Medication
If the patient remains in ventricular fibrillation, pharmacological treatment should begin. Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes. If epinephrine is not effective, the next medication in the algorithm is amiodarone 300 mg.
Procedures
Continued VF calls for another shock, followed by good CPR once again for 2 minutes. If the patient remains in ventricular fibrillation, pharmacological treatment should begin. Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes.
Nutrition
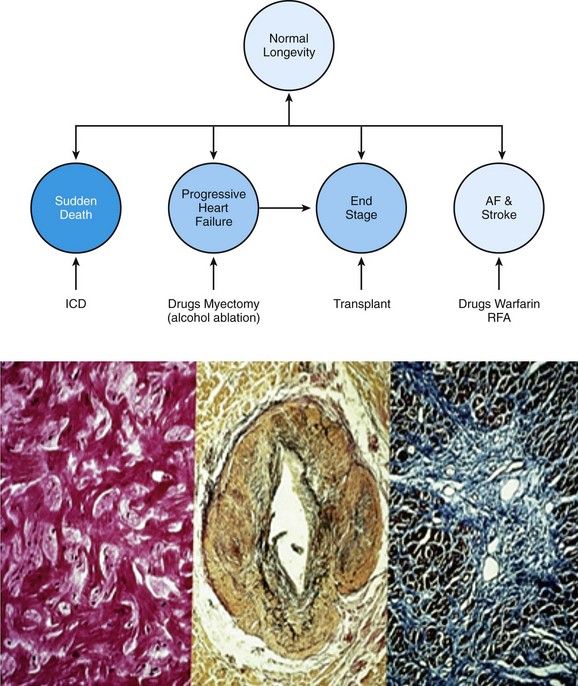
Reducing your risk If you’re at risk for ventricular fibrillation and its serious consequences, your doctor may recommend: Arrhythmia medications, which can help control rhythm disturbances An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), which can correct abnormal heart rhythms
What is the first drug given for ventricular fibrillation?
A disorganised chaotic contraction of the ventricle that fails to effectively eject blood from the ventricle. During ventricular fibrillation the patient is unconscious and will die if emergency intervention is not undertaken The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition. Activity ?
What is the initial treatment for ventricular fibrillation (VF)?
How can I reduce my risk for ventricular fibrillation?
What is ventricular fibrillation?
What is the first line treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
If the patient remains in ventricular fibrillation, pharmacological treatment should begin. Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes. If epinephrine is not effective, the next medication in the algorithm is amiodarone 300 mg.
What is ventricular fibrillation and how it can be treated?
Ventricular fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, that affects your heart's ventricles. Ventricular fibrillation is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. CPR and defibrillation can restore your heart to its normal rhythm and may be life saving.
What triggers ventricular fibrillation?
Ventricular fibrillation is most commonly caused by the following: Heart disease. Heart attack or chest pain (angina). Diseases that change the structure of the heart by making its walls thicker or weaker.
Which antiarrhythmic drug is best for continuous ventricular fibrillation?
As a result of its greater efficacy, amiodarone is the most common antiarrhythmic agent used for suppression of VT in patients with structural heart disease and ICDs.
Can ventricular fibrillation stop on its own?
Ventricular fibrillation seldom terminates spontaneously, since several re-entrant wavefronts, independent from each other, coexist, and the simultaneous extinction of all the circuits is unlikely.
Which is worse atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia?
Is AFib or VFib more serious and dangerous? By far, VFib is more serious. If ventricular fibrillation isn't treated immediately, the patient will have a “sudden death” or “cardiac arrest” and die.
How do you fix ventricular fibrillation?
Treatment for ventricular fibrillation includes medications, medical devices and surgery....Surgery or other proceduresImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). ... Cardiac ablation. ... Coronary angioplasty and stent placement. ... Coronary bypass surgery.
How long can ventricular fibrillation last?
