Medication
Oct 04, 2018 · Oral antiviral medications Entecavir Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) Lamivudine Adefovir
Procedures
Current treatments for hepatitis B fall into two general categories: Immune modulator Drugs – These are interferon-type drugs that boost the immune system to help get rid of the hepatitis B virus. They are given as a shot (similar to how insulin is given to people with diabetes) over 6 months to 1 year.
Self-care
Mar 09, 2015 · Supportive therapy and monitoring of liver function are the recommended treatments for acute hepatitis B, while antivirals can be used to treat chronic hepatitis B. Antiviral treatment for hepatitis B is more complex when individuals are co …
Nutrition
Feb 18, 2020 · The 2018 AASLD Hepatitis B Guidance recommends initiating HBV treatment in the following situations in persons with chronic HBV. Decompensated Cirrhosis : Initiation of oral antiviral treatment is recommended in conjunction with referral for consideration of liver transplantation.
When to initiate HBV treatment?
Mar 30, 2022 · The combination of hepatitis B immune globulin (known as HBIG) and hepatitis B vaccine can be given to infants born to mothers with hepatitis B within 12 hours of birth to protect them from infection.
Does HBV have a treatment?
Mar 30, 2022 · How is HBV infection treated? People with acute infection are provided supportive treatment depending on their symptoms. For people with chronic infection, several antiviral medications are available ( 16 ); these patients require linkage to care with regular monitoring to prevent liver damage and/or hepatocellular carcinoma.
When to treat chronic HBV?
Jan 14, 2022 · People living with chronic hepatitis B should be monitored regularly by their health care provider for signs of liver disease and evaluated for …
Who should get tested for HBV?
Aug 25, 2021 · For people with chronic hepatitis B, treatment may be necessary to prevent liver damage and reduce the risk of transmitting the virus. This includes treatment with antiviral medications like entecavir (Baraclude), telbivudine (Tyzeka), adefovir (Hepsera), and tenofovir (Viread), and lamivudine (Epivir).

What is the most common treatment for hepatitis?
Hepatitis C infection is treated with antiviral medications intended to clear the virus from your body. The goal of treatment is to have no hepatitis C virus detected in your body at least 12 weeks after you complete treatment.Aug 31, 2021
What is the treatment and prevention of HBV?
Hepatitis B infection can be prevented by getting vaccine and HBIG (hepatitis B immune globulin) soon after coming into contact with the virus. Persons who have recently been exposed to HBV should get HBIG and vaccine as soon as possible and preferably within 24 hours, but not more than 2 weeks after the exposure.
What is the first-line treatment for hepatitis B?
Pegylated interferon alfa-2a, entecavir, and tenofovir are recommended as first-line treatment options for chronic hepatitis B.Mar 1, 2019
What is the first-line of treatment in hepatitis?
Currently, pegylated interferon alfa (PEG-IFN-a), entecavir (ETV), and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) are the first-line agents in the treatment of hepatitis B disease.
Is there a medication for hepatitis A Why?
No specific treatment exists for hepatitis A. Your body will clear the hepatitis A virus on its own. In most cases of hepatitis A, the liver heals within six months with no lasting damage.Aug 28, 2020
Is hepatitis B curable or treatable?
There's no cure for hepatitis B, but there are several treatments that can help with managing symptoms and reducing the risk of long-term health problems, such as cirrhosis. If you have hepatitis B, try to get in for a blood test every six months or so to monitor your viral load and liver health.
When should hepatitis B treatment start?
