
Explore
Home remedies for bronchitis
- Ginger. Some researchers have found evidence that ginger can have an anti-inflammatory effect against respiratory infection.
- Garlic. Garlic is believed to have a number of healing properties. ...
- Turmeric. ...
- Steam. ...
- Salt water. ...
- Sleep. ...
- Lifestyle changes. ...
- Take OTC medications with caution. ...
- Honey and lemons. ...
- Pineapple. ...
What are the best home remedies for bronchitis?
Top 10 Home Remedies to Cure Bronchitis Fast Permanentl
- utes of the first step you will feel the.
- To cure bronchitis naturally, just take a mortar and pestle and crush the garlic coarsely. ...
- Naturally Treat Bronchitis with Home Remedies These cheap and cost-effective natural remedies for bronchitis can keep your airways clear, remove mucus, and help you stay as comfortable as possible. ...
Do any bronchitis home remedies actually work?
Technically, bronchitis doesn't kill you. It's the inflammation of the main air passage that leads to the lungs. Because bronchitis is cause by a virus antibiotics will not cure it (Antibiotics kill bacteria), and if it remains untreated, it can develop into pneumonia, and THAT can kill you.
Can bronchitis kill you?
The body can rid itself of acute bronchitis in around 3 weeks for as long as exposure to irritants is kept to a minimum. Although bronchitis can definitely go away by itself, it is generally much better to be on the side of caution and to have yourself undergone treatment for better results.
Can bronchitis go away by itself?
What is the best treatment for chronic bronchitis?
How is chronic bronchitis treated?Quitting smoking.Staying away from secondhand smoke and other lung irritants.Taking medicines by mouth (oral) to open airways and help clear away mucus.Taking inhaled medicines, such as bronchodilators and steroids.Getting oxygen from portable containers.More items...
What is the first line treatment for chronic bronchitis?
Short-acting beta-adrenergic receptor agonists (SABAs) are the first line of chronic bronchitis therapy because they promote mucus clearance and prevent bronchospasm.
What three treatments are considered for bronchitis?
Symptoms can be treated using a variety of methods, including drugs, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, surgery, or a combination of these. Your doctor might prescribe a mucus clearing device, also called an airway clearance device, to help you bring up mucus easily.
Do you need medication for chronic bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis treatment Your doctor may prescribe a medicine called a bronchodilator to treat your chronic bronchitis. This medicine dilates (or opens) the airways in your lungs and helps you breathe better. This medicine is usually inhaled (breathed in) rather than taken as a pill.
Should I take steroids for bronchitis?
Bottom line: Steroids do not help improve patient-oriented or clinical outcomes in nonasthmatic acute bronchitis, so do not prescribe them.
Does prednisone help bronchitis?
The results of a new study from the United Kingdom reveal that oral prednisone had no effect on the severity and duration of symptoms in adult patients suffering from bronchitis. Bronchitis is a respiratory infection caused by inflammation of the pathways that carry air to an individual's lungs, the bronchial tubes.
What medications treat chronic bronchitis?
Bronchodilator Medications Inhaled as aerosol sprays or taken orally, bronchodilator medications may help to relieve symptoms of chronic bronchitis by relaxing and opening the air passages in the lungs. Steroids Inhaled as an aerosol spray, steroids can help relieve symptoms of chronic bronchitis.
How long does prednisone take to work for bronchitis?
Official answer. The immediate-release prednisone formulation, which comes in tablet or solution form, absorbs into your bloodstream in 2 hours. On the other hand, the delayed-release tablets start working in about 6 hours.
What is the best antibiotic for bronchitis?
Types of Antibiotics for BronchitisExtended macrolides like Zithromax (azithromycin)Fluoroquinolones like Cipro (ciprofloxacin) and Levaquin (levofloxacin)Aminopenicillins like Principen (ampicillin), Moxatag (amoxicillin), and Hetacin (hetacillin)Cephalosporins.