Duration: The estimated disappearance rate of VF was slow. Thirty minutes after collapse approximately 40% of the patients were in VF. Survival: Overall survival to 1 month was only 1.6% for patients with non-shockable rhythms and 9.5% for patients found in VF.
Can stress cause ventricular fibrillation?
Out of the 96 studies related to psychosocial aspects of arrhythmic risk conducted among different populations, 92% of the studies demonstrated positive correlation between psychosocial stressors and arrhythmias [10]. Emotional stressors can lead to ventricular ectopic beats and ventricular tachycardia.
What is the safest antiarrhythmic drug?
Of all antiarrhythmic agents, dofetilide and amiodarone have been proven safe in patients with heart failure.
Which is better amiodarone or flecainide?
Flecainide, at the doses administered in this study, is more effective than propafenone and amiodarone for conversion of acute atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm. Propafenone and amiodarone have similar conversion rates, although propafenone was faster in achieving the conversion to sinus rhythm.
Which is safer amiodarone or flecainide?
Overall, these analyses suggest that acute and chronic therapy with flecainide does not confer a mortality benefit or risk compared with controls in patients with AF, but that flecainide may confer a lower mortality risk compared with sotalol and amiodarone.
What is the most important intervention for cardiac arrest?
Irrespective of the cause of cardiac arrest, the most important interventions are early recognition and calling for help—including appropriate management of the deteriorating patient—early defibrillation, high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) with minimal interruption of chest compressions, and treatment of reversible causes. 6
What is VF in cardiac arrest?
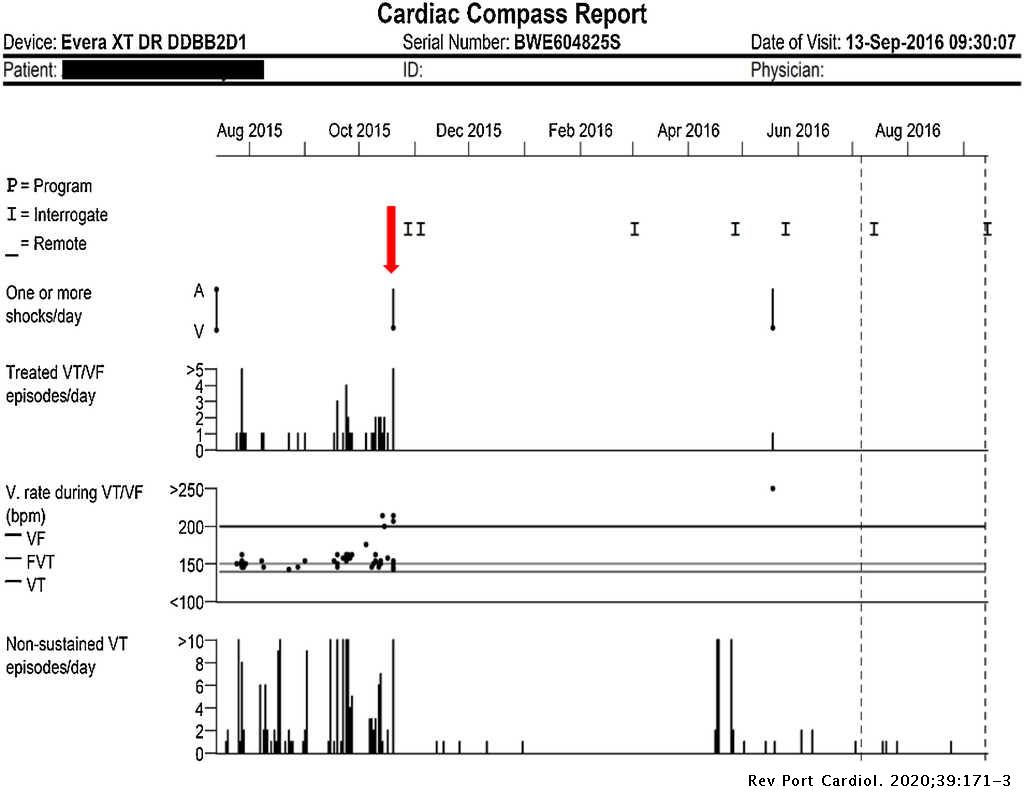
Ventricular fibrillation (VF or V-fib) is the most common initial heart rhythm in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), and the most salvageable one . 5 In VF, the etiology of arrest is often attributed to either acute ischemia or non-ischemic arrhythmia. 8
How many joules should a defibrillator be?
