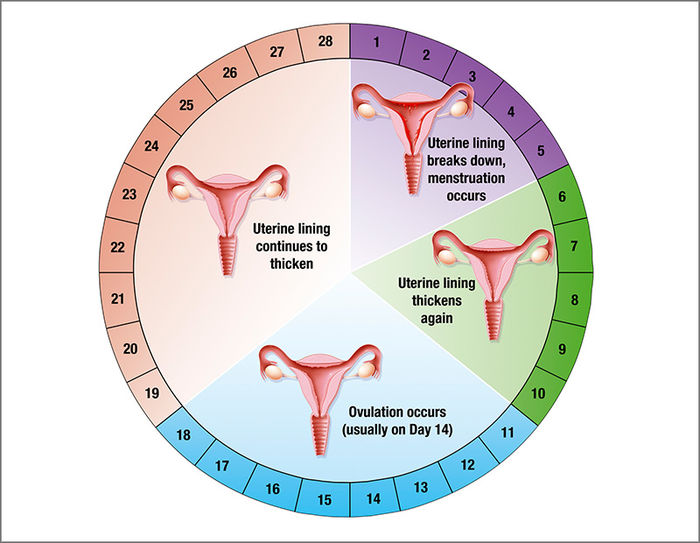
What are the causes of recurrent miscarriage?
1. Black Haw...
2. False Unicorn Root...
3. The Combination Of False Unicorn And Lobelia...
4. Maca...
5.progesterone cream...
6.Vitex...
7.Cramp Bark...
8. Partridgeberry...
Learn More...What causes missed miscarriage at 9 weeks?
What causes recurrent pregnancy loss?
- Genetic (embryo or parents) Random chromosomal abnormalities of the embryo are common and comprise 50-80% of all first trimester losses.
- Uterine anomalies. About 15% of all repeated miscarriages are caused by a uterine structural problem. ...
- Endocrine issues. ...
- Autoimmune diseases: Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. ...
- Environmental factors. ...
What are the medicines that can cause miscarriage?
Why will miscarriage happen at 9 weeks?
- Genetic anomalies ( the commonest)
- Advanced age more than 35 years
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Infections
- Abnormal uterus
- Drug abuse

How to cure a recurrent miscarriage?
Recurrent miscarriage treatment is based on their causes, but the most effective treatment to cure recurrent miscarriage is In Vitro Fertilization. During the IVF process, chromosomes abnormalities and embryos genetics are treated, and normal embryos would be used to expand the chances of pregnancy.
How to reduce the chances of a miscarriage?
To reduce the chances of recurrent miscarriages and expand the chances of a successful pregnancy, you need to change your daily routine, such as limiting alcohol and smoking, which reduces the chances of a successful pregnancy.
How many weeks before a miscarriage can you have a recurrent miscarriage?
The recurrent miscarriage can even be diagnosed after two pregnancies according to the guidelines of the USA and Europe. The loss of pregnancy in three rows before 24 weeks of pregnancies with no successful pregnancy happening between them is defined as recurrent miscarriage in the UK.
What are the leading causes of miscarriage?
Chromosomal abnormalities is one of the leading factors of recurrent miscarriage. You can ask your doctor to analyse your chromosomes and how they can treat them.
What does it mean when you hear the word "recurrent miscarriage"?
Recurrent miscarriage refers to pregnancy loss or defined as two to three times loss of a fetus before the 20 weeks of gestation which means before the fetus can live inside the womb of women.
What is the condition that leads to a recurrent miscarriage?
Antiphospholipid Syndrome is the condition that leads to clotting of the blood, which further increase the chance of recurrent miscarriage. Thrombophilia is a condition in which blood clots are more likely to be than normal, leading to recurrent miscarriage.
What are the emotional challenges of a miscarriage?
Women who face the issue of recurrent miscarriage may undergo several emotional challenges such as anxiety and depression. They might feel jitters to think about the prospect of becoming pregnant again or embracing their dreams of parenthood. In addition to this, women even might experience relationship strain with their male partners.
What is a recurrent miscarriage?