Can you live a long life with chronic bronchitis?
The 5-year life expectancy for people with COPD ranges from 40% to 70%, depending on disease severity. This means that 5 years after diagnosis 40 to 70 out of 100 people will be alive. For severe COPD, the 2-year survival rate is just 50%.
Why won't my bronchitis cough go away?
Most cases of acute bronchitis go away on their own in 7 to 10 days. You should call your doctor if: You continue to wheeze and cough for more than 2 weeks, especially at night when you lie down or when you are active. You continue to cough for more than 2 weeks and have a bad-tasting fluid come up into your mouth.
What are 6 signs and symptoms of chronic bronchitis?
For either acute bronchitis or chronic bronchitis, signs and symptoms may include:Cough.Production of mucus (sputum), which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color — rarely, it may be streaked with blood.Fatigue.Shortness of breath.Slight fever and chills.Chest discomfort.
How to treat bronchitis?
It may include: Quitting smoking. Staying away from secondhand smoke and other lung irritants. Taking medicines by mouth (oral) to open airways and help clear away mucus. Taking inhaled medicines, such as bronchodilators and steroids.
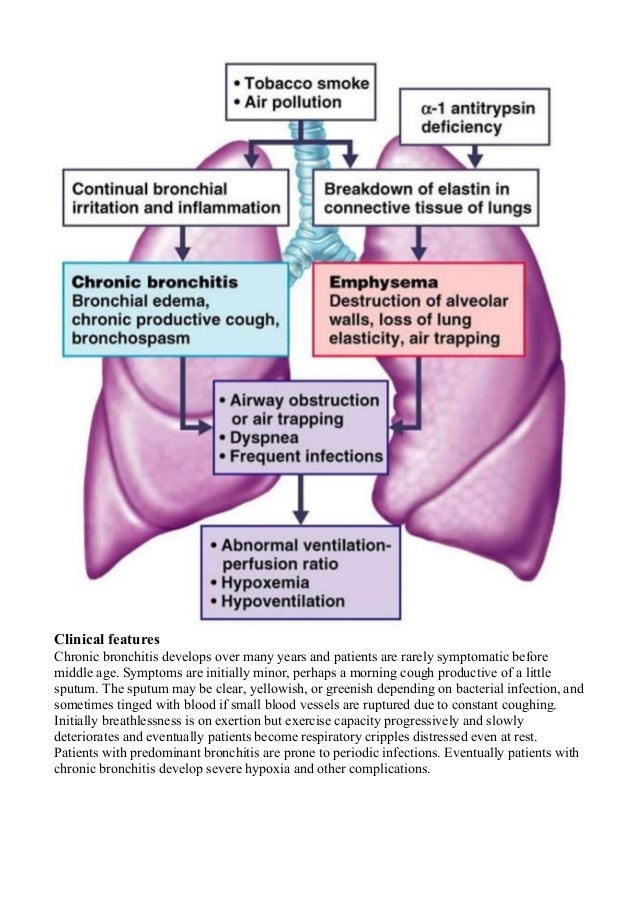
What is chronic bronchitis?
Key points about chronic bronchitis. Bronchitis is inflammation of the breathing tubes (bronchi). There are several types of bronchitis, but the most common are acute and chronic. Chronic bronchitis is often part of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This is a group of lung diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing problems.
How long do you have to cough for bronchitis?
People with chronic bronchitis tend to get lung infections more easily. They also have episodes of acute bronchitis, when symptoms are worse. To be classified as chronic bronchitis: You must have a cough and mucus most days for at least 3 months a year, for 2 years in a row.
What is the inflammation of the bronchi?
This inflammation causes too much mucus production and other changes. There are different types of bronchitis. But the most common are acute and chronic. Chronic bronchitis is long-term inflammation of the bronchi. It is common among smokers.
What is it called when you cough up mucus?
