
Medication
Nov 25, 2021 · AEDs are the most common used therapy for epilepsy. They assist manipulate seizures in round 7 out of 10 of people. AEDs work through converting the degrees of chemical substances to your brain. They do now no longer therapy epilepsy, however can forestall seizures happening. Common sorts include: ️ Sodium valproate. ️ Carbamazepine
Procedures
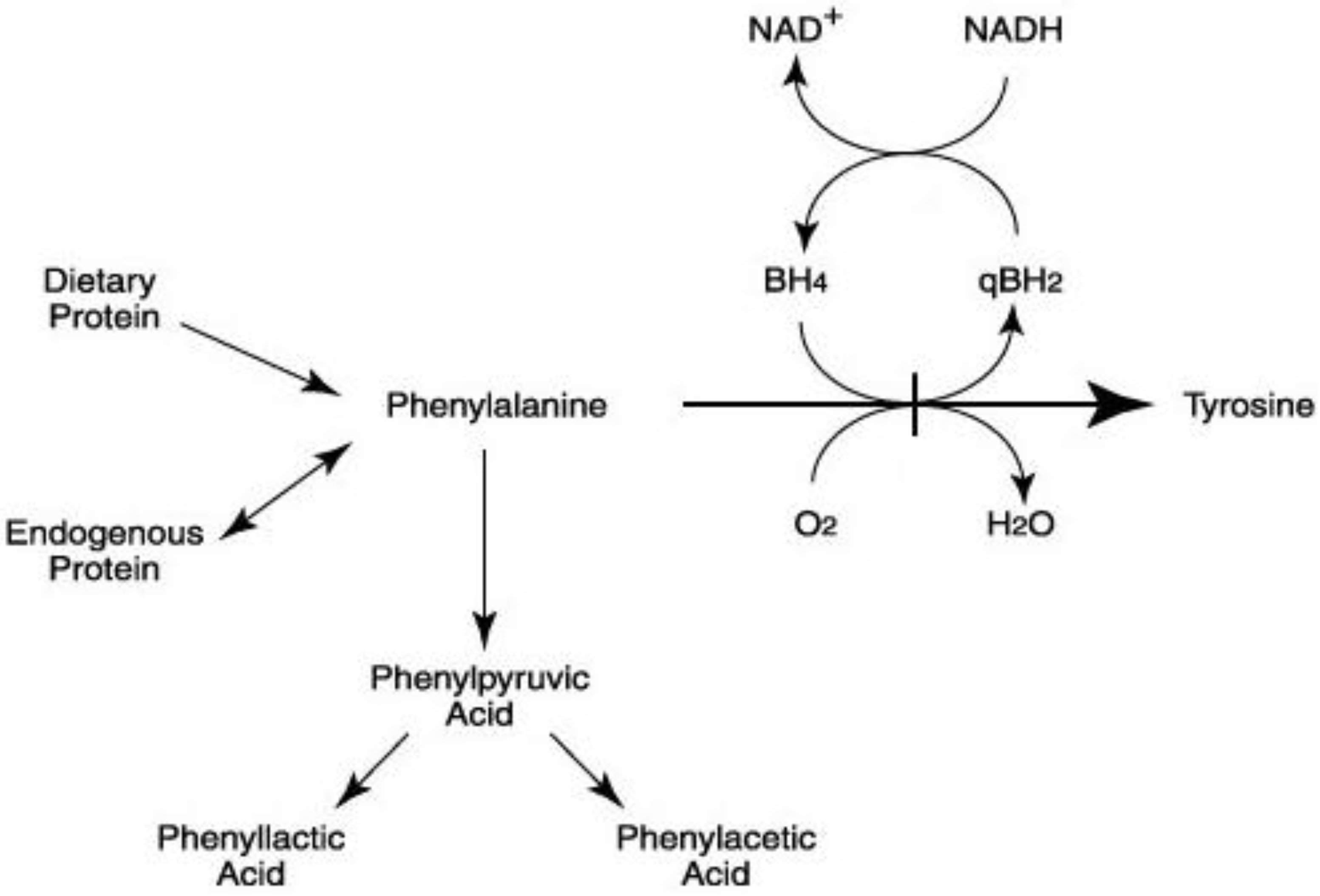
The medications treat the symptoms of epilepsy (the seizures), rather than curing the underlying condition. They are highly effective and completely control seizures in the majority (approximately 70%) of patients. The drugs prevent seizures from starting by reducing the tendency of brain cells to send excessive and confused electrical signals.
