
A stepwise (step-up if necessary and step-down when possible) approach to asthma management continues to be used in the current guidelines and is now divided into 3 groups based on age (0-4 y, 5-11 y, 12 y and older). For all patients, quick-relief medications include rapid-acting beta2 agonists as needed for symptoms.
What are the steps of asthma?
4 STEPS OF ASTHMA FIRST AID Call emergency assistance immediately. Dial Triple Zero (000): Sit the person upright Give 4 separate puffs of blue/grey reliever puffer – Shake puffer – Put 1 puff into spacer – Take 4 breaths from spacer Repeat until 4 puffs have been taken Remember: shake, 1 puff, 4 breaths
What are the stages of asthma?
What are the stages of asthma?
- Intermittent asthma. This is the least severe type. ...
- Mild persistent asthma. This is the least severe form of persistent asthma.
- Moderate persistent asthma. This is the second most severe form of asthma.
- Severe persistent asthma. A person will need to use an inhaler several times a day if they have severe persistent asthma. ...
What are the guidelines for asthma?
- Using inhaled corticosteroids when needed for recurrent wheezing or persistent asthma. ...
- Using long-acting antimuscarinic agents (LAMAs) with inhaled corticosteroids for long-term asthma management. ...
- Using one or more methods to reduce exposure to indoor asthma triggers.
How do you manage asthma?
This breathing aid helps customers with asthma to strengthen their lungs and clean the airway. The newly expanded store gives more customers the chance to buy the award-winning device to manage their respiratory condition. It’s suitable even for those ...
What does a stepwise approach to treatment mean?
The stepwise approach to therapy, in which the dose and number of medications and frequency of administration are increased as necessary and decreased when possible, is used to achieve and maintain this control.
What is the purpose of the stepwise approach to asthma?
A stepwise approach to pharmacologic therapy is recommended to gain and maintain control of asthma in both the impairment and risk domains. The type, amount, and scheduling of medication is dictated by asthma severity (for initiating therapy) and the level of asthma control (for adjusting therapy).
What are the various approaches for the treatment of asthma?
TreatmentLong-term asthma control medications, generally taken daily, are the cornerstone of asthma treatment. ... Quick-relief (rescue) medications are used as needed for rapid, short-term symptom relief during an asthma attack. ... Allergy medications may help if your asthma is triggered or worsened by allergies.
What is the first step in treatment for asthma?
First aid stepsStep 1: Sit the person upright.Step 2: Give 4 separate puffs of blue/grey reliever puffer.Step 3: Wait 4 minutes.Step 4: If breathing does not return to normal, call triple zero (000) for an ambulance.
Who asthma management guidelines?
Reducing the burden of asthmabronchodilators (such as salbutamol), that open the air passages and relieve symptoms; and.steroids (such as beclometasone), that reduce inflammation in the air passages. This improves asthma symptoms and reduces the risk of severe asthma attacks and death.
What are 4 treatments for asthma?
Types of asthma medicationsInhaled corticosteroids.Leukotriene modifiers.Long-acting beta agonists (LABAs)Theophylline.Combination inhalers that contain both a corticosteroid and a LABA.
What are 5 treatments for asthma?
These are the most common long-term control medications for asthma. These anti-inflammatory drugs include fluticasone (Flovent HFA), budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler), beclomethasone (Qvar RediHaler), ciclesonide (Alvesco, Omnaris) and mometasone (Asmanex HFA).
What is the best treatment for asthma?
Long-term control medications such as inhaled corticosteroids are the most important medications used to keep asthma under control. These preventive medications treat the airway inflammation that leads to asthma symptoms. Used on a daily basis, these medications can reduce or eliminate asthma flare-ups.
What is step 3 asthma?
Moderate persistent asthma: Step 3 Doctors also use long-term daily medication to treat moderate asthma that persists over long periods. These medications are often different from those that treat milder forms of asthma.
Why is asthma management important?
Why asthma management is important. Medication is essential to manage asthma well. Good asthma care also involves treating other conditions that can affect asthma, such as hay fever. A healthy lifestyle can help you stay in control of your asthma symptoms and feel well.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
Moderate and severe persistent asthma are often treated with a combination of an ICS and a long-acting beta adrenergic (LABA). The two common LABAs are formoterol (Foradil) and salmeterol (Serevent). LABAs are inhaled twice daily, along with their ICS counterpart. Recently, the safety of LABAs was questioned.