Cough, often called smoker’s cough. Coughing up mucus (expectoration) Wheezing. Chest discomfort. People with chronic bronchitis often have a cough and make mucus for many years before they have shortness of breath. Chronic bronchitis may cause: Disability. Frequent and severe infections that affect your airways.
What tests are used to diagnose bronchitis?
Tests that help measure how well your lungs are working are used to diagnose chronic bronchitis. Blood, breathing, and imaging tests may also be used to see how severe the problem is and watch it over time. The goal of treatment is to live more comfortably by controlling symptoms.
Can smokers cough?
This condition causes a cough that’s often called smoker’s cough. It also causes you to cough up mucus, wheeze, and have chest discomfort. These may get worse over time and lead to severe breathing problems. Tests that help measure how well your lungs are working are used to diagnose chronic bronchitis.
What is the best treatment for bronchitis?
If you have chronic bronchitis, you may benefit from pulmonary rehabilitation — a breathing exercise program in which a respiratory therapist teaches you how to breathe more easily and increase your ability to exercise.
How to get rid of coughing and sneezing?
Use a humidifier. Warm, moist air helps relieve coughs and loosens mucus in your airways. But be sure to clean the humidifier according to the manufacturer's recommendations to avoid the growth of bacteria and fungi in the water container. Consider a face mask outside.
What to do if you have a cough and you can't sleep?
If your cough keeps you from sleeping, you might try cough suppressants at bedtime. Other medications. If you have allergies, asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), your doctor may recommend an inhaler and other medications to reduce inflammation and open narrowed passages in your lungs.
What tests can help you know if you have pneumonia?
In some cases, your doctor may suggest the following tests: Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray can help determine if you have pneumonia or another condition that may explain your cough. This is especially important if you ever were or currently are a smoker. Sputum tests. Sputum is the mucus that you cough up from your lungs.
How to get rid of a swollen lung?
Lifestyle and home remedies. To help you feel better, you may want to try the following self-care measures: Avoid lung irritants. Don't smoke. Wear a mask when the air is polluted or if you're exposed to irritants, such as paint or household cleaners with strong fumes. Use a humidifier.
Can antibiotics help with bronchitis?
Because most cases of bronchitis are caused by viral infections, antibiotics aren't effective. However, if your doctor suspects that you have a bacterial infection, he or she may prescribe an antibiotic. In some circumstances, your doctor may recommend other medications, including: Cough medicine.
What is the treatment for bronchitis?
There are several treatment options, including medications, lifestyle changes, oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation.
What is the first line of treatment for chronic bronchitis?
Prescription medications are the first line of treatment for chronic bronchitis. These medications focus on stabilizing your condition and preventing or treating exacerbations, which are characterized by severe shortness of breath and chest tightness.
What are some examples of COPD surgery?
Examples of surgeries that could be used in severe cases of chronic bronchitis and COPD include lung volume reduction surgery and lung transplants. 1.
How long does it take for bronchodilators to wear off?
Short-acting bronchodilators work quickly so that you get relief from symptoms fast, but they wear off in a few hours. Long-acting bronchodilators provide relief for many hours, but the effect may be slower. Short- and long-acting bronchodilators include beta2-agonists and anticholinergics: 5.
What is the oxygenation goal for COPD?
Typically, in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), of which chronic bronchitis is a type, the oxygenation goal is set at 92% or above. You may need to wear oxygen for only short periods, while you are sleeping, or continuously in severe cases.
What to do if you have bronchitis?
The first thing your doctor will talk to you about is making lifestyle changes to preserve your lung function. Most cases of chronic bronchitis are caused by cigarette smoking, so if you are still smoking, your doctor will strongly advise you to quit. 1
How to improve your breathing?
Physical activity can strengthen the muscles that help you breathe and improve your overall wellness. Your doctor may also recommend pulmonary rehabilitation , a program that helps improve the well-being of people who have chronic breathing problems.
What to do if you smoke and have bronchitis?