Recurrent miscarriages are defined as three or more consecutive miscarriages .[1] The Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine[3] defines recurrent pregnancy loss as by two or more failed clinical pregnancies. The risk of recurrent spontaneous miscarriage is much higher in patients with previous losses. The risk of miscarriage after two consecutive losses is 17% to 25% and the risk of miscarrying fourth pregnancy after three consecutive losses is between 25% and 46%. The risk gets worse with increasing maternal age.[4] The evidence suggests higher frequency of spontaneous miscarriages amongst subfertile couples and a higher prevalence of subfertility in women with recurrent spontaneous miscarriages when compared with the general population.[5] Self-reported losses by patients may not be accurate. In one study, only 71% of self-reported clinical pregnancy losses could be verified in hospital records.[6] It is important to define pregnancy as a clinical pregnancy documented by ultrasonography or histo-pathological examination (Evidence level IV).
How many women have spontaneous miscarriages?
Spontaneous miscarriage is a major loss for all pregnant women. It affects 1% of all women.[1] The incidence of spontaneous miscarriage may be much greater than is clinically recognized. Spontaneous miscarriage occurs in 12% to 15% of all pregnancies. Thirty percent pregnancies are lost between implantation and sixth week. Maternal age and previous miscarriages increases risk of subsequent miscarriages.[2] The management of recurrent miscarriages is an unsolved problem; up to 50% of cases of recurrent losses will not have a clearly defined etiology. The investigations and management of recurrent miscarriages is one of the most debated topics. This review is aimed to provide evidence-based approach to manage recurrent pregnancy loss. This review is structured to be clinically relevant.
What percentage of miscarriages are caused by chromosome abnormalities?
The prevalence of chromosome abnormalities in women facing a single sporadic miscarriage is to be 45%. [7] Approximately 50% to 60% of early spontaneous miscarriages are associated with a chromosomal anomaly of conceptus. Most common abnormality is aneuploidy, with autosomal trisomy accounting for more than 50% of chromosomally abnormal abortuses.[8] A strong family history of recurrent miscarriage or genetic anomaly suggests a parental karyotypic abnormality, and a chromosomal analysis of the affected partner is appropriate in the primary evaluation. Chromosomal analysis of the miscarriage offers an explanation in at least 50% of cases.[9] Parental karyotyping is not predictive of a subsequent miscarriage.[10] Routine karyotyping of couples with recurrent miscarriage is not recommended. Cytogenetic analysis may be performed on products of conception to avoid unnecessary evaluation and treatment and because an aneuploid conceptus indicates a somewhat greater likelihood of success with a subsequent pregnancy[10] (Evidence Level III).
Does insulin resistance cause recurrent miscarriages?
Insulin resistance plays a significant role in recurrent pregnancy loss.[53] Insulin resistance can be independent of polycystic ovarian status. Women with a history of recurrent miscarriage are at an increased risk for insulin resistance during the first trimester of a new pregnancy.[54,55] Recent meta-analysis concluded that insulin resistance is associated with the susceptibility to recurrent miscarriages, and it may contribute to the occurrence of recurrent miscarriages.[56] Therefore, insulin resistance might be one of the direct causes that lead to recurrent miscarriage.[57]
Can a polycystic ovary cause a miscarriage?
It has been reported that hypersecretion of basal LH with or without polycystic ovaries is a risk factor for miscarriage. Women with elevated LH, a frequent feature of the polycystic ovary syndrome, are at increased risk for miscarriage after either spontaneous or assisted conception. However, suppression of endogenous LH release before conception, in women with elevated circulating LH concentrations and a history of recurrent miscarriage, did not improve the live birth rate. Neither an elevated serum luteinizing hormone concentration (>10 IU/l) nor an elevated serum testosterone concentration (>3 nmol/l) was associated with an increased miscarriage rate.[52]
Is a shortened luteal phase considered a pregnancy loss?
The shortened luteal phase has been associated with pregnancy loss but the assessment and interpretation of a putative luteal phase defect is problematic. The use of histological and biochemical endpoints as diagnostic criteria for endometrial dating are unreliable (Evidence level III).
What to do if you have two miscarriages?
However, if you’ve had two or more miscarriages and haven’t had any successful pregnancies, you must consult a fertility specialist ASAP.
How many miscarriages occur in the first 12 weeks?
75% of miscarriages happen in the first 12 weeks and many of those women are not even aware that they are pregnant when the loss occurs.
