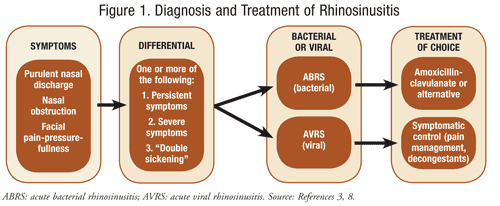
Many ailments and illnesses have similar symptoms whether they are viral or bacterial—the biggest difference between the two types of infections is that bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics, while viral infections cannot. Bacterial Respiratory Tract Infection Symptoms
How to tell a viral from a bacterial infection?
In addition to risk factors by age and people who live in group settings, people with certain medical conditions, including HIV infection or not having a spleen, are at higher risk for types of bacterial meningitis, according to the CDC. A severe headache is one of the hallmark signs of meningitis, Clarke said.
What is the difference between viral and bacterial?
When a doctor listens to the lungs and finds breathing sounds are not clear on either side of the chest, a viral cause over bacterial is even more highly suspected. Viruses affect both sides of the lungs by producing a more homogeneous inflammatory reaction that causes increased cellular debris and mucus where previously open lung pockets were present.
Can I tell if my infection is from virus or bacteria?
How to Tell a Viral from a Bacterial Infection
- Pay attention to the color of your mucus. When you blow your nose or cough up mucus,...
- Observe your throat. A sore throat is common for both viral and bacterial infections.
- Evaluate your fever. Fevers can be present in both viral and bacterial infections.
- Reflect on your likelihood...
What are the symptoms of a viral respiratory infection?
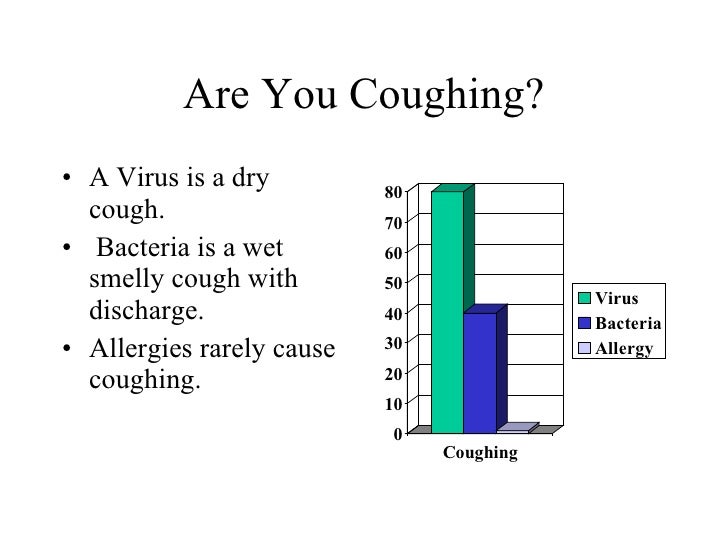
Viral infections are notorious for the symptoms that they cause that affect the respiratory system. That's why coughing is one of the most common symptoms of many viral infections. As the body fights the virus, it may produce a large quantity of phlegm, causing a cough to appear. Coughs may be dry or wet, depending on the amount of phlegm produced.
How are treatments for bacterial and viral infections different?
Answer From Pritish K. Tosh, M.D. As you might think, bacterial infections are caused by bacteria, and viral infections are caused by viruses. Perhaps the most important distinction between bacteria and viruses is that antibiotic drugs usually kill bacteria, but they aren't effective against viruses.
Do you treat viral or bacterial with antibiotics?
Viruses are germs different from bacteria. They cause infections, such as colds and flu. However, antibiotics do not treat infections caused by viruses. For more information on common illnesses and when antibiotics are and aren't needed, visit Common Illnesses.
Can bacterial and viral infections be treated the same way?
While bacteria and viruses can both cause mild to serious infections, they are different from each other. This is important to understand, because bacterial and viral infections must be treated differently. Misusing antibiotics to treat viral infections contributes to the problem of antibiotic resistance.
How do you tell the difference between a bacterial and a viral upper respiratory infection?
Bacterial Infections Symptoms persist longer than the expected 10-14 days a virus tends to last. Fever is higher than one might typically expect from a virus. Fever gets worse a few days into the illness rather than improving.
What are 3 differences between viruses and bacteria?
Bacteria are single-celled, living organisms. They have a cell wall and all the components necessary to survive and reproduce, although some may derive energy from other sources. Viruses are not considered to be “living” because they require a host cell to survive long-term, for energy, and to reproduce.
How are viral infections treated?
For most viral infections, treatments can only help with symptoms while you wait for your immune system to fight off the virus. Antibiotics do not work for viral infections. There are antiviral medicines to treat some viral infections. Vaccines can help prevent you from getting many viral diseases.