Therapy
Apr 23, 2021 · The most common treatment methods for epilepsy include anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs), epilepsy surgery, and device therapies such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), and dietary changes like the ketogenic diet. There is no current cure for epilepsy, but treatment can help control your seizures.
Self-care
Medication remains the most common treatment for people with epilepsy. Most epilepsy syndromes and the vast majority of genetic syndromes …
Nutrition
What is the most common treatment for epilepsy? Ictal EEG proves localisation related epilepsy. The localisation is not to an eloquent part of the brain (i.e. you can cope without that brain part). At least three anti-epilepsy medications taken at full dose for many months prove ineffective. ...
What is the strongest medication for epilepsy?
What is the natural cure for epilepsy?
What are some nonpharmacologic treatment options for epilepsy?
What medications do people with epilepsy use?

What is the first line treatment for epilepsy?
Lamotrigine and levetiracetam are emerging as first-line treatments for epilepsy, which people may be more likely to keep taking than carbamazepine. Reducing the risk of adverse events and treatment withdrawal is important when selecting an anti-epilepsy drug as it usually will need to be taken long-term.Sep 12, 2017
What is the latest treatment for epilepsy?
In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a deep brain stimulation (DBS) device, manufactured by Medtronic, that sends electrical pulses through the brain to reduce the frequency of seizures. (It works by stimulating an important relay station deep in the brain called the thalamus.)Mar 24, 2021
What are 4 drugs to treat epilepsy?
Medicines used to treat epilepsy Carbamazepine, clobazam, clonazepam, eslicarbazepine, ethosuximide, gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, perampanel, phenobarbital, phenytoin, pregabalin, primidone, rufinamide, sodium valproate, tiagabine, topiramate, vigabatrin and zonisamide.
What is the safest epilepsy medication?
"[Lamictal] seems to be the winner," Marson says. The second trial looked at 716 patients newly diagnosed with generalized epilepsy. It compared the older drug valproic acid (in the U.S., Depakote is the most popular member of this drug family) to Lamictal and Topamax.Mar 22, 2007
What is the drug of choice for epilepsy?
Sodium valproate and lamotrigine are the two drugs of choice for generalized epilepsies, as well as for undetermined epilepsies. Lamotrigine is often prefered for women of childbearing age.
What is the most effective seizure medication?
Conclusion: In this study of older adults with epilepsy, lamotrigine was the most effective AED as measured by 12-month retention and seizure freedom, with levetiracetam a close second. Oxcarbazepine was consistently less effective than most other AEDs.
What drugs should epileptics avoid?
Some medicines for seizures can prevent birth control pills from working. Epilepsy drugs known to have this effect include Carbatrol, Dilantin, phenobarbital, Mysoline, Trileptal, and Topamax. Take special precautions if you're older.Apr 28, 2021
What is Keppra used for?
Levetiracetam is used to treat seizures (epilepsy). It belongs to a class of drugs known as anticonvulsants. Levetiracetam may decrease the number of seizures you have.
Where is epilepsy surgery done?
The most common location in the brain for epilepsy surgery is the temporal lobe. About 60 percent to 80 percent of patients become seizure-free with this type of surgery. A new technique is laser surgery, which involves destroying the seizure focus with heat rather than removing it.
How to stop seizures?
Brain surgery. Brain surgery to remove the seizure focus is the most effective method to completely stop seizures. First, we must find the seizure focus and make sure it can be safely removed. This always involves a stay in the epilepsy monitoring unit to record seizures with simultaneous video and EEG.