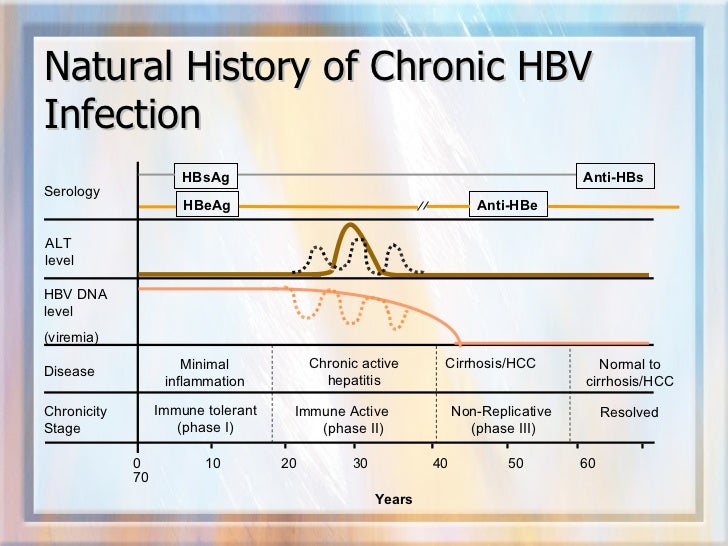
Current guidelines recommend initiating antiviral therapy in HBeAg-positive patients who have ALT levels ≥2 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) and HBV DNA levels ≥20,000 IU/ml.
How long should I take entecavir?
A standard dose is 0.5 mg once daily for one year. The dose is doubled for people who have persistent hepatitis viremia (the presence of virus in the blood) while taking lamivudine or have lamivudine resistance.Nov 22, 2020
Is milk good for hepatitis B patient?
Olive oil, canola oil and flaxseed oil are all healthy fats that are recommended as part of a diet for patients with Hepatitis. Healthy proteins in the form of low-fat milk and dairy products along with lean meats, beans, eggs and soy products can also be a part of a healthy liver diet.Nov 10, 2014
How long can you live with hepatitis B untreated?
The estimated carrier life expectancy is 71.8 years, as compared to 76.2 years among noncarriers (Figure 5). These results are consistent with other estimates, which indicate that 15% to 40% of HBV carriers die of liver complications.
Can tenofovir cure hepatitis B?
Tenofovir will not cure hepatitis B and may not prevent complications of chronic hepatitis B such as cirrhosis of the liver or liver cancer. Tenofovir may not prevent the spread of hepatitis B to other people.
Is a cure for hepatitis B coming?
There is no cure or medication that totally eliminates the virus or makes HBsAg negative, but there is hope. There are approved therapies for hepatitis B and many in development. First-line therapies in the U.S. and globally are entecavir, tenofovir (TDF) and tenofovir (TAF), which are antivirals.Feb 9, 2022
How to treat hepatitis B?
Current treatments for hepatitis B fall into two general categories: 1 Immune modulator Drugs – These are interferon-type drugs that boost the immune system to help get rid of the hepatitis B virus. They are given as a shot (similar to how insulin is given to people with diabetes) over 6 months to 1 year. 2 Antiviral Drugs – These are drugs that stop or slow down the hepatitis B virus from reproducing, which reduces the inflammation and damage of your liver. These are taken as a pill once a day for at least 1 year and usually longer.
How many drugs are there for hepatitis B?
There are now 7 approved drugs for hepatitis B in the United States -- 2 types of injectable interferons and 5 oral antivirals – that control the hepatitis B virus. A cure, however, may be in the near future because there is exciting research being done today to generate promising new drugs.
What is considered a decompensated cirrhosis?
Persons with cirrhosis are considered to have decompensated cirrhosis if certain liver-related complications develop, including jaundice, ascites, esophageal variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, or impaired hepatic synthetic function (as reflected by elevated prothrombin time or total bilirubin). Decompensated cirrhosis is formally defined as a Child Pugh score of 7 or greater (class B or C). Because antiviral therapy has been shown to improve transplant-free survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, they should also be started on oral antiviral therapy regardless of ALT or HBV DNA levels. Patients with more advanced disease should also be referred for liver transplantation, if eligible.
What is a child Pugh score?
Decompensated cirrhosis is formally defined as a Child Pugh score of 7 or greater (class B or C). Because antiviral therapy has been shown to improve transplant-free survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, they should also be started on oral antiviral therapy regardless of ALT or HBV DNA levels.
What is the ALT level for hepatitis C?
