
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the use of HIV medicines to treat HIV infection. People on ART take a combination of HIV medicines (called an HIV regimen) every day. ART is recommended for everyone who has HIV. ART can’t cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives.
How to cure HIV naturally?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they... Talk to your health care provider about any medical conditions you may have or any other medicines you are taking. Let your ...
What are the treatment options for HIV infection?
Mar 29, 2019 · HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are.
What is the best medicine for HIV?
Feb 08, 2022 · The treatment of HIV/AIDS with medicines is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). It is recommended for everyone who has HIV. The medicines do not cure HIV infection, but they do make it a manageable chronic condition. They also reduce the risk of spreading the virus to others. How do HIV/AIDS medicines work?
How to optimize HIV treatment?
high-dose daily rifapentine (RPT) with moxifloxacin (MOX), isoniazid (INH), and pyrazinamide (PZA).

What is the best treatment for HIV?
The most effective treatment for HIV is antiretroviral therapy (ART). This is a combination of several medicines that aims to control the amount of virus in your body.
What is a method of treatment for HIV infections?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV.
What is the first line treatment for HIV?
The recommended first-line HIV treatment regimens include antiretroviral (ARV) drugs that are safe, effective, and convenient for most people with HIV who have never taken ARVs before.
When should HIV treatment start?
People with HIV should start taking HIV medicines as soon as possible after HIV is diagnosed. A main goal of HIV treatment is to reduce a person's viral load to an undetectable level. An undetectable viral load means that the level of HIV in the blood is too low to be detected by a viral load test.Aug 16, 2021
What treatment is given for low CD4 count?
Antiretroviral drugs interrupt this process. The aim of treatment is to reduce levels of HIV in your body (often called your 'viral load'), so your CD4 count increases and your body's ability to fight infections improves.Jan 29, 2021
WHO recommended PEP regimen?
Wherever PEP is indicated and source is ART naive or unknown: recommended regimen is Tenofovir 300 mg + Lamivudine 300 mg + Efavirenz 600 mg once daily for 28 days. Wherever available, single pill containing these formulations should be used. Dual drug regimen should not be used any longer in any situation for PEP.
What does Second line treatment mean?
Second-line treatment is treatment for a disease or condition after the initial treatment (first-line treatment) has failed, stopped working, or has side effects that aren't tolerated.Jun 9, 2020
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is n...
When should I start treatment?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the vir...
What if I delay treatment?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infecti...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Treatment Reduces the Amount of HIV in the Blood The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load. Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will h...
Does HIV medicine cause side effects?
HIV medicine can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vom...
Will HIV treatment interfere with my hormone therapy?
There are no known drug interactions between HIV medicine and hormone therapy. Talk to your health care provider if you are worried about taking HI...
What if my treatment is not working?
Your health care provider may change your prescription. A change is not unusual because the same treatment does not affect everyone in the same way.
Sticking to my treatment plan is hard. How can I deal with the challenges?
Tell your health care provider right away if you’re having trouble sticking to your plan. Together you can identify the reasons you’re skipping med...
What to do if you think you have HIV?
If you think you might have HIV infection, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. You may be referred to an infectious disease specialist — who additionally specializes in treating HIV / AIDS.
What drugs are used to make copies of HIV?
Combination drugs also are available, such as emtricitabine/tenofovir (Truvada) and emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (Descovy). Protease inhibitors (PIs) inactivate HIV protease, another protein that HIV needs to make copies of itself.
What is the CD4 T cell count?
CD4 T cell count. CD4 T cells are white blood cells that are specifically targeted and destroyed by HIV. Even if you have no symptoms, HIV infection progresses to AIDS when your CD4 T cell count dips below 200. Viral load (HIV RNA). This test measures the amount of virus in your blood.
What are some ways to reduce stress?
Mind-body practices. Practices such as yoga, meditation and tai chi have been shown to reduce stress, as well as improve blood pressure and quality of life. While they need more study, these practices may be helpful if you're living with HIV / AIDS.
