
Explore
ECMO is only a “life-sustaining treatment.” It does not cure or treat the disease or injury that led to heart and/or lung failure. This means it is a treatment that can prolong life to allow for more time to try to fix the problem. Sometimes patients do not get better while they are on ECMO because their disease or injury cannot be fixed.
Why is ECMO treatment so costly?
Dec 17, 2020 · ECMO has been used as a short-term rescue therapy in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) caused by COVID-19 and refractory hypoxemia. However, there is no conclusive evidence that ECMO is responsible for better clinical outcomes regardless of the cause of hypoxemic respiratory failure. 1-4
What risks are there with ECMO?
Jun 02, 2021 · ECMO is a therapy used to treat people with life-threatening heart and lung failure. ECMO involves the use a machine to replace some of the functions of a patient’s lungs or heart, or both simultaneously. While ECMO therapy can be life-saving, it is not itself a treatment.
How long can a critically ill patient stay on ECMO?
Oct 21, 2020 · What Is ECMO for COVID-19? Cannulas. . These plastic tubes are inserted in large blood vessels, such as the femoral artery at the groin or the... Oxygenator. . The drainage cannula sends blood from the patient to the oxygenator. This artificial lung, or membrane,... Blender. . The blender provides ...
How long can you live on ECMO?
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation ( ECMO ), also known as extracorporeal life support ( ECLS ), is an extracorporeal technique of providing prolonged cardiac and respiratory support to persons whose heart and lungs are unable to provide an adequate amount of gas exchange or perfusion to sustain life.
Recommendation
There is insufficient evidence to recommend either for or against the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in adults with COVID-19 and refractory hypoxemia.
Rationale
ECMO has been used as a short-term rescue therapy in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) caused by COVID-19 and refractory hypoxemia. However, there is no conclusive evidence that ECMO is responsible for better clinical outcomes regardless of the cause of hypoxemic respiratory failure. 1-4
What is ECMO therapy?
ECMO is a therapy used to treat people with life-threatening heart and lung failure. ECMO involves the use a machine to replace some of the functions of a patient’s lungs or heart, or both simultaneously. While ECMO therapy can be life-saving, it is not itself a treatment. Instead, it provides a kind of bridge, ...
When is ECMO used?
But in most cases, ECMO therapy is used only when all other conventional treatments have failed to resolve the underlying heart or lung disorders. “ECMO is really the most advanced supportive therapy that is available to critically ill patients suffering from acute or chronic cardiac and respiratory failure,” says Arnar Geirsson, MD, ...
What are the conditions for ECMO?
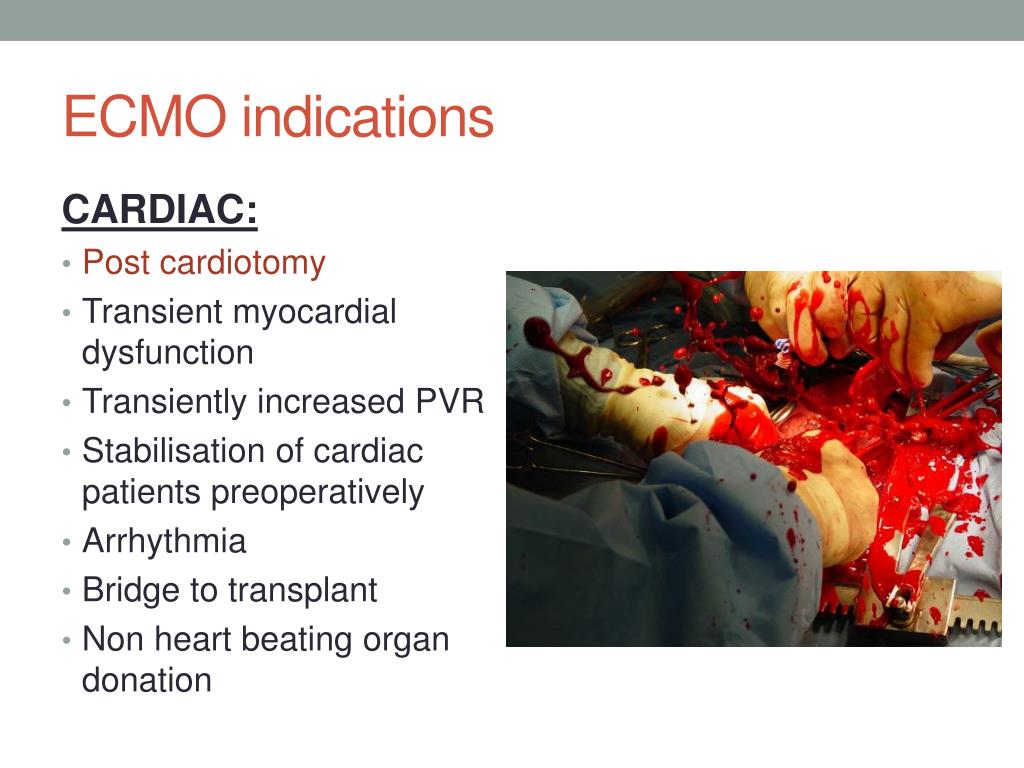
