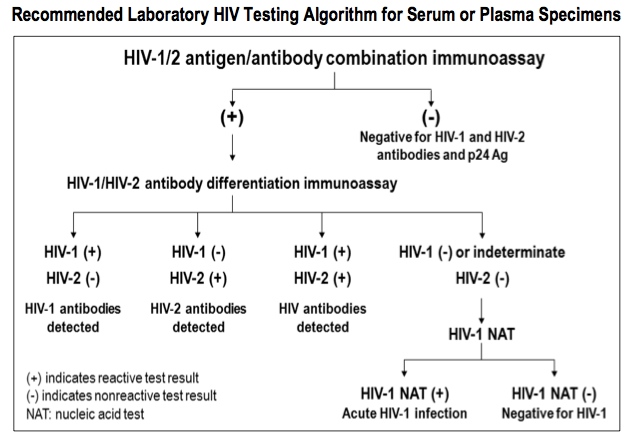
What test is used to confirm a diagnosis of HIV?
The primary tests for diagnosing HIV and AIDs include: ELISA Test ELISA, which stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, is used to detect HIV infection. If an ELISA test is positive, the Western blot test is usually administered to confirm the diagnosis.
What made you get tested for HIV?
The Duke of Sussex has urged Britons to “go and get a test” for HIV. Harry and former rugby star Gareth Thomas, who are friends, chatted in depth on a 30-minute video call to mark National HIV Testing Week.
What does blood test show HIV?
The lab tests look at:
- how well your immune system is functioning (CD4 count)
- how rapidly HIV is replicating, or multiplying (viral load)
- how well your body is functioning (tests to look at your kidneys, liver, cholesterol, and blood cells)
- whether you have other diseases that are associated with HIV (tests for certain infections)
What are the most common types of HIV testing?
- A nucleic acid test (NAT) can usually tell you if you have HIV infection 10 to 33 days after an exposure.
- An antigen/antibody test performed by a laboratory on blood from a vein can usually detect HIV infection 18 to 45 days after an exposure. ...
- Antibody tests can take 23 to 90 days to detect HIV infection after an exposure. ...

What is the test for HIV drug effectiveness?
HIV genotypic antiretroviral resistance testing is used to help select a drug regimen that will likely be effective in treating a person with an HIV infection. The test is used to determine whether the HIV strain infecting an individual is resistant or has developed resistance to one or more drugs used to treat HIV.
How can you monitor the effectiveness of HIV treatment?
HIV viral load tests provide a picture of viral activity, while CD4 cell counts shed light on the status of the immune system and can help physicians to predict and prevent the development of opportunistic infections. These tests can help guide treatment decisions and indicate whether treatment is working.
What test is used to give a more accurate confirmation of a HIV diagnosis?
The results of both tests together are more than 99% accurate. The tests used to confirm HIV infection are either the Western blot or indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) test. If your screening test went to a laboratory, they can do this additional testing on the same blood sample.
What tests are done on HIV positive individuals to monitor their disease status?
The test that for decades had been most commonly used for diagnosing infection with HIV was referred to as an ELISA. If the ELISA found HIV antibodies, the results needed to be confirmed, typically by a test called a Western blot. Newer tests look for these same antibodies in saliva.
What specifically do screening tests such as the Elisa and rapid test kits measure?
HIV antibody tests are the most commonly used tests to determine if someone has HIV. Antibody testing is usually done on a blood sample, often using an enzyme-linked assay called an ELISA or EIA. In this test, a person's serum is allowed to react with virus proteins that have been produced in the laboratory.
What is p24 antigen test?
An antigen test checks your blood for an HIV antigen, called p24. When you're first infected with HIV, and before your body has a chance to make antibodies to the virus, your blood has a high level of p24. The p24 antigen test is accurate 11 days to 1 month after getting infected.
How accurate is the Western blot test?
The Western blot test separates the blood proteins and detects the specific proteins (called HIV antibodies) that indicate an HIV infection. The Western blot is used to confirm a positive ELISA, and the combined tests are 99.9% accurate.
Is p24 antigen test reliable?
This HIV DUO test, including p24 antigen, is considered 99.8 percent accurate at 28 days.
Does CBC show CD4 count?
