
What is the accounting treatment of contingent liabilities?
So a contingent liability has no accounting treatment as such. Now such contingent liabilities have to be reviewed on a yearly basis. Click to see full answer. Besides, how are contingent liabilities treated in the financial statements?
When can contingent liabilities be reported in financial statements?
Contingent liabilities must pass two thresholds before they can be reported in financial statements: it must be possible to estimate the value of the contingent liability, and the liability must have greater than a 50% chance of being realized.
What are contingent liabilities under GAAP and IFRS?
Both GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) and IFRS (international financial reporting standards) require companies to record contingent liabilities in accordance with the three accounting principles: full disclosure, materiality, and prudence.
What are the thresholds for reporting contingent liabilities?
Contingent liabilities need to pass two thresholds before they can be reported in the financial statements. First, it must be possible to estimate the value of the contingent liability. If the value can be estimated, the liability must have a greater than 50% chance of being realized.
What is the treatment of a contingent liability?
The four contingent liability treatments are probable and estimable, probable and inestimable, reasonably possible, and remote. Recognition in financial statements, as well as a note disclosure, occurs when the outcome is probable and estimable.
Is contingent liability included in financial statements?
A contingent liability is not recognised in the statement of financial position. However, unless the possibility of an outflow of economic resources is remote, a contingent liability is disclosed in the notes.
What is the treatment of contingent liabilities in the financial statements quizlet?
What is the financial reporting treatment for contingent liabilities? A contingent liability is (a) a possible obligation or (b) a present obligation that is not recognized as a provision because (1) an outflow of resources to settle the obligation is not probable or (2) the obligation cannot be reliably estimated.
Is contingent liability recorded in accounting records?
Key Takeaways. A contingent liability is a potential liability that may occur in the future, such as pending lawsuits or honoring product warranties. If the liability is likely to occur and the amount can be reasonably estimated, the liability should be recorded in the accounting records of a firm.
Where are contingent liabilities recorded in balance sheet?
A contingent liability is recorded first as an expense in the Profit & Loss Account and then on the liabilities side in the Balance sheet.
When should contingent liabilities be recorded?
Rules specify that contingent liabilities should be recorded in the accounts when it is probable that the future event will occur and the amount of the liability can be reasonably estimated. This means that a loss would be recorded (debit) and a liability established (credit) in advance of the settlement.
What are contingent liabilities?
Description: A contingent liability is a liability or a potential loss that may occur in the future depending on the outcome of a specific event. Potential lawsuits, product warranties, and pending investigation are some examples of contingent liability.
What is a provision and when must a provision be recognized?
A provision is a liability of uncertain timing or amount. A provision must be recognized when: (1) there is a present obligation, (2) an outflow of resources to settle the obligation is probable, and (3) the obligation can be reliably estimated. 2.
Why Is A Contingent Liability recorded?
Both GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) and IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) require companies to record contingent...
Using Knowledge of A Contingent Liability in Investing
Since a contingent liability can potentially reduce a company’s assets and negatively impact a company’s future net profitability and cash flow, kn...
Impact of Contingent Liabilities on Share Price
Contingent liabilities are likely to have a negative impact on a company’s share price, as they threaten to negatively impact the company’s ability...
Recording Contingent Liabilities
Per GAAP, contingent liabilities can be broken down into three categories based on the likelihood of occurrence of each contingent event. The first...
Incorporating Contingent Liabilities in A Financial Model
Modeling contingent liabilities can be a tricky concept due to the level of subjectivity involved. The opinions of analysts are divided in relation...
What are contingent liabilities?
Contingent liabilities, liabilities that depend on the outcome of an uncertain event, must pass two thresholds before they can be reported in financial statements. First, it must be possible to estimate the value of the contingent liability.
What are the three categories of contingent liabilities?
There are three GAAP-specified categories of contingent liabilities: probable, possible, and remote. Probable contingencies are likely to occur and can be reasonably estimated. Possible contingencies do not have a more-likely-than-not chance of being realized but are not necessarily considered unlikely either. ...
How many thresholds are required for contingent liabilities?
Contingent liabilities must pass two thresholds before they can be reported in financial statements: it must be possible to estimate the value of the contingent liability, and the liability must have greater than a 50% chance of being realized.
