Explore
If the sarcoma returns at a distant site, chemo may be given. If the sarcoma has spread only to the lungs, it may be possible to remove all the areas of spread with surgery. Radiation is used to treat sarcomas that spread to the brain, as well as any recurrences that cause symptoms such as pain.
What are the treatment options for lung sarcoma?
In rare cases, amputation is needed to remove the entire limb with the tumor. Radiation therapy with or without chemo can be used alone when the tumor's location or size or the patient's health in general makes surgery impossible. Stage IV soft tissue sarcoma A sarcoma is considered stage IV when it has spread to distant parts of the body.
What are the treatment options for Stage IV soft tissue sarcoma?
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be administered by pill or through a vein (intravenously). Some forms of soft tissue sarcoma respond better to chemotherapy than do others. For instance, chemotherapy is often used to treat rhabdomyosarcoma.
How is chemotherapy used to treat soft tissue sarcoma?
A subset analysis suggested that patients with sarcomas of the extremities may have benefited from adjuvant chemotherapy, with a reported 7% absolute OS improvement at 10 years (hazard ratio [HR] death, 0.8; P = .029). [ 41]
How effective is adjuvant chemotherapy for sarcoma of the extremities?

How is soft tissue sarcoma treated?
Treatment of recurrent soft tissue sarcoma may include the following:Surgery (wide local excision) with or without radiation therapy.Surgery (amputation; rarely done).Surgery to remove cancer that has recurred in the lungs.Targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (pazopanib or imatinib).Chemotherapy.More items...•
What is the latest treatment for soft tissue sarcoma?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted accelerated approval to olaratumab (Lartruvo®) for the treatment of some patients with soft tissue sarcoma.
How long does sarcoma treatment take?
In general, sarcoma treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery. For example, treatment for osteosarcoma may involve nine weeks of chemotherapy, surgery to remove the tumor and rebuild the bone and another five months of chemotherapy. However, experiences may differ for different people.
Do you need chemo for soft tissue sarcoma?
You usually have chemotherapy before surgery if you have a soft tissue Ewing sarcoma and a type of rhabdomyosarcoma called embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. For some types of soft tissue sarcoma, radiotherapy may be better at shrinking the tumour before surgery.
Does Chemo work on sarcoma?
Sarcoma chemotherapy uses powerful medications to destroy cancerous cells. Chemo can be used to treat both osteosarcomas and soft tissue sarcomas, and it can be given at any point in a patient's treatment plan.
How often is chemo given for sarcoma?
Chemotherapy for soft tissue sarcoma is most often given through a needle into a vein (intravenously). It is usually given for a few days every 3 weeks. How often and how long chemotherapy is given depends on the type of drug or drug combination used. It is usually given for several months.
How long do you stay in hospital after sarcoma surgery?
Some people stay in hospital for a day or two, but others stay for longer – in some cases several weeks or, rarely, months. Along with discharge papers, the medical team may give you: scan and test results.
What is the prognosis for soft tissue sarcoma?
Overall, the 5-year survival rate for soft tissue sarcomas is about 65%. The 5-year survival rate for cancer that has reached nearby organs or lymph nodes is about 50%. Once soft tissue sarcoma has spread to other parts of the body, the 5-year survival rate is about 18%.
Is sarcoma surgery painful?
Surgery for sarcoma frequently causes nerve damage as the dissection often violates the internervous plane. Nerve damage may cause neuropathic pain (NP), which can result in persistent pain after surgery.
What is the most effective treatment for sarcoma?
Small low-grade sarcomas can usually be effectively removed by surgery alone. Those that are high grade and larger than 2 inches (5 cm) are often treated with a combination of surgery and radiation therapy. Radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be used before surgery to shrink the tumor and make removal easier.
Can radiotherapy cure sarcoma?
Radiation therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses high-energy X-rays to destroy sarcoma cells. Doctors usually recommend radiation in combination with surgery to remove a soft tissue sarcoma. Whether you receive radiation therapy before or after surgery depends on the size and location of the tumor.
Does sarcoma spread quickly?
Most stage II and III sarcomas are high-grade tumors. They tend to grow and spread quickly. Some stage III tumors have already spread to nearby lymph nodes. Even when these sarcomas have not yet spread to lymph nodes, the risk of spread (to lymph nodes or distant sites) is very high.
