How to tell if you have tuberculosis?
Jul 28, 2021 · Tuberculosis prognosis can be improved by following a course of treatment exactly as prescribed. Treatment cures the disease in most cases. In areas where people can be easily screened, diagnosed and treated, the treatment success rate nears 90% and the prognosis is …
Does tuberculosis ever go away?
Apr 03, 2021 · Tuberculosis Diagnosis. During the physical exam, your doctor will check your lymph nodes for swelling and use a stethoscope to... Treatment. If you have latent TB, your doctor might recommend treatment with medication if you're at high risk of... Clinical trials. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing ...
What are the warning signs of tuberculosis?
What happens if TB is untreated?
What is the prognosis for a patient with tuberculosis?
Can you survive tuberculosis with treatment?
How long can you live after TB treatment?
What is the outcome of TB treatment?
What percentage of people survive tuberculosis?
Is TB curable at any stage?
Does tuberculosis shorten lifespan?
Does TB damage lungs permanently?
Does TB reduced life expectancy?
At what intervals TB patients are evaluated during the course of TB treatment?
What is relapse in TB?
What is the best treatment for tuberculosis?
The most common medications used to treat tuberculosis include: Isoniazid. Rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane) Ethambutol (Myambutol) Pyrazinamide. If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for tuberculosis?
For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
What is the most common test for tuberculosis?
The most commonly used diagnostic tool for tuberculosis is a skin test, though blood tests are becoming more commonplace. A small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just below the skin on the inside of your forearm. You should feel only a slight needle prick.
What to do if chest X-ray shows tuberculosis?
If your chest X-ray shows signs of tuberculosis, your doctor might take samples of your sputum — the mucus that comes up when you cough. The samples are tested for TB bacteria.
What to do if you have a positive skin test?
If you've had a positive skin test, your doctor is likely to order a chest X-ray or a CT scan. This might show white spots in your lungs where your immune system has walled off TB bacteria, or it might reveal changes in your lungs caused by active tuberculosis.
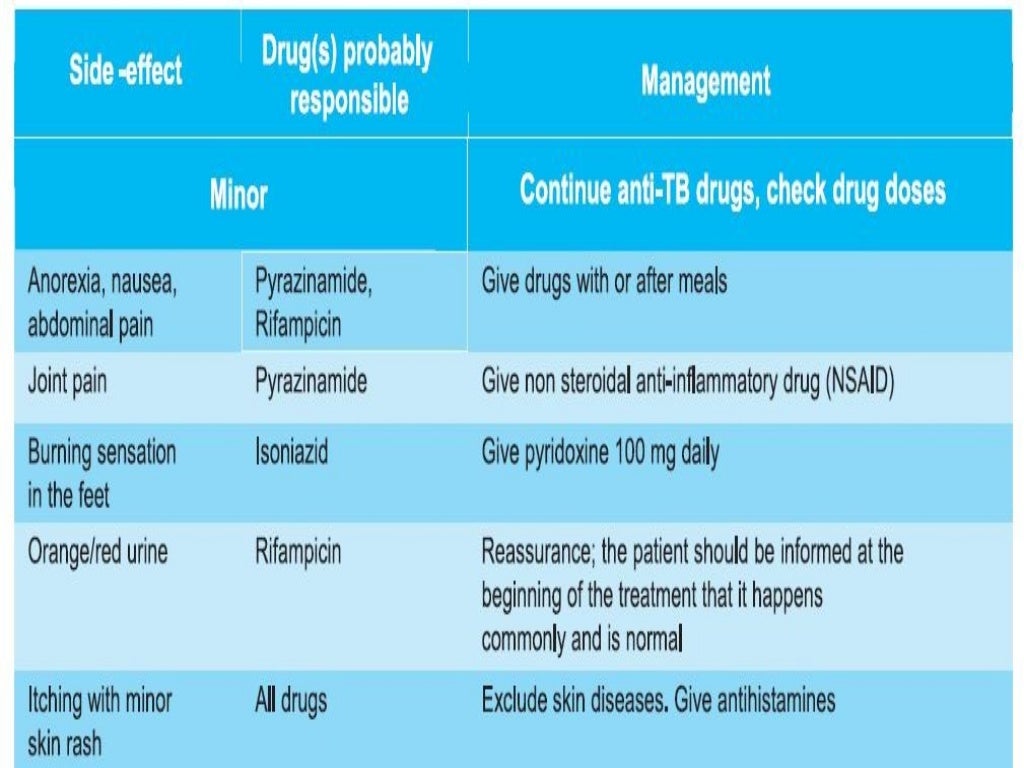
Can TB drugs cause liver damage?
Serious side effects of TB drugs aren't common but can be dangerous when they do occur. All tuberculosis medications can be toxic to your liver. When taking these medications, call your doctor immediately if you have any of the following:
How does physical health affect mental health?
Your physical health can affect your mental health. Denial, anger and frustration are normal when you must deal with something as challenging as tuberculosis. Talking to someone such as a therapist might help you develop coping strategies.
