How do you give somatostatin analogs?
You usually have somatostatin analogues as an injection under the skin (subcutaneously) or into the muscle (intramuscularly). You usually have treatment every 4 weeks. Your nurse usually gives you the injections. If you have lanreotide, they may show you how to give the injections yourself.
What are the side effects of somatostatin analogs?
Somatostatin analogues do not usually cause many side effects. The most common side effects are: Having somatostatin analogues over many months can cause gallstones. Gallstones are small stones that form in the gallbladder.
What is the role of somatostatin in the treatment of intestinal cancer?
It can reduce abdominal blood flow therefore somatostatin analogs can be used to reduce bleeding from esophageal varices. Somatostatin analogs are used for treatment of tumors secreting vasoactive intestinal peptide, carcinoid tumors, glucagonomas and various pituitary adenomas.
What are the benefits of somatostatin analogs for esophageal varices?
Somatostatin also decreases the release of most gastrointestinal hormones and reduces gastric acid and pancreatic secretion. It can reduce abdominal blood flow therefore somatostatin analogs can be used to reduce bleeding from esophageal varices. Somatostatin analogs are used for treatment...
Which is a long acting analogue of somatostatin?
The long-lasting formulation of the somatostatin analogue octreotide (octreotide-LAR) can be administered once-monthly and has been shown to provide similar efficacy to subcutaneous octreotide administered three times a day in the control of flushing and diarrhoea associated with the carcinoid syndrome.
How are somatostatin analogs administered?
Somatostatin analogs are given as intramuscular and subcutaneous injections and oral tablets to treat the following: Acromegaly. Carcinoid tumor. VIPoma (a type of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor)
What is the half life of somatostatin?
Its half-life is between 1 to 3 minutes. Somatostatin produces predominantly neuroendocrine inhibitory effects across multiple systems.
What is SSA treatment?
Somatostatin analogue (SSA) therapy has been a mainstay of antisecretory therapy in functioning neuroendocrine tumors, which cause various clinical symptoms depending on hormonal hypersecretion.
How long can you take Sandostatin?
Extended-release Sandostatin LAR Depot is also used to treat acromegaly if you have tolerated immediate-release Sandostatin treatment. For this purpose, the typical starting dosage is 20 mg injected into your buttocks every 4 weeks. This dosage is given for at least 3 months.
How long can you take octreotide?
For long-acting injection dosage form: For treatment of acromegaly: Adults—At first, 20 milligrams (mg) injected into the buttocks once every 4 weeks for 3 months. Your doctor will adjust your dose as needed and tolerated.
What is somatostatin analogue?
Somatostatin analogues are drugs that stop your body from making too many hormones. Some neuroendocrine tumours (NETs) make large amounts of hormones that cause a group of symptoms called carcinoid syndrome. Somatostatin analogues are a possible treatment for people with carcinoid syndrome.
How do you give a somatostatin infusion?
Posology and Method of Administration The recommended dose is 3.5 mcg/kg body weight, ie, one 250 mcg vial for a 75-kg patient, diluted immediately prior to use with a solvent of 2 mL sodium chloride 0.9 w/v provided and given as a slow intravenous bolus over not less than 1 minute.
Does somatostatin increase blood glucose?
In studies on healthy human subjects, infusion of natural somatostatin results in a transient increase in glucose for about 6 h, despite a sustained suppression of insulin and glucagon (Rizza et al.
Is somatostatin a chemotherapy?
by Drugs.com Sandostatin is not a chemotherapy drug, it is a man-made hormone that has similar effects to somatostatin, a hormone produced naturally in our bodies by our hypothalamus and some other tissues such as the pancreas and the gastrointestinal tract.
What are the common side effects associated with somatostatin analogues?
The side effects of somatostatin analogs consist mainly of steatorrhea, which can be controlled; diarrhea and loose stools; malabsorption; gastrointestinal cramps; and occasional nausea. Somatostatin inhibits gallbladder contractions, and approximately 27% of patients treated with Sandostatin developed gallstones.
How does a somatostatin work?