How to cure soft tissue sarcoma?
The only way to cure a soft tissue sarcoma is to remove it with surgery, so surgery is part of the treatment for all soft tissue sarcomas whenever possible. Treatment of Soft Tissue Sarcomas, by Stage.
What kind of doctor treats sarcomas in the abdomen?
These doctors could include: An orthopedic surgeon: specializes in diseases of the bones, muscles, and joints (for sarcomas in the arms and legs) A surgical oncologist: treats cancer with surgery (for sarcomas in the abdomen [belly] ...
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What is the process of finding out if a sarcoma has spread?
After adult soft tissue sarcoma has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread within the soft tissue or to other parts of the body. The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the soft tissue or to other parts of the body is called staging.
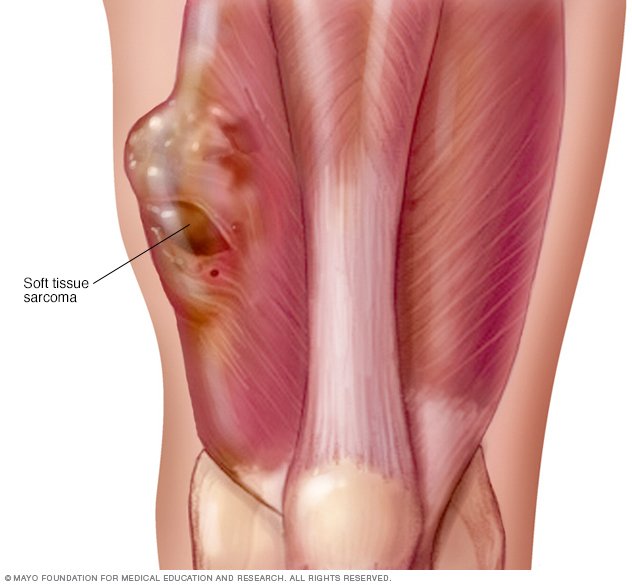
What is soft tissue sarcoma?
Adult soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the soft tissues of the body. The soft tissues of the body include the muscles, tendons (bands of fiber that connect muscles to bones), fat, blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves, and tissues around joints. Adult soft tissue sarcomas can form almost anywhere in ...
How do pathologists find out the grade of a tumor?
A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells and to find out the grade of the tumor. The grade of a tumor depends on how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope and how quickly the cells are dividing. High-grade tumors usually grow and spread more quickly than low-grade tumors.
Where does sarcoma form?
Soft tissue sarcoma forms in soft tissues of the body, including muscle, tendons, fat, blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves, and tissue around joints. There are many types of soft tissue sarcoma. The cells of each type of sarcoma look different under a microscope, based on the type of soft tissue in which the cancer began.
How does chemo work?
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body ( systemic chemotherapy ).
Can inherited disorders cause sarcoma?
Having certain inherited disorders can increase the risk of adult soft tissue sarcoma. Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer.
Is metastatic sarcoma the same as primary cancer?
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if soft tissue sarcoma spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually soft tissue sarcoma cells. The disease is metastatic soft tissue sarcoma, not lung cancer. YouTube.
What is the best way to treat sarcoma?
Biopsy. If a soft tissue sarcoma is suspected, it's often best to seek care at a medical center that sees many people with this type of cancer. Experienced doctors will select the best biopsy technique to ensure proper surgical treatment and planning. Options include: Core needle biopsy. Tiny tubes of tumor material can be obtained by this method.
How to treat soft tissue sarcoma?
Surgery. Surgery is a common treatment for soft tissue sarcoma. Surgery generally involves removing the cancer and some healthy tissue surrounding it. When soft tissue sarcoma affects the arms and legs, radiation and chemotherapy may be considered to shrink the tumor to avoid amputation.
What kind of doctor treats soft tissue sarcoma?
If your family doctor suspects you have soft tissue sarcoma, you'll likely be referred to a cancer doctor (oncologist) who specializes in sarcomas. Soft tissue sarcoma is fairly rare and is best treated by someone who has experience with it, often at an academic or specialized cancer center.
How does chemo help with sarcoma?
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be administered by pill or through a vein (intravenously). Some forms of soft tissue sarcoma respond better to chemotherapy than do others. For instance, chemotherapy is often used to treat rhabdomyosarcoma.
What is intraoperative radiation?
During intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT), radiation is directed through the surgical incision onto a specific site. The dose of IORT can be much higher than is possible with standard radiation therapy given from the outside of the body. Radiation therapy involves treating cancer with high-powered beams of energy.
Why is it important to determine the exact nature of each tumor?
Diagnosis. Because there are so many different types of soft tissue sarcoma, it's important to determine the exact nature of each tumor so that the best treatments can be chosen.
What is the best way to remove a tumor?
Options include: Core needle biopsy. Tiny tubes of tumor material can be obtained by this method. Doctors typically try to take samples from several sections of the tumor. Surgical biopsy. In some cases, your doctor might suggest surgery to obtain a larger sample of tissue or to simply remove a small tumor entirely.
What is the best way to treat sarcoma?
Staging has an important role in determining the most effective treatment for soft tissue sarcoma. Clinical staging involves magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and/or computed tomography (CT) of the primary tumor area and a chest CT scan to look for metastasis to the lung (the most common site of distant spread).
Why is it so difficult to resection a retroperitoneal sarcoma?
Complete surgical resection of retroperitoneal sarcomas is often difficult because of their large size before detection and anatomical location. [ 1, 2] As opposed to soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities, local recurrence is the most common cause of death in patients with retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcomas.
What is isolated limb perfusion?
Isolated limb perfusion is under investigation as a means to deliver high doses of chemotherapy and permit limb salvage in unresectable primary or recurrent extremity soft tissue sarcomas that would otherwise require amputation, in the opinion of the surgeon. [ 59, 60] Common drugs used in the procedure are tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, melphalan, and interferon-gamma. Experience is limited to case series with response rates and reported avoidance of amputation as the outcome. [ 59, 60 ] [ Level of evidence: 3iiiDiv] The technique requires specialized expertise to avoid severe local and systemic toxicity including systemic effects of TNF-alpha. The technique has not been directly compared with standard approaches using combined systemic and local therapy.
What is the DFS rate for preoperative chemotherapy?
In retrospective studies, preoperative chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy has resulted in DFS rates of 80% to 90% compared with about 60% in historical controls. [ 48 - 50]
What is the role of radiation in limb preservation?
Radiation plays an important role in limb-sparing therapy . Pre- and postoperative external-beam radiation therapies (EBRT), as well as brachytherapy, have been shown to decrease the risk of local recurrence. They have not been shown to increase OS in prospective trials but are used to avoid amputation for all but the most locally advanced tumors or for limbs seriously compromised by vascular disease, where acceptable functional preservation is not possible. In the case of EBRT, irradiation of the entire limb circumference is avoided to preserve vascular and nerve structures that are critical to function and preservation of the limb.
What is the eighth edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual?
The eighth edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual has designated staging by the following criteria: tumor size, nodal status, histologic grade, metastasis, and anatomic primary tumor site (head and neck; trunk and extremities; abdomen and thoracic visceral organs; retroperitoneum; and unusual histologies and sites). [ 4 - 8] For information on unusual histologies and sites, refer to the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual . [ 8]
Is brachytherapy an adjuvant therapy?
Brachytherapy has also been investigated as an adjuvant therapy for soft tissue sarcomas. Although it has possible advantages of convenience and less radiation to normal surrounding tissue relative to EBRT, the two treatment strategies have not been directly compared in terms of efficacy or morbidity. However, adjuvant brachytherapy has been compared with surgery without radiation.
Overview
Soft tissue sarcoma is the term for a large group of rare cancers with one thing in common: Each one affects your muscles, tendons, fat, lymph and blood vessels, and nerves. Nearly all soft tissue sarcomas in adults develop in your arms and legs, chest and stomach.
Symptoms and Causes
Soft tissue sarcoma symptoms can seem like common problems that will go away. The difference is the problems persist, and usually become more noticeable. You might have:
Diagnosis and Tests
Healthcare providers will use a variety of imaging tests to begin diagnosis:
Prevention
While researchers don’t know all risk factors for soft tissue sarcoma, they believe the following factors might increase your risk:
Living With
Soft tissue sarcoma treatment is a marathon, not a sprint. Here are some suggestions to help you through that journey:
Frequently Asked Questions
Children and adults respond differently to soft tissue sarcoma treatment. Children might have slightly better outcomes than adults.
What is the treatment for R2?
