
The purpose of medical care for wounds is to prevent complications and preserve function. While important, cosmetic results are not the primary consideration for wound repair. Animal and human bites should always be seen by a medical professional because of the high rate of infection.
What are the basics of wound care?
Wound Care Basics
- Wash the wound at least once a day with plain water or a mild cleanser.
- Soaking can help remove scabs and dead skin.
- Don’t use harsh cleansers or scrub too hard. This can cause further damage to the wound.
- Antibiotic ointments can also help. ...
- Other ointments, like ordinary Vaseline, may also be a good idea. ...
What is the importance of wound care?
- Re-epithelialisation occurs with the migration of cells from the periphery of the wound and exudate levels are very low. The new skin is fragile.
- Aim of management: the same rules apply as for managing granulation wounds.
- A cover of semi-permeable film or thin hydrocolloid is recommended and left in place until re-epithelialisation is complete.
What are the principles of wound care?
The basic principles for the management of a wound or laceration are:
- Haemostasis
- Cleaning the wound
- Analgesia
- Skin closure
- Dressing and follow-up advice
How long does it take for a wound to heal?
What to Expect During the 4 Stages of Wound Healing
- Stages of wound healing. Your body heals a wound in four main stages. ...
- Poor wound healing. Blood supply is one of the most important factors in wound healing. ...
- Signs of infection. A wound may heal slowly if it’s infected. ...
- When to see a doctor. See your healthcare provider if you think you have an infected wound, no matter how small it is. ...
- The bottom line. ...
What are the goals of wound care?
The goal of wound cleansing is to: Remove visible debris and devitalised tissue. Remove dressing residue. Remove excessive or dry crusting exudates.
What is the goal for topical wound care therapy?
Goals of topical wound management are speeding repair, preventing infection, reducing pain, removing dead tissue, providing a moist environment, reducing edema, and increasing blood flow. Occlusive dressings, which maintain wounds in the moist state, are an effective choice for topical wound management.
How do you write a wound care goal?
Ensure the goal is measurable; for example, “The skin will remain intact during the patient's stay” or “The pressure ulcer on the coccyx will show signs of healing, such as a decrease in dimension size and filling in of the wound base in 2 weeks.” You also want to ensure the goal is realistic.
What are the goals for an infected wound?
The goal of treatment is to kill the microorganisms while not damaging healthy tissue. Local treatment of the wound focuses on reduction of the bioburden. The bioburden is the metabolic load imposed by bacteria in the tissue.
Why is wound care important in nursing?
The importance of wound care in nursing relates to the ability to reduce a patient's pain and promote healing as quickly and completely as possible. To become a certified wound care nurse, you will need to enroll in specialized wound care courses.
What are the 5 principles of wound management?
In this article, the authors offer five generalisable principles that colleagues providing community care can apply in order to achieve timely wound healing: (1) assessment and exclusion of disease processes; (2) wound cleansing; (3) timely dressing change; (4) appropriate (dressing choice; and (5) considered ...
How do you write a smart goal in nursing?
SMART is an acronym for the guidelines nurses should use when setting their goals:Be specific. Setting broad nursing goals allows them to be open for interpretation. ... Keep it measurable. For goals to be effective, there must be some way to measure your progress. ... Keep it attainable. ... Be realistic. ... Keep it timely.
What are the 7 Steps to Effective wound care management?
7 Steps for Caring for WoundsStep #1 Wash Your Hands Clean. ... Step #2 Stop the Bleeding. ... Step #3 Clean the Wound. ... Step #4 Apply Antibacterial Ointment. ... Step #5 Protect the Wound. ... Step #6 Change the Dressing. ... Step #7 Observe Symptoms. ... Wound Care in Rochester, New York.
What is a smart goal for skin integrity?
GOAL: Promote circulation to tissues by reducing or eliminating pressure. Possible risk factors that decrease circulation or cause unrelieved pressure to tissues: ▪ Immobility (diagnosis that leads to immobility, such as CVA, MS, end stage Alzheimer's, etc.) ▪ Decreased sensory perception (inability to feel.
