Medication
31 rows · Mar 01, 2022 · Penicillin (10 days of oral therapy or one injection of intramuscular benzathine penicillin) is the treatment of choice because of …
Self-care
Sep 11, 2016 · Gerber 1999a found no difference in bacteriologic treatment success rates between cefadroxil and penicillin groups among participants classified clinically as likely to have true GABHS pharyngitis, but cephalosporins seemed to be more successful in eradicating GABHS in patients classified as clinically likely to be streptococcal carriers.
Nutrition
Penicillin has remained the drug of choice for treatment of patients with streptococcal pharyngitis for the past four decades. From the early 1950s into the 1970s, a single injection of intramuscular penicillin G benzathine, alone or in combination with penicillin G procaine, was the preferred treatment.
How to heal a strep throat naturally?
Nov 20, 2020 · For people with a penicillin allergy, treat Strep throat with either a narrow-spectrum cephalosporin (such as cephalexin or cefadroxil ), clindamycin, azithromycin, or clarithromycin. Note that resistance to azithromycin and clarithromycin has been reported.
What happens when strep throat goes untreated?
Jul 15, 2021 · Given its narrow spectrum, low cost, and efficacy in preventing ARF, penicillin is the drug of choice for treatment of GAS pharyngitis. Amoxicillin is a more palatable suspension than penicillin V and is equally effective when used as a single …
How long does strep throat last without antibiotics?
61 rows · Your doctor will examine your neck and lymph nodes and may take a swab of your throat if Strep throat is suspected. Strep Throat Treatment. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin to treat your Strep throat. It is important to take these as prescribed and finish the course of treatment.
What to do if exposed to strep throat?
Apr 15, 2001 · For almost five decades, penicillin has been the drug of choice for the treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis.

What is the drug of choice for most streptococcal infections?
Which medication is the treatment of choice for bacterial pharyngitis?
What is the first line treatment for pharyngitis?
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating |
|---|---|
| Penicillin is the first-line antibiotic for treating GABHS pharyngitis. | A |
| Symptomatic treatment of GABHS pharyngitis can include medicated throat lozenges, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and topical anesthetics. | B |
What is the antibiotic of choice for strep throat?
How is streptococcus infection treated?
Does azithromycin treat strep throat?
Does doxycycline treat strep throat?
Is doxycycline an antibiotic?
What is strep pharyngitis?
Group A strep pharyngitis is an infection of the oropharynx caused by S. pyogenes. S. pyogenes are gram-positive cocci that grow in chains ( see figure 1 ). They exhibit β -hemolysis (complete hemolysis) when grown on blood agar plates. They belong to group A in the Lancefield classification system for β-hemolytic Streptococcus, and thus are called group A streptococci.
How is strep pharyngitis transmitted?
Typically transmission occurs through saliva or nasal secretions from an infected person. People with group A strep pharyngitis are much more likely to transmit the bacteria to others than asymptomatic pharyngeal carriers.
What is the most common cause of pharyngitis in children?
Viruses are the most common cause of pharyngitis in all age groups. Experts estimate that group A strep, the most common bacterial cause, causes 20% to 30% of pharyngitis episodes in children. In comparison, experts estimate it causes approximately 5% to 15% of pharyngitis infections in adults.
Can you take penicillin for pharyngitis?
Clinicians should not treat viral pharyngitis with antibiotics. Penicillin or amoxicillin is the antibiotic of choice to treat group A strep pharyngitis. There has never been a report of a clinical isolate of group A strep that is resistant to penicillin.
Can strep pharyngitis cause suppurative complications?
Rarely, suppurative and nonsuppurative complications can occur after group A strep pharyngitis. Suppurative complications result from the spread of group A strep from the pharynx to adjacent structures. They can include:
Can a RADT be positive?
Clinicians can use a positive RADT as confirmation of group A strep pharyngitis in children. However, clinicians should follow up a negative RADT in a child with symptoms of pharyngitis with a throat culture. Clinicians should have a mechanism to contact the family and initiate antibiotics if the back-up throat culture is positive.
How to prevent group A strep?