White blood cells include lymphocytes, neutrophils and monocytes. Some CBC reports include a differential section that breaks out their numbers and percentages. B cells and T cells (CD4 and CD8 cells) are types of lymphocytes, but they are not typically broken out in a standard CBC report (see CD4 Cell Count, above).
What kinds of tests are available, and how do they work?
There are three types of tests available: nucleic acid tests (NAT), antigen/antibody tests, and antibody tests. HIV tests are typically performed o...
How long does it take to get results?
Laboratory tests (NATand antigen/antibody) require blood to be drawn from your vein into a tube and then that blood is sent to a laboratory for tes...
How soon after an exposure to HIV can a test detect if I have the virus?
No HIV test can detect HIV immediately after infection. If you think you’ve been exposed to HIV in the last 72 hours, talk to your health care prov...
What is the antigen test for HIV?
Antigens are foreign substances that cause your immune system to activate. If you have HIV, an antigen called p24 is produced even before antibodies develop.
What is the only HIV test approved?
Most rapid tests and the only currently approved HIV self-test are antibody tests. Talk to your health care provider about what type of HIV test is right for you.
How long does it take for a blood test to detect HIV?
An antigen/antibody test performed by a laboratory on blood from a vein can usually detect HIV infection 18 to 45 days after an exposure . Antigen/ antibody tests done with blood from a finger prick can take longer to detect HIV (18 to 90 days after an exposure). Antibody tests can take 23 to 90 days to detect HIV infection after an exposure.
What are the different types of HIV tests?
What kinds of tests are available, and how do they work? There are three types of tests available: nucleic acid tests (NAT), antigen/antibody tests, and antibody tests. HIV tests are typically performed on blood or oral fluid. They may also be performed on urine. A NAT looks for the actual virus in the blood and involves drawing blood from a vein.
How long does it take to get results from a rapid antibody test?
The rapid antigen/antibody test is done with a finger prick and takes 30 minutes or less. The oral fluid antibody self-test provides results within 20 minutes. How soon after an exposure to HIV can a test detect if I have the virus? No HIV test can detect HIV immediately after infection.
How does NAT test work?
A NAT looks for the actual virus in the blood and involves drawing blood from a vein. The test can either tell if a person has HIV or tell how much virus is present in the blood (known as an HIV viral load test). While a NAT can detect HIV sooner than other types of tests, this test is very expensive and not routinely used for screening individuals ...
What is the time between when a person may have been exposed to HIV and when a test can tell for sure
The time between when a person may have been exposed to HIV and when a test can tell for sure whether they have the virus is called the window period. The window period varies from person to person and depends on the type of test used to detect HIV.
What test can help determine if you have HIV?
If you receive a diagnosis of HIV / AIDS, several tests can help your doctor determine the stage of your disease and the best treatment, including: CD4 T cell count. CD4 T cells are white blood cells that are specifically targeted and destroyed by HIV. Even if you have no symptoms, HIV infection progresses to AIDS when your CD4 T cell count dips ...
How to diagnose HIV?
Diagnosis. HIV can be diagnosed through blood or saliva testing. Available tests include: Antigen/antibody tests. These tests usually involve drawing blood from a vein. Antigens are substances on the HIV virus itself and are usually detectable — a positive test — in the blood within a few weeks after exposure to HIV.
What is HIV RNA?
Viral load (HIV RNA). This test measures the amount of virus in your blood. After starting HIV treatment the goal is to have an undetectable viral load. This significantly reduces your chances of opportunistic infection and other HIV -related complications.
How long does it take to get tested for HIV?
Most rapid HIV tests, including self-tests done at home, are antibody tests. Antibody tests can take three to 12 weeks after you're exposed to become positive. Nucleic acid tests (NATs). These tests look for the actual virus in your blood (viral load). They also involve blood drawn from a vein.
What are some examples of anti-HIV drugs?
Examples include efavirenz (Sustiva), rilpivirine (Edurant) and doravirine (Pifeltro).
What is the treatment for HIV?
However, there are many medications that can control HIV and prevent complications. These medications are called antiretroviral therapy (ART). Everyone diagnosed with HIV should be started on ART, regardless of their stage of infection or complications.
What to do if you think you have HIV?
If you think you might have HIV infection, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. You may be referred to an infectious disease specialist — who additionally specializes in treating HIV / AIDS.
Why is it important to know about HIV?