Is HIV a life threatening illness?
Receiving a diagnosis of any life-threatening illness is devastating. The emotional, social and financial consequences of HIV / AIDS can make coping with this illness especially difficult — not only for you but also for those closest to you.
What is HIV RNA?
Viral load (HIV RNA). This test measures the amount of virus in your blood. After starting HIV treatment the goal is to have an undetectable viral load. This significantly reduces your chances of opportunistic infection and other HIV -related complications.
How to diagnose HIV?
Diagnosis. HIV can be diagnosed through blood or saliva testing. Available tests include: Antigen/antibody tests. These tests usually involve drawing blood from a vein. Antigens are substances on the HIV virus itself and are usually detectable — a positive test — in the blood within a few weeks after exposure to HIV.
What is the treatment for HIV?
HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are.
How successful is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment is most likely to be successful when you know what to expect and are committed to taking your medicines exactly as prescribed. Working with your health care provider to develop a treatment plan will help you learn more about HIV and manage it effectively.
How long do HIV side effects last?
Some side effects can occur once you start a medicine and may only last a few days or weeks.
What happens if your CD4 is low?
If your CD4 cell count falls below a certain level, you are at risk of getting an opportunistic infection. These are infections that don’t normally affect people with healthy immune systems but that can infect people with immune systems weakened by HIV infection.
How soon can you start ART for HIV?
Treatment guidelines from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommend that a person living with HIV begin ART as soon as possible after diagnosis. Starting ART slows the progression of HIV and can keep you healthy for many years.
Can HIV cause drug resistance?
Drug resistance can be a cause of treatment failure for people living with HIV. As HIV multiplies in the body, it sometimes mutates (changes form) and produces variations of itself. Variations of HIV that develop while a person is taking ART can lead to drug-resistant strains of HIV. With drug resistance, HIV medicines that previously controlled ...
What is drug resistance testing?
Drug-resistance testing identifies which, if any, HIV medicines won’t be effective against your specific strain of HIV. Drug-resistance testing results help determine which HIV medicines to include in an HIV treatment regimen. Taking HIV medication every day, exactly as prescribed helps prevent drug resistance.
How does HIV medicine help the immune system?
HIV/AIDS medicines reduce the amount of HIV (viral load) in your body, which helps by. Giving your immune system a chance to recover. Even though there is still some HIV in your body, your immune system should be strong enough to fight off infections and certain HIV-related cancers. Reducing the risk that you will spread HIV to others.
What does HIV stand for?
What is HIV/AIDS? HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. It harms your immune system by destroying CD4 cells. These are a type of white blood cells that fight infection. The loss of these cells makes it hard for your body to fight off infections and certain HIV-related cancers. Without treatment, HIV can gradually destroy ...
What is ART treatment?
What is antiretroviral therapy (ART)? The treatment of HIV/AIDS with medicines is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). It is recommended for everyone who has HIV. The medicines do not cure HIV infection, but they do make it a manageable chronic condition. They also reduce the risk of spreading the virus to others.
Does HIV affect CD4 cells?
Some HIV/AIDS medicines interfere with HIV's ability to infect CD4 immune system cells: CCR5 antagonists and post-attachment inhibitors block different molecules on the CD4 cells. To infect a cell, HIV has to bind to two types of molecules on the cell's surface. Blocking either of these molecules prevents HIV from entering the cells.
What is an attachment inhibitor?
Attachment inhibitors bind to a specific protein on the outer surface of HIV. This prevents HIV from entering the cell. In some cases, people take more than one medicine: Pharmacokinetic enhancers boost the effectiveness of certain HIV/AIDS medicines. A pharmacokinetic enhancer slows the breakdown of the other medicine.
What is the difference between PEP and PEP?