Is contingent loss reflected on the balance sheet?
If the contingent loss is remote, meaning it has less than a 50% chance of occurring, the liability should not be reflected on the balance sheet. Any contingent liabilities that are questionable before their value can be determined should be disclosed in the footnotes to the financial statements.
What happens if contingent liability is remote?
If the contingent liability is considered remote, it is unlikely to occur and may or may not be estimable. This does not meet the likelihood requirement, and the possibility of actualization is minimal. In this situation, no journal entry or note disclosure in financial statements is necessary.
What is the difference between IFRS and GAAP?
However, two primary differences exist between US GAAP and IFRS: the reporting of (1) debt due on demand and (2) contingencies.
Is a note disclosure required in financial statements?
In this case, a note disclosure is required in financial statements, but a journal entry and financial recognition should not occur until a reasonable estimate is possible. If the contingency is reasonably possible, it could occur but is not probable. The amount may or may not be estimable.
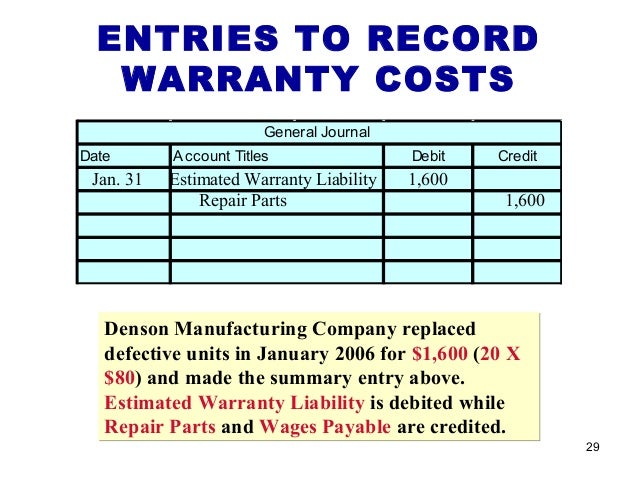
Can warranty expense be increased?
If it is determined that not enough is being accumulated, then the warranty expense allowance can be increased. Since this warranty expense allocation will probably be carried on for many years, adjustments in the estimated warranty expenses can be made to reflect actual experiences.
What are contingent liabilities?
Contingent liabilities takes place when an outcome is uncertain in a future point of time, which may lead to debt or obligation for a corporation. These get treated through two factors- likelihood of occurrence & measurement.
What is GAAP compliance?
Under GAAP compliance, any potential liability losses depend on the future event which turns into actual expenses.
What are some examples of contingent liabilities?
Some examples of contingent liabilities include pending litigation (legal action), warranties, customer insurance claims, and bankruptcy.
What is contingency in business?
A contingency occurs when a current situation has an outcome that is unknown or uncertain and will not be resolved until a future point in time. The outcome could be positive or negative.
What is the difference between IFRS and GAAP?
However, two primary differences exist between US GAAP and IFRS: the reporting of (1) debt due on demand and (2) contingencies.
Is Sierra Sports a contingent liability lawsuit?
Sierra Sports may have more litigation in the future surrounding the soccer goals. These lawsuits have not yet been filed or are in the very early stages of the litigation process. Since there is a past precedent for lawsuits of this nature but no establishment of guilt or formal arrangement of damages or timeline, the likelihood of occurrence is reasonably possible. The outcome is not probable but is not remote either. Since the outcome is possible , the contingent liability is disclosed in Sierra Sports’ financial statement notes.
Is a settlement of responsibility in a lawsuit probable?
A settlement of responsibility in the case has been reached, but the actual damages have not been determined and cannot be reasonably estimated. This is considered probable but inestimable, because the lawsuit is very likely to occur (given a settlement is agreed upon) but the actual damages are unknown.
Do positive contingencies require adjustments?
Positive contingencies do not require or allow the same types of adjustments to the company’s financial statements as do negative contingencies, since accounting standards do not permit positive contingencies to be recorded.
What are contingencies in accounting?