How long does it take to cure TB?
The right treatment can cure about 90 percent of the patients. People who have Tb have to be on medication for about 6 to 9 months. Most people get better in a few weeks, but the bacteria is still in the body. To be completely cured from TB you need many months of treatment.
What happens if you don't take TB medicine?
If you don't take the medicine you will increase the risk of complications and death from TB. TB can't go away without any type of treatment, Prognosis of people with untreated TB is far way worse than those who had treatment. Data shows that about 50 percent of people who aren't treated from TB die in 5 years.
What happens if you stop taking a drug?
If you stop taking the medication you where supposed to take it can make it more difficult and you may develop Drug-resistant TB. This does not respond to the general medications, it needs more medications, it's more harder to treat and has a bigger risk of death than the people who don't have drug-resistant TB.
Is tuberculosis a curable disease?
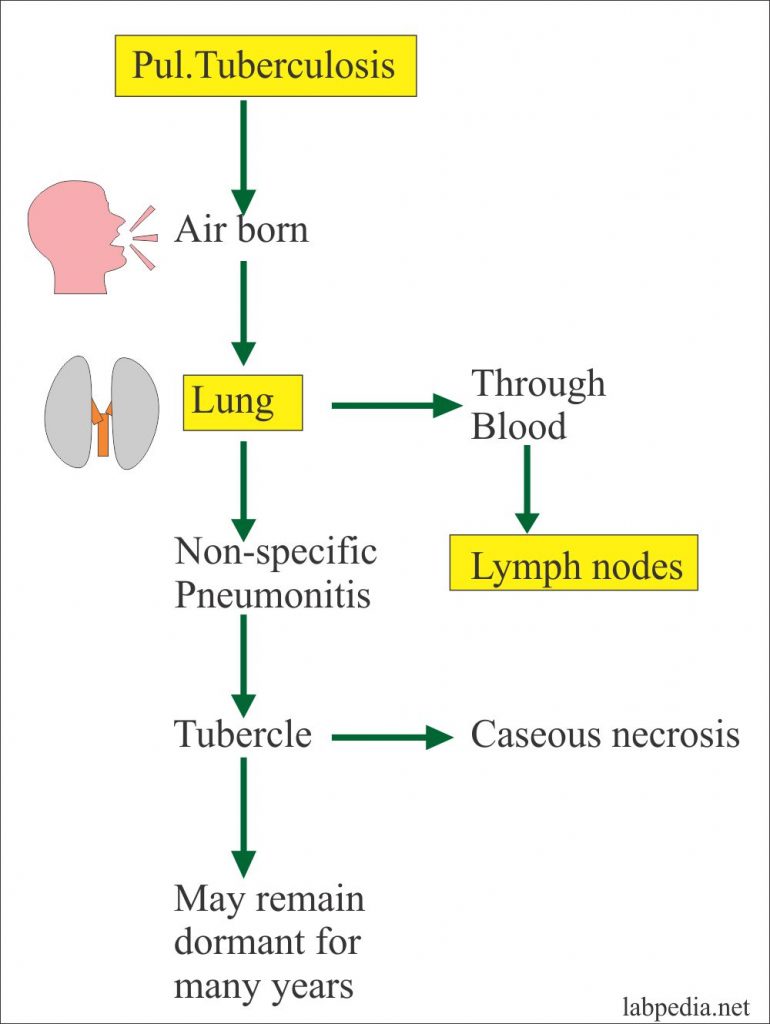
Tuberculosis is a curable disease. Progress of tuberculosis from infection to frank illness involves overcoming of the immune system defences by the bacteria. As the bacteria start to multiply, it affects the immune system and finally overwhelms it to cause the disease.
How does tuberculosis progress?
Progress of tuberculosis from infection to frank illness involves overcoming of the immune system defences by the bacteria. As the bacteria start to multiply, it affects the immune system and finally overwhelms it to cause the disease.
Does smoking increase the risk of tuberculosis?
Other risk factors that increase the risk of poor prognosis include smoking more than 20 cigarettes a day that raises risk of tuberculosis itself by two to four times . Diabetes also worsens the prognosis and outcome of tuberculosis. Other disease states that raise risk of tuberculosis and worsen prognosis include: Hodgkin lymphoma.
What are the predictors of poor prognosis?
Predictors of poor prognosis. Some predictors of a poorer prognosis include extreme ages and other medical conditions. In Africa, tuberculosis mainly affects young adults and teenagers. In some developed countries, however, tuberculosis mainly affects the elderly.
What happens when the immune system weakens?
When the immune system weakens for some reason (e.g. HIV infection, diabetes, renal disease etc.) there is reactivation of the infection. The risk of this reactivation rises when immunity is suppressed. For example, those with concomitant HIV infection have an increased risk of reactivation of tuberculosis of 10% each year of infection.
How long does it take to treat TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
What is the best treatment for TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: 1 isoniazid (INH) 2 rifampin (RIF) 3 ethambutol (EMB) 4 pyrazinamide (PZA)
Can TB make you sick?
TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours. It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed.
How many drugs are there for TB?
There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF) ethambutol (EMB) pyrazinamide (PZA) TB Regimens for Drug-Susceptible TB.
What is the first line of anti-TB drugs?
Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF) ethambutol (EMB) pyrazinamide (PZA) TB Regimens for Drug-Susceptible TB.
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
How long does it take to treat TB?
The treatment for this type of TB takes much longer, 20 to 30 months to complete, and you may experience more side effects.
What is the best treatment for TB?
The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three other drugs—rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol. You may begin to feel better only a few weeks after starting to take the drugs but treating TB takes much longer than other bacterial infections.
What are the side effects of TB?
While you are in treatment for active TB disease, you will need regular checkups to make sure your treatment is working. Everyone is different, but there are side effects associated with taking the medications, including: 1 Upset stomach, nausea and vomiting or loss of appetite 2 Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet 3 Itchy skin, rashes or bruising 4 Changes in your eyesight or blurred visions 5 Yellowish skin or eyes 6 Dark-colored urine 7 Weakness, fatigue or fever that for three or more days
How to protect yourself from TB?
If you have active TB disease, it will take a few weeks of treatment before you can't spread TB bacteria to others. Until your healthcare provider tells you to go back to your daily routine, here are ways to protect yourself and others near you: 1 Take your medicine exactly as the healthcare provider directed. 2 When you cough, sneeze or laugh, cover your mouth with a tissue. Put the tissue in a closed bag and throw it away. 3 Do not go to work or school until your healthcare provider says it's okay. 4 Avoid close contact with anyone. Sleep in a bedroom alone. 5 Air out your room often so the TB germs don't stay in the room and infect someone else.
Can you get TB from taking too much medicine?
You must finish your medicine and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If you stop taking the drugs too soon you can become sick again and potentially spread the disease to others. Additionally, by taking the drugs incorrectly, TB germs that are still alive may become drug-resistant, making it harder for you to get better next time.
What are the symptoms of TB?
Yellowish skin or eyes. Dark-colored urine. Weakness, fatigue or fever that for three or more days. It is important to tell your doctor or TB nurse immediately if you begin having any unusual symptoms while taking medicine for either preventive therapy or for active TB disease.
Can TB cause liver damage?
TB drugs can be toxic to your liver, and your side effects may be a warning sign of liver damage . If you are having trouble with tingling and numbness, your doctor may prescribe a vitamin B6 supplement while you are in treatment. It may also be possible to change TB medications if your side effects are serious.
What are the complications of tuberculosis?
Back pain and stiffness are common complications of tuberculosis. Joint damage. Arthritis that results from tuberculosis (tuberculous arthritis) usually affects the hips and knees. Swelling of the membranes that cover your brain (meningitis).
Can tuberculosis be treated with antibiotics?
Many tuberculosis strains resist the drugs most used to treat the disease. People with active tuberculosis must take many types of medications for months to get rid of the infection and prevent antibiotic resistance.
How is tuberculosis spread?
The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread from person to person through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes.
Where is tuberculosis common?
This recommendation includes people who: Are from a country where TB is common, such as several countries in Latin America, Africa and Asia.
Is tuberculosis contagious?
Although tuberculosis is contagious, it's not easy to catch. You're much more likely to get tuberculosis from someone you live or work with than from a stranger. Most people with active TB who've had appropriate drug treatment for at least two weeks are no longer contagious.
Why did tuberculosis increase in the 1980s?
HIV and TB. Since the 1980s, tuberculosis cases have increased dramatically because of the spread of HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. HIV suppresses the immune system, making it difficult for the body to control TB bacteria.
Can TB cause symptoms?
Symptoms. Although your body can harbor the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, your immune system usually can prevent you from becoming sick. For this reason, doctors make a distinction between: Latent TB. You have a TB infection, but the bacteria in your body are inactive and cause no symptoms.

Primary Tuberculosis
- In primary tuberculosis, that forms around 1 to 5% of all cases, the progression of the infection to frank disease occurs soon after infection. In many, the initial infection is latent tuberculosis. The disease may remain dormant within the body with the immune system capable of containing the infection. When the immune system weakens for some reason (e.g. HIV infection, diabetes, rena…
Tuberculosis Concomitant with HIV Infection
- Tuberculosis concomitant with HIV infections is on the rise and this makes detection and treatment a challenge. In addition, the rise of drug-resistant strains of tuberculosishave contributed to the epidemic and there are 20% of cases of tuberculosis which are caused by strains of tuberculosis that are resistant to standard treatments and 2% of the strains are resista…
Predictors of Poor Prognosis
- Some predictors of a poorer prognosis include extreme ages and other medical conditions. In Africa, tuberculosis mainly affects young adults and teenagers. In some developed countries, however, tuberculosis mainly affects the elderly. Other risk factors that increase the risk of poor prognosis include smoking more than 20 cigarettes a day that rais...
Further Reading