HIV medicines are not just used for treatment. Some people take them to prevent HIV. PrEP (pre- exposure prophylaxis) is for people who don't already have HIV but are at very high risk of getting it. PEP (post-exposure prophylaxis) is for people who have possibly been exposed to HIV. NIH: Office of AIDS Research.
What is the name of the drug that blocks reverse transcriptase?
This prevents HIV from copying itself, which reduces the amount of HIV in the body. Several medicines do this: Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) block an enzyme called reverse transcriptase. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) bind to and later change reverse transcriptase.
How to treat TB in HIV?
The recommended treatment of TB disease in adults infected with HIV is a 6-month daily regimen consisting of: 1 An intensive phase of isoniazid (INH), a rifamycin (see Drug Interactions below), pyrazinamide (PZA), and ethambutol (EMB) for the first 2 months. 2 A continuation phase of INH and a rifamycin for the last 4 months.
How long does HIV treatment last?
In the uncommon situation in which HIV-infected patients do NOT receive antiretroviral therapy during TB treatment, prolonging treatment to 9 months (extend continuation phase to 7 months) is recommended. Prolonging treatment to 9 months (extend continuation phase to 7 months) for HIV-infected patients with delayed response to therapy (e.g., ...
What is the first step in HIV testing?
The first step is to ensure that people with HIV are tested for TB infection. If found to have TB infection, further tests are needed to rule out TB disease. The next step is to start treatment for latent TB infection or TB disease based on test results.
How long does isoniazid last?
For those taking antiretroviral medications with clinically significant drug interactions with once-weekly rifapentine or daily rifampin, nine months of daily isoniazid is an alternative treatment. for more information on the drug interactions.
When should antiretroviral therapy be initiated?
Anti-retroviral therapy should ideally be initiated within the first 2 weeks ...
What is DOT therapy?
Directly observed therapy (DOT) and other adherence promoting strategies should be used in all patients with HIV-related TB. The care for HIV-related TB should be provided by, or in consultation with, experts in management of both TB and HIV. The care for persons with HIV-related TB should include close attention to adherence to both regimens of TB and antiretroviral treatment, drug-drug interactions, paradoxical reaction or Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS), side effects for all drugs used, and the possibility of TB treatment failure or relapse.
Is rifabutin a drug?
Rifabutin, which has fewer problematic drug interactions, may be used as an alternative to RIF for HIV-infected patients. As new antiretroviral agents and more pharmacokinetic data become available, these recommendations on managing interactions are likely to be modified.
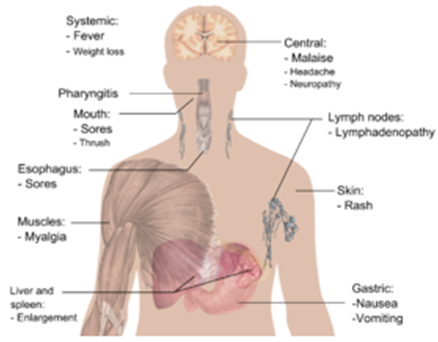
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Along with receiving medical treatment, it's essential to take an active role in your own care. The following suggestions may help you stay healthy longer: 1. Eat healthy foods.Make sure you get enough nourishment. Fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein help keep you strong, give you more energy and support your immune system. 2. Avoid raw meat, eggs and mo…
Alternative Medicine
- People who are infected with HIV sometimes try dietary supplements that claim to boost the immune system or counteract side effects of anti-HIVdrugs. However, there is no scientific evidence that any nutritional supplement improves immunity, and many may interfere with other medications you're taking. Always check with your doctor before taking any...
Coping and Support
- Receiving a diagnosis of any life-threatening illness is devastating. The emotional, social and financial consequences of HIV/AIDScan make coping with this illness especially difficult — not only for you but also for those closest to you. But today, there are many services and resources available to people with HIV. Most HIV/AIDSclinics have social workers, counselors or nurses wh…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you think you might have HIV infection, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. You may be referred to an infectious disease specialist — who additionally specializes in treating HIV/AIDS.