What percentage of miscarriages have anomalies?
13% of recurrent miscarriage patients are noted to have anomalies in their uterine cavity—arcuate uterus, septate uterus, unicornuate or bicornuate uterus and a didelphys uterus.
Why is IVF so unsuccessful?
Unsuccessful IVF or early loss of IVF pregnancy is often attributed to poor genetic condition of the female egg.
What percentage of pregnancy losses are attributed to chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus?
60% of pregnancy losses are attributed to chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.
How many chances are there of having a baby if you have one pregnancy?
If you have successfully achieved one pregnancy, you have 80 percent chances of having healthy pregnancies and babies in the future, said Henry Lerner, MD, clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Harvard Medical School and author of ‘Miscarriage: Why it Happens and How Best to Reduce Your Risks.’
Can you have a miscarriage if you have two pregnancies?
American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) is now considering that the term ‘Recurrent Miscarriage’ may be used even if you’ve lost two pregnancies consecutively.
What is a recurrent miscarriage?
Recurrent miscarriage is when a woman has two or more clinical pregnancy losses (miscarriages). After three miscarriages, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends a physical exam and further testing, but Women & Infants Fertility Center initiates an evaluation after two miscarriages.
How many patients have a clear diagnosis of a recurrent miscarriage?
Approximately 50 percent of patients who are evaluated for recurrent miscarriage have a clear diagnosis. The remaining patients do not have a defined cause of their recurrent miscarriage diagnosis.
How many women have a recurrent miscarriage?
The likelihood of recurrent miscarriage is small. According to ACOG, about 5 percent of women have two or more consecutive miscarriages and 1 percent will have three or more. The risk of recurrent miscarriage is higher in women who are over the age of 35 or who have had previous miscarriages.
What causes miscarriage in the neck?
Thyroid/hormonal issues – An overactive or underactive thyroid (endocrine gland at the base of the neck) can result in hormonal imbalances. Hormonal imbalances can cause a miscarriage if the uterine lining doesn’t develop normally for implantation and nourishment of a fertilized egg. Elevated prolactin (reproductive hormone produced in the pituitary gland) levels can alter proper development of the uterine lining.
Why do miscarriages occur?
The majority of miscarriages occur as a result of genetic abnormalities in the embryo or fetus, such as an extra chromosome or missing chromosomes. These are typically random mutations that are not likely to recur. In recurrent miscarriage, however, the situation is different and the doctor will look for a specific type of mutation called a balanced translocation. While associated with recurrent miscarriage, it is still a very uncommon occurrence.
How much does a woman's risk of miscarriage increase as she ages?
As a woman ages, the risk of miscarriage due to genetic abnormalities increases from 15 to 20 percent if she is under age 35, to more than 50 percent if she is over 40 years old. A genetic abnormality can occur when an embryo (fertilized egg) receives an abnormal number of chromosomes during fertilization.
What is the term for a condition in which scar tissue forms inside the uterus and may result in misc?
Asherman’s syndrome – A condition in which scar tissue forms inside the uterus and may result in miscarriage.
What to do if you have a miscarriage?
If you have signs or symptoms of miscarriage, contact your health care provider right away. Depending on the circumstances, you might need immediate medical care.
What is the procedure called when you have a miscarriage?
Surgical treatment. Another option is a minor surgical procedure called suction dilation and curettage (D&C). During this procedure, your health care provider dilates your cervix and removes tissue from the inside of your uterus. Complications are rare, but they might include damage to the connective tissue of your cervix or the uterine wall. Surgical treatment is needed if you have a miscarriage accompanied by heavy bleeding or signs of an infection.
How long does it take for a miscarriage to happen?
Usually this happens within a couple of weeks of determining that the embryo has died. Unfortunately, it might take up to three or four weeks. This can be an emotionally difficult time.
How many weeks before a miscarriage?
Complete miscarriage. If you have passed all the pregnancy tissues, it's considered a complete miscarriage. This is common for miscarriages occurring before 12 weeks.
How long does it take to recover from a miscarriage?
In most cases, physical recovery from miscarriage takes only a few hours to a couple of days. In the meantime, call your health care provider if you experience heavy bleeding, fever or abdominal pain.
What test can be used to confirm a miscarriage?