While there is no fixed list of conditions for which ECMO is used, doctors may recommend its use in the following situations: 1 Respiratory failure (when the lungs fail to maintain adequate oxygen levels or remove enough carbon dioxide from the blood) 2 Heart transplantation 3 Lung transplantation 4 Cardiac arrest (when the heart fails to pump blood effectively) 5 Cardiogenic shock (when the ventricles of the heart do not function properly, resulting in insufficient blood flow) 6 Pulmonary embolism (when an artery in the lungs is blocked) 7 Birth defects of the heart 8 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, ARDS (a type of respiratory failure that prevents adequate oxygen from getting to the lungs and blood)
How does an ECMO machine work?
The ECMO machine connects to a patient through plastic tubes called cannulas. After giving the patient an anticoagulant, a medication that prevents blood from clotting, the doctor inserts cannulas into large arteries and veins located in the chest, neck, or legs.
What are the risks of ECMO?
Stroke: In rare cases, ECMO patients develop small blood clots that can reduce the flow of blood to the brain. This raises risk for stroke.
How long does it take to recover from ECMO?
Some patients need it for only a few hours while others may require days or weeks of ECMO support.
Can ECMO cause kidney failure?
Kidney Failure: In some cases, patients on ECMO do not circulate enough blood to their kidneys, resulting in kidney failure and the potential need for dialysis, a machine that does some of the work normally done by kidneys.
What is ECMO treatment?
ECMO removes carbon dioxide waste from the blood and returns oxygen-rich blood back to the body. "ECMO is akin to dialysis for the lungs – in that the same way that dialysis cleans the blood of toxins when the kidneys have failed, ...
When to use ECMO?
ECMO is generally used in patients who are younger than 65 and who were previously healthy , Hodgson says: "People who are older, frail or have other medical conditions do not respond as well.". The decision to put a patient on ECMO is painstaking, with assistance from the ELSO COVID-19 Guidelines.
What are the risks of ECMO?
ECMO treatment has major risks, including: 1 The large ECMO cannulas, or tubes, can cause nerve or blood vessel damage. 2 Bleeding can occur as patients are often being managed with anti-clotting medication to prevent clotting within the ECMO circuit. 3 Infection can result whenever tubes are placed in the body.
What is ECMO in medical terms?
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation , or ECMO, replaces the function of the heart and lungs. ECMO is helping some COVID-19 patients for whom standard treatments have failed and a mechanical ventilator alone is not enough to safely support their breathing.
How long does it take to recover from ECMO?
It usually takes several days to wean patients, she says. However, she adds, some patients recover quickly and are weaned within 24 hours or so.
What is the function of a drainage cannula?
