Explore
Remember, fear and pain can make shock worse by increasing the body’s demand for oxygen, so try to reassure the casualty and keep them calm if you can. Monitor their level of response. If they become unresponsive at any point, prepare to treat an unresponsive casualty .
What is the most important remember when treating for shock?
Shock Treatment
- Lay the Person Down, if Possible. Elevate the person's feet about 12 inches unless head, neck, or back is injured or you suspect broken hip or leg bones.
- Begin CPR, if Necessary. For a child, start CPR for children. ...
- Treat Obvious Injuries
- Keep Person Warm and Comfortable. Loosen restrictive clothing. ...
- Follow Up. ...
What are the steps for preventing or treating shock?
Then immediately take the following steps:
- Lay the person down and elevate the legs and feet slightly, unless you think this may cause pain or further injury.
- Keep the person still and don't move him or her unless necessary.
- Begin CPR if the person shows no signs of life, such as not breathing, coughing or moving.
How to treat someone with shock and identify symptoms?
There are several main causes of shock:
- Heart conditions (heart attack, heart failure)
- Heavy internal or external bleeding, such as from a serious injury or rupture of a blood vessel
- Dehydration, especially when severe or related to heat illness.
- Infection (septic shock)
- Severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock)
- Spinal injuries (neurogenic shock)
- Burns
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhea
What are 5 causes of shock?

What is shock in Mayo Clinic?
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Shock is a critical condition brought on by the sudden drop in blood flow through the body. Shock may result from trauma, heatstroke, blood loss, an allergic reaction, severe infection, poisoning, severe burns or other causes.
How to help someone in shock?
Seek emergency medical care. If you suspect a person is in shock, call 911 or your local emergency number. Then immediately take the following steps: Lay the person down and elevate the legs and feet slightly, unless you think this may cause pain or further injury. Keep the person still and don't move him or her unless necessary.
What happens when you are in shock?
When a person is in shock, his or her organs aren't getting enough blood or oxygen. If untreated, this can lead to permanent organ damage or even death. Signs and symptoms of shock vary depending on circumstances and may include: Cool, clammy skin. Pale or ashen skin.
What are the main treatments for shock?
Immobilization, anti-inflammatories such as steroids and surgery are the main treatments. Shock prevention includes learning ways to prevent heart disease, injuries, dehydration, and other causes of shock.
What to do if you suspect shock?
If you suspect shock after an injury, even if the person seems stable, call 911 or get them to an emergency department immediately. Prompt treatment can save a person's life. The sooner shock is treated, the better. When treated quickly there is less risk of damage to a person's vital organs.
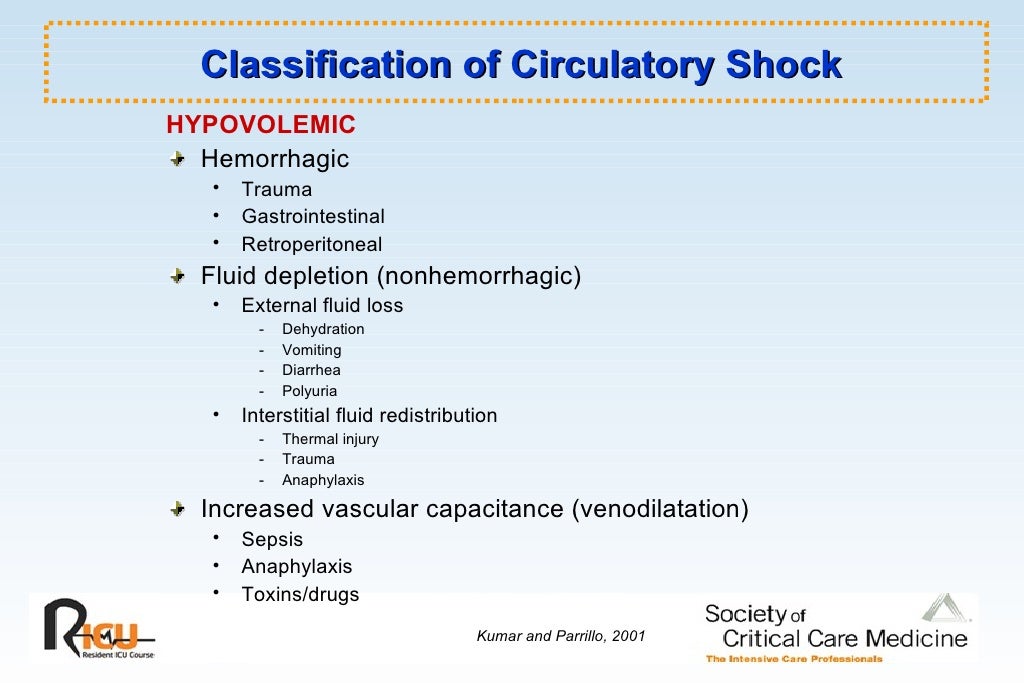
What are the different types of shock?