Tissue tests . If you have passed tissue, it can be sent to a lab to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred — and that your symptoms aren't related to another cause.
Can you forget your dreams about your pregnancy?
You'll likely never forget your hopes and dreams surrounding this pregnancy, but in time acceptance might ease your pain. Talk to your health care provider if you're feeling profound sadness or depression.
What is the treatment for RPL?
In cases where an abnormality of chromosome structure is causing RPL, one possible therapy is in vitro fertilization (IVF), with biopsy and chromosomal evaluation of each embryo, called pre-implantation genetic diagnosis.
What tests are used to evaluate the uterine cavity?
Anatomical Abnormalities. Diagnostic tests such as hysterosalpingograms, saline sonohysterograms and hysteroscopy (an endoscopic inspection of the uterus) can be used to evaluate the uterine cavity. Many abnormalities within the uterine cavity can be corrected with minor surgery.
Can blood thinners prevent miscarriage?
Currently, there is no evidence that blood thinning medications can prevent miscarriage, although studies are ongoing.
What can be done to fix a miscarriage?
Surgery can fix some problems in the uterus (womb), like extra tissue that divides the uterus (septum), some fibroids (benign tumors), or scar tissue. Correcting the shape of the inside of the uterus can often lower the chance for miscarriage.
How to prevent miscarriage?
In general, whatever is healthy for a woman improves the chance of a healthy pregnancy. Stopping cigarette smoking and stopping illicit drug use (such as cocaine) will lower the risk for miscarriage. Limiting alcohol and caffeine intake may also help.
What is recurrent pregnancy loss?
This is called recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL). Women and families often grieve these losses deeply. Women may also worry that they are sick or did something to cause the losses. RPL, however, is often a natural process. Less than half of recurrent miscarriages have an obvious or treatable cause. Almost two-thirds of women with RPL will eventually ...
What happens after IVF?
During IVF, eggs and sperm are mixed outside of the body in a laboratory. After IVF, before the embryos are returned to the uterus, they can be tested (preimplantation genetic screening). This allows embryos without translocations to be chosen to increase the chance of a healthy pregnancy. Lifestyle Choices.
What are the best ways to prevent a full term pregnancy?
Treating medical conditions such as diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, or high prolactin levels can improve the chances of having a healthy, full-term pregnancy. Genetic screening. In about 5% of couples with RPL, one of the parents has a rearrangement (translocation) of their chromosomes.
What to do if you have two miscarriages?
If you have suffered two or more miscarriages, you should talk with your health-care provider. Often, women decide to continue trying to get pregnant naturally. However, in certain situations, your doctor might suggest treatments to help reduce your risk for miscarriage. Surgery.
How long does it take to heal a uterus?
This is usually a 1-day procedure and recovery time is a few days to a week. Women with autoimmune or clotting (thrombophilia) problems may be treated with low-dose aspirin and heparin.
Why do you have to have blood tests for miscarriages?
You may have blood tests to detect problems with the immune system . Testing may be done to help detect genetic causes of repeated miscarriages. Imaging tests may be considered to find out if a uterine problem is causing repeated miscarriages.
What are the problems with reproductive organs associated with repeated miscarriages?
Are problems with reproductive organs associated with repeated miscarriages? Certain congenital problems of the uterus are linked to repeated miscarriages . Although there are many such disorders, one of the most common that has been associated with miscarriage is a septate uterus. In this condition, the uterus is partially divided ...
Can polycystic ovary syndrome cause miscarriage?
Women with a condition called polycystic ovary syndrome also have an increased risk of miscarriage. How common is it that a cause for repeated miscarriages cannot be identified? In 50–75% of women with repeated miscarriages, no cause can be found for the pregnancy loss.
Can repeated miscarriages be genetic?
Are there other genetic problems associated with repeated miscarriages? In a small number of couples who have repeated miscarriages, one partner has a chromosome in which a piece is transferred to another chromosome. This is called a translocation.
Can APS cause miscarriage?
APS is associated with repeated miscarriages and fetal deaths. Another disease that can lead to miscarriage is diabetes mellitus. In this disease, high levels of a sugar called glucose are present in the blood. Women with diabetes, especially those in whom the disease is poorly controlled, have an increased risk of pregnancy loss.
