
The microstructure of a hypoeutectoid steel upon cooling would contain proeutectoid ferrite plus pearlite (α+ Fe3C). The size, type and distribution of phases present can be altered by not waiting for thermodynamic equilibrium. Steels are often cooled so rapidly that metastable phases appear.
Full Answer
What is heat treated steel used for?
Heat treating is applied on steel to optimize grain structure for specific properties, relieve internal hardness, creating the hard cases and tough core for impact applications. Depending upon the cycle given during heat treatment, steel properties can be controlled. What temperature do you heat treat steel?
Does heat treatment affect mechanical properties and microstructure change of selected specimen?
In this study EN 31, EN 24 and EN 8 (alloy steel) are selected as specimens for testing various mechanical properties and microstructure change. The effects of heat treatment on the mechanical properties and microstructure characteristics change of selected specimen are analyzed.
How does heat treatment affect the hardness of steel?
In general, heat treatment is carried out to bring balance between hardness and toughness. With an increase in time and temperature, the hardness of steel decreases. Martensitic transformation is always accompanied by stresses.
What is the final microstructure of hypoeutectoid steel with annealed temperature?
So final microstructure of Hypoeutectoid steel with annealed temperature of 800 o C exists like below; Hypereutectoid region as shown in the figure above is the right side of the eutectoid reaction line starting from 0.8% C to 1.78% C.
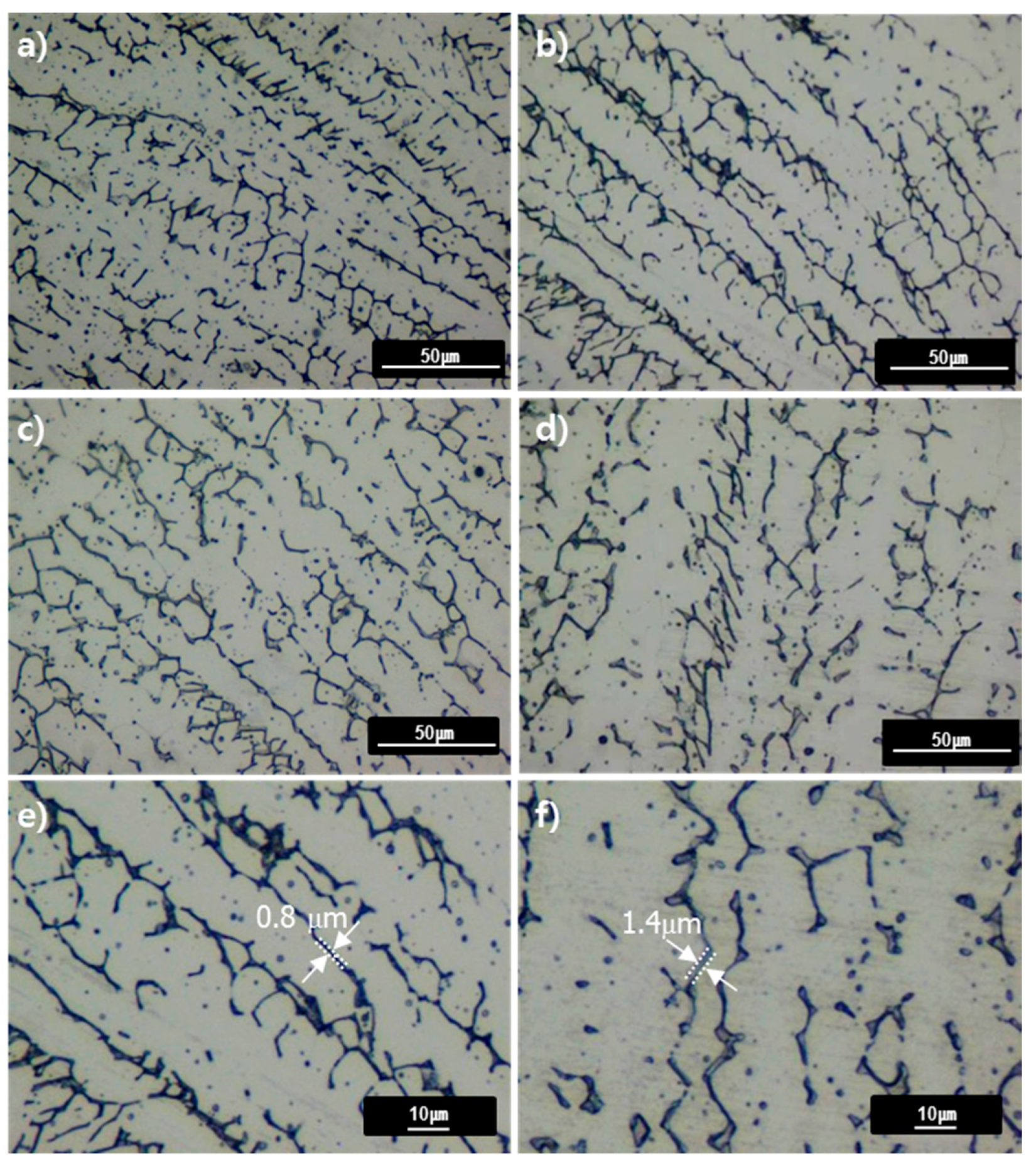
Does heat treatment change microstructure?