Your first step, if you smoke, is to quit. Your lungs will not fully recover, but the rate of decline will be much slower. Airway openers ( bronchodilators ): These drugs relax your air passages to make it easier to breathe and relieve your bronchitis symptoms.
What is the number one cause of bronchitis?
Cigarette smoking is by far the No. 1 cause of chronic bronchitis. More than 90% of people with the disease smoke or used to smoke. Other things that raise your chances for it include:
How to breathe easier?
First, inhale through your nose to a count of 2. Then pucker your lips as if you’re about to kiss. Release your breath through your mouth to a count of 4. Practice pursed breathing whenever you’re in the middle of something hard, like climbing stairs.
How long does coughing last?
That’s when the air tubes in your lungs called bronchi get irritated and inflamed, and you have coughs for at least 3 months a year for 2 years in a row. It’s a long-term illness that keeps coming back or never fully goes away. It’s a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The other type is emphysema.
What tests do you take to check your lungs?
Your doctor will ask about your smoking history and listen to your lungs with a stethoscope. You may take tests, including: Pulmonary function tests: This is a series of measurements of how much air your lungs can hold while breathing in and out.
How do you know if you have bronchitis?
Other signs of chronic bronchitis may include: Cough, often with mucus. Wheezing. Tight chest. Shortness of breath. Feeling tired. Your symptoms may be worst in the winter, when humidity and temperatures drop.
What is the best treatment for a swollen lungs?
Anti-inflammatory drugs: Steroids lessen the swelling that narrows your air passages. Oxygen therapy: This is for serious cases, where your lungs are so damaged that blood oxygen levels are extremely low. You can inhale oxygen from a portable machine at home as needed.
How to get rid of bronchitis?
You may want to consider the following: Breathing in warm, moist air from a humidifier can ease coughs and loosen the mucus in your airways.
What are the symptoms of chronic bronchitis?
Other symptoms of chronic bronchitis may include: fatigue. a fever.
What is the inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes?
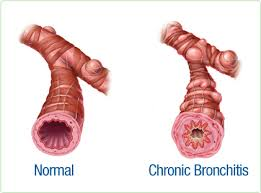
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes. These are the tubes that carry air to and from your lungs. People who have bronchitis often have a persistent cough that brings up thickened, discolored mucus. They may also experience wheezing, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Bronchitis may be either acute or chronic.
Why does bronchitis make my lungs swell?
Chronic bronchitis occurs when the lining of the bronchial tubes repeatedly becomes irritated and inflamed. The continuous irritation and swelling can damage the airways and cause a buildup of sticky mucus, making it difficult for air to move through the lungs. This leads to breathing difficulties that gradually get worse.
What is the name of the condition where the lungs are blocked?
Together, the two conditions are referred to as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD.
How long does bronchitis last?
It’s characterized by recurrent episodes of bronchitis that last for several months or years.
What is the X-ray for bronchitis?
If you’re uncertain about whether or not your symptoms are those of chronic bronchitis, tests are available to help your doctor make a definitive diagnosis: A chest X-ray can help rule out other lung conditions, such as pneumonia, that may be causing your cough. Sputum is the mucus that you cough up from your lungs.
How long does bronchitis last?
Episodes of acute bronchitis can be related to and made worse by smoking. Acute bronchitis could last for 10 to 14 days, possibly causing symptoms for three weeks. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is bronchitis in the lungs?
What is bronchitis? Bronchitis occurs when the bronchioles (air-carrying tubes in the lungs) are inflamed and make too much mucus. There are two basic types of bronchitis: Chronic bronchitis is defined as cough productive of sputum that persists for three months out of the year for at least two consecutive years.
What is the name of the condition that falls in between the common cold and pneumonia in severity?
Bronchitis . The condition that falls in between the common cold and pneumonia in severity is called bronchitis. Symptoms include a frequent cough that produces mucus, fatigue, fever, and a wheezing sound when breathing. Find out how to treat, or better yet, prevent bronchitis. Appointments 216.444.6503.