Why is wound management important?
The Importance of Wound Care in Recovery Proper wound care prevents infection and other complications, and also helps speed up the healing process with less scarring.
What are smart goals examples?
Examples of SMART GoalsGoal 1: I want to complete a project.Goal 2: I want to improve my performance.SMART goal: I want to complete a project.SMART goal: I want to improve my performance.Related:
What principles of wound care should the nurse include when completing wound care for a client with sutures?
The basic principles for the management of a wound or laceration are:Haemostasis.Cleaning the wound.Analgesia.Skin closure.Dressing and follow-up advice.
What is wound care article?
This wound care article is designed to present information on wounds involving mainly the skin; it is not meant to cover all wounds (for example, gunshot, degloving wounds, tendon lacerations, and others).
How to treat a wound?
Most wounds can be treated at home with routine first aid including thorough washing and dressing to prevent infection. Seek medical care for wounds if: 1 The wound is due to significant force or trauma and other injures are be present. 2 Bleeding cannot be stopped even with persistent pressure and elevation. 3 There is concern that wound requires repair with sutures ( stitches ). The size and location of the wound are important considerations. Most facial wounds may need to be repaired for cosmetic reasons, especially if they involve the lip or eye. 4 The wound is caused by an animal bite. There is also a need to consider rabies immunizations, if appropriate. 5 The wound is very dirty and cannot be easily cleaned. 6 There is evidence of infection including redness, swelling, increased pain, and pus at the wound. 7 Tetanus immunizations are not up to date, then a booster is needed within 48 hours. If the patient has never been immunized, the initial tetanus prevention with immunoglobulin should be given immediately.
How do you know if you have a laceration?
The most common symptoms of a wound are pain, swelling, and bleeding. The amount of pain, swelling, and bleeding of a wound depends upon the location of the injury and the mechanism of injury. Some large lacerations may not hurt very much if they are located in an area that has few nerve endings, while abrasions of fingertips (which have a greater number of nerves) can be very painful. Some lacerations may bleed more if the area involved has a greater number of blood vessels, for example, the scalp and face.
How to treat a wound that is bleeding?
Often, bleeding can be controlled with direct pressure to the wound, and if possible, elevating the bleeding site above the level of the heart. This allows gravity to help decrease blood flow to the injury. Most bleeding will stop within 10 minutes, at which point, a dressing can be placed over the wound.
What is superficial wound?
Superficial (on the surface) wounds and abrasions leave the deeper skin layers intact. These types of wounds are usually caused by friction rubbing against an abrasive surface. Deep abrasions ( cuts or lacerations) go through all the layers of the skin and into underlying tissue like muscle or bone.
Why do facial wounds need stitches?
Most facial wounds may need to be repaired for cosmetic reasons, especially if they involve the lip or eye. The wound is caused by an animal bite.
What is a puncture wound?
Puncture wounds are usually caused by a sharp pointed object entering the skin. Examples of puncture wounds include a needle stick, stepping on a nail, or a stab wound with a knife. Human and animal bites can be classified as puncture wounds, abrasions, or a combination of both.
What is appropriateness in wound care?
The same goes for appropriateness, defined as a specific intervention to meet the patient's needs.
What does "doing the right thing well" mean?
Everyone benefits. "Doing the right thing well" also means providing timely care. When you are managing a wound, time is tissue.
What are the components of evidence based practice?
In the original definition of evidence-based practice, Sackett 5 outlines three intertwined components: (1) best available literature, (2) individual clinician expertise and (3) patient preferences. As with a three-legged stool, each element is dependent on the others. When one leg is broken, short or absent, outcomes are compromised. In the worst scenario, the patient's safety is at risk. What is the best available evidence? Well, it may depend on clinician expertise. When I entered the wound care specialty, I wasn't reading about molecular and cellular interactions in the wound bed. I was trying to find out the difference between a hydrocolloid and a calcium alginate. I was a novice. I was reading the best available literature for my level of expertise. As expertise increases, our lifelong effort to seek out the best available evidence— which can be a moving target as science makes new discoveries—must also change.
