
What is a control treatment in a clinical trial?
Jun 09, 2021 · When conducting an experiment, a control is an element that remains unchanged or unaffected by other variables. It is used as a benchmark or a point of comparison against which other test results are measured. Controls are typically used in science experiments, business research, cosmetic testing and medication testings.
What is the control in an experiment?
A “control treatment” is employed in double blind experiments that are the standard for Phase III medical trials. Test subjects (humans or animals) are divided in to control and treatment groups. Each subject is administered a “treatment” of some kind.
What is the difference between control and treatment groups?
The control group and the treatment groups are treated exactly the same way in every regard except for a single condition, the effects of which is what the experiment is designed to observe. Think of a drug test, where the control group gets a placebo, and the treatment group gets a dose of experimental medication.
What is control treatment in a double blind experiment?
Control and Treatment Groups: A control group is used as a baseline measure. The control group is identical to all other items or subjects that you are examining with the exception that it does not receive the treatment or the experimental manipulation that the treatment group receives.
What is a control treatment examples?
The experimental group is given the experimental treatment and the control group is given either a standard treatment or nothing. For example, let's say you wanted to know if Gatorade increased athletic performance. Your experimental group would be given the Gatorade and your control group would be given regular water.Oct 1, 2015
How do you find the control treatment in an experiment?
Control and Treatment Groups. Control and Treatment Groups: A control group is used as a baseline measure. The control group is identical to all other items or subjects that you are examining with the exception that it does not receive the treatment or the experimental manipulation that the treatment group receives.
What is the purpose of control treatments in an experiment?
Controls allow the experimenter to minimize the effects of factors other than the one being tested. It's how we know an experiment is testing the thing it claims to be testing. This goes beyond science — controls are necessary for any sort of experimental testing, no matter the subject area.Nov 2, 2018
What is a control in an experiment example?
An example of a control in science would be cells that get no treatment in an experiment. Say there is a scientist testing how a new drug causes cells to grow. One group, the experimental group would receive the drug and the other would receive a placebo. The group that received the placebo is the control group.Nov 19, 2021
What is a control in science?
A control group in a scientific experiment is a group separated from the rest of the experiment, where the independent variable being tested cannot influence the results. This isolates the independent variable's effects on the experiment and can help rule out alternative explanations of the experimental results.Jan 29, 2020
What is a controlled experiment in biology?
A controlled experiment is a scientific test done under controlled conditions, meaning that just one (or a few) factors are changed at a time, while all others are kept constant.
Why is it important to have control treatment for the experiments described how the control treatment would increase the validity of the results?
Control variables enhance the internal validity of a study by limiting the influence of confounding and other extraneous variables. This helps you establish a correlational or causal relationship between your variables of interest.Mar 1, 2021
What are some examples of control?
Control is defined as to command, restrain, or manage. An example of control is telling your dog to sit. An example of control is keeping your dog on a leash. An example of control is managing all the coordination of a party.
How does a controlled experiment work?
A controlled experiment is an experiment where the independent variable is systematically manipulated while its effects on the dependent variable are measured. Furthermore, the presence of any extraneous variables are accounted for and are controlled.
What is control in an experiment?
When you do an experiment, you do something to something. The control is an identical something to which you did nothing. Then you compare the outcomes, to see what change was effected. For example, in the NASA Twin Study, one identical twin spent a year in space while the other twin stayed on Earth.
What is a control test?
A control is something where the test procedure is not subjected to the same conditions or manipulation as the other tests. For instance, let's say we want to test whether talking to a plant makes it grow faster.
What is the placebo effect?
In the case of the Placebo, any measurable improvement over their pre-treatment condition is called “The Placebo Effect.”.
What happens if your control group differs from the treatment group?
If your control group differs from the treatment group in ways that you haven’t accounted for, your results may reflect the interference of confounding variables instead of your independent variable.
What is treatment in research?
The treatment is any independent variable manipulated by the experimenters, and its exact form depends on the type of research being performed. In a medical trial, it might be a new drug or therapy. In public policy studies, it could be a new social policy that some receive and not others.
Why are control groups important?
Importance of control groups. Control groups help ensure the internal validity of your research. You might see a difference over time in your dependent variable in your treatment group. However, without a control group, it is difficult to know whether the change has arisen from the treatment.
What is a control group in science?
Revised on April 19, 2021. In a scientific study, a control group is used to establish a cause-and-effect relationship by isolating the effect of an independent variable. Researchers change the independent variable in the treatment group ...
How to reduce confounding variables?
There are several methods you can use to decrease the impact of confounding variables on your research: restriction, matching, statistical control and randomization. In restriction, you restrict your sample by only including certain subjects that have the same values of potential confounding variables.
What is the treatment group?
The treatment group (also called the experimental group) receives the treatment whose effect the researcher is interested in. The control group receives either no treatment, a standard treatment whose effect is already known, or a placebo (a fake treatment). The treatment is any independent variable manipulated by the experimenters, ...