In your pancreas, somatostatin prevents (inhibits) the release of pancreatic hormones, including insulin, glucagon and gastrin, and pancreatic enzymes that aid in digestion. In your gastrointestinal (GI) tract, somatostatin reduces gastric secretion, which is stimulated by the act of eating.
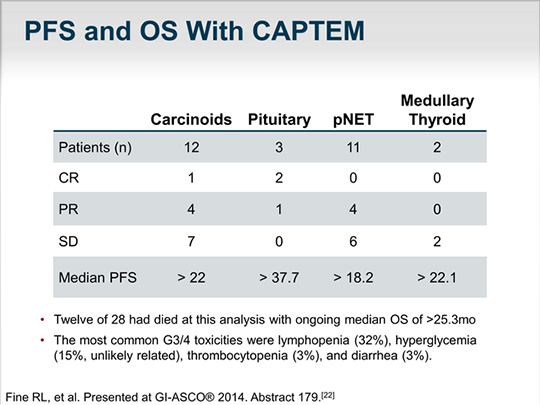
SOMATOSTATIN ANALOG THERAPIES
To date, in appropriate patients, somatostatin analogs are the only proven therapy for the management of hormonal symptoms resulting from NETs. In addition, some studies have shown that somatostatin analog treatment may also help to stabilize disease in patients with NETs.
Lanreotide acetate – Somatuline
The treatment of enteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours in adult patients with Grade 1 or a subset of Grade 2 (equivalent to Ki67<10%) unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic disease, to delay progression.
Octreotide – Sandostatin (subcutaneous and intravenous infusion)
SANDOSTATIN* is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of metastatic carcinoid tumors where it suppresses or inhibits the severe diarrhea and flushing episodes associated with the disease.
Octreotide acetate – Sandostatin LAR (intramuscular)
SANDOSTATIN* LAR* is indicated for the treatment of the severe diarrhea and flushing episodes associated with carcinoid tumors in patients in whom symptoms are adequately controlled on s.c. treatment with SANDOSTATIN*.
Octreotide acetate – Ocphyl
OCPHYL is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of metastatic carcinoid tumors where it suppresses or inhibits the severe diarrhea and flushing episodes associated with the disease.
What is somatostatin analog?
What are Somatostatin and somatostatin analogs? Somatostatin is a hormone produced by the hypothalamus and some other tissues such as the pancreas and the gastrointestinal tract. It inhibits the release of growth hormone from the anterior pituitary, and insulin and glucagon from the pancreas. Somatostatin also decreases the release ...
Does somatostatin help with esophageal varices?
It can reduce abdominal blood flow therefore somatostatin analogs can be used to reduce bleeding from esophageal varices.
How often do you get somatostatin injections?
You usually have treatment every 4 weeks. Your nurse usually gives you the injections. If you have lanreotide, they may show you how to give the injections yourself.
What is somatostatin analogue?
A somatostatin analogue is a man made (synthetic) version of somatostatin. It slows down the production of hormones, especially the growth hormone and serotonin. This helps to control the symptoms of carcinoid syndrome such as diarrhoea and flushing of the skin. It may also shrink the NET.
What is the name of the analogue of somatostatin?
The most common somatostatin analogue drugs used are octreotide (also known as Sandostatin) and lanreotide (also known as Somatuline Autogel). We have more information about octreotide and lanreotide.
What gland is somatostatin made of?
It is made by: a gland in the brain called the hypothalamus. the stomach. the pancreas. the bowel. Somatostatin does a number of things. It slows down or stops the production of a number of hormones such as insulin and gut hormones. It also controls the emptying of the stomach and bowel.
What are the different types of somatostatin?
Somatostatin is a hormone made naturally in the body. It is made by: 1 a gland in the brain called the hypothalamus 2 the stomach 3 the pancreas 4 the bowel
Can somatostatin cause gallstones?
Somatostatin analogues do not usually cause many side effects. The most common side effects are: Having somatostatin analogues over many months can cause gallstones. Gallstones are small stones that form in the gallbladder.