
Surgery is the last option for calcified abdominal aorta treatment and is generally used for more severe cases of calcification. The first surgical method involves inserting a catheter into the narrow part of the abdominal aorta, and then a balloon is inflated.
Can You reverse calcification of the arteries?
aortic calcification treatment A 60-year-old member asked: i was told i have aorta calcification (not sure is it abdomen or?) what is the risk and treatment if available
How serious is calcification of the aorta?
Dec 31, 2010 · Calcified abdominal aorta treatment mainly consists of lowering your cholesterol. As we explained earlier, calcification of the aorta is almost always associated with atherosclerosis, thus lowering one’s cholesterol is key. There are three main ways of lowering your cholesterol: making lifestyle changes, taking medication or undergoing surgery.
How long does someone with aortic stenosis live?
Feb 19, 2021 · Aortic valve sclerosis — thickening and stiffness of the valve and mild aortic calcification — usually doesn't cause significant heart problems, but requires regular checkups to make sure your condition isn't worsening. If the valve becomes severely narrowed (stenotic), aortic valve replacement surgery may be necessary.
What are the symptoms associated with abdominal aorta calcification?
Apr 11, 2022 · 2 abdominal aortic calcification patients report no pain (12%) What people are taking for it. Ibuprofen Ketorolac. Common symptom. Fatigue. How bad it is. 5 abdominal aortic calcification patients report severe fatigue (33%) 6 abdominal aortic calcification patients report moderate fatigue (40%)

How serious is calcification of the aorta?
Aortic valve calcification is a condition in which calcium deposits form on the aortic valve in the heart. These deposits can cause narrowing at the opening of the aortic valve. This narrowing can become severe enough to reduce blood flow through the aortic valve — a condition called aortic valve stenosis.
How do you get rid of calcification in the aorta?
At present there is no specific treatment for arterial calcification; medications such as statins, vasodilators and other therapy for atherosclerosis and calcific aortic stenosis have negligible effect, although they are beneficial in lowering low density lipoprotein (LDL), a key risk factor for CAD, preventing against ...Apr 21, 2015
How long can you live with aortic calcification?
And, treatment is absolutely necessary. “Aortic stenosis is a deadly disease,” Dr. Hatch said. “Once patients with severe aortic stenosis develop symptoms related to their valve disease, these patients have a survival rate as low as 50% at 2 years and 20% at 5 years without aortic valve replacement.”May 3, 2019
What causes the aorta to calcify?
Calcium is a mineral found in your blood. As blood repeatedly flows over the aortic valve, calcium deposits can build up on the heart valves (aortic valve calcification).Feb 26, 2021
Can you Stent a calcified artery?
Heavily calcified coronary arteries are the bane of an interventionalist's existence, and can make stent deployment technically difficult to nearly impossible.
Can a calcified aorta be reversed?
Aortic calcification: is it a treatable disease? Arterial calcifications have long been thought to be an irreversible endpoint of atherosclerotic disease. However, increasing evidence suggests that it is an actively regulated process that can be halted or even reversed.Apr 28, 2020
What is the life expectancy of someone with aortic stenosis?
Severe symptomatic aortic stenosis is associated with a poor prognosis, with most patients dying 2–3 years after diagnosis.
How common is aortic calcification?
Aortic arch calcification was present in 1.9% of men and in 2.6% of women. Its prevalence increased with age in both sexes (Figure 1). The sex difference was particularly apparent in participants who were 65 years and older; 10.6% of men and 15.9% of women in this age range had aortic arch calcification.
What foods to avoid if you have aortic stenosis?
Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables, low-fat or fat-free dairy products, poultry, fish, and whole grains. Avoid saturated and trans fat, and excess salt and sugar.Feb 26, 2021
What removes calcification?
You can remove mineral deposits with these acidic household items and cleaners:Lemon juice.White vinegar.CLR cleaner.Phosphoric acid cleaners.Sulfuric acid.Muriatic acid (very strong- use only for tough deposits) Mix 1 part muriatic acid with 5 parts water.Jul 11, 2016
Is aortic calcification normal?
This narrowing can become severe enough to reduce blood flow through the aortic valve — a condition called aortic valve stenosis. Aortic valve calcification may be an early sign that you have heart disease, even if you don't have any other heart disease symptoms.Feb 27, 2019
How to treat calcification of the aorta?
The first step is to begin eating a healthy diet. Increase your intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat proteins such as meat.
How to get rid of a swollen thigh?
Stay away from foods high in saturated fats and trans fat as well as red meat. Rather than deep-frying foods, poach, grill, or bake your food. The next step is to include exercise as part your daily routine.
Does exercise have to be done in a gym?
Exercise does not have to take place exclusively within the confines of a gym, try walking around the neighborhood, mowing your lawn, or dancing to your favorite tunes. Other important lifestyle changes include, stopping smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing diabetes if applicable.
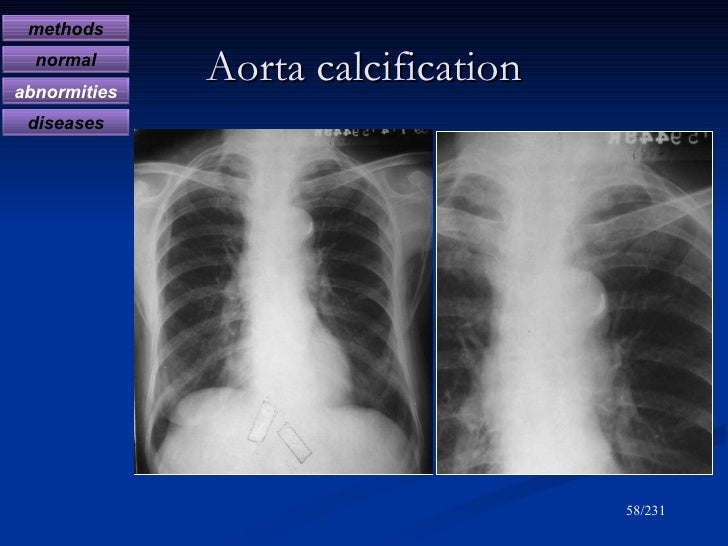
What is abdominal aortic calcification?