Treatment options following an R2 resection include definitive RT, systemic therapy, radical surgery, ablation procedures, or observation. RT may be administered definitively or in the adjuvant setting (following an R1/R2 resection).
When is a short course of observation considered?
In the event of disease progression, a short course of observation may again be considered if the patient is minimally symptomatic or the anatomic location is not critical. For patients who exhibit ongoing progression with potential morbidity and significant symptoms, intervention is recommended.
Is a sarcoma a bone tumor?
Collectively, sarcomas are a heterogenous group of solid tumors of mesenchymal origin. They can be divided broadly into sarcomas arising from soft tissues (such as fat, muscle, blood vessels, nerve/nerve sheath, and other connective tissues) and those arising from bone. Although bone sarcomas are covered in the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) for Bone Cancer, and Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs) are now detailed in their own separate NCCN Guidelines, the NCCN Guidelines for Soft Tissue Sarcoma address in depth the following soft tissue sarcoma (STS) subtypes: STS of extremity/body wall, head/neck, retroperitoneal and intraabdominal STS, desmoid tumors (aggressive fibromatosis), and rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS).
How do you treat sarcoma?
Treatment. Sarcoma is usually treated with surgery to remove the cancer. Other treatments might be used before or after surgery. Which treatments are best for you will depend on the type of sarcoma, its location, how aggressive the cells are and whether cancer has spread to other parts of your body.
What is the goal of sarcoma surgery?
Surgery. The goal of surgery for sarcoma is to remove all of the cancer cells. Sometimes it's necessary to amputate an arm or leg to remove all of the cancer, but surgeons try to preserve limb function when possible.
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy drugs work by interfering with that process. Ablation therapy. Ablation therapy treatments destroy cancer cells by applying electricity to heat the cells, very cold liquid to freeze the cells or high-frequency ultrasound waves to damage the cells. Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Immunotherapy . Immunotherapy is a drug treatment that uses your immune system to fight cancer. Your body's disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells. Immunotherapy drugs work by interfering with that process. Ablation therapy.
How to make decisions about sarcoma?
Learn enough about sarcoma to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your cancer, including your test results, treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As you learn more about cancer, you may become more confident in making treatment decisions. Keep friends and family close. Keeping your close relationships strong will ...
What tests are used to diagnose sarcoma?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose sarcoma and determine its extent (stage) include: A physical exam. Your doctor will likely do a physical exam to better understand your symptoms and look for other clues that will help with your diagnosis. Imaging tests. Which imaging tests are right for you will depend on your situation.
How to deal with cancer?
Keep friends and family close. Keeping your close relationships strong will help you deal with your cancer. Friends and family can provide the practical support you'll need, such as helping take care of your home if you're in the hospital. And they can serve as emotional support when you feel overwhelmed by cancer.
What is the FDA approved treatment for soft tissue sarcoma?
FDA-approved indication: In combination with doxorubicin, for the treatment of adult patients with soft tissue sarcoma (STS) with a histologic subtype for which an anthracycline-containing regimen is appropriate and which is not amenable to curative treatment with radiotherapy or surgery. FDA-approved indication: Advanced soft tissue sarcoma (STS) ...
What is soft tissue sarcoma?
Listen. Soft tissue sarcoma is a form of cancer that occurs due to abnormal and uncontrolled cell growth of the "soft tissues" of the body. These tissues connect, support and surround other body parts and may include muscle, fat, blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves, tendons and the lining of joints. Many people with early soft tissue sarcoma have ...
Can soft tissue sarcoma cause pain?
Many people with early soft tissue sarcoma have no signs or symptoms of the condition. When present, symptoms depend on the location and size of the tumor but may include a palpable lump under the skin, pain, or difficulty breathing. [1] [2] [3] Most cases occur sporadically in people with little to no family history of the condition.
Can radiation therapy cause soft tissue sarcoma?
People who have previously received radiation therapy and those with certain inherited disorders (such as Gorlin syndrome, Gardner syndrome, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Tuberous sclerosis, neurofibromatosis type 1, and Werner syndrome) have an increased risk of developing a soft tissue sarcoma. [1] . The best treatment options depend on many factors ...
Does Mayo Clinic have a soft tissue sarcoma page?
Mayo Clinic has an information page on Soft tissue sarcoma. MedlinePlus was designed by the National Library of Medicine to help you research your health questions, and it provides more information about this topic.
