
Cell Wall Function The cell wall provides mechanical strength and support. The cell wall prevents mechanical injury. The cell wall helps a cell withstand turgor pressure. The cell wall helps to maintain the osmolarity of the cell. The cell wall has a role in cell growth regulation.
What is true about a cell wall?
A cell wall is defined as the non-living component, covering the outmost layer of a cell. Its composition varies according to the organism and is permeable in nature. The cell wall separates the interior contents of the cell from the exterior environment. It also provides shape, support, and protection to the cell and its organelles.
What are some functions of cell wall?
Functions of Cell wall:
- Cell walls primary function is mechanical support. ...
- Cell wall is tough and has high tensile strength. ...
- Cell wall shows plasticity and elasticity during cell growth.
- It helps to maintain the balance of intracellular osmotic pressure with that of its surroundings
Does cell wall have its own wall?
Cell Wall. Only plant-like cells have a cell wall and its main purpose is to act as a protective barrier for the cell. Since the cell wall is designed to give the cell structure and stability, they are mostly made up of cellulose fibers as well as pectin, and hemicellulose.
What does the cell wall provide for the cell?
The main functions of the cell wall are:
- Protecting the cell against physical damage and invading pathogens.
- Regulates and controls the direction of cell growth.
- Providing the strength, structural support and maintaining the shape of the cell.
- Functions as a storage unit by storing carbohydrates for use in plant growth, especially in seeds.
What is the function of cell walls?
The cell wall surrounds the plasma membrane of plant cells and provides tensile strength and protection against mechanical and osmotic stress. It also allows cells to develop turgor pressure, which is the pressure of the cell contents against the cell wall.
What is the importance of the bacteria cell wall in regards of antibiotic treatment?
The cell wall is the first barrier that an antimicrobial agent must counteract [12]. In contrast to Gram positive bacteria, Gram-negative organisms have an additional membrane, the so called outer membrane (OM), that lies over and covers both the cytoplasmic membrane and the peptidoglycan layer.
How does the cell wall influence the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment?
Many antibiotics, including penicillin, work by attacking the cell wall of bacteria. Specifically, the drugs prevent the bacteria from synthesizing a molecule in the cell wall called peptidoglycan, which provides the wall with the strength it needs to survive in the human body.
How does cell wall structure affect susceptibility to antibiotics?
A bacterium's ability to hold onto a stain is dependent on the structure of their cell wall. A Gram positive organism lacks an outer (LPS) membrane but has a thick layer of peptidoglycan and no LPS outer membrane. This facilitates access of cell-wall active antibiotics (eg.
Which antibiotics act on the cell wall bacteria?
β-Lactam antibiotics are a broad class of antibiotics that includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins (cephems), monobactams, and carbapenems. β-Lactam antibiotics are bacteriocidal and act by inhibiting the synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls.
How do cell walls help bacteria living in such environments?
How do cell walls help bacteria living in such environments? Hypotonic environment is where the solute concentration inside the cell exceeds that outside of the cell, so the water will move by osmosis INTO the cell. Cells that have a cell wall can better withstand changes in osmotic pressure and maintain their shape.
How does the cell wall affect virulence of bacteria?
Like many other surface components, S-layers contribute to virulence by protecting the bacterium against complement and attack by phagocytes. The cell wall of a bacterium is an essential structure that protects the delicate cell protoplast from osmotic lysis.
How does the cell wall protects bacterial cells from osmotic shock?
The peptidoglycan of the cell wall prevents osmotic lysis when water moves into the cell, but ONLY if the cell wall peptidoglycan is cross-linked. Anything which prevents the cross links from forming or which cuts the cross-links will weaken the peptidoglycan so that it no longer can prevent osmotic lysis.
How antibiotics affect cell wall synthesis?
β-Lactam antibiotics, including penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, and carbapenems, are distinguished by a lactam ring in their molecular structure and act by inhibiting the synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls.
Does bacterial cell wall protects the cell from phagocytosis?
The bacterial capsule (glycocalyx) can inhibit this attachment, making the pathogen cell resistant to phagocytosis. Ingestion: The ingested pathogen is called the phagosome, which fuses with the lysosome.
How does penicillin work on bacterial cell walls?
Penicillin interferes with the production of a molecule called peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan molecules form strong links that give the bacterial cell strength as well as preventing leakage from the cytoplasm. Nearly every bacterium has a peptidoglycan cell wall.
How do bacteria become resistant to antibiotics?
