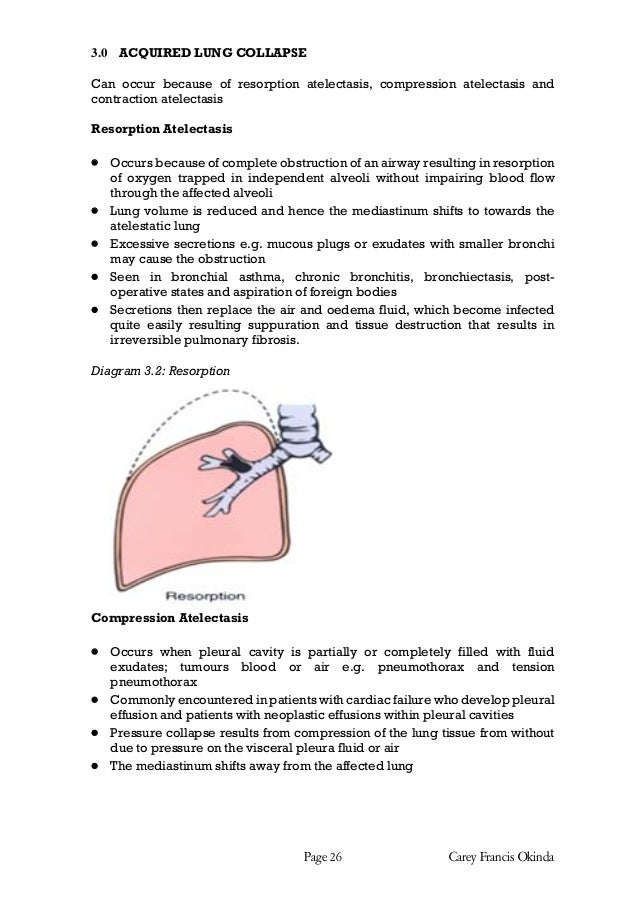
What is a Trapped lung pathology?
Trapped lung syndrome refers to a condition in which the lung does not fully expand during pleural drainage to oppose the chest wall. This form of non-expandable lung is the sequela of prior pleural inflammation that results in the creation of a fibrous peel on the visceral pleura. The resulting negative pleural pressure causes a pleural effusion ex-vacuo.
Is it necessary to treat a Trapped lung?
Trapped lung is one of the outcomes of fibrinous or granulomatous pleuritis and is a cause of chronic, benign, unilateral pleural effusion. It is characterized by inability of the lung to expand and fill the thoracic cavity due to a restricting fibrous visceral pleural peel.
What is the difference between lung entrapment and Trapped lung?
A ‘trapped lung’ is when fluid from the chest is drained away but instead of the lung filling with air again like a balloon the lung stays squashed down. This happens because the cancer causes the outer lining of the lung to become thickened which stops the lung from moving like it …
What is the pressure curve of Trapped lung syndrome?
Trapped lung presents as pleural thickening and loculation without clinically active disease (Figure 20). Silver lining: Imaging manifestations of pleural pathology (7) Drainage by surgical …

How long can you live with a trapped lung?
The management of MPE in the presence of trapped lung is hugely challenging because these patients generally have a poor long-term prognosis with a median survival time of 7 months for mesothelioma up to ∼30 months for metastatic breast carcinoma (7,8).Jun 25, 2020
What does it mean when a lung is trapped?
The trapped lung is defined as the inability of the lung to expand and fill the thoracic cavity because of a fibrinous restrictive pleural layer that prevents normal visceral and parietal pleural apposition. It is caused by remote inflammation of the pleura and typically presents as chronic stable pleural effusion.Sep 22, 2021
How do you get a trapped lung?
Common causes of lung entrapment include malignant pleural effusions, complicated parapneumonic effusions, and endobronchial obstruction that causes a post-obstructive pneumonia with atelectasis.
What causes lung entrapment?
Lung entrapment may result from a visceral pleural peel secondary to active pleural inflammation, infection, or malignancy. In these cases, the underlying malignant or inflammatory condition is the primary clinical problem, which may or may not be complicated by unexpandable lung due to visceral pleural involvement.Oct 21, 2010
Can a trapped lung be cured?
The definitive treatment is surgery including pleurectomy and decortication to remove the fibrosed visceral pleura from the lung to relieve pressure and allow for expansion of the trapped lung.Oct 12, 2021
Is trapped lung fatal?
The long-term impact of pneumothorax can vary. If only a small amount of air is trapped in the pleural space, there may be no further complications. If the volume of air is larger or it affects the heart, it can be life-threatening.Oct 19, 2021
What causes lungs to not fully expand?