The industrial and scientific application of any metal or alloy is determined by its properties. Heat treatment methods are used to alter the microstructure and mechanical properties of steel.
How does heat affect microstructure?
The heating and cooling treatment of the steel specimens have a great effect on the phase of the microstructure of the steel specimen. The addition of alloys or coarsening of the austenitic grain structure increase the hardenability of steel.
What is the microstructure of steel?
The microstructure is predominantly martensite but also has allotriomorphic ferrite, Widmanstätten ferrite, bainite and pearlite. Notice that the spherical shape of a pearlite colony is obvious in this sample because of the lack of impingment.
What happens if you don't heat treat steel?
Watch For Brittleness If you don't temper your metal properly, you'll expose your metal products to potential brittleness. Brittleness occurs when metal is tempered for too short of a time.
What effect does heat treatment have on the resultant steel microstructure?
The heat treatment develops hardness, softness, and improves the mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, ductility, corrosion resistance and creep rupture. These processes also help to improve machining effect, and make them versatile.
How does heat treatment affect a steel grain structure?
Annealing changes a metal's properties by altering and realigning the grain structure using heat, making the metal softer and more ductile. In this process, the steel is heated to just above its re-crystallization point, allowing it to cool slowly.
How many types of microstructure are there in steel?
One is bcc (body centered cubic) and the other is fcc (face centered cubic). The bcc crystalline form (?-iron) is stable until a temperature of 912 deg C when it is transformed to fcc (?-iron). The ?-iron remains stable until 1394 deg C, and then it reverts to bcc structure (?-iron). ?-
What are the types of microstructure?
Microstructures of sand grains.Single grains. Almost entirely formed of sand grains, without, or with very little, fine material between the grains. ... Bridged grains. Sand grains joined by bridges of fine material.Pellicular grains. ... Intergrain vesicles. ... Intergrain channels. ... Compact grains.
What is the strongest steel microstructure?
Martensite: the hardest and strongest microstructure, yet the most brittle.
Why heat treatment of steel is necessary?
Heat treating can improve wear resistance by hardening the material. Metals (including steel, titanium, inconel, and some copper alloys) can be hardened either on the surface (case hardening) or all the way through (through hardening), to make the material stronger, tougher, more durable and more resistant to wear.
What happened to the steel when cooled?
Cooling even faster—for instance, by quenching the steel at about 1,000° C per minute—results in a complete depression of carbide formation and forces the undercooled ferrite to hold a large amount of carbon atoms in solution for which it actually has no room. This generates a new microstructure, martensite.
What happens to steel when heated and cooled?
Summary. 1. In cyclic heating above 780°C (l435°F) and cooling, there is a fall in strength which increases with increase in the carbon content of the steel. This is due to a decrease of the cleavage resistance of the steel as its carbon content increases.
How do you do tempering process?
Tempering steel process after hardening is the heat treatment process carried on as-quenched steel to a temperature that is lower than a lower crit...
How do you temper steel?
Before the start of the post-quench heat treatment process, it is better to bring some insight from the article, “Martensitic transformation” about...
What is quenching and tempering process?
Quenching is name of severe cooling of steel resulting in martensitic steel. Tempering steel process after hardening is the heat treatment process...
What is the difference between hardening and tempering?
Hardening is name of severe cooling of steel resulting in martensitic steel. While, on the other hand, Tempering steel process after hardening is t...
What happens during tempering?
Before the start of the post-quench heat treatment process, it is better to bring some insight from the article, “Martensitic transformation” about...
What is the purpose of tempering steel?
Tempering of steel is post quenching process being used for various reasons including stress relieving, increase in hardness or decress in hardness...
What is difference between annealing and tempering?
Annealing is the process of furnace cooling of steel. While Tempering is post quenching low temperature process.
What is the process of annealing steel?
“ Annealing or softening of steel is the process involved slow heating to a higher temperature above the A1 line to convert pearlite and other low-temperature phases into austenite. ”
What happens to the energy of annealing grains?