Abdominal aortic calcification occurs when calcium crystals are deposited in the abdominal aorta. This can cause the aorta to narrow and restrict blood flow.
Common symptoms reported by people with abdominal aortic calcification
Reports may be affected by other conditions and/or medication side effects. We ask about general symptoms (anxious mood, depressed mood, fatigue, pain, and stress) regardless of condition.
Treatments taken by people for abdominal aortic calcification
Let’s build this page together! When you share what it’s like to have abdominal aortic calcification through your profile, those stories and data appear here too.
Compare treatments taken by people with abdominal aortic calcification
Let’s build this page together! When you share what it’s like to have abdominal aortic calcification through your profile, those stories and data appear here too.
Lifestyle
Changes to your lifestyle can help prevent and slow the progression of coronary calcification. These can include dieting (especially to limit cholesterol, fat, and sodium), exercising, quitting smoking, avoiding alcohol and losing weight.
Medications
If you’re at risk of coronary calcification your doctor may prescribe cholesterol medications to reduce low density lipoproteins (LDL) known as the "bad" cholesterol (eg, statins) or to increase high density lipoproteins (HDL) known as the "good" cholesterol (eg, niacin).
Procedures & Surgery
For severe atherosclerosis that has caused—or threatens to cause—symptoms or disease, further intervention may be necessary. This can include:
Why is it important to change your diet?
Dietary Changes- It is important to bring about certain changes in the daily intake of food. A balanced diet involving fruits and vegetables reduces the risk of aortic calcification. Fruits and vegetables clean up the patient’s bodily systems thereby reducing the deposition of plague in the blood vessels.
What causes aortic calcification?
Calcification of aorta occurs when the aortic valve gets blocked due to calcium deposition. This condition can be quite as gradual deposition narrows down the opening of the valve in the heart, which may limit the proper flow of blood through the valve of the aorta.
What is an echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram can show your doctor how blood flows through your heart and heart valves. It can help identify a weakened heart muscle and determine the severity of aortic valve stenosis. If your doctor needs a closer look at your aortic valve, a transesophageal echocardiogram may be done. In this test, a flexible tube containing ...
How to diagnose aortic valve stenosis?
To diagnose aortic valve stenosis, your doctor will review your signs and symptoms, discuss your medical history, and do a physical examination. He or she will listen to your heart with a stethoscope to determine if you have a heart murmur that may signal an aortic valve condition.
Do biological valves need to be replaced?
Biological tissue valves break down over time and may eventually need to be replaced. People with mechanical valves will need to take blood-thinning medications for life to prevent blood clots. Your doctor will discuss with you the benefits and risks of each type of valve. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
What can an EKG show?
An EKG can detect enlarged chambers of your heart, heart disease and abnormal heart rhythms. Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray can help your doctor determine whether your heart is enlarged, which can occur in aortic valve stenosis. It can also show swelling of the aorta and calcium buildup on your aortic valve.
How does a balloon catheter work?
In this procedure, a doctor inserts a long, thin tube (catheter) with a balloon on the tip into an artery in your arm or groin and guides it to the aortic valve. Once in place, the balloon is inflated, which widens the valve opening . The balloon is then deflated, and the catheter and balloon are removed.
What is a cardiac CT scan?
Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan. A cardiac CT scan combines several X-ray images to provide a more detailed cross-sectional view of the heart. Doctors may use cardiac CT to measure the size of your aorta and look at your aortic valve more closely. Cardiac MRI.
What is a TAVR?
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is a minimally invasive procedure to replace a narrowed aortic valve that fails to open properly (aortic valve stenosis). In this procedure, doctors insert a catheter in your leg or chest and guide it to your heart.
Is calcification dangerous?
It’s dangerous, and if not treated properly, can increase your risk of heart disease and other life-threatening medical dilemmas. Luckily, there are ways to treat a calcification naturally and lower your risk of developing any further heart conditions.
How to keep arteries clean?
Right next to regular exercise, a healthy diet is vital in regulating heart health. Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables, five to nine servings per day, will help you keep your arteries clean and prevent a calcium backlog.
Lifestyle Changes
- Changes to your lifestyle can help prevent and slow the progression of coronary calcification. These can include: 1. Dieting (especially to limit cholesterol, fat and sodium) 2. Exercising 3. Quitting smoking 4. Avoiding alcohol 5. Losing weight
Medications
- If you’re at risk of coronary calcification, your doctor may prescribe cholesterol medications to reduce low density lipoproteins (LDL) known as the "bad" cholesterol (eg, statins) or to increase high density lipoproteins (HDL) known as the "good" cholesterol (eg, niacin). Newer medications such as PCSK 9 inhibitors (eg, Repatha, Praluent) are given by injection and can help lower chole…
Procedures and Surgery
- For severe atherosclerosis (plaque)that has caused — or threatens to cause — symptoms or disease, further intervention may be necessary. This can include: 1. Coronary stenting is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a catheter (a thin, flexible tube) that is guided into the blocked artery and a tiny balloon is inflated to pry open the plaque and restore blood flow. A sten…
Ready For An appointment?
- If you need to be evaluated for coronary calcification or want to discuss treatment options, schedule an appointmentor call 800-TEMPLE-MED (800-836-7536) today. Learn more about our doctors and care team who diagnoseand treat coronary calcification.