If the defibrillator is biphasic, the manufacturer recommended joules should be selected (usually 120 to 200 joules). If the amount is unknown, use the maximum available and subsequent doses should be equivalent, and possibly higher. 1.
What are the causes of VF?
The easiest way to remember the most common causes of VF are to review the reversible “Hs and Ts” in cardiac arrest. The Hs include hypoxia, hypovolemia, hypothermia, hyper/hypokalemia, and hydrogen ions (acidosis). The Ts are tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, toxins, and thrombosis (pulmonary or coronary).
What is the most important algorithm for resuscitation?
Ventricular fibrillation falls under the ACLS Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm and is the most important algorithm to know for adult resuscitation. 1 Ventricular fibrillation treatment starts with early and effective CPR with the application of oxygen and monitor/defibrillator placement. Keeping the brain, heart, ...
Drugs used to treat Ventricular Fibrillation
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What is the best treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
Reducing your risk. If you’re at risk for ventricular fibrillation and its serious consequences, your doctor may recommend: Arrhythmia medications , which can help control rhythm disturbances. An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), which can correct abnormal heart rhythms.
What is the most serious cardiac rhythm disturbance?
Ventricular fibrillation, or V-fib, is considered the most serious cardiac rhythm disturbance. Disordered electrical activity causes the heart’s lower chambers (ventricles) to quiver, or fibrillate, instead of contracting (or beating) normally. This prohibits the heart from pumping blood, causing collapse and cardiac arrest.
What to do if you suspect someone is in cardiac arrest?
No normal breathing (the victim is not breathing or is only gasping) If you suspect someone is suffering from cardiac arrest, it’s vital to respond appropriately and quickly. Call 911, give CPR and use an automated external defibrillator (AED) (PDF) if one is available.
What is the best medication for atrial fibrillation?
These medications include dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban. They are shorter acting than warfarin and usually don't require regular blood tests or monitoring by your doctor.
What to do if you think you have atrial fibrillation?
If you think you may have atrial fibrillation, it is critical that you make an appointment with your family doctor. If atrial fibrillation is found early, your treatment may be easier and more effective. However, you may be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist).
How does catheter ablation help with atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is often caused by rapidly discharging triggers, or "hot spots." In catheter ablation to treat atrial fibrillation, a doctor inserts long, thin tubes (catheters) into your groin and guides them through blood vessels to your heart. The electrodes at the tips of the catheters help your doctor determine where these triggers are located. Electrodes at the catheter tips can use radiofrequency energy, extreme cold (cryotherapy) or heat to destroy these triggers, scarring the tissue so that the erratic signals are normalized.
What is the procedure called when a catheter is placed in the left atrium?
Left atrial appendage closure. Your doctor may also consider a procedure called left atrial appendage closure. In this procedure, doctors insert a catheter through a vein in the leg and eventually guide it to the upper left heart chamber (left atrium).
How to diagnose atrial fibrillation?
To diagnose atrial fibrillation, your doctor may review your signs and symptoms, review your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition, including:
What is an ECG test?
Electrocardiogram (ECG). An ECG uses small sensors (electrodes) attached to your chest and arms to sense and record electrical signals as they travel through your heart. This test is a primary tool for diagnosing atrial fibrillation. Holter monitor.
How does cardioversion work?
In this brief procedure, an electrical shock is delivered to your heart through paddles or patches placed on your chest. The shock stops your heart's electrical activity for a short moment. The goal is to reset your heart's normal rhythm.

Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support