There are several types of shock: septic shock caused by bacteria, anaphylactic shock caused by hypersensitivity or allergic reaction, cardiogenic shock from heart damage, hypovolemic shock from blood or fluid loss, and neurogenic shock from spinal cord trauma. Treatment for shock depends on the cause.
How is cardiogenic shock treated?
Cardiogenic shock is treated by identifying and treating the underlying cause. Hypovolemic shock is treated with fluids (saline) in minor cases, and blood transfusions in severe cases. Neurogenic shock is the most difficult to treat as spinal cord damage is often irreversible.
Why is prompt treatment important?
Prompt treatment of medical shock is essential for the best outcome. Moreover, the outlook depends on the cause of the shock, the general health of the patient, and the promptness of treatment and recovery. Generally, hypovolemic shock and anaphylactic shock respond well to medical treatment if initiated early.
What is the treatment for septic shock?
Usually, IV fluids are administered in addition to medications that raise blood pressure. Septic shock is treated with antibiotics and fluids. Anaphylactic shock is treated with diphenhydramine ( Benadryl ), epinephrine (an "Epi-pen"), and steroid medications (solumedrol).
What causes anaphylactic shock?
Common causes of this are pneumonia, urinary tract infections, skin infections ( cellulitis ), intra-abdominal infections (such as a ruptured appendix ), and meningitis . Anaphylactic shock is a type of severe hypersensitivity or allergic reaction. Causes include allergy to insect stings, medicines, or foods (nuts, berries, seafood), etc.
What are the 5 types of shock & First Aid treatment?
From excessive bleeding to an allergic reaction, shock is a life-threatening condition that can be caused by many different things. There are different types of shock that patients might experience, each with its own set of causes and symptoms.
What is shock?
Shock has many different causes, symptoms, and types, but generally, it is when the body is not able to facilitate proper blood flow, affecting the organs. If a patient is exhibiting nausea, dizziness, chills, or a weak pulse, they might have shock. Because there are many different causes of shock, the symptoms can vary in severity and onset speed.
What are the different types of shock?
Knowing the different types of shock will help you identify potential shock cases and determine the best possible treatment. Here are 5 types of shock that you might encounter…
What are first aid treatments for shock?
As with any medical emergency, dial 911 and contact emergency services if you are a bystander. Explain to the operator that you believe the patient may be exhibiting shock. Then, begin administering first aid for shock.
What is shock therapy?
"Shock therapy" was so-called, as an electric shock is used to induce a controlled seizure intended as a treatment , primarily for mood disorders, although other conditions may be treated as well. Shock therapy is now known as electroconvulsive therapy or ECT.
Where is shock therapy performed?
Shock therapy is performed in a hospital, sometimes in an area specifically set aside for this treatment. An intravenous (IV) is inserted to provide anesthetic medication. Vital signs are taken initially and continuously throughout the shock therapy treatment.
How does shock therapy feel?
How Shock Therapy Feels. When you awake from the anesthesia, you may be confused and tired. You will likely experience short-term memory loss around the time of the procedure. With multiple treatments, this may increase. Adverse cognitive effects tend to be the most concerning factors around ECT and tend to affect the frequency and duration ...
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat seizures?
A paralyzing agent called succinylcholine is then administered to prevent the seizure from spreading to your body. The electrodes are then applied to your head with conducting jelly and a brief shock (less than 2 seconds) is administered.
How to know if you are recovering from shock?
Your vital signs will be monitored closely after the shock treatment to ensure proper recovery. You may feel head, muscle or back pain. Such discomfort tends to be relieved by mild medications. If any post-treatment effect is concerning you, you should talk to the treating physician immediately.
Is electroconvulsive therapy effective?
Electroconvulsive therapy has also shown effectiveness in treating other disorders such as neuroleptic malignant syndrome (a rare, severe, adverse reaction to antipsychotic medication). Shock treatment for depression and other disorders is indicated when the patient needs rapid improvement because the patient is:
Does mania respond to shock?
Mania also often responds well to shock treatment. The picture is not as bright for schizophrenia, which is more difficult to treat and is characterized by frequent relapses. A small number of patients are placed on maintenance shock therapy.
What is shock in medical terms?
Shock is a condition that occurs when there is not enough blood that circulates all over the body, affecting the organs and tissues and hindering them from functioning normally. The shock comes as a result of an injury or an illness that affects the natural blood flow in the system.
What is shock first aid?
The word “shock” can be linked to several meanings. First, it may refer to a psychological response from a traumatic experience. Next, it can be a physiological outcome when there is an impaired process in the body. In most cases, shock is attributed to the psychological circumstances ...
What happens when too much damage to the tissues and organs has been done?