There are two main ways that bacterial cells can acquire antibiotic resistance. One is through mutations that occur in the DNA of the cell during replication. The other way that bacteria acquire resistance is through horizontal gene transfer.
Q.1. What is lignification?
Ans: Lignification is the polymerization of lignin on cell walls to make it harder and make the plant disease resistant.
Q.2. Why do plants need cell walls?
Ans: Plant cells need cell walls for protection, strength, turgidity, and osmolarity.
Q.3. Who discovered the cell wall?
Ans: Robert Hooke observed it for the first time and called it the "wall" surrounding the cell.
Q.4. Differentiate between gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria based on their cell wal...
Ans: Gram-positive bacteria have three layers of peptidoglycan, whereas gram-negative bacteria have a single layer of peptidoglycan with an additio...
Q.5. Name the organism that lacks a cell wall.
Ans: Animals and Protozoa lack a cell wall around the plasma membrane.
What is the cell wall?
A cell wall is a rigid, semi-permeable protective layer in some cell types. This outer covering is positioned next to the cell membrane (plasma membrane) in most plant cells, fungi, bacteria, algae, and some archaea. Animal cells however, do not have a cell wall. The cell wall has many important functions in a cell including protection, structure, ...
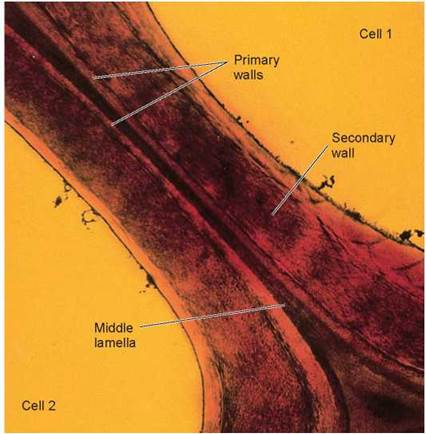
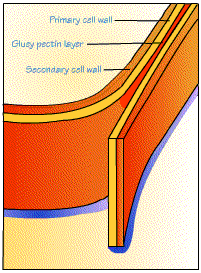
What is the primary cell wall?
The primary cell wall provides the strength and flexibility needed to allow for cell growth. Secondary cell wall: This layer is formed between the primary cell wall and plasma membrane in some plant cells. Once the primary cell wall has stopped dividing and growing, it may thicken to form a secondary cell wall.
How do pectins help cells?
Pectins aid in cell adhesion by helping the cell walls of adjacent cells to bind to one another. Primary cell wall: This layer is formed between the middle lamella and plasma membrane in growing plant cells.
What are the layers of the plant cell wall?
From the outermost layer of the cell wall, these layers are identified as the middle lamella, primary cell wall, and secondary cell wall. While all plant cells have a middle lamella and primary cell wall, not all have a secondary cell wall.
What is inside a plant cell?
Inside the cell wall are chloroplasts (dark green), the site of photosynthesis, and the nucleus (orange), which contains the cell's genetic information.
What is the force exerted against the cell wall as the contents of the cell push the plasma membrane against the cell
It also controls the direction of cell growth. Withstand turgor pressure: Turgor pressure is the force exerted against the cell wall as the contents of the cell push the plasma membrane against the cell wall. This pressure helps a plant to remain rigid and erect, but can also cause a cell to rupture.
What is the cell wall of prokaryotic bacteria?
Unlike in plant cells, the cell wall in prokaryotic bacteria is composed of peptidoglycan. This molecule is unique to bacterial cell wall composition. Peptidoglycan is a polymer composed of double-sugars and amino acids (protein subunits). This molecule gives the cell wall rigidity and helps to give bacteria shape.
What is the function of the cell wall?
The cell wall has a few different functions. It is flexible, but provides strength to the cell, which helps protect the cell against physical damage. It also gives the cell its shape and allows the organism to maintain a certain shape overall. The cell wall can also provide protection from pathogens such as bacteria that are trying to invade the cell. The structure of the cell wall allows many small molecules to pass through it, but not larger molecules that could harm the cell.
Why is the cell wall important?
The cell wall is an essential part of survival for many bacteria. It provides mechanical structure to bacteria, which are single-celled, and it also protects them from internal turgor pressure.
What are the cell walls of fungi?