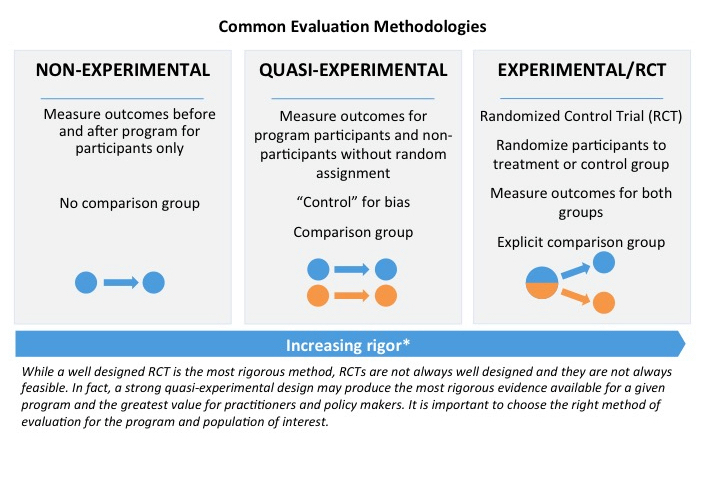
What is quasi-experimental design?
While true experiments rely on random assignment to the treatment or control groups, quasi-experimental design uses some criterion other than randomization to assign people. Often, these assignments are not controlled by researchers, but are pre-existing groups that have received different treatments.
What is the purpose of an experiment?
In many experiments, the purpose is to determine whether some treatment has a particular effect. To determine this, the experimenter sets up two groups of subjects, which undergo exactly the same conditions except that one group gets the treatment and the other doesn’t.
What is a control group?
the "control" is usually a group kept under "regular" environment and its meant to act as "default". It's not mandatory in all experiments, only in those which involve "guinea pigs", where the subjects does not react unilaterally or multiple variables.
What is experimental control?
An experimental control is used in scientific experiments to minimize the effect of variables which are not the interest of the study. The control can be an object, population, or any other variable which a scientist would like to “control.”. You may have heard of experimental control, but what is it?
Why is control important in an experiment?
A control is important for an experiment because it allows the experiment to minimize the changes in all other variables except the one being tested. To start with, it is important to define some terminology.
Why is advertising important in science?
This helps scientists ensure that there have been no deviations in the environment of the experiment that could end up influencing the outcome of the experiment, besides the variable they are investigating. Let’s take a closer look at what this means.
Why do scientists use the scientific method?
Scientists use the scientific method to ask questions and come to conclusions about the nature of the world. After making an observation about some sort of phenomena they would like to investigate, a scientist asks what the cause of that phenomena could be.
What is a positive control?
A positive control is a group or variable that receives a treatment with a known positive result. Randomization. A randomized controlled seeks to reduce bias when testing a new treatment. Blind experiments.
What is the difference between independent and dependent variables?
The independent variable is the variable which the experimenter either manipulates or controls in an experiment to test the effects of this manipulation on the dependent variable. A dependent variable is a variable being measured to see if the manipulation has any effect. Photo: frolicsomepl via Pixabay, CC0.
What is control in science?
By definition the control in a science experiment is a sample that remains the same throughout the experiment. The control must remain the same or equal at all times in order to receive accurate results. You can have as many controls as necessary to achieve results.
Why are controls important in science?
Controls are a vital part of a science experiment. If at any point, your variable could affect the end result of your experiment, it should be considered the control. Your control may change as your experiment changes. For instance, you may need a different sample to prove a different hypothesis.
What is a controlled variable?
Controlled variables are any other outside variables that may affect the dependent variable. The three variables can sometimes be easily mistaken. If you have not identified the control in a science experiment, you may be mistaking one of your controls as an independent variable. Remember that the control should never change.
What is a control pot?
The control pot uses regular potting soil and the same daily routine of water and sun. The other pots have different soil mixtures and may be exposed to varying lights and temperatures. Depending on your science experiment, determine a variable or sample set that must remain the same at all times.
What are the three types of variables?
The three types of variables should not be confused as they are completely different. Independent variables are changes occurring due to the person doing the experiment. Dependent variables change based upon changes in the independent variables.
What are some examples of control?
Another great example of creating a control is determining how fast an object sinks, or the object’s density. The control would be using the same amount of water in the exact same size container. Be sure to use the same type of water as well, such as filtered or unfiltered.
Do all experiments require a control?
Not all science experiments require a control, but many do. You can create your own control sample by following a few simple steps. One great example of creating a control in a relatively simple experiment is working with plants. The basis is to determine how plants grow in different types of soil mixtures. The control pot uses regular potting soil ...

Control Groups in Experiments
- Control groups are essential to experimental design. When researchers are interested in the impact of a new treatment, they randomly divide their study participants into at least two groups: 1. The treatment group (also called the experimental group) receives the treatment whose effect the researcher is interested in. 2. The control groupreceives e...
Control Groups in Non-Experimental Research
- Although control groups are more common in experimental research, they can be used in other types of research too. Researchers generally rely on non-experimental control groups in two cases: quasi-experimental or matching design.
Importance of Control Groups
- Control groups help ensure the internal validityof your research. You might see a difference over time in your dependent variable in your treatment group. However, without a control group, it is difficult to know whether the change has arisen from the treatment. It is possible that the change is due to some other variables. If you use a control group that is identical in every other way to t…