Why it’s important: For women living with HIV, abnormal cell growth in the cervix is common, and abnormal anal cells are common for both men and women living with HIV. These abnormal cells may become cancerous if they aren’t treated. Why it’s important: Some people who are living with HIV are also coinfected with hepatitis.
Why is it important to get a viral load test?
It’s important to get a viral load test to see the level of HIV in your blood before starting treatment and help guide the choice of HIV medications and then to get repeat tests to track your response to HIV treatment. Complete Blood Count (CBC): This is a measure of the concentration of red blood cells, white blood cells, ...
Why is it important to check for hepatitis?
Why it’s important: Some people who are living with HIV are also coinfected with hepatitis. Checking you for hepatitis A, B, and C infection can help your provider to determine if you need to be treated, or if you are a candidate for one of the existing hepatitis A or B vaccines. (Read more about how hepatitis affects people living with HIV.)
Why is drug resistance important?
Why it’s important: Drug resistance test results help your provider determine which HIV medicines are most likely to work for you. Serum Chemistry Panel: This panel is comprised of a series of several blood tests and helps provide information about your body's metabolism. It gives your provider information about how your kidneys ...
Why is CD4 count important?
Why it’s important: A CD4 count is a good measure of your risk of opportunistic infections and an indicator of how well your immune system is working. Treatment with antiretroviral therapy (ART), medications that control the HIV, is recommended for everyone with HIV, no matter how high or low their CD4 count is.
Why are lab tests important?
Lab Tests and Why They Are Important. As part of your HIV care , your provider will order several laboratory tests. The results of these lab tests, along with your physical exam and other information you provide , will help you and your provider work together to develop the best plan to manage your HIV care so that you can get ...
What is a CD4 test?
The lab tests may include: CD4 count: CD4 cells are a type of white blood cell. They are specialized cells of the immune system that are destroyed by HIV. A CD4 count measures how many CD4 cells are in your blood. The higher your CD4 cell count, the healthier your immune system. The CD4 count of an uninfected adult/adolescent who is generally in ...
How accurate are HIV tests?
HIV tests are between 99% and 100% reliable. Newer, so-called combination or fourth generation tests and other lab-based tests are close to 100% accurate. Rapid or at-home tests are right around 99% of the time if you’ve been infected for a while. But if you were recently exposed, they may not be as trustworthy.
How to test for HIV at home?
You can do this quick, easy test at home. Just rub a swab in the area between your gums and teeth to collect a sample of oral fluid (it isn’t the same as saliva) for antibodies against HIV. If you’ve have had the virus for a while, the rapid oral test is highly accurate.
How long does it take for HIV to show up on a blood test?
An antibody/antigen test that uses blood from a vein can find HIV 18 to 45 days after you’re exposed to the virus.
How accurate is a rapid blood test for HIV?
One type looks for antibodies using a drop of blood from a prick of your fingertip. It’s about as accurate as a laboratory-based antibody test, but its window period could be longer -- between 18 and 90 days.
How long does it take for a blood test to show antibodies?
It can find antibodies (proteins your immune system makes when you’ve been exposed to the virus) 23 to 90 days after infection.
How long does it take to get HIV results?
For these tests, a technician will take a sample of your blood and test it. You’ll get results within a few days. Rapid tests. These tests provide results in around 20 minutes. You can get them done in a community clinic or take them at home.
What is HIV load test?
You may also hear this called an HIV RNA or a viral load test. It uses blood taken from a vein. You probably won’t get this expensive test unless you have symptoms and the doctor thinks you have a recent infection. It’s most often used to see how people who already have HIV respond to treatment.
What is the fourth generation test for HIV?
HIV antigen/antibody tests are also known as combination tests or fourth generation tests. This type of test can detect proteins (or antigens) from HIV, as well as antibodies for HIV. If a person contracts HIV, the virus will produce a protein known as p24 before the immune system produces antibodies.
How does the immune system detect HIV?
When the body is exposed to viruses or bacteria, the immune system produces antibodies. An HIV antibody test can detect HIV antibodies in blood or saliva. If a person contracts HIV, it takes time for the body to produce enough antibodies to be detected by an antibody test.
How long does it take for a virus to show up in an antigen test?
As a result, an antigen/antibody test can detect the virus before an antibody test can. Most people develop detectable levels of p24 antigen 13 to 42 days (about 2 to 6 weeks) after contracting HIV. For some people, the window period may be longer.