Good hand hygiene and respiratory etiquette can reduce the spread of all types of group A strep infection. Hand hygiene is especially important after coughing and sneezing and before preparing foods or eating. Good respiratory etiquette involves covering your cough or sneeze.
What is the best treatment for strep throat?
Penicillin or amoxicillin are considered the best first-line treatments for Strep throat. According to the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) “ There has never been a report of a clinical isolate of group A strep that is resistant to penicillin ”.
What antibiotics are used for strep throat?
For people with a penicillin allergy, treat Strep throat with either a narrow-spectrum cephalosporin (such as cephalexin or cefadroxil ), clindamycin, azithromycin, or clarithromycin. Note that resistance to azithromycin and clarithromycin has been reported.
Does strep throat get better?
Although most Strep throats will get better by themselves , there is a risk of acute rheumatic fever and other complications (such as oral abscesses or mastoiditis [a bacterial infection in the mastoid process, which is the prominent bone behind the ear]) occurring.
Can you take antibiotics for a sore throat?
Viral sore throats should not be treated with antibiotics. Treatment is usually given for ten days and liquid antibiotics can be given to children who are unable to swallow tablets or capsules. Some patients may benefit from a single shot of penicillin intramuscularly.
How do you know if you have a strep throat?
Symptoms of a Strep throat may include: Swollen and tender glands (lymph nodes) in the neck. Children are more likely to feel sick (develop nausea) and vomit. People with a Strep throat do NOT typically have a cough, runny nose, hoarseness, mouth ulcers, or conjunctivitis.
Why does my throat feel like sandpaper?
Some people (usually children aged 4 to 8years) are susceptible to the toxins (poisons) produced by the S. pyrogenes bacteria and develop a bright red rash that feels like sandpaper to the touch.
How long does it take for strep throat to pass?
Without treatment, people with Strep throat can pass on the bacteria to others for one to two weeks after symptoms appear. The best way to prevent infection is to wash your hands often and always before eating or after being in contact with an infected person. Do not share utensils, linen, or personal items.
What are the symptoms of rheumatic fever?
Rheumatic fever can also develop following a Strep throat infection or scarlet fever. Rheumatic fever has the potential to cause life-long cardiac problems if not treated promptly or properly and it can also affect the joints, skin, and the brain. Symptoms of rheumatic fever include: 1 Fever 2 Abdominal pain 3 Chest pain or shortness of breath 4 Joint swelling, pain, redness, or warmth 5 Nose bleeds 6 A rash on the upper part of the arms or legs (usually ring-shaped or snake-like 7 Skin nodules or lumps 8 In young children, unusual crying or laughing or quick jerky movements of the face, hands, or feet.
How to treat a sore throat?
Other remedies that can help relieve the symptoms of a sore throat include: 1 Acetaminophen or ibuprofen to relieve pain 2 Lemon and honey warm drinks, tea 3 Cool liquids or iceblocks to help numb the throat 4 Sucking throat lozenges 5 Apple cider vinegar 6 Marshmallow root 7 Slippery elm.
What is a strep throat?
Strep throats are a type of bacterial sore throat caused by Streptococcus pyrogene bacteria, a type of Group A streptococci. They are common in children aged five to fifteen years, but rare in children under the age of three. Generally, Strep sore throats tend to be very painful and symptoms persist for a lot longer than sore throats due ...
What is the cause of a sore throat?
Strep throats are a type of bacterial sore throat caused by Streptococcus pyrogene bacteria, a type of Group A streptococci. They are common in children aged five to fifteen years, but rare in children under the age of three.
What are the symptoms of a strep throat?
Other symptoms that are more likely to occur with a Strep throat include: A very red and swollen-looking throat and tonsils; sometimes streaks of pus or red spots on the roof of the mouth are visible. Headache. Fever and Chills.
How do you know if you have a strep throat?
Other symptoms that are more likely to occur with a Strep throat include: A very red and swollen-looking throat and tonsils; sometimes streaks of pus or red spots on the roof of the mouth are visible. Headache. Fever and Chills. Swollen and tender glands (lymph nodes) in the neck. Vomiting or nausea (mostly in children).