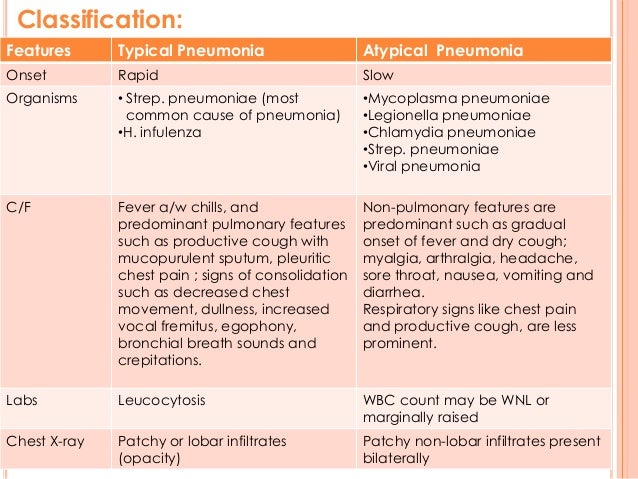
Is pneumonia viral or bacterial?
Pneumonia is an infection of one or both of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. There are more than 30 different causes of pneumonia, and they're grouped by the cause. The main types of pneumonia are bacterial, viral, and mycoplasma pneumonia.
Which antibiotic is best for viral infection?
The drugs used for viral infection are Acyclovir (Zovirax), famciclovir (Famvir), and valacyclovir (Valtrex) are effective against herpesvirus, including herpes zoster and herpes genitalis. Drugs used for treatment for viral fever are Acetaminophen(Tylenolothers)ibuprofen (Advil,motrin IB others).
What is the fastest way to get rid of a upper respiratory infection?
Most of the time, viruses cause upper respiratory infections. Viruses don't respond to antibiotics. You can most likely treat the symptoms at home through pain relievers, rest and drinking fluids. If you have a bacterial infection, such as strep throat, you'll take antibiotics.
How do doctors know if it's viral or bacterial?
Diagnosis of Bacterial and Viral Infections But your doctor may be able to determine the cause by listening to your medical history and doing a physical exam. If necessary, they also can order a blood or urine test to help confirm a diagnosis, or a "culture test" of tissue to identify bacteria or viruses.
How do I know if my cough is bacterial or viral?
In addition to lab tests, sputum or mucus from a cough can be visually examined to determine whether bronchitis is viral, bacterial, or both. Clear or white mucus often indicates a viral infection, while yellow or green mucus may suggest a bacterial infection.
Which antibiotic is best for respiratory infection?
The recommended first-line treatment is a 10-day course of penicillin. Erythromycin can be used in patients who are allergic to penicillin. Amoxicillin, azithromycin (Zithromax), and first-generation cephalosporins are appropriate alternatives.
Why are bacterial and viral infections dissimilar?
But bacterial and viral infections are dissimilar in many other important respects, most of them due to the organisms' structural differences and the way they respond to medications.
Why are viral infections so difficult to treat?
But the treatment of viral infections has proved more challenging, primarily because viruses are relatively tiny and reproduce inside cells. For some viral diseases, such as herpes simplex virus infections, HIV/AIDS, and influenza, antiviral medications have become available.
Why are antibiotics important?
The discovery of antibiotics for bacterial infections is considered one of the most important breakthroughs in medical history. Unfortunately, bacteria are very adaptable, and the overuse of antibiotics has made many of them resistant to antibiotics. This has created serious problems, especially in hospital settings.
What are the two types of infections?
Bacterial and Viral Infections. Bacterial and viral infections have many things in common. Both types of infections are caused by microbes -- bacteria and viruses, respectively -- and spread by things such as: Coughing and sneezing. Contact with infected people, especially through kissing and sex.
What are the symptoms of a viral infection?
Bacterial and viral infections can cause similar symptoms such as coughing and sneezing, fever, inflammation, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and cramping -- all of which are ways the immune system tries to rid the body of infectious organisms. But bacterial and viral infections are dissimilar in many other important respects, ...
How long have bacteria been around?
Fossilized records show that bacteria have existed for about 3.5 billion years, and bacteria can survive in different environments, including extreme heat and cold, radioactive waste, and the human body.
What are the causes of acute infection?
Coughing and sneezing. Contact with infected people, especially through kissing and sex. Contact with contaminated surfaces, food, and water. Contact with infected creatures, including pets, livestock, and insects such as fleas and ticks. Microbes can also cause: Acute infections, which are short-lived.
What is the best treatment for upper respiratory infections?
Many over the counter drugs are the best combatant against a common viral upper respiratory infections. In some cases, antivirals are prescribed, but usually, patients can best be served by using a myriad of over the counter medicines in combination with home remedies and a few different foods.
How to tell if an infection is viral or bacterial?
Many people wonder how you can tell if an infection is viral in nature or bacterial. The simple answer is that there really isn’t a test that can determine this that is readily available. Viruses often have a rapid onset , and brings with it fever right away . Bacterial infections may not present with a fever, or if they do, it’s much later, ...
How long does a viral infection last?
Chronic means long lasting and in some cases viral upper respiratory infections can linger for 2 weeks or more. If you suspect that you have a chronic infection you should mention these concerns to a doctor.
How long does a fever last with a yellow discharge?
If you have green or yellow discharge, and your symptoms have lasted more than 10 days, you should see a doctor. SmartDocMD is an online doctor service that is available to patients like you.
Where do upper respiratory infections occur?
Upper respiratory infections occur in the lungs, chest, sinuses, and throat. Viral germs are spread easily from one person to another when infected people cough, sneeze, touch their nose, or rub their eyes, and distribute tiny droplets of the virus to surfaces or the air. It is important to determine if your upper respiratory infection is caused by ...
Can a viral infection turn into a bacterial infection?
Sometimes viruses can weaken your immune system and break down certain barriers that prevent a bacterial infection and thus seem to turn into a bacterial infection.
Can you treat upper respiratory infections with antibiotics?
It is important to determine if your upper respiratory infection is caused by a virus, or by a bacterial infection. Bacterial infections can be treated with an antibiotic. A viral infection cannot be treated with antibiotics. Doing so actually furthers the drug resistant antibiotic health crisis. Many people wonder how you can tell ...
Why are doctors holding off prescribing antibiotics?
With inappropriate prescribing being one of the chief reasons behind the global crisis of antibiotic resistance, it seems slamming on the brakes is tough – for many reasons. But maybe this is about to get a little easier.
Do anti-microbials kill bacteria?
Aside from antibiotic resistance, anti-microbials are not pathogen-specific so they are liable to kill off healthy bacteria as well dangerous ones, creating a potentially lethal imbalance in the body’s natural defenses. Hopefully, some research at Duke University, recently published in Science Translational Medicine, ...
Why is it important to understand the difference between a virus and a bacteria?
This is important to understand, because bacterial and viral infections must be treated differently. Misusing antibiotics to treat viral infections contributes to the problem of antibiotic resistance .
What is the difference between a virus and a bacterium?
Bacteria and viruses are too tiny to be seen by the naked eye, can cause similar symptoms and are often spread in the same way, but that’s where the similarities end. A bacterium is a single, but complex, cell.
What are some examples of bacterial infections?
Examples of bacterial infections include whooping cough, strep throat, ear infection and urinary tract infection (UTI). Viral infections include the common cold, flu, most coughs and bronchitis, chickenpox and HIV/AIDS. It can be difficult to know what causes an infection, because viral and bacterial infections can cause similar symptoms.
What is the best way to stop viral reproduction?
stopping viral reproduction using antiviral medicines, such as medicines for HIV/AIDS and cold sores. preventing infection in the first place, such as vaccines for flu and hepatitis. Remember: Antibiotics won’t work for viral infections.
Can a swab be used to find out what infection you have?
It can be difficult to know what causes an infection, because viral and bacterial infections can cause similar symptoms. Your doctor may need a sample of your urine, stool or blood, or a swab from your nose or throat to see what sort of infection you have.
Can bacteria survive on their own?
It can survive on its own, inside or outside the body. Most bacteria aren’t harmful. In fact, we have many bacteria on and inside our body, especially in the gut to help digest food. Viruses are smaller and are not cells. Unlike bacteria, they need a host such as a human or animal to multiply.
Can antibiotics kill bacteria?
Doctors usually treat bacterial infections with antibiotics. They either kill bacteria or stop them multiplying. But since antibiotic resistance is a growing problem, antibiotics may be prescribed only for serious bacterial infections.
How to diagnose a viral infection?
In order to diagnose a bacterial or viral infection, a doctor will ask a person about their medical history and symptoms. The doctor may then order tests to look for signs of bacteria or viruses in the person’s blood or urine, or from a throat or nasal swab.
How to prevent infection?
However, some infections are untreatable. The best way to prevent infection is to practice good hygiene. Vaccines are an effective method for preventing certain viruses, such as measles, mumps, and polio. A person should visit their doctor if they suspect they may have an infection.
What are the different types of microorganisms?
Bacteria, viruses, and fungi are different types of microorganisms. Pathogens are microorganisms that have the potential to cause illness or disease. Bacterial pathogens cause bacterial infections, whereas viral pathogens cause viral infections. Sometimes, both bacteria and viruses can cause illness. Examples include pneumonia and meningitis.
Where do Viridans group streptococci live?
Viridans group streptococci. V iridans group streptococci most commonly exist in the mouth, gut, and genital region. Severe infections can occur if the bacteria enter other parts of the body. A Viridans group streptococci infection that enters the bloodstream can infect the inner lining of the heart.
What are the benefits of bacteria?
helping people to digest food. providing vitamins. getting rid of cells that could cause disease. Less than 1% of bacterial species can cause bacterial infections. Such infections occur when the bacteria enter the body and invade the body’s immune system, where they quickly multiply and produce harmful toxins.
How many types of staph are there?
There are more than 30 types of Staphylococcus, or staph, bacteria. Most staph infections are due to the species Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). This bacteria lives on the skin or inside the nose and can enter the body through an open wound.
Where does group B strep live?
Group B strep. Group B strep, such as Streptococcus agalactiae usually live harmlessly inside the digestive system and female genital tract. Group B strep most commonly affects newborns. This is because the bacteria can pass from mother to fetus in the womb.
What is the difference between a viral infection and a bacterial infection?
What's the difference between a bacterial infection and a viral infection? As you might think, bacterial infections are caused by bacteria, and viral infections are caused by viruses. Perhaps the most important distinction between bacteria and viruses is that antibiotic drugs usually kill bacteria, but they aren't effective against viruses.
Can viruses survive?
Viruses. Viruses are even smaller than bacteria and require living hosts — such as people, plants or animals — to multiply. Otherwise, they can't survive. When a virus enters your body, it invades some of your cells and takes over the cell machinery, redirecting it to produce the virus.
Can bacteria cause a person to die?
Most bacteria cause no harm to people, but there are exceptions. Infections caused by bacteria include: Strep throat. Tuberculosis. Urinary tract infections. Inappropriate use of antibiotics has helped create bacterial diseases that are resistant to treatment with different types of antibiotic medications.
What is the difference between a viral infection and a bacterial infection?
The difference between bacterial and viral infections is simple: bacterial infections are caused by bacteria (single-celled microorganisms), while viral infections are caused by viruses (smaller than bacteria and require a living host to multiply).
What is a bacterial respiratory infection?
A bacterial respiratory tract infection is an infection of the sinuses, throat, airway, or lungs. Bacterial infections may develop after having a viral illness like a cold or the flu. Symptoms tend to localize to one particular area.
What is the most common bacterial infection in the lower respiratory system?
Pneumonia is the most common bacterial lower respiratory infection. It’s an infection that inflames air sacs in one or both lungs—these air sacs may fill with fluid or pus. Pneumonia symptoms include: Cough that produces phlegm or pus. Fever.
How do bacteria spread?
Both viral and bacterial respiratory tract infections are contagious and spread from person to person through respiratory droplets emitted by coughing or sneezing.
What test is used to diagnose respiratory tract infection?
If a respiratory tract infection is suspected, your doctor may perform the following tests to provide the best diagnosis and treatment plan possible: Throat swab: your physician will take a sterile cotton swab and swipe it across the back of your throat.
How to tell if a cold is a viral infection?
Low-grade fever . A few warning signs that your cold has progressed from a viral infection to a bacterial infection are: Symptoms lasting longer than 10–14 days. A fever higher than 100.4 degrees. A fever that gets worse a couple of days into the illness, rather than getting better. White pus-filled spots on the tonsils.
What is the best test for bacterial infection in throat?
They will then be tested in a lab to determine whether you have a bacterial infection in your throat. Lateral neck x-ray: your doctor may order a lateral neck x-ray to rule out epiglottitis, especially if you’ve been having difficulty breathing. Chest x-ray: if pneumonia is suspected, your doctor may order a chest x-ray.
Classic Viral Pneumonia
Often viral cases of pneumonia begin as congestion and cough with or without fever in the first few days. When a doctor listens to the lungs and finds breathing sounds are not clear on either side of the chest, a viral cause over bacterial is even more highly suspected.
Classic Bacterial Pneumonia
When a provider hears lung sounds that seem normal on one side but absent on the other, bacterial pneumonia is more likely. Bacteria tend to aggressively attack one lobe or section of the lungs causing a specific area of inflammation to take over the cells that were filled with air.
Critical Role of Pneumococcal Vaccine in Preventing Pneumonia
In children aged three months to four years, the most common type of bacterial pneumonia is Strep. pneumoniae. In children greater than age four, it remains in the top three most common types. The pneumococcal vaccine series, started at two months of age, significantly reduces the rates of bacterial pneumonia from Strep. Pneumoniae.