What are the similarities between pneumonia and bronchitis?
Bronchitis can sometimes progress to pneumonia. Despite similarities, the conditions are different. First, bronchitis involves the bronchial tubes, while pneumonia affects the alveoli, or the air sacs in the lungs.
What are the drugs used for COPD?
Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as corticosteroids (also called steroids), to reduce swelling and mucus output.
Can you take antibiotics for bronchitis?
If you have acute bronchitis, you might not need any treatment. Or you might use over-the-counter drugs that break up mucus or that treat fever or pain. If you have a bacterial infection, your doctor might prescribe antibiotics. If you have chronic bronchitis, treatment will be different.
Can smoking cause bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis is usually, but not always, caused by smoking tobacco. It can also be caused by exposure to secondhand cigarette smoke, air pollution, dust, or toxic gases. Your risk can be increased by family history of bronchitis, having asthma and allergies, and having gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
What is the best treatment for bronchitis?
The best treatment for bronchitis includes rest, fluids, a humidifier, honey, lozenges and prescription medications and interventions, if necessary. Acute bronchitis is sometimes referred to as a chest cold. It can develop after an upper respiratory infection (URI), which you probably know better as the common cold .
How to diagnose bronchitis?
To diagnose acute bronchitis, your doctor will listen to your symptoms and do a physical exam. There are no specific tests for bronchitis, but your doctor may do blood tests to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms. Your doctor may order a chest x-ray if you have a fever in order to rule out pneumonia.
What causes a cough that lasts for 3 months?
Chronic Bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis is a cough that occurs daily with production of sputum that lasts for at least 3 months, 2 years in a row. Causes of chronic bronchitis include cigarette smoking, inhaled irritants, and underlying disease processes (such as asthma, or congestive heart failure).
What is the inflammation of the air-carrying tubes in the lungs called?
Bronchitis refers to the inflammation of the air-carrying tubes in the lungs (bronchioles). The condition is often associated with persistent, nagging cough with mucus. The condition often starts as an infection of the nose, throat, ears, or sinuses that later moves to the bronchi.
What is the other name for bronchitis?
There is another type of bronchitis called chronic bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis is caused by the irritation of your airways. This is usually from smoking or your exposure to other irritants such as toxic gasses. Chronic bronchitis is actually a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( COPD ).
How long does bronchitis last?
Acute bronchitis is short in duration (10-20 days) in comparison with chronic bronchitis, which lasts for months to years. Causes of acute bronchitis include viruses and bacteria, which means it can be contagious.
What tests are done to check for pneumonia?
Your doctor may order a chest x-ray if you have a fever in order to rule out pneumonia. To diagnose chronic bronchitis, your doctor may call for pulmonary function tests to see how your lungs function. When testing your lung function, your doctor may use a spirometer, which is a device that you blow into.
Diagnosis
- During the first few days of illness, it can be difficult to distinguish the signs and symptoms of bronchitis from those of a common cold. During the physical exam, your doctor will use a stethoscope to listen closely to your lungs as you breathe. In some cases, your doctor may suggest the following tests: 1. Chest X-ray.A chest X-ray can help determine if you have pneumo…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- To help you feel better, you may want to try the following self-care measures: 1. Avoid lung irritants.Don't smoke. Wear a mask when the air is polluted or if you're exposed to irritants, such as paint or household cleaners with strong fumes. 2. Use a humidifier.Warm, moist air helps relieve coughs and loosens mucus in your airways. But be sure to ...
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. If you have chronic bronchitis, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in lung diseases (pulmonologist).
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
Over-The-Counter (OTC) Therapies
Prescriptions
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Summary
- The best treatment plan for chronic bronchitis is a combination of lifestyle changes and medications. Quitting smoking and staying away from lung irritants like secondhand smoke can help, as can prescription medications. You may also use some OTC drugs for symptom relief.
A Word from Verywell