What is NAT test?
Nucleic acid test (NAT) An HIV nucleic acid test (NAT) is also known as an HIV RNA test. It can detect genetic material from the virus in blood. In general, NAT can detect the virus before an antibody or antigen/antibody test can.
What happens if a HIV test is positive?
If the result from an initial HIV test is positive, a healthcare provider will order follow-up testing to learn if the result is accurate. If the first test was conducted at home, a healthcare provider will draw a sample of blood to test in a lab.
How long does it take for a blood test to show antibodies?
To perform this type of antibody test, a healthcare professional may draw a sample of blood and send it to a lab for analysis. It may take several days for the results to become available.
What happens if you don't have HIV?
A false-positive result happens when a person who doesn’t have HIV receives a positive result after being tested for the virus. This can happen if laboratory staff mislabel or improperly handle a test sample. It can also happen if someone misinterprets the results of a test.
What to do if your HIV test is positive?
If your test result is positive, you should go to a health care provider to get follow-up testing. Counselors providing the test should be able to answer questions and provide referrals for follow-up testing as well. You can use the HIV.gov locator to find a provider near you.
How long does it take for an antibody test to detect HIV?
Antibody Test —An antibody test can take 23 to 90 days to detect HIV infection after an exposure. Most rapid tests and self-tests are antibody tests. In general, antibody tests that use blood from a vein detect HIV sooner after infection than tests done with blood from a finger prick or with oral fluid.
How long does it take for HIV to show up on a blood test?
Types of HIV Tests and Their Window Periods. Nucleic Acid Test (NAT) —A NAT can usually tell you if you have HIV infection 10 to 33 days after exposure. Antigen/Antibody Test —An antigen/antibody test performed by a laboratory on blood from a vein can usually detect HIV infection 18 to 45 days after exposure.
How long does it take to get HIV results?
If it’s a rapid test, you may be able to wait for the results, but if it’s a laboratory test, it can take several days for your results to be available.
What is the time between HIV testing?
The time between when a person gets HIV and when a test can accurately detect it is called the window period. The window period varies from person to person and also depends upon the type of HIV test.
Can you get tested after a window period?
Remember, you can only be sure you are HIV-negative if:. You haven’t had a potential HIV exposure during the window period. If you do have an exposure, then you will need to be retested.
Is HIV screening covered by insurance?
HIV screening is covered by health insurance without a co-pay, as required by the Affordable Care Act. If you don’t have health insurance, some testing sites may offer free tests. See HIV Testing Locations for information about finding a testing site or other HIV services near you. Topics. Testing HIV Testing.
What to do if your blood test confirms you are infected with HIV?
If your follow-up test result confirms you are infected with HIV, the next thing is to take steps to protect your health and prevent transmission to others. Begin by talking to your health care provider about antiretroviral therapy (ART).
What does HIV stand for in testing?
HIV testing shows whether a person is infected with HIV. HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection. Learn about what a positive and negative HIV test result mean.
How to lower your risk of HIV?
To lower your risk of transmitting HIV, Take medicines to treat HIV (antiretroviral therapy or ART) the right way every day so that you achieve and maintain an undectable viral load. Use condoms the right way every time you have sex. Learn the right ways to use a male condom and a female condom.
What happens if you have a positive HIV test?
If you have a positive HIV test result, a follow-up test will be conducted. If the follow-up test is also positive, it means you are HIV-positive. If you had a rapid screening test, the testing site will arrange a follow-up test to make sure the screening test result was correct.
What does a negative HIV test mean?
A negative result doesn't necessarily mean that you don't have HIV. That's because of the window period—the time between when a person gets HIV and when a test can accurately detect it. The window period varies from person to person and is also different depending upon the type of HIV test. Ask your health care provider about ...
How long after HIV exposure can you get tested again?
If you get an HIV test within 3 months after a potential HIV exposure and the result is negative, get tested again in 3 more months to be sure. If you learned you were HIV-negative the last time you were tested, you can only be sure you’re still negative if you haven’t had a potential HIV exposure since your last test.
What is confidential testing?
Confidential testing means that your name and other identifying information will be attached to your test results. The results will go in your medical record and may be shared with your health care providers and your health insurance company.
How does HIV medicine work?