The cell walls of fungi contain chitin , which is a glucose derivative that is similar in structure to cellulose. Layers of chitin are very tough; chitin is the same molecule found in the rigid exoskeletons of animals such as insects and crustaceans. Glucans, which are other glucose polymers, are also found in the fungal cell wall along with lipids and proteins. Fungi have proteins called hydrophobins in their cell walls. Found only in fungi, hydrophobins give the cells strength, help them adhere to surfaces, and help control the movement of water into the cells. In fungi, the cell wall is the most external layer, and surrounds the cell membrane.
Why do plants have cell walls?
The cell walls of plant cells help them maintain turgor pressure, which is the pressure of the cell membrane pressing against the cell wall. Ideally, plants cells should have lots of water within them, leading to high turgidity. Whereas a cell without a cell wall, such as an animal cell, can swell and burst of too much water diffuses into it, ...
What are the proteins that are found in the cell walls of fungi?
Glucans, which are other glucose polymers, are also found in the fungal cell wall along with lipids and proteins. Fungi have proteins called hydrophobins in their cell walls. Found only in fungi, hydrophobins give the cells strength, help them adhere to surfaces, and help control the movement of water into the cells.
What is the cell wall of a bacteria?
The cell walls of bacteria usually contain the polysaccharide peptidoglycan, which is porous and lets small molecules through. Together, the cell membrane and cell wall are referred to as the cell envelope. The cell wall is an essential part of survival for many bacteria. It provides mechanical structure to bacteria, which are single-celled, ...
What is the cell wall?
A cell wall is an outer layer surrounding certain cells that is outside of the cell membrane. All cells have cell membranes, but generally only plants, fungi, algae, most bacteria, and archaea have cells with cell walls. The cell wall provides strength and structural support to the cell, and can control to some extent what types and concentrations of molecules enter and leave the cell. The materials that make up the cell wall differ depending on the type of organism. The cell wall has evolved many different times among different groups of organisms.
What is the function of the cell wall?
The main function of the cell wall is to provide structural strength and support, and also provide a semi-permeable surface for molecules to pass in and out of the cell.
What is the cell wall?
The cell wall is the outer covering of a cell, present adjacent to the cell membrane, which is also called the plasma membrane. As mentioned earlier, the cell wall is present in all plant cells, fungi, bacteria, algae, and some archaea.
What are the cell walls of prokaryotes made of?
The prokaryotic cell walls are composed of large polymers known as peptidoglycans. Cell walls in prokaryotes serve as a form of protection and prevent lysis (bursting of the cell and expulsion of cellular contents). Structurally, prokaryotic cell walls consist of two layers: An inner layer that is made up of peptidoglycans.
What is the primary cell wall?
Primary Cell Wall. The primary cell is situated closest to the inside of the cell and is the first-formed cell wall. It is mainly made up of cellulose, allowing the wall to stretch for the purpose of growth. Several primary cells contain pectic polysaccharides and structural proteins.
Why is the cell wall important in bacteria?
The cell wall in bacteria is essential for survival as it helps to keep the contents of the cell intact. Antibiotics usually work on this principle by targeting the bacterial cell wall and causing lysis. This leads to the expulsion of cellular contents and the eventual death of the cell.
Why is water important in cell growth?
It helps to control cell expansion due to the intake of water. Also helps in preventing water loss from the cell. It is responsible for transporting substances between and across the cell. It acts as a barrier between the interior cellular components and the external environment.
Why are animal cells irregular?
An animal cell is irregular in their shape and this is mainly due to the lack of cell wall in their cells. The compositions of the cell wall usually vary along with organisms. Also, read Cell Wall and Cell Membrane.
What is a Cell Wall?
The cell wall is a non-living, rigid, and permeable structure surrounding the plasma membrane. It is found in most plants, bacteria, fungi, and algae. Animals and protozoans lack this rigid structure. The composition of cell walls varies greatly among bacteria, fungi, plants, and algae.
Summary
The cell wall is a protective layer present around bacterial, fungal, algal, and plant cells. The cell wall of plant cells is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. The cell wall of a plant cell comprises three layers: middle lamella, which is made up of calcium and magnesium pectate.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Cell Wall
Q.1. What is lignification? Ans: Lignification is the polymerization of lignin on cell walls to make it harder and make the plant disease resistant.
Footer
Embibe is India’s leading AI Based tech-company with a keen focus on improving learning outcomes, using personalised data analytics, for students across all level of ability and access.
What is the cell wall?
The cell wall is a tough semi-permeable membrane that is located outside the cell membrane. This cell wall plays an integral role in the cell and has numerous functions. Depending on the type of organism and the type of developmental stage it is in, the cell wall itself is highly variable.