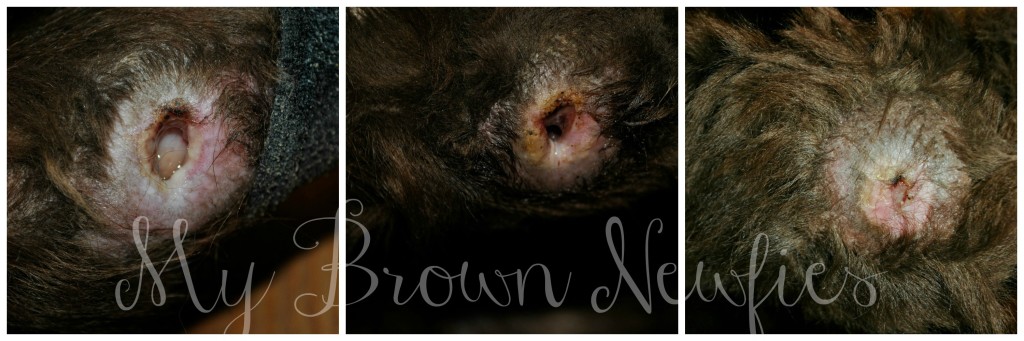
What is the color of a wound?
The wound is covered or partially covered in soft, moist, dead tissue, mainly yellow in colour but possibly ranging from white through to dark grey or brown. This tissue is composed of dead cells accumulated in exudate and should be removed to reduce the risk of infection.
Do surgical wounds heal?
In the main, intentionally created, acute surgical wounds and simple lacerations will heal without a problem in an otherwise healthy person. Acute wounds are expected to heal within an anticipated timeframe with no patient or environmental factors delaying healing. 3 Minimal or no tissue loss allows clean, acute wounds to rapidly seal and heal through a complicated process that is not yet fully understood, especially in terms of why some patients heal efficiently and others take extended times or do not heal.
Can wounds be a mixture of colors?
Few wounds will fall into a single colour classification; many will be a mixture of several colours at the same time. The clinician must decide the aims of treatment and priorities at each wound assessment and dressing change.
What is the goal of wound care?
Determine why it's not healing. Create a treatment plan. Treatment goals include: Healing the wound. Preventing the wound from getting worse or becoming infected. Preventing limb loss.
What is the best treatment for a wound?
Your providers may recommend other types of treatment, including: Compression stockings -- tight-fitting stockings or wraps that improve blood flow and help with healing. Ultrasound -- using sound waves to aid healing. Artificial skin -- a "fake skin" that covers the wound for days at a time as it heals.
What is the purpose of a wound dressing?
After the wound is clean, your doctor will apply a dressing to keep the wound moist, which promotes healing, and help prevent infection. There are many different types of dressings, including: Gels.
How to remove dead tissue from a limb?
Other ways to remove dead or infected tissue are to: Sit or place your limb in a whirlpool bath. Use a syringe to wash away dead tissue. Apply wet-to-dry dressings to the area . A wet dressing is applied to the wound and allowed to dry.
What is a wound care center?
A wound care center, or clinic, is a medical facility for treating wounds that do not heal. You may have a non-healing wound if it: Has not started to heal in 2 weeks. Has not completely healed in 6 weeks.
What is a wet dressing?
A wet dressing is applied to the wound and allowed to dry. As it dries, it absorbs some of the dead tissue. The dressing is wet again and then gently pulled off along with dead tissue. Put special chemicals, called enzymes, on your wound. These dissolve dead tissue from the wound.
How to prevent new wounds from occurring?
Helping you stay mobile. In order to treat your wound, your provider will clean out the wound and apply dressing. You also may have other types of treatment to help it heal.
Why do you need a wound care plan?