Serum ALT levels provide a rapid and noninvasive measure that can indicate hepatic inflammation. In 2002, investigators suggested using upper limits of normal for ALT levels of greater than 19 U/L in women and 30 U/L in men as the recommended cutoffs to accurately identify those with underlying hepatitis C viremia. Subsequently, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) hepatitis B guidelines suggested using these same threshold values as the upper limit of normal for ALT levels. [ 23, 24, 25] More recently, however, the 2018 AASLD Hepatitis B Guidance has changed the upper limit of normal for treatment purposes to 25 U/L for women and 35 U/L for men. [ 4] These cutoffs are lower than the upper limit of normal defined by many commercial laboratories, which generally derive their range from the general population and more specifically from blood donors without evidence of hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection. Due to the high prevalence of fatty liver in "healthy" donors (who may have elevated ALT levels), use of the upper limit of normal obtained from such healthy donor pools may not maximize detection of individuals with underlying liver disease due to viral hepatitis. [ 26] Therefore, even though a patient may have a “normal” ALT result as defined by a local or referral laboratory, the more stringent cutoffs would reduce the likelihood of missing underlying liver disease caused by hepatitis B. It is also important to note that a treatment decision should not be made on the basis of a single serum ALT measurement. These values often vary and the phase of HBV infection will need to be confirmed with multiple measurements of serum ALT over time, typically drawn every 3 to 4 months, particularly given the dynamic nature of HBV infection.
What is AASLD in liver?
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) The American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (AASLD) hepatitis B guidance has served as the dominant HBV treatment guidance in the United States and it includes comprehensive recommendations.
What is the APASL?
The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) hepatitis B guidance was generated by a panel of experts in this region, predominantly from the specialties of hepatology and gastroenterology. The most recent guidance was published in 2015. [ 36] The 2015 APASL Hepatitis B Guidelines recommend initiating HBV treatment in the following situations for persons with chronic HBV. [ 36]
What is EASL in hepatitis?
European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) The European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) hepatitis B clinical practice guidelines is the major hepatitis B guidance for Europe and this document was primarily written by gastroenterology and hepatology specialists. [ 35] .
What is the HBV primary care workgroup?
The HBV Primary Care Workgroup includes members in the United States from hepatology, infectious diseases, pharmacy, primary care, and public health. [ 37] The 2020 HBV Primary Care Workgroup Guidance was first released in early 2020 and is accessible on this web site (Hepatitis B Online), with the aim to have regular updated versions posted online. [ 37] The goal of this document is to provide simplified, up-to-date, and readily accessible HBV management guidance for primary care medical providers. Note, this guidance does not incorporate HBeAg status in the initial decision-making process, but persons positive for HBeAg are recommended to undergo monitoring of HBeAg for evidence of HBeAg seroconversion. The 2020 HBV Primary Care Workgroup Guidance recommends initiating HBV treatment in the following situations. [ 37]
What is the cause of hepatitis?
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can all cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common hepatitis viruses are hepatitis A virus, ...
How long does it take for hepatitis B to show symptoms?
Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis B virus. Some people with acute hepatitis B have no symptoms at all or only mild illness. For others, acute hepatitis B causes a more severe illness that requires hospitalization.
Who should be tested for hepatitis B?
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for: People born in certain countries where hepatitis B is common. People born in the United States not vaccinated as infants whose parents were born in countries with high rates of hepatitis B. Men who have sex with men. People who inject drugs.
Is hepatitis A a short term infection?
Hepatitis A is usually a short-term infection. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C can also begin as short-term infections but in some people, the virus remains in the body and causes chronic, or lifelong, infection. There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B; however, no vaccine is available for hepatitis C.
How does age affect hepatitis B?
The younger a person is when infected with the hepatitis B virus, the greater the chance of developing chronic infection. About 9 in 10 infants who become infected go on to develop life-long, chronic infection. The risk goes down as a child gets older.
Can you have hepatitis B without symptoms?
Talk to your health-care provider if you have risk factors for or think you might have hepatitis B. Since many people with hepatitis B do not have symptoms, blood tests are used to diagnose the infection. Several different hepatitis B tests are available. Depending on the test, they can determine whether you.