When the grains are plastically deformed, stain energy is induced in the grains. When the annealing temperature is increased the thermal energy is also induced. At low temperature-induced thermal energy is very low that results in negligible softening and the softening takes place due to strain energy.
What is the recovery and recrystallization stage?
Normally, recovery and recrystallization stages are linked to cold-worked structures that have developed internal stresses developed in the form of point defects, dislocations, precipitates, and many more. Growth takes place after all internal stresses are released. While, in the absence of cold working and internal stresses, growth is a major phenomenon that occurred during the softening of steel.
What is annealing in chemistry?
When the grains are plastically deformed, stain energy is induced in the grains. When the annealing temperature is increased the thermal energy is also induced. At low temperature-induced thermal energy is very low that results in negligible softening and the softening takes place due to strain energy.
What is a tempering microstructure used for machine tools?
The structure of this type developed during this post-quench heat treatment range is termed as Sorbite. Sorbite is a tempering microstructure used for machine tools.
Why is heat treatment used?
In general, heat treatment is carried out to bring balance between hardness and toughness. With an increase in time and temperature, the hardness of steel decreases. Martensitic transformation is always accompanied by stresses. That’s why post-quench heat treatment can be used for stress relie ve as well.
What causes hardness to decline?
Formation of softer phase ferrite and coarsening of carbides is causing hardness declining trend. The softening stage involves coarsening and loss of coherence by carbides. Increase in hardness due to precipitation of alloy carbides initially dissolved in the matrix.
What happens to the temperature of an alloy steel?
In alloy steels the temperature at which transformations take place changes as a result of which the rate of softening is retarded. The transition carbides (e.g. -iron carbide) and the supersaturated martensitic structure becomes stable at higher tempering temperature and the precipitation and growth of cementite are also delayed.
What is the first stage of tempering steel?
First Stage. The first stage of the tempering steel process exists between 100-250oC. During the first stage, carbon starts nucleating from martensite and results in the formation of epsilon carbide. With depletion go carbon from carbon saturated BCT martensite, it transforms into low carbon martensite.
What equipment is used to measure hardness?
For measurement of hardness, equipment’s like Brinell hardness tester, Vicker hardness tester, and Rockwell hardness tester are employed.
What is the process of tempered steel?
Tempering steel process after hardening is the heat treatment process carried on as-quenched steel to a temperature that is lower than a lower critical temperature line to induce ductility and toughness .
What is the microstructure of ferrous metals?
On a microscopic level, ferrous alloys usually comprise of a granular microstructure that differs according to the alloying elements used, and the temperature to which the metal is heated. Each of these microstructures has specific properties, rendering it suitable or unsuitable for particular applications. Heat treatment processes aim to alter the microscopic structure to the form best suited to the metal component’s intended end-use.
What is decarburization in heat treatment?
In some cases, this is intentional, while in others, it is an unintended side effect of a heat treatment process gone wrong. To avoid decarburization during heat treatment processes, these processes must be carried out in an inert atmosphere.
What are the processes that produce internal stresses?
Manufacturing processes, such as machining, forging, and welding , produce internal stresses in metals. These stresses could reduce the wear- and impact-resistance of the metals, and should thus be remedied, hence the normalizing process.
How hot is brass?
To eliminate these adverse effects, soft-annealing is administered to the final product. Here, brass is heated to between 425 and 650°C (797 and 1202°F) and cooled slowly.
How is copper treated?
Copper and its alloys are usually heat treated through annealing and solution heat treatment . It is also suitable for stress relief heat treatment, similar to that of ferrous alloys. All of these methods reduce stresses formed during cold-working processes, improving the alloy’s ductility and strength.
What is hardening metal?
Hardening is a common heat treatment technique for ferrous metals (metals containing iron). It involves slowly heating the metal to the desired temperature and cooling it rapidly through quenching (discussed later). At the microscopic level, the metal’s grain structure is predictable. This structure depends on the alloy’s constituents and its temperature. Each structural type has specific mechanical properties, such as hardness, tensile strength, and flexibility.
How is aluminum treated?
During the solution heat treatment process, the alloy is heated to 527°C (980°F) and held there for an hour. After this, the metal is quenched in water to retain the desired microstructure. Annealing takes a bit longer and requires lower temperatures. Here, the metal is heated to between 163 and 204°C (325 and 400°F) and held there for one to eight hours. The lower the temperature, the longer the time required.
What is steel heat treating?
Steel Heat treating is a process which involves cooling and heating of a metal substance at usually high temperature and conditions. It is useful for softening, hardening, and changing physical properties. Moreover, you can manufacture various metal structures like glass by passing it through different thermal techniques.
What is the process of hardening steel called?
Quenching heat treatment. The third process of heat treatment of steel is named as Quenching. This process is also called hardening due to the characteristics of metals. In this technique, the solid metal is first heated above the conditions and then quickly allowed to cool down.
What happens to steel when it is soaked in water?
During heat treatment, after soaking steel in the austenite region, it is quenched in water, brine, or oil which drastically increases the hardness of steel. Details can be studies in the Effect of austenitizing temperature and Quenching media on hardening of steel.
What is nitriding in metal?
Nitriding. Nitriding is the sixth process of heat treatment of steels. As Carburizing uses carbon alloy to make the metal hard, this Nitriding process diffuses nitrogen gas on the surface of the solid metal substance. The nitrogen gas absorbs on the surface of the metal and makes it sturdy and more robust.
What is the process of annealing?
The first process through which metal passes through is termed as Annealing. The procedure involves both cooling and heating processes. As a result, the microstructure increases, thus ensuring a change in electrical and mechanical properties. This steel heat-treating process heats the metal at a critical temperature.
How does a metal cool down?
After heating above the critical temperature, the metal can cool down by passing it through the nitrogen air, water, or any polymer. This process is used for hardening the metal as in the previous method of Normalizing, and the steel was softened. The Quenching process has one drawback as it can make the metal brittle.
What is stress normalizing?
The main goal of stress Normalizing is to reduce stress from the heat-treating prestressed machining, and casting-induced stress is also removed by this method. The temperature goes up, then the critical temperature, and then allowed to cool down in the air.
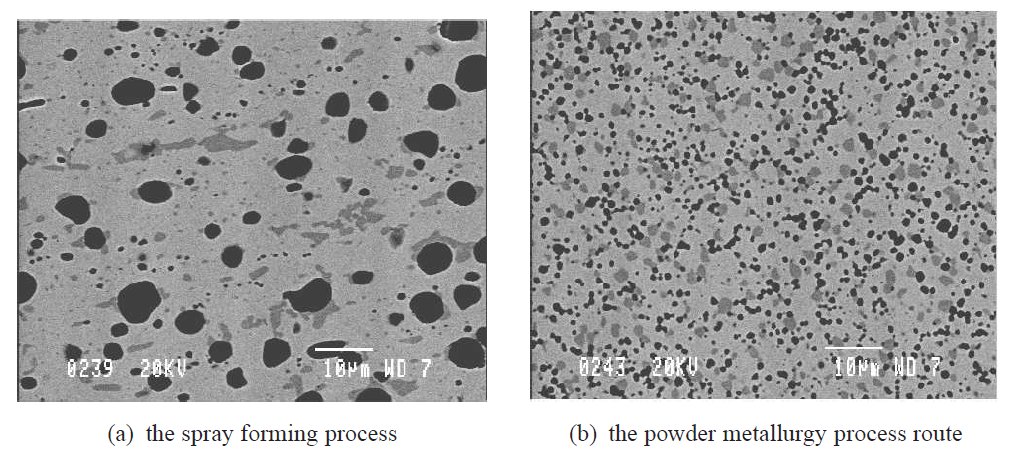
Annealing Definition and Annealing Microstructure
Stages of Annealing
- Steel Annealing is a thermally activated process of stress relieving and microstructure optimization. There are three overlapping stages of Softening as follows; 1. Recovery 2. Recrystallization Normally, recovery and recrystallization stages are linked to cold-worked structures that have developed internal stresses developed in the form of point defects, dislocat…
Types of Annealing
- There are nine types of steel annealingbased on temperature, purpose, and atmosphere of softening, which are as follows; 1. Full Steel Annealing 2. Iso-thermal annealing 3. Diffusion Annealing 4. Partial annealing 5. Recrystallization Steel Annealing 6. Process annealing 7. Spheroidization annealing 8. Bright Steel Annealing 9. Stress-relieve annealing Details of these s…
Steel Annealing Microstructure and Characterization
- Experimentation was carried out on the Mild steel sample in the form of strip. First of all mild steel strip was cold-rolled in the rolling machine in order to get a 25% reduction of the initial thickness. Three small samples were cut from the strip with the help of hand saw and their Rockwell hardness values were recorded. One sample was annealed at 600oC, the second was annealed …
Steel Annealing Conclusion
- Steel samples got recrystallized at all given annealed temperatures which result in a decrease in hardness, grain size, and orientation. But with subsequent increase in annealing temperature, the three factors are reduced to a greater extent due to the excessive growth of grains. The appropriate recrystallization temperature for a 35% reduction is 600 deg C but for a 25 % reducti…