What is an epileptic seizure?
An epileptic seizure is an excessive, uncontrolled burst of electrical activity from nerve cells in the brain – essentially an electrical storm. There are many types of seizures that cause symptoms ranging from lightning-fast muscle jerks lasting less than a second ...
When are patients invited to participate in a trial?
Often, patients are invited to join a trial after they have failed a number of other FDA-approved medications.
What is the first do no harm movie?
For many years, a special diet has been used to control certain types of epilepsy. One in particular – the ketogenic diet – gained public attention with the 1997 movie “First Do No Harm.” In this film, which is based on a true story, Meryl Streep plays the mother of a son whose epilepsy fails to respond to conventional treatments, including epilepsy surgery. She takes him to Johns Hopkins Medical Center, which pioneered the use of the ketogenic diet and demonstrated its effectiveness. Her son responded wonderfully to the diet and became seizure-free.
What percentage of patients do not respond to medications?
Unfortunately, about 30 percent to 40 percent of patients do not respond to medications at all, and we must consider other therapies. 4. Medical marijuana. Medical marijuana is a term that now refers to one of more than 80 chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant – cannabidiol oil or CBD oil.
What is Ma Huang?
Ma huang is a natural ephedra, which is similar to a stimulant hormone in our bodies. Stimulants tend to worsen seizures, so doctors are hesitant to recommend any herbal remedies at this time. 2. Diet. For many years, a special diet has been used to control certain types of epilepsy.
How to stop seizures in epilepsy?
Treatment can help most people with epilepsy have fewer seizures, or stop having seizures completely. Treatments include: medicines called anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) surgery to remove a small part of the brain that's causing the seizures. a procedure to put a small electrical device inside the body that can help control seizures.
How does epilepsy surgery work?
The surgeon makes a small cut in your scalp and creates an opening in your skull so they can remove the affected part of the brain. The openings in your skull and scalp are closed at the end of the operation.
What is the test for epilepsy?
This will usually involve having several tests, such as: brain scans. an electroencephalogram (EEG) – a test of your brain's electrical activity.
What is keto diet?
A ketogenic diet is a diet high in fats, and low in carbohydrates and protein. In children, the diet is thought to make seizures less likely by changing the levels of chemicals in the brain. The ketogenic diet was one of the main treatments for epilepsy before AEDs were available.
How do AEDs work?
They help control seizures in around 7 out of 10 of people. AEDs work by changing the levels of chemicals in your brain. They do not cure epilepsy, but can stop seizures happening.
What does it mean when you get a rash on a med?
rashes – contact your GP or specialist if you get a rash, as it might mean you're having a serious reaction to your medicine. Contact your GP or specialist if you have symptoms similar to being drunk, such as unsteadiness, poor concentration and being sick. This could mean your dose is too high.
How long does it take for side effects to show on AEDs?
Side effects are common when starting treatment with AEDs. Some may appear soon after starting treatment and pass in a few days or weeks, while others may not appear for a few weeks.
What is the best diet for epilepsy?
Diet therapy may be utilized in some patients with specific forms of epilepsy. The most common diets utilized are the ketogenic diet and the modified Atkins diet. The ketogenic diet is a special high-fat, adequate protein and low carbohydrate diet that is initiated over three to four days in the hospital.
What is the diagnosis of epilepsy?
A doctor makes his or her epilepsy diagnosis based on symptoms, physical signs and the results of such tests as an electroencephalogram (EEG), computed tomography (CT or CAT scan) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is essential that the type of epilepsy and the type of seizures both are diagnosed properly.
What is epilepsy disorder?
Check out the new videos at the bottom of the page. Epilepsy is a disorder of the brain characterized by repeated seizures. A seizure is usually defined as a sudden alteration of behavior due to a temporary change in the electrical functioning of the brain.
How does epilepsy affect the brain?