How many cases of hepatitis B in 2018?
In 2018, a total of 3,322 cases of acute (short-term) hepatitis B were reported to CDC. Since many people may not have symptoms or don’t know they are infected, their illness is often not diagnosed so it can’t be reported or counted.
What is HBV reactivation?
HBV reactivation is the abrupt reappearance or rise in HBV DNA in a patient with previously inactive chronic or resolved hepatitis B. It is often accompanied by a flare in disease activity with elevation of liver enzymes with or without symptoms. HBV reactivation can be severe, resulting in death ( 13 ).
How many children are infected with HBV?
Approximately 90% of infants and 25%–50% of children aged 1–5 years will remain chronically infected with HBV. By contrast, approximately 95% of adults recover completely from HBV infection and do not become chronically infected ( 6 ).
What is the cause of liver inflammation?
Hepatitis B. Hepatitis B is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis B can be an acute, short-term infection or a chronic, long-lasting infection.
How does hepatitis B spread?
It is spread by: Having unprotected sex with an infected person. Sharing contaminated razors, toothbrushes, or needles. Coming in contact with infected blood like from an open wound or transfusion. Mother to baby during vaginal or cesarean birth.
What is the best treatment for hepatitis B?
Antiviral medications: Medications taken by mouth to help your body fight the virus and reduce the risk of liver damage. Interferon injections: Injections consisting of interferons, which are substances produced by cells in the body to help fight the infection. Liver transplant: If chronic hepatitis B leads to liver failure or liver cancer, ...
How long does hepatitis B last?
Hepatitis B infection may be acute (short term) or chronic (long term). Acute HBV symptoms can last from a few weeks to up to six months and may include: Chronic HBV infection occurs when the virus remains in a person’s body.
What is the procedure to remove a liver from a donor?
Liver transplant : If chronic hepatitis B leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant as a last resort. A transplant is a surgical procedure that removes your unhealthy liver and replaces it with a healthy liver from a donor.
What to do if you think you have been exposed to HBV?
If you think you’ve been exposed to HBV, ask your health care provider to get tested. Blood tests can determine whether a person was infected in the past, is currently infected, or has never been infected.
Can HBV cause nausea?
Nausea and/or vomiting. Chronic HBV infection occurs when the virus remains in a person’s body. People living with chronic HBV can spread the virus to others, even if they do not feel or look sick themselves. Over time, chronic HBV can cause scarring of the liver, liver failure, liver cancer, or even death.
General Goals of HBV Treatment
Carefully Review Criteria Before Initiating Antiviral Treatment For HBV
First Line
Related Resources
Specialist to consult
Diagnosis
- To suppress HBV DNA and normalize ALT
- To achieve loss of HBeAg (if initially HBeAg positive)
- To achieve loss of HBsAg (this occurs rarely)
- To reduce the likelihood of cirrhosis and HCC
- To suppress HBV DNA and normalize ALT
- To achieve loss of HBeAg (if initially HBeAg positive)
- To achieve loss of HBsAg (this occurs rarely)
- To reduce the likelihood of cirrhosis and HCC
Treatment
- In general, patients with active HBV (HBV DNA ≥ 2,000 IU/mL if HBeAg-negative and HBV DNA ≥ 20,000 IU/mL if HBeAg-positive, and high ALT or evidence of advanced fibrosis) should be considered for HBV antiviral treatment. Patients with inactive HBV (HBV DNA < 2,000 IU/mL and low ALT without evidence of advanced fibrosis) may need HBV treatment in certain situations s…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF, Vemlidy®) Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF, Viread®) Entecavir (ETV, Baraclude®) Peginterferon (PEG, Pegasys®) - in select patients
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Your doctor will examine you and look for signs of liver damage, such as yellowing skin or belly pain. Tests that can help diagnose hepatitis B or its complications are: 1. Blood tests.Blood tests can detect signs of the hepatitis B virus in your body and tell your doctor whether it's acute or chronic. A simple blood test can also determine if you're immune to the condition. 2. Liver ultras…