, also called cavernous angioma, cavernoma, or cerebral cavernoma ( CCM) (when referring to presence in the brain) is a type of benign vascular tumor or hemangioma, where a collection of dilated blood vessels form a lesion.
What is the most common radiographic appearance of a cavernous hemangioma?
The radiographic appearance is most commonly described as "popcorn" or "mulberry"-shaped.
How big is a hemangioma tumor?
Their sizes can range from a few millimeters to 20 centimetres. Those over 5 cm are often referred to as giant hemangiomas. Ultrasound of hemangioma in the liver.
How many hemangiomas are present at birth?
About one third of hemangiomas are present at the time of birth. The other two thirds arise in the initial months life.
What is cavernous malformation?
Cavernous hemangioma or cavernous malformations are an abnormal build up of blood vessels within internal organs or the skin. These malformations arise from very small vessels that separate the arterial system from the venous system. Cavernous hemangiomas are well-defined and clearly visible lesions that can reach a significant size. These malformations account for about 8% to 15% of all the intracranial and spinal vascular malformations. They can cause hemorrhage; and, sometimes can be life threatening if they arise in a critical area of an internal organ.
What type of scan is used for deep lesions?
In case of deep or complicated lesions, computerized tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans might be used.
Can a doctor treat a malformation?
No Surgery: If the lesion is in a difficult area or small in size, a doctor may choose to leave the malformation alone. The same is true if the risk/benefit ratio does not favor treatment. In most cases, a doctor will then keep observing the malformation with a series of periodic CT or MRI scans.
Can a cavernous hemangioma be removed?
Surgical Removal: If a cavernous hemangioma is large and easily accessible, a doctor may choose to remove it surgically. Once a cavernous hemangioma is removed, the lesion is cured completely. Difficulties arise when there are multiple hemangiomas or if they occur deep inside an internal organ. Cavernous hemangiomas present significant difficulties for surgeons when they are within the brain.
What is a cavernous hemangioma?
A cavernous hemangioma is a collection of abnormal, dilated blood vessels in the brain. A cavernous hemangioma may also be known as a cavernoma, a ‘cav-mal’, a cavernous angioma, or a cerebral cavernous malformation. All these terms are equivalent, meaning they describe the exact same thing.
What treatments are available?
There are several treatment options available to help manage cavernomas. Some possible treatments for cavernoma include observation, surgery, radiosurgery, or laser ablation. Regardless of the treatment strategy proposed by your neurosurgeon, the key things they will consider are the risk of any proposed intervention versus the risk of harm from the CCM itself.
Do Cavernomas always need to be treated?
The short answer to this question is no, every CCM does not always need an intervention to treat it.
Can a Cavernoma kill you?
Unfortunately, the answer to this question is yes, a CCM can kill you.
What are the symptoms of CCM?
Patients with CCM may not have any symptoms just from the presence of the CCM. Instead, the most common cause of symptoms in patients with CCM is due to the leaking of blood or hemorrhage into the surrounding brain tissue. Depending on the location of the CCM as well as the severity of the hemorrhage, possible symptoms include: 1 New seizures 2 Headache 3 Nausea or vomiting 4 Sudden altered mental status or increased fatigue 5 New numbness / weakness/ tingling 6 Difficulty with understanding or producing speech
Who can discuss CCM?
The exact risks posed by a CCM are best discussed by a neurosurgeon or neurologist who has reviewed your specific medical history as well as imaging studies and can offer personalized medical advice to you regarding the risks associated with hemorrhage of your CCM.
Is there a risk of cavernous hemangioma causing a stroke?
Yes, there is a risk of CCMs causing a stroke. Stroke is the medical word for damage to the brain from changes in blood flow and there are two main types of stroke: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. Ischemic stroke is the most common form of stroke and results from a blocked artery which causes a lack of blood flow to an area of the brain.
What is the treatment for orbital hemangioma?
Treatment of orbital hemangioma is indicated when there is evidence of growth, optic nerve compression, and corneal exposure (with secondary keratitis sicca), or evidence of vision loss. The goal of orbitotomy for choroidal hemangioma should be complete removal of the tumor. This usually involves careful dissection of the tumor to protect ...
Where is hemangioma found in the orbit?
Cavernous hemangioma of the orbit is most commonly seen in middle-aged women. Most are found within the muscle cone, but can be found anywhere in the orbit.
Is cavernous hemangioma slow growing?
Cavernous hemangioma of the orbit is usually a slow-growing tumor. If the tumor has not damaged the eye, cavernous hemangioma can be observed for growth prior to considering intervention. Should tumor growth occur, it will be measured by eye examinations including (but not limited to) visual acuity, color vision assessment, ...

Overview
Treatment
Asymptomatic lesions may not require treatment but may need to be monitored for any change in the size. A change in size of lesions in the nose, lips, or eyelids can be treated with steroid drugs to slow its progress. Steroids can be taken orally or injected directly into the tumor. Applying pressure to the tumor can also be used to minimize swelling at the site of the hemangioma. A procedure that uses small particles to close off the blood supply is known as sclerotherapy. Thi…
Symptoms
People with this condition in the brain may or may not experience symptoms. Some complications of the condition are life-threatening or cause major disruptions to normal functioning. Dangerous seizures due to compression of the brain, bleeding inside the brain tissue, vision problems, difficulty with speaking or using words, memory loss, ataxia, or hydrocephalus can occur. Less serious symptoms may include headaches and weakness or numbness in the arms …
Presentation
Cavernous hemangiomas can arise nearly anywhere in the body where there are blood vessels. They are sometimes described as resembling raspberries because of the appearance of bubble-like caverns. Unlike capillary hemangiomas, cavernous ones can be life-threatening and do not regress.
Most cases of cavernomas are thought to be congenital; however they can develop over the cour…
Variations
Cavernous hemangiomas located in the brain or spinal cord are referred to as cerebral cavernomas or more usually as cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), and can be found in the white matter, but often abut the cerebral cortex. When they contact the cortex, they can represent a potential seizure focus for the patient. Unlike other cavernous hemangiomas, there is no tissue within th…
Mechanism
There are several known causes for cavernous hemangiomas, but some cases are still unknown. Radiation treatment used for other medical conditions has been suggested to cause cavernous malformation in some patients. Hemangioma tumors are a result of rapid proliferation of endothelial cells and pericytic hyperplasia, or the enlargement of tissue as a result of abnormal cell …
Diagnosis
Gradient-Echo T2WI magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is most sensitive method for diagnosing cavernous hemangiomas. MRI is such a powerful tool for diagnosis, it has led to an increase in diagnosis of cavernous hemangiomas since the technology's advent in the 1980s. The radiographic appearance is most commonly described as "popcorn" or "mulberry"-shaped. Computed tomo…
Epidemiology
The true incidence of cavernous hemangiomas is difficult to estimate because they are frequently misdiagnosed as other venous malformations. Cavernous hemangiomas of the brain and spinal cord (cerebral cavernous hemangiomas (malformations) (CCM)), can appear at all ages but usually occur in the third to fourth decade of a person's life with no sexual preference. In fact, CCM is present in 0.5% of the population. However, approximately 40% of those with malformati…