When is alternative therapy considered for asthma?
Alternative therapy is considered in the event of side effects.
What age is asthma diagnosed?
There is a similar chart used to classify asthma in children 5 to 11 and 0 to 4 years of age. Spirometry is introduced in the 5 to 11 years of age population, as children younger than age 5 are often not good candidates for spirometry. So the first step in caring for a patient with asthma beyond diagnosis is classification of severity.
How does EPR-3 help asthma?
Use of the EPR-3 to guide the diagnosis and therapy of asthma has improved from the EPR-2 by providing an evidence base. Clinicians may be assured that when following the EPR-3 guidelines, therapy is being administered based on the best evidence available at the time the guidelines were written.
How long does asthma therapy take?
If the asthma is not well controlled, therapy is stepped up by one step and reevaluated in 2 to 6 weeks.
What are the symptoms of asthma?
Symptoms usually included in the assessment of impairment are frequency of cough, wheeze, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. The severity of asthma corresponds to the most frequently occurring symptom or worst assessment finding.
How many children are affected by asthma?
Asthma is a chronic, inflammatory disease of the airways affecting 22 million Americans, of whom 6 million are children. It is the leading cause of missed school days and lost productivity for the caregiver who must leave work to care for the child. Hospitalizations remain high, at more than 497,000 annually, and there is a disparate impact on ...
What is asthma management?
Management is a dynamic process that will change based on the patient’s needs over time. Effective asthma management requires a proactive, preventative and stepwise approach. Control of asthma is viewed in the context of impairment and risk.
What is stepwise approach?
The guidelines note that “The stepwise approach is meant to help, not replace, the clinical decision making needed to meet individual patient needs. ”.
How long does it take to complete the asthma activity?
2. Describe the recommended approach to monitoring patients with asthma. Estimated time to complete activity: 0.5 hours. Faculty:
What is PIM in medical school?
Postgraduate Institute for Medicine (PIM) requires instructors, planners, managers and other individuals who are in a position to control the content of this activity to disclose any real or apparent conflict of interest (COI) they may have as related to the content of this activity.
How to treat asthma in 2016?
March 7, 2016. The main treatment for asthma is using asthma control medicine on a regular basis. Asthma control drugs reduce inflammation in the airways. When the airways are less inflamed, they become less sensitive, or hyperresponsive. This reduces your risk of having an asthma attack. You may need 1 or more drugs to get your asthma ...
What is the best medicine for asthma?
Oral corticosteroids reduce inflammation. These drugs may be used short-term at the start of an asthma attack or after an attack. Common names of oral steroids include methylprednisolone, prednisolone, and prednisone. 1
What does it mean to go down a step?
Going down a step means your doctor will try a lower dose or cutting out a drug to see if your asthma stays under control. 1. In general, the types of asthma control medicines prescribed for the 6 steps of asthma severity include: 1. Inhaled steroids. Short-acting beta agonists (SABAs)
How long does it take for asthma to go down?
This may mean increasing the dose or adding another drug. If your asthma is well controlled for at least 3 months, you may go down 1 step.
Do steroids help with asthma?
Inhaled steroids make the airways less inflamed and less sensitive. This leads to less severe asthma symptoms and better lung function. You are less likely to have an asthma attack or need to visit the emergency room if you take inhaled corticosteroids. 1,2.
Can LTRAs be used for asthma?
These are pills taken by mouth. 1,2. LTRAs can be used instead of inhaled steroids for people with mild to moderate asthma (Step 2). Leukotriene modifiers can also be used in addition to inhaled corticosteroids for moderate asthma (Steps 3 and 4).
How to control asthma?
You can control your asthma and avoid an attack by taking your medicine exactly as your doctor or other medical professional tells you to do and by avoiding things that can cause an attack. Not everyone with asthma takes the same medicine. Some medicines can be inhaled, or breathed in, and some can be taken as a pill.
Can you take long term control if you have asthma?
If you need to use your quick-relief medicines more and more, you should visit your doctor or other medical professional to see if you need a different medicine. Long-term control medicines help you have fewer and milder attacks, but they don’t help you if you’re having an asthma attack.
Can asthma medicine be taken with a doctor?
Asthma medicines can have side effects, but most side effects are mild and soon go away. Ask your doctor or other medical professional about the side effects of your medicines. The important thing to remember is that you can control your asthma. With your doctor’s or other medical professional’s help, make your own asthma action plan ...
What is asthma treatment?
Asthma treatment is based on a stepwise and control-based approach that involves an iterative cycle of assessment, adjustment of the treatment and review of the response aimed to minimize symptom burden and risk of exacerbations. Anti-inflammatory treatment is the mainstay of asthma management.
What is the difference between asthma control and quick relief?
Evolution of a concept. Asthma control medications reduce airway inflammation and help to prevent asthma symptoms; among these, inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are the mainstay in the treatment of asthma, whereas quick-relief (reliever) or rescue medicines quickly ease symptoms that may arise acutely.
What are some examples of asthma exacerbations?
A typical example of this mechanism is given by viral infections, the most frequent triggers of asthma exacerbations. Rhinoviruses, the most common viruses found in patients with asthma exacerbations, interfere with the mechanism of action of corticosteroids making the anti-inflammatory treatment transiently ineffective.
How many people are affected by asthma?
Background. Asthma, a major global health problem affecting as many as 235 million people worldwide [ 1 ], is a common, non-communicable, and variable chronic disease that can result in episodic or persistent respiratory symptoms (e.g. shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, cough) and airflow limitation, ...
Is asthma a chronic disease?
Asthma is a chronic disease requiring ongoing and comprehensive treatment aimed to reduce the symptom burden (i.e. good symptom control while maintaining normal activity levels), and minimize the risk of adverse events such as exacerbations, fixed airflow limitation and treatment side effects [ 3, 4 ]. Asthma treatment is based on ...

Expert Panel Guidelines
Asthma Medication Decisions
- Before discussing the steps of therapy, it would be useful to discuss asthma medications. All patients with asthma, regardless of severity, need to have a rescue inhaler, which is a SABA: albuterol (ProAir, Proventil, or Ventolin), levalbuterol (Xopenex), or pirbuterol (Maxair). A SABA is used for quick relief of sudden symptoms or for the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospa…
The Stepwise Approach
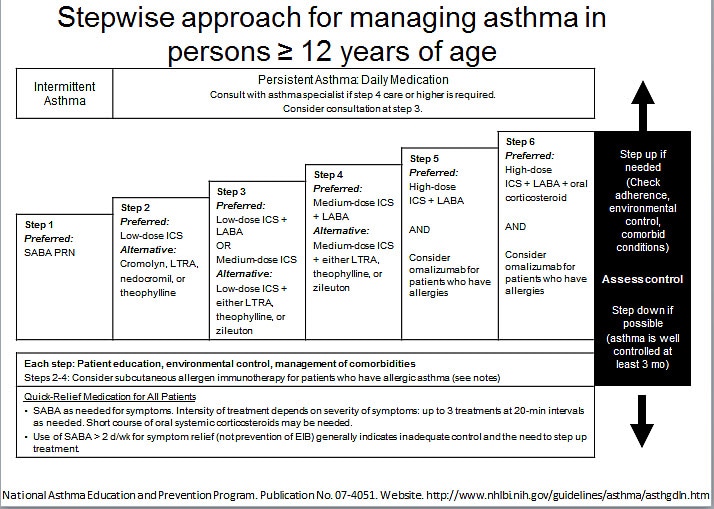
- The stepwise approach for managing asthma in youths =12 years of age and adults is depicted in Figure 3. Step 1 therapy consists of a SABA prn. Since the patient has only intermittent symptoms, this is the only treatment necessary. For patients with mild persistent asthma, the patient should take a low-dose ICS daily and SABA prn. At each level of ...
Follow-Up
- The goal for therapy is to control asthma by reducing impairment and reducing risk. Once the patient has been started on the appropriate step and has received education on triggers, environmental controls, symptoms, etc, control is assessed at 2- to 6-week intervals with regular follow-up contacts at 1- to 6-month intervals. Reduced impairment is defined as prevention of ch…