Lung damage or scarring can cause the lungs to shrink or become unable to expand fully. Conditions, such as tuberculosis, fibrosis, and other chronic destructive lung conditions, often lead to lung damage.Nov 22, 2020
Can you fly with a trapped lung?
This significant difference from the air pressure at ground level can cause expansion of the air trapped in the patient's pleural space and a worsening of existing pneumothorax. Therefore, if you have an acute pneumothorax, taking a scheduled flight is normally not advisable.
What is decortication surgery?
Decortication is a type of surgical procedure performed to remove a fibrous tissue that has abnormally formed on the surface of the lung, chest wall or diaphragm. Generally, there is a space (called pleural space) in between the lungs and the chest wall, which is lined with a very thin fluid layer for lubrication.
Is respiratory failure a disease?
Chronic respiratory failure is a serious illness that gets worse over time. As the condition increases in severity, people may develop an abnormal heart rhythm, stop breathing, or slip into a coma. To help meet the challenges of living with COPD, we'll send support and advice for both patients and caregivers.
How do you code trapped lung in ICD 10?
J98. 19 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is para pneumonia?
A parapneumonic effusion refers to the accumulation of exudative pleural fluid associated with an ipsilateral lung infection, mainly pneumonia. Parapneumonic effusions are mainly associated with bacterial infections.
Abstract
Study objectives: To review the pleural fluid characteristics, pleural manometry, and radiographic data of patients who received a diagnosis of trapped lung in our pleural diseases service.
Key words
The cause of a pleural effusion can usually be determined by the medical history, physical examination, and pleural fluid analysis. However, some pleural effusions defy diagnosis by such means, and even biopsy may not yield a specific diagnosis.
Materials and Methods
We performed a retrospective review of 247 consecutive patients referred for therapeutic thoracentesis in our database at the Medical University of South Carolina between October 2002 and November 2005. We identified 11 patients in whom a diagnostic pneumothorax was performed in accordance with the clinical protocol that we established in 2001.
Results
Eleven patients with a clinical diagnosis of trapped lung were identified in this series.
Discussion
At our pleural disease service, we are frequently asked to evaluate patients with chronic, persistent pleural effusions that have defied diagnosis and have undergone multiple thoracenteses. In our database, there were patients in whom a diagnostic pneumothorax was induced that provided a confident clinical diagnosis of trapped lung.
Conclusions
Trapped lung represents the end stage of dysfunctional healing of pleural injury that begins as a form of lung entrapment that results in the formation of a visceral pleural peel and a persistent pleural effusion.
Tables
CPE = complicated parapneumonic effusion; L = lymphocyte; Mono = mononuclear cells; Mø = macrophage; NA = not available; Peri = pericardiotomy; Rad = radiation; SBPL = spontaneous bacterial pleuritis.
How to do pursed lip breathing?
Follow these steps to successfully practice pursed-lip breathing: 1 Sit down in a chair with your back straight and your arms stretched out in front of you. 2 Relax your shoulders and back muscles. 3 Breathe in slowly through your nose while keeping your mouth closed. To make sure you are inhaling slowly, count slowly to three. 4 Open your mouth slightly as you would if you were going to whistle. 5 Exhale all of the air in your lungs slowly through your pursed lips. The goal is for this to take longer than the time it took to inhale the air so that you eliminate all of the excess air that has been trapped inside the lungs. 6 Repeat this process until your breathing has returned to normal.
Why is it important to breathe with a pursed lip?
Pursed-lip breathing is effective because it brings oxygen into your lungs and pushes the carbon dioxide out of your lungs. This allows the trapped air to escape while the oxygen saturates the blood in the body.
What is static hyperinflation?
Static hyperinflation is the type of hyperexpanded lungs that relates to most respiratory illnesses. Hyperexpanded lungs can be caused by many different respiratory illnesses that cause air to become trapped inside the lungs. The most common and severe respiratory illnesses that cause hyperexpanded lungs include COPD, emphysema, chronic bronchitis, ...
How to prevent hyperexpanded lungs?
You can improve and potentially prevent hyperexpanded lungs from occurring by practicing your breathing through a technique called pursed-lip breathing. Pursed-lip breathing will slow your breathing down to a rate where the air trapped inside your lungs will escape, allowing oxygen to fully fill your lungs rather than trapped air.
Does smoking cause emphysema?
Smoking is the leading cause of COPD and emphysema, which are the two leading respiratory illnesses that cause hyperexpanded lungs. By reducing or quitting smoking, you significantly lower the causes and symptoms of hyperexpanded lungs by allowing clean, fresh oxygen to enter your body and carbon dioxide and other toxins to be removed.
What is the difference between static and dynamic hyperinflation?