What is the function of the cell wall in bacteria?
Protection. The main function of the cell wall in bacteria is to provide protection by encircling the cell’s cytoplasm with a tough material. By doing so, it avoids the entry of foreign material that may harm it. 2.
Why is the cell wall important in plants?
One of the most important functions of the cell wall in plants and fungi is the resistance to turgor pressure. While the turgor pressure is important to keep the cells rigid, too much of it can break the cells. Hence, a sturdy structure is needed to balance such force.
What is the cell wall of fungi made of?
Fungal Cell Wall (Source: Wikimedia) The cell walls of fungi, on the other hand are made up of the polymer chitin. Chitin is a polymer of N-acetylglucosamine residues that are also connected via β (1→4) linkages. Chitin is also the structural component of arthropod exoskeleton.
What is the structure that surrounds cells?
Although the plasma membrane (or cell membrane) had already set the boundaries for the inside and outside cellular environment, many cells are still encircled by a wide array of insoluble components. For instance, the cells of bacteria, plants and algae, and fungi are enclosed by a rigid structure called the cell wall.
What are the components of the cell walls of plants?
Unlike those of the prokaryotes, the components of eukaryotic (higher plants, algae, and fungi) cell walls are mainly polysaccharides. The basic structural component of the cell walls of higher plants and most algae is cellulose. Cellulose is a polymer of glucose residues that are connected via β (1→4) linkages.
Do fungal cells have the same functions as plant cells?
Hence, they possess almost the same attributes and functions as well.
What is the function of the cell wall?
That is a lot of pressure for the plasma membrane to withstand! The cell wall can keep out certain molecules, such as toxins, particularly for gram negative bacteria. And lastly, the bacterial cell wall can contribute to the pathogenicity or disease –causing ability of the cell for certain bacterial pathogens.
Why is the bacterial cell wall important?
It also helps maintain the cell shape, which is important for how the cell will grow , reproduce, obtain nutrients, and move.
What is the cell wall of Gram positive bacteria?
Gram Positive Cell walls. The cell walls of gram positive bacteria are composed predominantly of peptidoglycan. In fact, peptidoglycan can represent up to 90% of the cell wall, with layer after layer forming around the cell membrane. The NAM tetrapeptides are typically cross-linked with a peptide interbridge and complete cross-linking is common.
How do teichoic acids contribute to cell division?
There is also evidence that teichoic acids participate in cell division, by interacting with the peptidoglycan biosynthesis machinery. Lastly, teichoic acids appear to play a role in resistance to adverse conditions such as high temperatures and high salt concentrations, as well as to β-lactam antibiotics.
What is the cell wall of bacteria?
A cell wall, not just of bacteria but for all organisms, is found outside of the cell membrane. It’s an additional layer that typically provides some strength that the cell membrane lacks, by having a semi-rigid structure. Both gram positive and gram negative cell walls contain an ingredient known as peptidoglycan (also known as murein ).
How many types of cell walls do bacteria have?
Having said that though, it is also important to note that most bacteria (about 90%) have a cell wall and they typically have one of two types: a gram positive cell wall or a gram negative cell wall. The two different cell wall types can be identified in the lab by a differential stain known as the Gram stain.
Which phylum has a cell wall that is not a cell wall?
Bacteria belonging to the phylum Tenericutes lack a cell wall altogether, which makes them extremely susceptible to osmotic changes.
What is the cell wall made of?
The cell wall, which is responsible for initiating inflammation, is composed of interlinked disaccharide peptides that form a network.27 This backbone is decorated with a polyribitol teichoic acid which is unusual in that it contains phosphorylcholine. 55 The phosphorylcholine and the chemical composition of the cell wall building blocks are critical to the inflammatory activity of the cell wall. 28
What are cell wall PMWs? What are their properties?
The most noticeably changed properties of cell-wall PMWs are those which depend on moisture movement and uptake, including swelling, water vapor diffusion coefficient, and weathering. Wood-destroying organisms do not degrade them and they are highly resistant to acids and bases. However, cell-wall PMWs are more brittle than the parent wood cell wall, which is their chief disadvantage. The dark-brown color of furfuryl alcohol-based PMWs is useful for dark-colored products, but the darkness sometimes limits their usefulness.
What are the proteins in the cell wall?