In epilepsy the brain's electrical rhythms have a tendency to become imbalanced, resulting in recurrent seizures.
What are the two types of seizures?
Typically, seizures belong in one of two basic categories: primary generalized seizures and partial seizures. The difference between these types is in how they begin.
How many people have epilepsy?
According to the Epilepsy Foundation, epilepsy affects three million people in the U.S. and 50 million worldwide. Epileptic seizures may be tied to a brain injury or genetics, but for 70 percent of epilepsy patients, the cause is unknown.
Do seizures need medication?
Some patients who only have a single seizure and whose tests do not indicate a high likelihood of se izure recurrence may not need medications. The medications treat the symptoms of epilepsy (the seizures), rather than curing the underlying condition.
What is the best treatment for epilepsy?
The most common treatment methods for epilepsy include anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs), epilepsy surgery, and device therapies such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), and dietary changes like the ketogenic diet. There is no current cure for epilepsy, but treatment can help control your seizures.
How to stop epilepsy?
These methods include sleeping regularly, managing stress, eating healthy, avoiding illicit drugs and alcohol, and avoiding bright, flashing lights.
What are the side effects of epilepsy?
Different drugs result in various side effects, but the most common side effects of epilepsy medications are: 1 Drowsiness 2 Nausea or vomiting 3 Mood changes 4 Dizziness or blurred vision 5 Confusion or clumsiness 6 Rash
Why is epilepsy so difficult to diagnose?
Epilepsy used to be a mysterious condition that was difficult to diagnose and treat, especially because approximately one-third of patients develop drug-resistant seizures. But with medical advancements in the past decade, new technologies are helping to make treatment more effective.
What is the test for epilepsy?
Other tests for diagnosing epilepsy may include blood tests, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
Where do seizures occur?
Seizures can occur either in a localized section of the brain (focal epilepsy) or throughout the brain (generalized epilepsy). People who typically experience focal epilepsy may be prescribed a narrow-spectrum AED like Neurontin ( gabapentin) or Lyrica ( pregabalin ).
What to do after diagnosis of epilepsy?
After receiving a diagnosis for epilepsy, your health care provider should go over all of your treatment options with you. Treatment plans will vary by case, and be determined based on the types of seizures you have, how they affect you, your age, and your lifestyle.
What are the best treatments for epilepsy?
When epilepsy isn't being controlled by medication and surgery isn't an option, we turn to devices. There are two on the market now: 1 vagus nerve stimulator (VNS). 2 NeuroPace - a reactive neurostimulator
How many people have epilepsy?
This all adds up to a good prognosis for the nearly 3,4 million people with epilepsy in the U.S. With proper treatment, most people with epilepsy can live healthy lives without seizures.
Can you have seizures with epilepsy?
That's what we're aiming for: no seizures, no side effects. If you're still having seizures or side effects with treatment, then you have to seek expert care.
Can epilepsy be cured?
Surgery can lead to long-term remission. It can be a true cure for epilepsy. One study came out in 2001 that showed that about 60% of people who had a temporal lobectomy (in which the temporal lobe located on the side of the brain is removed) had no seizures, or at most, a few auras afterward.
Is keto diet safe for epilepsy?
The Ketogenic Diet for Epilepsy. It can be a valuable tool in certain children with catastrophic epilepsy. About a quarter of the people who go on it get good control of the seizures. The problem is that the safety of the diet for long-term use is in question.
What is a neuropace?
The NeuroPace is a reactive neurostimulator that detects seizures and shocks the brain to stop them. The device is set to send out pulses of a certain duration at certain intervals and it goes around the clock. It uses the technology from cardiac defibrillator devices to respond to electrical activity in your brain.
How does VNS work?
VNS therapy works by sending an electrical pulse to the vagus nerve in the neck. It's not clear how VNS therapy stops seizures, but it's believed that the device blocks certain brain impulses that direct the body to start a seizure. The VNS device is powered by a small battery implanted in the chest.
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment