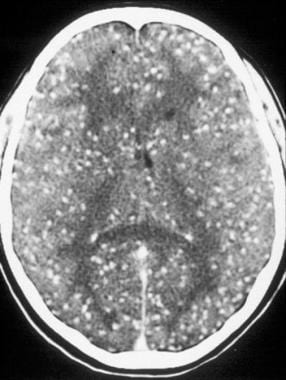
What causes calcium deposits on the brain?
What Is Basal Ganglia Calcification?
- Causes. Basal ganglia calcification sometimes happens when you age, but many times comes from genes passed to you by your parents.
- Symptoms. You may have no symptoms at all. ...
- Diagnosis. There is no one test for the condition. ...
- Genetic Testing and Counseling. If one of your parents has it, you have a 50% chance of having it as well. ...
- Treatment. ...
What causes calcium deposits and calcification?
What causes calcification on your teeth? Calcium deposits occur when the calcium phosphate in your saliva sticks to plaque on your teeth. Plaque is a sticky biofilm composed of bacteria in your mouth that feed on sugar and starches. Without proper care, calcium phosphate can harden into tartar. Is calcification on teeth bad?
What are the symptoms of brain problems?
- Experts say some symptoms linked to menopause may in fact be something else
- Hot flushes, night sweats and mood disorders can stem from other conditions
- It's risky to assume menopause is behind every ill affecting women in mid-life
What does calcium do in the brain?
The Journal of Neuroscience, 2018. Calcium doesn’t just make your bones strong — it’s a crucial element in how the cells in your brain communicate. As an electrical signal speeds down the axon, it opens pores that let calcium ions rush into the cell.

Can brain calcification be removed?
Brain calcifications induce neurological dysfunction that can be reversed by a bone drug. J Neurol Sci.
What is the best treatment for calcification?
Most cases of calcific tendonitis can be treated with steroid injections, physical therapy and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
What infections cause brain calcification?
Intracranial calcifications are relatively common computed tomographic findings in the field of neurosurgery, and cysticercosis, tuberculosis, HIV, and cryptococcus are acquired intracranial infections typically associated with calcifications.
Can calcification be cured?
Calcification is generally not treatable and cannot be reversed. However, calcific band keratopathy, a calcification of the cornea of the eye, can be treated. In addition, disorders that are complications of or associated with calcification are often very treatable.
Is calcification in the brain normal?
Basal ganglia calcification is a very rare condition that happens when calcium builds up in your brain, usually in the basal ganglia, the part of your brain that helps control movement. Other parts of your brain can be affected as well.
Why does brain calcification occur?
Causes. Primary familial brain calcification is caused by mutations in one of several genes. The most commonly mutated gene is called SLC20A2, and accounts for an estimated 40 percent of cases, followed by the PDGFRB gene, which is mutated in about 10 percent of cases.
What are the symptoms of brain calcification?
Muscle cramping (dystonia), uncontrollable spasmodic irregular movements (chorea), and seizures can also occur. Occasional symptoms include sensory changes, headaches and urinary incontinence. Associated symptoms include loss of contact with reality (psychosis), mood swings and loss of acquired motor skills.
Can MRI detect calcifications?
Some radiologists call these “unidentified bright objects,” or UBOs. MRI also cannot detect calcifications (calcium deposits in breast tissue that could be a sign of cancer). Finally, MRI can dislodge certain metal devices, such as pacemakers, in some people.
What causes calcification in the body?
Causes of calcification. Many factors play a role in calcification. These include: infections. calcium metabolism disorders that cause hypercalcemia (too much calcium in the blood) genetic or autoimmune disorders affecting the skeletal system and connective tissues. persistent inflammation.
How to diagnose calcification?
Diagnosing calcification. Calcifications are usually found via X-rays. X-ray tests use electromagnetic radiation to take pictures of your internal organs and usually cause no discomfort. Your doctor will likely detect any calcification issues right away with X-rays. Your doctor may also order blood tests.
What are the soft tissues that are affected by calcium buildup?
soft tissues like breasts, muscles, and fat. kidney, bladder, and gallbladder. Some calcium buildup is harmless. These deposits are believed to be the body’s response to inflammation, injury, or certain biological processes. However, some calcifications can disrupt organ function and affect blood vessels.
What happens when calcium builds up in the body?
Calcification happens when calcium builds up in body tissue, blood vessels, or organs. This buildup can harden and disrupt your body’s normal processes. Calcium is transported through the bloodstream. It’s also found in every cell. As a result, calcification can occur in almost any part of the body. According to the National Academy of Medicine. ...
What is the most common type of breast calcification?
According to the National Cancer Institute, macrocalcifications in the breasts are most common in women over 50 years old.
What medications affect calcium levels?
Some medications can affect your body’s calcium levels. Cholesterol medication, blood pressure medication, and hormone replacement therapy are common medications that affect how calcium is used in your body.
Can you get calcifications at 65?
If you’re under 65 years old and were born with a heart defect or kidney-related issues, calcifications can be more common for you than for others of your age. If you are aware of any of these conditions, ask your doctor about getting tested for calcifications. Some medications can affect your body’s calcium levels.
What is calcium in the brain?
Calcium deposits in the brain is a health ailment, which may lead to symptoms ranging from mild headaches to severe mental disabilities. Know more about its causes, symptoms, and treatment, through this article. Calcium deposits in brain, also termed as cranial calcification, is a condition wherein small spots of calcium get accumulated in ...
What are the symptoms of calcium deposits in the brain?
Calcium deposits in the brain is a health ailment, which may lead to symptoms ranging from mild headaches to severe mental disabilities. Know more about its causes, symptoms, and treatment, through this article.
What tests are done to check for calcium deposits in the brain?
It mainly depends upon the underlying cause and diagnosis. The doctor will perform certain diagnostic tests like overall physical exam, neurologic exam to check for the alertness, coordination, reflexes, and response to pain, CT scan, and MRI of the brain to detect the locations of the calcium deposits in the brain.
Can calcium be dangerous?
Calcium deposits in the brain, in some cases, can be extremely severe and may need immediate medical attention, while in other cases it possesses no harm to the patient. However, to be on the safer side, if you notice any of the aforementioned symptoms, do not delay and instantly consult your doctor to elucidate the case.
Can calcium cause dementia?
As said before, calcium deposits can be found anywhere in the brain, and may lead to some mild to severe mental disabilities, due to loss of brain cells. The symptoms mainly include progressive deterioration of mental abilities or dementia, loss of previous motor development, spastic paralysis, and in some cases, even athetosis, the twisting movements of the hands and feet. Some other less common symptoms are vision disturbances (optic atrophy), blurred vision, ear infections, traits of Parkinson’s Disease including tremors and rigidity, muscle cramping or dystonia, a mask-like facial expression, uncontrollable spasmodic irregular movements or chorea, seizures, shuffling walk, and a pill rolling motion of the fingers.
Skull Patterns
Intracranial calcifications are a common finding on plain film radiographs and on CT scans of the skull. Although most represent physiologic calcifications of limited clinical significance, more aggressive pathologies (e.g., tumor, infection, vascular disturbance) should be considered in the differential diagnosis.
Neurogenetics, Part I
Beatriz Quintáns, ... María-Jesús Sobrido, in Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 2018
Syndromes
FIGURE 2-267. Third-trimester fetus with cytomegalovirus. (A) Coronal view through the frontal horns shows multiple calcifications in the region of the thalami and basal ganglia. (B) Transvaginal scan of the same fetus shows multiple calcifications (arrows) in the basal ganglia and an intraventricular adhesion in the posterior horn.
Cysticercosis
Hector H. Garcia, ... A. Clinton WhiteJr., in Tropical Infectious Diseases (Third Edition), 2011
Skull and Brain
Miral D. Jhaveri MD, ... Chang Yueh Ho MD, in Expertddx: Brain and Spine (Second Edition), 2018
Skull and Brain
Miral D. Jhaveri MD, ... Chang Yueh Ho MD, in Expertddx: Brain and Spine (Second Edition), 2018
Pediatric Neurology Part III
The presence of intracranial calcification is not per se a particularly specific diagnostic sign. In the neonatal form of AGS, congenital infection represents the main differential diagnosis.
How to treat brain calcification?
Some treatment options for dystonia include: physical therapy. speech and voice therapy. relaxation and stress management.
Where does calcification occur in the brain?
Brain calcification. Primary familial brain calcification occurs when abnormal calcium deposits form in the blood vessels in the brain. These deposits typically form in the basal ganglia, which initiate and control bodily movement.
What causes calcification in the joints?
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal disease is often the cause of joint calcification. In fact, research suggests that around 45%#N#Trusted Source#N#of people aged 85 and over have calcium deposits in the cartilage of their joints.
What is it called when you have calcium in your urine?
Calcium deposits can also form in the kidneys. This is called nephrocalcinosis. People with nephrocalcinosis may also have high levels of calcium or phosphate in their blood or urine. Doctors classify nephrocalcinosis as molecular, microscopic, or macroscopic.
What causes kidney calcification?
Kidney calcification can develop due to vitamin D therapy, primary hyperparathyroidism, or sarcoidosis, among other things. Treatment will depend and focus on the cause.
Why do people not know they have calcification?
People may not know they have calcification because it does not always cause any symptoms. Some types of calcification are irreversible, but depending on the type, there may be ways to reduce pain and lower the risk of complications. Last medically reviewed on January 27, 2020. Biology / Biochemistry.
When does calcification start?
Artery calcification. Artery calcification can start at a young age , but a doctor may only notice it once the deposit is large enough to appear in an imaging scan. Artery calcification at a detectable level typically occurs in adults over 40 years of age. Trusted Source.
What are the symptoms of calcification in the brain?
The main signs and symptoms of primary familial brain calcification are movement disorders and psychiatric or behavioral problems. These difficulties usually begin in mid-adulthood, and worsen over time.
How many people have calcification of the brain?
Recent research has indicated that primary familial brain calcification may occur in 2 to 6 per 1,000 people, with many affected individuals not showing signs and symptoms of the condition.
What are the effects of PDGFRB on the brain?
Alternatively, changes in PDGFRB signaling could disrupt processes that regulate levels of phosphate and calcium in brain cells, leading to the formation of calcium deposits. Other genes known to be associated with primary familial brain calcification also have roles in cell signaling and phosphate homeostasis.
What is a primary familial brain calcification?
Collapse Section. Primary familial brain calcification is a condition characterized by abnormal deposits of calcium (calcification) in blood vessels within the brain. These calcium deposits are visible only on medical imaging and typically occur in the basal ganglia, which are structures deep within the brain that help start and control movement ...
What happens when you get SLC20A2?
SLC20A2 gene mutations lead to the production of a PiT-2 protein that cannot effectively transport phosphate into cells. As a result, phosphate levels in the bloodstream rise. In the brain, the excess phosphate combines with calcium and forms deposits within blood vessels in the brain.
Can mutations cause calcification?
However, it is unclear how the mutations cause primary familial brain calcification. The altered signaling may result in an abnormally large amount of calcium entering the cells that line blood vessels in the brain, leading to calcification of these blood vessels. Alternatively, changes in PDGFRB signaling could disrupt processes ...
Is calcification inherited?
In most cases, primary familial brain calcification is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. In most cases, an affected person has one parent with the condition.
What causes calcification in the brain?
In brain it forms a cyst. The cyst after a period of treatment gets calcified. Toxoplasmosis is another parasitic infection caused by toxoplasma gondii which can cause calcification in brain. The parasite is present in feces of cats. Pregnant women are more susceptible to its infection.
Why is calcium deposited in the brain?
Secondly, calcium can get deposited in the event of inflammation or damage to the brain tissue. Both genders are equally affected. Medically, calcium deposits can be significant only when they cause problems in normal functioning of brain.
What is calcium in the brain called?
Calcium deposit in brain is a condition that we come to know only when it is noticed on X-ray or other imaging techniques. Some people also call it calcification in brain, calcinosis or Fahr’s syndrome.
What is metastatic calcification?
In metastatic calcification, there is excess of calcium and phosphorus circulating in the blood which eventually gets deposited in different organs of the body, brain being the one. Tuberculosis is common disease in developing countries.
What are the symptoms of brain tuberculosis?
Fever, headache, seizures, vomiting and malaise, neck rigidity and disorientation are common in brain tuberculosis. Neurocysticercosis is another inflammatory lesion which can lead to deposition of calcium in the brain.
Can calcification occur in the brain?
Calcification can occur in any part of the brain. The symptoms may depend on the size of calcified brain tissue. If the size is small, the symptoms may be mild to moderate. If the size is large, the symptoms may be severe as the area of brain cell destruction is large. Following are the symptoms that can be found:
What is intracranial calcification?
Intracranial calcifications are a common finding on plain film radiographs and on CT scans of the skull. Although most represent physiologic calcifications of limited clinical significance, more aggressive pathologies (e.g., tumor, infection, vascular disturbance) should be considered in the differential diagnosis. Intracranial calcifications typically are localized; they are associated commonly with infections or tuberous sclerosis when they present with a scattered pattern.
Is intracranial calcification a diagnosis?
The presence of intracranial calcification is not per se a particularly specific diagnostic sign. In the neonatal form of AGS, congenital infection represents the main differential diagnosis. We have recently delineated another congenital infection-like syndrome which can be differentiated from AGS by the presence of “band-like” calcification and polymicrogyria (which are not normally associated with AGS) ( Briggs et al., 2008a ). Other genetic conditions to consider include mitochondrial cytopathies, Cockayne syndrome, and Hoyeraal–Hreidarsson syndrome. In older children, intracranial calcification can occur in association with abnormalities of parathyroid metabolism and celiac disease, and we have seen cases of both Coats plus (CRMCC, cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts) and SPENCD (spondyloenochondrodysplasia) initially considered as AGS ( Briggs et al., 2008b; Navarro et al., 2008 ). Cases with later onset of a nonspecific leukoencephalopathy, where intracranial calcification may not be observed and CSF white cells may be normal, invoke a wide differential diagnosis and we emphasize the importance of considering AGS in this situation.
What is a calcification in the brain?
Perivascular calcifications within the brain form in response to a variety of insults. While considered by many to be benign, these calcium phosphate deposits or "brain stones" can become large and are associated with neurological symptoms that range from seizures to parkinsonian symptoms.
Can calcifications in the brain be reversed?
Brain calcifications induce neurological dysfunction that can be reversed by a bone drug. Perivascular calcifications within the brain form in response to a variety of insults. While considered by many to be benign, these calcium phosphate deposits or "brain stones" can become large and are associated with neurological symptoms ...
Can calcium phosphate cause seizures?
While considered by many to be benign, these calcium phosphate deposits or "brain stones" can become large and are associated with neurological symptoms that range from seizures to parkinsonian symptoms. Here we hypothesize that the high concentrations of calcium in these deposits produce reversible, toxic effects on neurons ...