The only difference between dynamic hyperinflation and static hyperinflation is that an activity or exercise typically causes dynamic hyperinflation. For example, climbing up a flight of stairs can cause you to have shortness of breath or difficulty inhaling. This is known as dynamic hyperinflation, which means you can pinpoint the exact cause ...
How to get air out of your lungs?
Exhale all of the air in your lungs slowly through your pursed lips. The goal is for this to take longer than the time it took to inhale the air so that you eliminate all of the excess air that has been trapped inside the lungs. Repeat this process until your breathing has returned to normal.
What is the condition where the chest is hard to breathe?
A collapsed lung occurs when air gets inside the chest cavity (outside the lung) and creates pressure against the lung. Also known as pneumothorax, collapsed lung is a rare condition that may cause chest pain and make it hard to breathe. A collapsed lung requires immediate medical care.
What is a collapsed lung?
A collapsed lung occurs when air enters the pleural space, the area between the chest wall and the lung. Air in the pleural space can build up and press against the lung, causing it to collapse partially or fully. Also called a deflated lung or pneumothorax, a collapsed lung needs immediate medical care.
What is the condition where the lung collapses?
Endometrial tissue lines the uterus. With endometriosis, it grows outside the uterus and attaches to an area inside the chest. The endometrial tissue forms cysts that bleed into the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse.
What is video assisted thoracoscopic surgery?
Surgery: Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a small camera to help the surgeon remove lung tissue. Your surgeon may also perform a chemical pleurodesis or a mechanical pleurodesis using a piece of gauze to attach the lung to the chest cavity.
How to diagnose a collapsed lung?
The most common way to diagnose a collapsed lung is with medical imaging. Usually, you’ll have a chest X-ray. But you may have a CT scan or ultrasound. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
Can a collapsed lung heal on its own?
If you have signs or symptoms of a collapsed lung, such as chest pain or trouble breathing, get medical care right away. Your lung may be able to heal on its own, or you may need treatment to save your life. Your provider can determine the best form of treatment for you.
How long do you stay in the hospital after a lung transplant?
After treatment, you may be in the hospital for a couple of days or longer. This allows your provider to check your progress and give you oxygen, if necessary. You will make an appointment for follow-up visits. You should contact your provider if symptoms of collapsed lung return.
What causes a lung to overinflation?
The condition might be caused by less elastic air sacs or air passage blockages, as both of these interfere with air expulsion from the lungs. Lung hyperinflation is commonly seen in those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease because of the emphysema symptoms. Other lung problems, like cystic fibrosis and asthma, can lead to the development of lung hyperinflation. While an x-ray is usually used to diagnose the condition, x-ray imaging sometimes shows lung hyperinflation even when none is present. Doctors may use a CT scan to confirm the diagnosis. Treatments vary depending on the severity and the underlying cause.
Can emphysema cause hyperinflation?
Lung hyperinflation is commonly seen in those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease because of the emphysema symptoms. Other lung problems, like cystic fibrosis and asthma, can lead to the development of lung hyperinflation. While an x-ray is usually used to diagnose the condition, x-ray imaging sometimes shows lung hyperinflation even ...
What is lung volume reduction surgery?
Lung volume reduction surgery is a surgery used to removed emphysematous and diseased lung tissue. When lung hyperinflation is caused by disease, surgery to remove the tissue may be an option. It's typically recommended for patients who have severe emphysema and one lung more noticeably affected by hyperinflation than the other. When the diseased lung is inflated, it takes up too much room in the chest cavity and presses on the second, functioning lung, decreasing its ability to expand. During lung volume reduction surgery, the diseased and inflated tissue is removed, creating room for the healthier lung to function properly.
Does oxygen help COPD?
In fact, supplemental oxygen has been shown to increase the lives of COPD patients. Lung hyperinflation leads to breathlessness and a reduction in exercise tolerance because part of the lungs isn't receiving fresh air. There have been a few studies specifically examining the effects of supplemental oxygen on hyperinflated lungs.
What is bronchodilator medication?
Bronchodilators are a type of medication that relax the muscle bands surrounding the airways. When these bands tighten, they can lead to restricted breathing, and if they obstruct an airway entirely, they may be the cause of lung hyperinflation. A bronchodilator medication opens a patient's airway to allow the easier flow of air to and from the lungs. In addition, the medication helps dislodge and move mucus out of the patient's lungs, where it can be coughed up.
Does COPD cause hyperinflation?
COPD is a progressive disease that leads to a decline in lung function. But patients who don't smoke and engage in regular exercise can significantly slow or even halt the progression of their disease. If the disease doesn't progress as quickly, there's also less chance for the hyperinflation to get worse.
Why do people with asthma need bronchodilators?
In addition, the medication helps dislodge and move mucus out of the patient's lungs, where it can be coughed up. The majority of individuals with asthma are prescribed bronchodilators.