Cell walls consist primarily of polysaccharides, i.e., cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of hemicellulose and pectin, but structural proteins, in the form of glycoproteins, may also form networks in the cell wall (Fig. 5-2 ). Four classes of structural proteins have been found in cell walls. Three of them are known by the most abundant amino acid they contain: hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs), proline-rich proteins (PRPs), and glycine-rich proteins (GRPs). The fourth class is arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs). Each of these protein groups is coded by a large multigene family. Upon their production they are inserted in the endoplasmic reticulum and, through signal peptides they encode, they are targeted to the cell wall through the secretory pathway. One of the HRGP proteins is extensin, which makes up only 0.5% of the cell wall mass in healthy tissue but increases to 5 to 15% of the wall mass on infection with fungi and helps add rigidity to the cell wall. Another group of cell wall proteins are the lectins, which bind to specific sugar molecules. The role of all of these groups of proteins is not clear, but they are thought to accumulate in response to elicitor molecules released by fungi and to play a role in the plant defense response. The breakdown of structural proteins is presumably advantageous to invading pathogens and is thought to be similar to that of proteins contained within plant cells. This is discussed later.
What are cell wall deficient bacteria?
Cell wall-deficient bacteria are strains of bacteria that lack cell walls. The peptidoglycan that makes up the cell wall can be destroyed or inhibited by physical, chemical, or biological factors. When gram-positive bacteria lack a cell wall, the cytoplasm is surrounded by the cell membrane, and the entire structure is known as a protoplast. When gram-negative bacteria do not have a cell wall, the cytoplasm is protected by the outer membrane, and the entire structure is called a spheroplast. Bacteria that have lost their cell wall are still capable of growing and dividing as cell wall-deficient bacteria. Examples of these were first isolated in 1935 by Emmy Klieneberger-Nobel, who named them “l -forms” after the Lister Institute in London where she was working at the time. l -form bacteria give rise to a variety of cell morphologies and sizes and can be spherical, rod-shaped, filiform, etc. The rate of growth and division of l -form bacteria is slow. They also form distinctive bacterial colonies when plated on agar. Some l -form strains have a tendency to revert to the normal phenotype when the conditions that were used to produce the cell wall deficiency are reduced. l -form bacteria are difficult to stain or stain unevenly. In a Gram stain test, l -form bacteria always show up as gram-negative, due to the lack of a cell wall.
What is the cell wall of plants?
It is the outer most boundary of the plant cells. Each cell whether isolated or occurring in tissues has its own cell wall. The chemical composition of cell wall is different from specie to. E.g. plant cell wall is composed of Cellulose, Hemicellulose and pectin.
What is the layer between the primary cell wall and the plasma membrane?
Once the primary cell wall has stopped dividing and growing, it may thicken to form a secondary cell wall. This rigid layer strengthens and supports the cell. In addition to cellulose and hemicellulose,
What is the role of expansion protein in cell formation?
It helps in the formation of cell by removing old microfibrils and adding new microfibrils , And also increases the size of the cell.
Cell Wall Definition
Cell Wall Functions
- The cell wall has a few different functions. It is flexible, but provides strength to the cell, which helps protect the cell against physical damage. It also gives the cell its shape and allows the organism to maintain a certain shape overall. The cell wall can also provide protection from pathogens such as bacteria that are trying to invade the ce...
Cell Wall Structure
- Plant Cell Walls
The main component of the plant cell wall is cellulose, a carbohydrate that forms long fibers and gives the cell wall its rigidity. Cellulose fibers group together to form bundles called microfibrils. Other important carbohydrates include hemicellulose, pectin, and liginin. These carbohydrates f… - Algae Cell Walls
Algae are a diverse group, and the diversity in their cell walls reflects this. Some algae, such as green algae, have cell walls that are similar in structure to those of plants. Other algae, such as brown algae and red algae, have cellulose along with other polysaccharides or fibrils. Diatoms h…
Related Biology Terms
- Cell membrane– A membrane found on the outside of all cells that separates them from the outside environment.
- Turgor pressure– Water pressure inside cells.
- Chitin– A polysaccharide that is a main component of fungal cell walls and also of the exoskeletons of certain animals like insects.
Quiz
- 1. Which is a function of the cell wall? A. To maintain turgor pressure B. To provide support to the cell C. To control what molecules enter and exit the cell D.All of the above 2. The cells of which group of organisms lack a cell wall? A. Archaea B. Bacteria C. Animals D.Fungi 3. Which organism has a cell wall containing chitin? A. Plants B. Algae C. Fungi D.Bacteria