HIV medicine works by lowering the amount of virus in your body to very low levels. HIV medicine can make the viral load so low that a test can’t detect it (called an undetectable viral load ). HIV medicine slows the progression of HIV and helps protect your immune system.
What are the emotions that people feel when they have HIV?
People can feel many emotions—sadness, hopelessness, or anger. Allied health care providers and social service providers, often available at your health care provider’s office, will have the tools to help you work through the early stages of your diagnosis and begin to manage your HIV. Learn more about living with HIV.
Why is it important to have an undetectable viral load?
Having an undetectable viral load also helps prevent transmitting the virus to others. For example, if you have an undetectable viral load, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. Learn more about being newly diagnosed with HIV and about protecting others.
What does it mean if a lab test is positive?
If the follow-up test is also positive, it means you have HIV (or are HIV-posi tive). It is important that you start medical care and begin HIV treatment ...
What to do if you have a positive antibody test?
If you use any type of antibody test and have a positive result, you will need another (follow-up) test to confirm your results. If you test in a community testing program or take a self-test and it’s positive, you should go to a health care provider to get follow-up testing. If your test is done in a health care setting or a lab and it’s positive, ...
Can you get AIDS if you are HIV positive?
No. Being HIV-positive does not mean you have AIDS. AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV disease. HIV can lead to AIDS if a person does not get treatment or take care of their health.

Diagnosis
- HIVcan be diagnosed through blood or saliva testing. Available tests include: 1. Antigen/antibody tests. These tests usually involve drawing blood from a vein. Antigens are substances on the HIV virus itself and are usually detectable — a positive test — in the blood within a few weeks after exposure to HIV.Antibodies are produced by your immune sy...
Treatment
- Currently, there's no cure for HIV/AIDS. Once you have the infection, your body can't get rid of it. However, there are many medications that can control HIV and prevent complications. These medications are called antiretroviral therapy (ART). Everyone diagnosed with HIV should be started on ART, regardless of their stage of infection or complications. ART is usually a combina…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Along with receiving medical treatment, it's essential to take an active role in your own care. The following suggestions may help you stay healthy longer: 1. Eat healthy foods.Make sure you get enough nourishment. Fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein help keep you strong, give you more energy and support your immune system. 2. Avoid raw meat, eggs and mo…
Alternative Medicine
- People who are infected with HIV sometimes try dietary supplements that claim to boost the immune system or counteract side effects of anti-HIVdrugs. However, there is no scientific evidence that any nutritional supplement improves immunity, and many may interfere with other medications you're taking. Always check with your doctor before taking any supplements or alter…
Coping and Support
- Receiving a diagnosis of any life-threatening illness is devastating. The emotional, social and financial consequences of HIV/AIDScan make coping with this illness especially difficult — not only for you but also for those closest to you. But today, there are many services and resources available to people with HIV. Most HIV/AIDSclinics have social workers, counselors or nurses wh…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you think you might have HIV infection, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. You may be referred to an infectious disease specialist — who additionally specializes in treating HIV/AIDS.
Lab Tests and Why They Are Important
Viral Load Test
- One important test is your HIV viral load test. It’s a lab test that measures how many HIV copies of HIV are in a sample of your blood. This is called your viral load. You want your viral load to be low. The higher your viral load, the greater your risk of becoming ill because of HIV and the more likely you are to transmit HIV. The viral load is highest during the acute (early) phase of HIV, and whe…
CD4 Cell Count
- A CD4 cell countmeasures how many CD4 cells are in your blood. CD4 cells are infection-fighting cells of the immune system. As HIV disease advances, your CD4 count drops. The higher your CD4 cell count, the healthier your immune system. The CD4 count of an adult/adolescent who is generally in good health ranges from 500 to 1,200 cells/mm3. In contrast, if a person has a CD4 …
Other Important Lab Tests
- There are other lab tests that will help your health care provider get important information about your health and work with you to choose the right HIV medications for you. 1. Blood Chemistry Tests: This group of tests measures several different chemicals in your blood to help monitor the health of your organs, especially your heart, liver, and ki...
Frequency and Timing of Testing
- After you start HIV treatment, not all lab tests will be conducted at every medical visit. Some will occur every few visits. Others will depend on whether you are stable on HIV treatment and doing well. View this chartabout the timing of various tests and talk to your provider about what is recommended for you.