Entities often make commitments that are future obligations that do not yet qualify as liabilities that must be reported. For accounting purposes, they are only described in the notes to financial statements. Contingencies are potential liabilities that might result because of a past event. The likelihood of loss or the actual amount of the loss is still uncertain. Loss contingencies are recognized when their likelihood is probable and this loss is subject to a reasonable estimation. Reasonably possible losses are only described in the notes and remote contingencies can be omitted entirely from financial statements. Estimations of such losses often prove to be incorrect and normally are simply fixed in the period discovered. However, if fraud, either purposely or through gross negligence, has occurred, amounts reported in prior years are restated. Contingent gains are only reported to decision makers through disclosure within the notes to the financial statements.
What is a probable loss?
“Probable” is described in Statement Number Five as likely to occur and “remote” is a situation where the chance of occurrence is slight.
Do you report contingent gains on financial statements?
Contingent gains are only reported to decision makers through disclosure within the notes to the financial statements.
Is the timing used in the recognition of gains the same as the timing used in the recognition of losses?
Answer: As a result of the conservatism inherent in financial accounting, the timing used in the recognition of gains does not follow the same rules applied to losses. Losses are anticipated when they become probable; that is a fundamental rule of financial accounting.
Does the $900,000 loss change in year one?
Restating the Year One loss to $900,000 does not allow them to undo and change the decisions that were made in the past. Consequently, no change is made in the $800,000 figure reported for Year One; the additional $100,000 loss is recognized in Year Two.
Is there a liability to report a truck delivery?
Although cash may be needed in the future, no event (delivery of the truck) has yet created a present obligation. There is not yet a liability to report; no journal entry is appropriate . The information is still of importance to decision makers because future cash payments will be required.
Is disclosure necessary in financial statements?
Answer: If the likelihood of loss is only reasonably possible (rather than probable) or if the amount of a probable loss does not lend itself to a reasonable estimation, only disclosure in the notes to the financial statements is necessary rather than actual recognition.
What are the three categories of contingent liabilities?
GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) recognizes three categories of contingent liabilities, namely probable, possible and remote. Probable contingent liabilities can be reasonably estimated and has to be reflected in the financial statements.
What are the accounting rules for contingent liability?
The accounting rules for reporting a contingent liability differ depending on the estimated dollar amount of the liability and the likelihood of the event occurring. The accounting rules ensure that financial statement readers receive sufficient information. An estimated liability is certain to occur; so, an amount is always entered into ...
What is contingent liability?
Key Takeaways. A contingent liability is a potential liability that may occur in the future, such as pending lawsuits or honoring product warranties. If the liability is likely to occur and the amount can be reasonably estimated, the liability should be recorded in the accounting records of a firm. Contingent liabilities are recorded to ensure ...
Does contingent liability apply to companies?
Contingent liability as a term does not apply only to companies, but to individuals as well. A contingent liability has to be recorded if the contingency is likely and the amount of the liability can be reasonably estimated.
Do you need to disclose contingent liabilities in financial statements?
Possible contingent liabilities are as likely to occur as not and need only be disclosed in the footnotes of financial statement. Remote contingent liabilities are extremely unlikely to occur and do not need to be included in financial statements.

The Reporting Requirements of Contingent Liabilities
Contingent Liabilities
- Two classic examples of contingent liabilities include a company warrantyand a lawsuit against the company. Both represent possible losses to the company, and both depend on some uncertain future event. Suppose a lawsuit is filed against a company, and the plaintiff claims damages up to $250,000. It's impossible to know whether the company should report a continge…
Journal Entries
- A business accounting journal is used to record all business transactions. Each business transaction is recorded using the double-entry accountingmethod, with a credit entry to one account and a debit entry to another. Contingent liabilities, although not yet realized, are recorded as journal entries. Contingent liabilities require a credit to the accrued liability account and a deb…
GAAP Compliance
- Companies operating in the United States rely on the guidelines established in the generally accepted accounting principles(GAAP). Under GAAP, a contingent liability is defined as any potential future loss that depends on a "triggering event" to turn into an actual expense. It's important that shareholdersand lenders be warned about possible losses—an otherwise sound i…
The Bottom Line
- Contingent liabilities are those that are likely to be realized if specific events occur. These liabilities are categorized as being likely to occur and estimable, likely to occur but not estimable, or not likely to occur. Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require contingent liabilities that can be estimated and are more likely to occur to be recorded in a company's finan…