What does it mean when your throat is red?
A very red and swollen-looking throat and tonsils; sometimes streaks of pus or red spots on the roof of the mouth are visible. Headache . Fever and Chills. Swollen and tender glands (lymp h nodes) in the neck. Vomiting or nausea (mostly in children).
What percentage of pharyngitis is caused by bacteria?
Bacteria are responsible for approximately 5 to 10 percent of pharyngitis cases, with group A beta-hemolytic streptococci being the most common bacterial etiology. A positive rapid antigen detection test may be considered definitive evidence for treatment; a negative test should be followed by a confirmatory throat culture when streptococcal ...
What is the most common bacterial etiology for pharyngitis?
Bacteria are responsible for approximately 5 to 10 percent of pharyngitis cases, with group A beta-hemolytic streptococci being the most common bacterial etiology. A positive rapid antigen detection test may be considered definitive evidence for treatment; a negative test should be followed by a confirmatory throat culture when streptococcal pharyngitis is strongly suspected. Treatment goals include prevention of suppurative and nonsuppurative complications, abatement of clinical signs and symptoms, reduction of bacterial transmission and minimization of antimicrobial adverse effects. Antibiotic selection requires consideration of patients' allergies, bacteriologic and clinical efficacy, frequency of administration, duration of therapy, potential side effects, compliance and cost. Oral penicillin remains the drug of choice in most clinical situations, although the more expensive cephalosporins and, perhaps, amoxicillin-clavulanate potassium provide superior bacteriologic and clinical cure rates. Alternative treatments must be used in patients with penicillin allergy, compliance issues or penicillin treatment failure. Patients who do not respond to initial treatment should be given an antimicrobial that is not inactivated by penicillinase-producing organisms (e.g., amoxicillin-clavulanate potassium, a cephalosporin or a macrolide). Patient education may help to reduce recurrence.
How long does it take for pharyngitis to develop?
Pharyngitis caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, commonly called “strep throat” or streptococcal pharyngitis, has an incubation period of two to five days and is most common in children five to 12 years of age. The illness can occur in clusters and is diagnosed most often in the winter and spring.
How are streptococci spread?
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci are ordinarily spread by direct person-to-person contact, most likely through droplets of saliva or nasal secretions. 3 Crowding increases transmission, and outbreaks of streptococcal pharyngitis are common in institutional settings, the military, schools and families.
What is the sensitivity of a throat culture?
Throat culture remains the gold standard for the diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis. Under ideal conditions, the sensitivity of throat culture for group A beta-hemolytic streptococci is 90 percent; in office settings, the sensitivity ranges from 29 to 90 percent. The specificity of throat culture is 99 percent under ideal conditions and can be anywhere from 76 to 99 percent in office settings. 5
What is the best antibiotic for pharyngitis?
For almost five decades, penicillin has been the drug of choice for the treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis. This antibiotic has proven efficacy and safety, a narrow spectrum of activity and low cost.
How long does amoxicillin last in children?
In children, the cure rates for amoxicillin given once daily for 10 days are similar to those for penicillin V. 16 – 18 The absorption of amoxicillin is unaffected by the ingestion of food, and the drug's serum half-life in children is longer than that of penicillin V.
Etiology
Clinical Features
Transmission
Risk Factors
Specialist to consult
Diagnosis and Testing
Special Considerations
Treatment
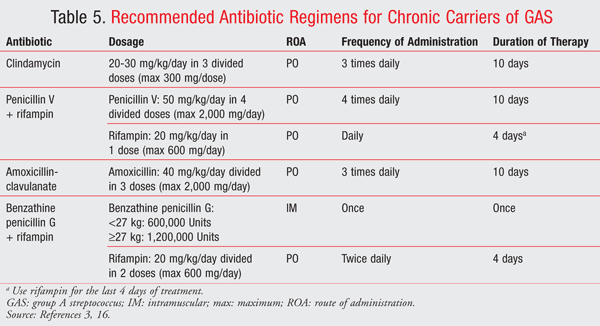
Carriage
Prognosis and Complications
Prevention