The drainage cannula sends blood from the patient to the oxygenator. This artificial lung, or membrane, removes carbon dioxide from the blood and adds oxygen, all from outside the body. Pump. Acting as the heart would, the rotating pump sends the oxygen-rich blood back to the patient via the return cannula. Blender.
Can ECMO be used for ARDS?
Currently, Agerstrand says, the use of ECMO for ARDS, whether it's due to COVID-19 pneumonia or regular pneumonia, is reserved for someone who has failed conventional, standard-of-care approaches to mechanical ventilation.
What is ECMO in medical terms?
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation ( ECMO ), also known as extracorporeal life support ( ECLS ), is an extracorporeal technique of providing prolonged cardiac and respiratory support to persons whose heart and lungs are unable to provide an adequate amount of gas exchange or perfusion to sustain life. The technology for ECMO is largely derived ...
What is ECMO management?
ECMO management is commonly performed by a registered nurse, respiratory therapist, or a perfusionist. Once it has been decided to inititiate ECMO, the patient is anticoagulated with intravenous heparin to prevent thrombus formation from clotting off the oxygenator. Prior to initiation, an IV bolus of heparin is given and measured to ensure that the activated clotting time (ACT) is between 300 and 350 seconds. Once the ACT is between this range, ECMO can be initiated and a heparin drip will be started after as a maintenance dose.
What are the contraindications for a syringe?
Most contraindications are relative, balancing the risks of the procedure versus the potential benefits. The relative contraindications are: 1 Conditions incompatible with normal life if the person recovers 2 Preexisting conditions that affect the quality of life ( CNS status, end-stage malignancy, risk of systemic bleeding with anticoagulation) 3 Age and size 4 Futility: those who are too sick, have been on conventional therapy too long, or have a fatal diagnosis.
What is an ECMO device?
The device used is a membrane oxygenator, also known as an artificial lung. ECMO works by temporarily drawing blood from the body to allow artificial oxygenation of the red blood cells and removal of carbon dioxide.
Why is left ventricular output monitored during VA ECMO?
Left ventricular output is rigorously monitored during VA ECMO because left ventricular function can be impaired from increased afterload, which can in turn lead to formation of thrombus within the heart.
What are the criteria for ECMO?
Criteria for the initiation of ECMO vary by institution, but generally include acute severe cardiac or pulmonary failure that is potentially reversible and unresponsive to conventional management. Examples of clinical situations that may prompt the initiation of ECMO include the following:
How are cannulae placed?
Cannulae can be placed percutaneously by the Seldinger technique , a relatively straightforward and common method for obtaining access to blood vessels, or via surgical cutdown. The largest cannulae that can be placed in the vessels are used in order to maximize flow and minimize shear stress.

Why It's Done
- ECMO may be used to help people who are very ill with conditions of the heart and lungs, or who are waiting for or recovering from a heart transplant. It may be an option when other life support measures haven't worked. ECMOdoes not treat or cure a disease, but can help you when your bo…
Risks
- The most common risks that may occur with ECMOinclude: 1. Bleeding 2. Blood clot (thromboembolism) 3. Blood clotting disorder (coagulopathy) 4. Infection 5. Loss of blood in hands, feet or legs (limb ischemia) 6. Seizures 7. Stroke (part of the brain is damaged by loss of blood or by a blood vessel that bursts)
How You Prepare
- ECMO is used when life support is needed after surgery, or when you are very ill and your heart or lungs need help so that you can heal. Your doctor will decide when it may be helpful. If you need ECMO, your doctor and trained respiratory therapists will prepare you.
What You Can Expect
- Your doctor will insert a thin, flexible tube (cannula) into a vein to draw out blood and a second tube into a vein or artery to return warmed blood with oxygen to your body. You will receive other medications, including sedation, to make you comfortable while receiving ECMO, and may not be able to talk during this time. Depending on your condition, ECMO can be used for a few days to …
Results
- The outcomes associated with ECMO depend upon the severity of the health condition that led to use of ECMO. Your doctor can explain how helpful ECMOmay be in your situation.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.