Creating a wound care plan for you and your patient can help you to set goals and measure the progress of the wound care you provide. It can also help you to decide when you change your treatment plan if the goals you have set are not being achieved.
How to plan a wound assessment?
Planning. Once you have completed your assessment using all necessary means, it’s time to plan. Start by identifying the problem (s), such as pain and infection. Remember that your goals and the patient’s goals may be different- you may be focused on a reduction in wound size, while your patient is focused only on the pain.
Why is it important to evaluate your progress?
It’s important to evaluate your progress. Assessment and reassessment using the same tools and methods of assessment each time will help you to evaluate whether you are meeting the goals you set in the planning phase . If the wound has stalled in the healing process, it may be time to consider changing tactics, but it’s also important ...
What to do if wound is stalled?
If the wound has stalled in the healing process, it may be time to consider changing tactics , but it’s also important to allow enough time to see whether a certain treatment will be effective. Signs of progress will encourage both you and your patient towards meeting measurable and specific goals. Establishing a wound care plan for you ...
Is it important to create a plan of care?
There is no point in creating a plan of care if your patient is not on board. To this end, it is important that you create goals that are specific, realistic and achievable. If you set goals that are unrealistic, you may lose your patient’s cooperation.
What is wound care competency?
Ongoing education of wound care competency is one way to improve the clinician’s knowledge, increase patient satisfaction, increase clinician satisfaction and retention, and improve facilities’ public relations. 3.
How much of wound claims are medicolegal?
Up to 20% of all US medicolegal claims and more than 10% of settlements are wound related. 1 Documentation is essential for all health care settings; however, there are differences in each setting. Knowing your clinical setting’s requirements from a documentation standpoint is critical in meeting documentation needs. Every setting has policies and procedures for skin and wound care that reflect current clinical and operational guidelines approved by the facility. Facilities should consider standardized workflow to provide a systematic process to capture, generate, track, store, retrieve, and retain documents of the medical record. These clinical workflows should be reviewed and updated routinely to avoid denial of claims based on missing documentation elements. 2,3
Why is clinical documentation important?
This is critical in providing continuity of care for patients . Documentation should be complete, detailed, and accurate to best communicate among health care professionals and to prevent ambiguity from a legal standpoint. The EMR workflow can help assist in making sure that all standards are met according to regulatory standards. Meeting standards will help prevent litigation, support reimbursement, and ensure patient care outcomes.
Why is documentation important in healthcare?
Documentation should be complete, detailed, and accurate to best communicate among health care professionals and to prevent ambiguity from a legal standpoint.
What is long term care documentation?
Long-Term Care#N#Wound care documentation in the long-term care setting is a critical component of resident care. It is stated by the Office of the Inspector General of the US Department of Health and Human Services that providers carry the burden of proving that care was actually rendered to the patients (residents). 4 The documentation must reflect the standards specifically found in Section 483.25 Appendix PP of the State Operations Manual for multiple F-tags in regard to quality of life, treatment or services to prevent or heal pressure injuries, and addressing minimum assessment, daily monitoring, and documentation requirements for any skin ulcer or wound. 5 Documentation standards are based on these guidelines; however, taking photos of wounds relies on each individual facility’s policies and procedures because facilities may have different policies on whether images can be included in documentation.
The Components of Evidence-Based Wound Care
Where Intervention and Outcome Meet
- The concept of performance improvement8 may have gotten its start because the "right thing" was not done. Even the IOM has said, "to err is human."1At its core, committing to the "right thing" means we must have interventions that have been shown to have a desired outcome. Although specific wound care treatments have been shown to have variable efficacy, it takes the clinician'…
Calibrating The Process of Care
- Unfortunately, the wound care community lacks clear and comprehensive data about the effectiveness of the many therapies it administers. We are frequently criticized by our non-wound care colleagues for not having heterogeneous groups in our studies, for low numbers of study participants, for poor research designs and for comparison of the study product to wet-to-dry dr…