When too much damage to the tissues and organs has been done, septic shock occurs. Neurogenic shock. This type of distributive shock comes as a result of damages to the central nervous system, particularly an injury to the spinal cord. These damages slow the heart rate and trigger the blood pressure to drop.
What is the term for a person who has a shortage of blood in the blood vessels?
Hypovolemic shock. This type of shock happens when there is a shortage of blood in the blood vessels to distribute oxygen to your organs. Hypovolemic shock often occurs when the person suffers from severe blood loss brought about by injuries. Intense dehydration can also lead to hypovolemic shock.
What is obstructive shock?
Obstructive shock. This type of shock occurs when the blood cannot go where it has to go. Conditions that produce a buildup of air or fluid in the chest cavity can cause obstructive shock. These conditions include: A condition in which the blood collects in the space between the chest wall and lung.
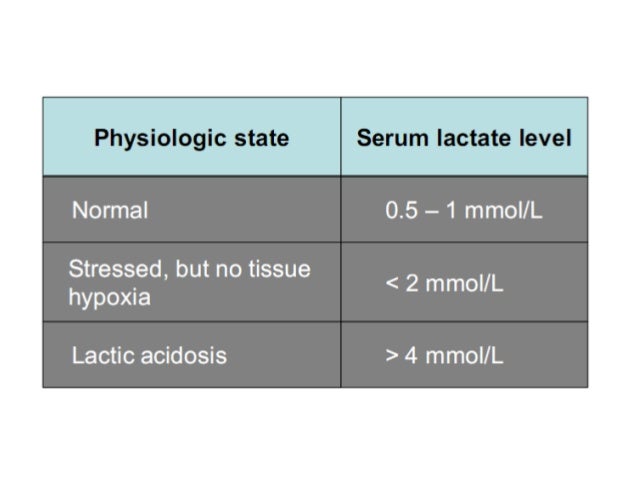
What tests are needed to determine shock?
Blood tests may also be needed to determine shock causes. The medical professionals may look for indications like blood loss, infections present in the blood, as well as drug or medication overdose.
What are the signs of shock?
However, medical professionals may also look for low blood pressure, weak pulse, and rapid heartbeat, which are all signs of shock.
Shock Therapy: Process, Preparation, Outcomes and more
Krystina is a Technical Writer with a background in healthcare. She has spent the last 10 years working for an internationally recognized medical facility where she found her passion for making complicated topics easier to understand.
The Electroconvulsive Therapy Process
An ECT treatment regimen will typically include sessions two to three days a week for a total of six to 12 treatments. The schedule works out to about one month of treatment, although the course may continue for longer.
How to Prepare for Your Treatment
ECT sessions generally do not require much preparation, though you will need to go over the specifics with your doctor. Your doctor may give you orders to follow based on other health conditions you have or medications you take.
Potential Outcomes of Shock Therapy
Most people who undergo ECT will see a noticeable change in their symptoms. Some people will notice an immediate improvement after one session. However, it is more common to not see or feel a significant difference in symptoms for several sessions.
Summary
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be used to treat major depressive disorde r, bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. It is often considered when other treatments have not helped.
A Word From Verywell
If you are wondering if shock therapy might be a treatment option for you, discuss it with your psychiatrist. While ECT can provide lasting relief from the symptoms of MDD, bipolar disorder, and similar conditions, it's not the right choice for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Even though ECT has been around for nearly 90 years, scientists still are not quite sure why or how it benefits some people with depression.
What Is Traumatic Shock?
Trauma is an emotional wound or rupture caused by an experience that threatens any dimension of wellness, 1 says Crystal Burwell, PhD, LPC, Director of Outpatient Services, Newport Healthcare, Atlanta.
Symptoms of Traumatic Shock
There are numerous physical and emotional signs and symptoms of traumatic shock as our bodies respond in a number of ways, 3 says Dr. Burwell.
Causes of Traumatic Shock
While anything that significantly disrupts your emotional equilibrium can be considered a traumatic event, these are some examples of events that can cause traumatic shock: 5
Diagnosing Traumatic Shock
If you or a loved one have experienced an emotional trauma and are struggling to cope with it, Dr. Burwell recommends seeking help from a healthcare professional.
Types of Traumatic Shock
Traumatic shock can be categorized into different types, depending on how it impacts the brain and which tissues and organs in the body are affected, says Dr. Burwell. “There are different types of emotional and physical trauma. Each type impacts particular regions of the brain and body, and manifests differently depending on the person.”
Emotional Trauma Treatment
If you have sustained an emotional trauma and are in shock, your body gradually begins to regain emotional equilibrium on its own and ground itself back in reality —this process can take longer for some than others, explains Dr. Burwell.
Coping With Traumatic Shock
Dr. Burwell also shares some coping strategies that can help you if you are dealing with a traumatic event that has shocked you: