What antibiotic is best for strep pneumonia?
- Otitis media. In cases of otitis media, S. ...
- Sinusitis. Acute purulent sinusitis is caused by the same organisms as acute otitis media; thus, S. ...
- Acute bronchitis. ...
- Pneumonia. ...
- Complications.Empyema, the most common infectious complication of pneumococcal pneumonia, occurs in approximately 2% of cases. ...
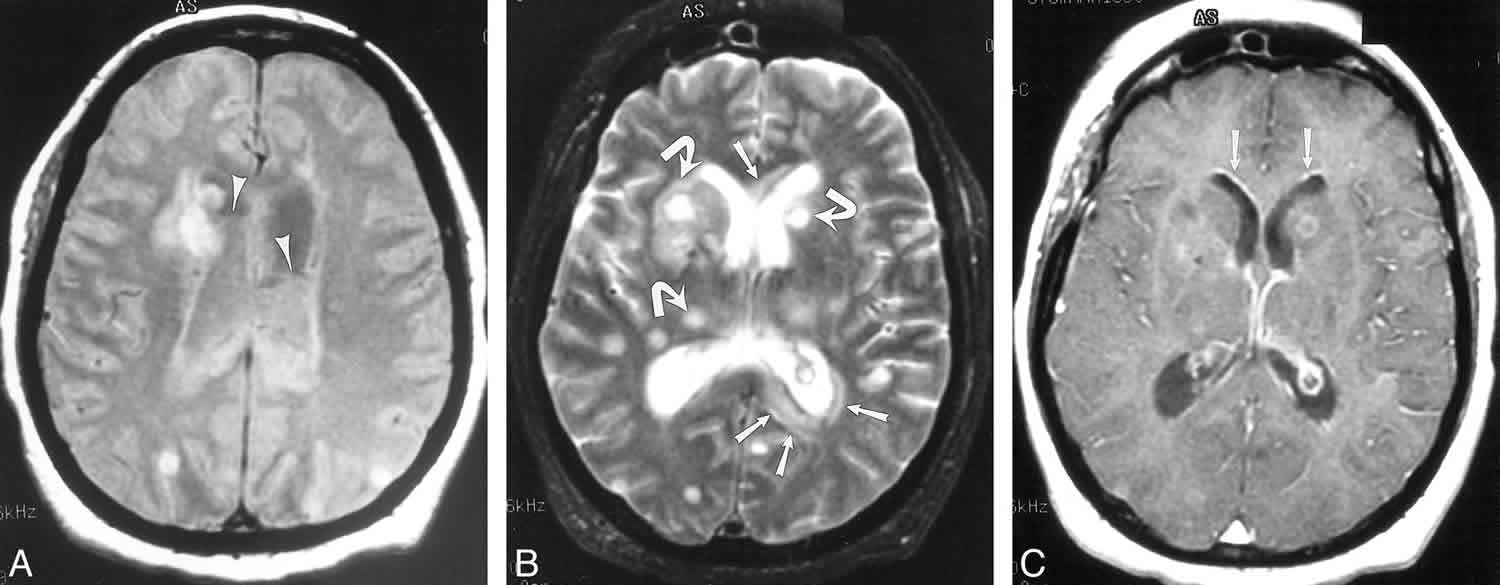
- Meningitis. ...
- Other infections. ...
Is Streptococcus pneumonia good or bad?
Streptococcus pneumonia paves the way to a lot of pneumococcal diseases in people that have very low immune systems, children and elderly people. These diseases are contagious and can spread from a person to another. Along with that, it could also be life-threatening.
What diagnostic tests should you use for pneumonia?
The microbiological tests carried out are:
- Sputum culture. ...
- Pathogenic microbes in urine (pneumococcus and Legionella ).
- Blood culture. ...
- Nasopharyngeal smear for respiratory viruses. ...
- Serological studies to detect any atypical bacteria.
- Pleural fluid culture (only in the case of pleural effusion).
- Bronchial aspirate culture (indicated in patients with mechanical ventilation and severe pneumonia).
What is the best medication for pneumonia?
The options include:
- Antibiotics. These medicines are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. It may take time to identify the type of bacteria causing your pneumonia and to choose the best antibiotic to treat ...
- Cough medicine. This medicine may be used to calm your cough so that you can rest. ...
- Fever reducers/pain relievers. You may take these as needed for fever and discomfort. ...
See more
What is the diagnosis of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Definitively diagnosing Streptococcus pneumoniae infection generally relies on isolating the organism from blood or other normally sterile body sites. Tests are also available to detect capsular polysaccharide antigen in body fluids.
What is the best treatment for Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Penicillin and its derivatives are inexpensive effective antibiotics for treating pneumococcal infections when they are used against susceptible isolates. Penicillins can be administered orally or parenterally and work by inhibiting cell wall synthesis.
What is the treatment for pneumococcal pneumonia?
Thus, based on current levels of resistance to penicillin and cephalosporin, most patients with mild/moderate pneumococcal pneumonia may respond to oral amoxicillin, and most with severe pneumonia may be successfully treated with intravenous ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, or amoxicillin-clavulanic acid.
What is the drug of choice for Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Penicillin G is the parenteral drug of choice for susceptible S pneumoniae infections, and other parenteral beta-lactams do not provide additional or improved coverage (nor do beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations).
How do you treat Streptococcus?
Doctors treat strep throat with antibiotics. Either penicillin or amoxicillin are recommended as a first choice for people who are not allergic to penicillin. Doctors can use other antibiotics to treat strep throat in people who are allergic to penicillin.
What antibiotic kills Streptococcus?
Doctors most often prescribe penicillin or amoxicillin (Amoxil) to treat strep throat. They are the top choices because they're safer, inexpensive, and they work well on strep bacteria.
What antibiotics treat pneumonia?
The first-line treatment for pneumonia in adults is macrolide antibiotics, like azithromycin or erythromycin. In children, the first-line treatment for bacterial pneumonia is typically amoxicillin.
What disease is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Pneumococcal disease is caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). People with pneumococcal disease can spread the bacteria to others when they cough or sneeze. Symptoms of pneumococcal infection depend on the part of the body affected.
How do you get Streptococcus pneumonia?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is spread from person to person by the inhalation of respiratory droplets (e.g. coughing, sneezing) from an infected person. It is not known why certain individuals develop invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae disease while others do not.
Where is Streptococcus pneumoniae found?
The Streptococcus pneumoniae is found and survives at the nose, skin, throat and nasal cavity more precisely the nasopharynx of a person. Although it does not cause any harm to the human body, this bacterium is known to pave the way for various diseases in the people who have weak immune systems. Therefore, certain people are at risk ...
What is the bacterium responsible for pneumonia?
Streptococcus Pneumoniae: Symptoms, Prevention and Treatment. Streptococcus Pneumoniae also referred to as pneumococcus is responsible for the maximum types of pneumonia in human beings. The infection that this bacterium causes could be dangerous and could pave way for a variety of life-threatening diseases.
Why do some people stay at higher risk of catching an infection through the bacteria whereas others don't?
This is because the immune systems of these human beings are low or weak in comparison to others.
Why do people get pneumonia?
This is because their immune system weakens in comparison to others.
Can you take antibiotics for otitis media?
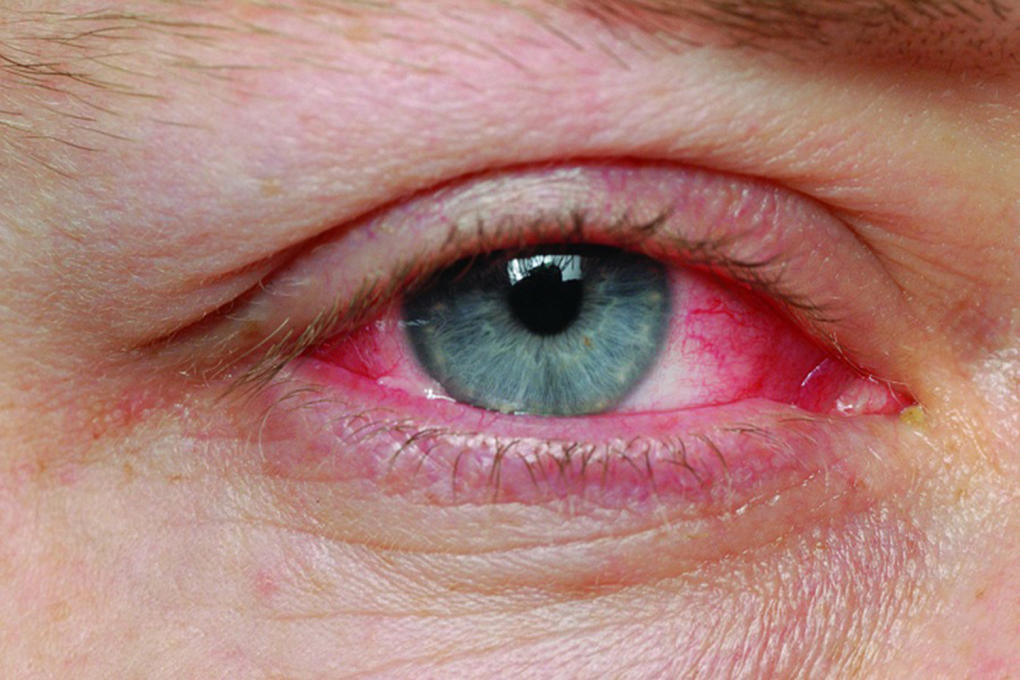
Many pneumococcal diseases like otitis media, bronchitis, trachea bronchitis, sinusitis, and conjunctivitis are mainly treated using antibiotics. However, there might also be people who would not require any treatment or consumption of any antibiotic.
Can pneumonia spread to other people?
These diseases are contagious and can spread from a person to another. Along with that, it could also be life-threatening. Therefore, it is recommended to watch out for the symptoms of pneumococcal disease. The infections of the pneumococcal disease mostly happen around the sinuses, bloodstream, lungs, middle ear and meninges which is the lining of the spinal cord and brain which ultimately results in meningitis.
What antibiotics are used for gram positive strep?
Even in case of gram positive bacteria, the antibiotics group for treating a Streptococcus pneumoniae infection and a Staphylococcus aureus infection of the lungs will differ! Coming back to treating pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, the preferred antibiotics are erythromycin and amoxicillin. In very severe cases or advanced stages of ...
What is the most significant pathogen responsible for bacterial pneumonia?
Streptococcus pneumoniae are the most significant pathogens that are responsible for bacterial pneumonia. Read all about streptococcus pneumoniae treatment in the following write up. Home / General Health / Streptococcus Pneumoniae Treatment. Streptococcus pneumoniae are the most significant pathogens that are responsible for bacterial pneumonia.
What is the color of sputum?
Typical symptoms of bacterial pneumonia include, besides fevers and chills, persistent cough accompanied by production of discolored sputum that appears yellowish-green in color. This discoloration is the most prominent indication that the infection is either caused by bacterial or fungal pathogens.
Is Streptococcus pneumoniae gram positive?
Read all about streptococcus pneumoniae treatment in the following write up. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a gram positive, anaerobic bacterial species which belongs to the Streptococcus genus of gram positive bacteria.
Can gram positive bacteria cause pneumonia?
Now, not all bacterial pneumonia are caused by streptococcus pneumoniae or gram positive bacteria alone for that matter. A small percentage of bacterial pneumonia may also be caused by certain species of gram negative bacteria such as Moraxella catarrhalis, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli.
What is the best treatment for pneumococcal infection?
For serious pneumococcal infections, treatment with a combination of antibiotics is recommended. Vancomycin combined with ceftriazone is used commonly for empiric treatment, followed by monotherapy with an effective cephalosporin, fluoroquinolone or vancomycin. Ceftriaxone can be used for meningitis caused by ceftriaxone-susceptible pneumococci. ...
How to identify S. pneumoniae?
S. pneumoniae is identified by its sensitivity to optochin (ethylhydrocupreine dihydrochloride). The isolate is streaked onto a blood agar plate and a disk saturated with optochin is placed in the middle of the inoculum. A zone of inhibited bacterial growth is seen around the disk after overnight incubation. Bile solubility test.
Can you take penicillin for pneumococci?
Most pneumococci are susceptible to penicillin. Other antibiotics, such as macrolides or selected fluoroquinolones with activity against pneumococci, are available for patients who are allergic to penicillin. Penicillin-resistant pneumococci are being increasingly documented.
How is the infective rate of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Streptococcus pneumoniae lacks the ability to form spores, and do not show any motility. For the first time in the nineteenth century, Streptococcus pneumoniae came into limelight due to several antibody-mediated immunity studies. It was then when scientists discovered that Streptococcus pneumoniae was root cause behind the pneumonia infection.
What are the existing facts about pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a distinct pulmonary infection that you can well identify by the inflammation of alveolar sacs present within lungs. When fluid accumulation occurs in the air sacs due to pneumococcus invasion, you suffer from pneumonia. There are very less chances of you getting fungal pneumonia.
When should you be alert about pneumonia?
The period of incubation for pneumococcal infections mostly rely on the form of pathogen that is causing the disease. The incubation time of viruses, fungi, and bacteria is significantly different from one another.
How contagious can pneumonia be?
Bacterial strains like Streptococcus pneumoniae are often less contagious than the other forms. However, that does not mean you can totally eradicate the chance of pneumonia transmitting via bacterial strains. Always remember, there is not a single strain of bacteria or virus that is non-infectious in nature.
Which microbes cause pneumonia?
Apart from Streptococcus pneumoniae, other bacterial strains are capable of causing pneumonia like-
What are the diagnostic tests for pneumonia?
If you experience any of the probable symptoms of pneumococcal pneumonia, do not think twice before visiting a doctor. The diagnosis of any forms of pneumonia always begins with your medical history, which will reveal the following factors-
How to identify the nature of the causative microbe?
Bronchoscopy is a technique to visualize the insides of your respiratory tract, in search of infectious microbes. The process includes insertion of a long, thin tube into your trachea and vital bronchial airways. Whenever there is a need, the tube will take tissue specimens from the airways.
How many cases of pneumococcal infection are resistant to antibiotics?
Available data. show that pneumococcal bacteria are resistant to one or more antibiotics in 3 out of every 10 cases. Antibiotic treatment for serious pneumococcal infections typically includes ‘broad-spectrum’ antibiotics until results of antibiotic sensitivity testing are available.
Can a doctor test for pneumonia?
Doctors can use a urine test to help make a diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia in adults. Doctors usually diagnose ear and sinus infections based on a history and physical exam findings that support pneumococcal infection.
Do antibiotics work against bacteria?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics work against a wide range of bacteria. Once the sensitivity of the bacteria is known, clinicians may choose a more targeted (or ‘narrow-spectrum’) antibiotic. The number of antibiotic-resistant pneumococcal infections has decreased due to the success of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine.
What is the best medicine for pneumonia?
To treat outpatients for pneumonia, the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends, in no particular order, a macrolide, doxycycline, amoxicillin (with or without clavulanic acid), or a quinolone.
How many pneumococci are susceptible to penicillin?
93% of all pneumococci are susceptible to penicillin if given parenterally or amoxicillin if given orally; 5% are intermediate, and 2% are resistant. In cases of meningitis, 65% of organisms are susceptible to penicillin and 35% are resistant (no intermediate resistance is defined).
How often should I use port scoring for pneumonia?
The importance of the decision to hospitalize or even to directly admit to intensive care cannot be overemphasized, and Pneumonia Patient Outcomes Research Team (PORT) scoring should be used to help decide whether hospitalization is needed. Pneumococcal pneumonia caused by organisms that are susceptible or intermediately resistant to penicillin responds to treatment with penicillin, one million units intravenously every 4 hours, ampicillin, 1g every 6 hours, or ceftriaxone, 1g every 24 hours. Ease of administration favors the use of ceftriaxone. The principal problem is that at the time treatment is begun, the etiology is likely not to be known. If a Gram stain of sputum at admission shows pneumococci, ceftriaxone is the preferred drug, unless the patient is extremely ill, in which case vancomycin should be added until the susceptibility of the infecting organism is known.
How long can you take amoxicillin for tympanic membrane?
In the absence of a perforated tympanic membrane or some other complication, therapy need not be continued beyond 5 days.
What is the MIC of penicillin?
For infections other than those involving the CNS that are treated with parenteral penicillin, susceptibility, intermediate resistance and resistance to penicillin are now defined as mean inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than 2μg/mL, 4μg/mL, and greater than or equal to 8μg/mL, respectively.
What causes pneumonia in the lungs?
S. pneumoniae causes infection of the middle ear, sinuses, trachea, bronchi, and lungs by direct spread of organisms from the nasopharyngeal site of colonization and causes infection of the CNS, heart valves, bones, and joints by hematogenous spread; the peritoneal cavity may be infected by local extension along the female genital tract or hematogenously. Infection of the pleura or peritoneal cavity and also of the CNS may occur by direct extension or by hematogenous spread; in any individual case, the route of infection can usually not be determined.
What is the MIC of a CNS infection?
In CNS infection, organisms with MIC less than or equal to 0.06μg/mL are susceptible; those with MIC greater than or equal to 0.12μg/mL are regarded as resistant. Similar approaches have been developed to define susceptibility to amoxicillin, ceftriaxone, and other beta-lactam antibiotics.
What is Streptococcus pneumoniae
The type Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) is a gram-positive, round-oval to lanceolate cocci with a size of 0.5 to 1.25 mm, which as the previous name "Diplococcus pneumoniae" expresses, are usually mounted in pairs. The adjacent cells are surrounded by a polysaccharide capsule.
Streptococcus pneumoniae pathogenesis
The crucial role for the pathogenicity has the polysaccharide capsule. The capsular polysaccharides are released during the propagation in the environment, thereby neutralizing antibodies and omitted the required opsonization for phagocytosis of pathogens. However, there are great differences in the virulence of individual capsule types.
Streptococcus pneumoniae diagnosis
The microbiological diagnosis made microscopically and culturally. Pneumococci can be well on blood agar plates or in liquid culture media containing blood cultured.
Streptococcus pneumoniae therapy
Antibiotic of first choice for pneumococcal infections is still penicillin (various trade names). With adequate dosage can also infections by strains with low-grade resistance to penicillin can be treated successfully with penicillin.
