Practitioners of the biomechanical model reduce the patient to separate, individual body parts in order to diagnose and treat disease. Utilization of this model has led, in part, to a quality of care crisis in medicine, in which patients perceive physicians as not sufficiently compassionate or empathic towards their suffering.
What are biomechanical models?
Biomechanical models use computer programs for the realization of multibody mechanics, which in turn either on the d'Alambert principle (realization of balance of power taking into account static and dynamic forces) or on the Lagrange function (a system is completely described by the energy of movement and the potential energy). Lars Hanson, ...
What is biomechanical physical therapy?
Biomechanics are used by physical therapists to study a person’s movements. Quick and complex motions—like those that take place when running or jumping—are slowed down and evaluated in order to identify components that can be changed or improved upon. Who can benefit from biomechanical physical therapy?
What is biomechanical evaluation in occupational therapy?
In Biomechanical evaluation OT uses different tools for assessment like Goniometer for Joint range of motion, Volumetry for edema, and manual muscle testing for strength. Along with these formal tests, OT also does clinical observation, including Skin’s appearance, End feel during range of motion and grip strength.
What are biomechanical services and how do they work?
Utilizing the field of kinesiology (the study of movement), biomechanical services are useful for a wide variety of individuals from toddlers with cerebral palsy to world-class athletes. This article will discuss this emerging area of physical therapy and its benefits. How Do Biomechanics Work?
What is the biomechanical model in OT?
The biomechanical model explains how the body produces the stability and movement required to perform occupations using three broad concepts: joint range of motion, strength, endurance.
How do occupational therapists use biomechanics?
Occupational therapist uses the biomechanical frame of reference in orthopedic cases, burn cases and patients with limited range of motion and strength. The Biomechanical frame of reference is based on Joint range of motion, Muscle strength, and Endurance with the intact central nervous system.
Why was the biomechanical frame of reference developed?
The goals are to prevent deterioration and maintain existing movements for occupational performance, to restore movements for occupational performance, and to compensate/adapt for loss of movements in occupational performance.
What is the PEO model in occupational therapy?
The Person-Environment-Occupation (PEO) model is a model that emphasizes occupational performance shaped by the interaction between person, environment, and occupation. The person domain includes role, self-concept, cultural background, personality, health, cognition, physical performance, and sensory capabilities.
What is biomechanical treatment?
Biomechanical treatment can be most simply summarized as the application of biomechanics to the diagnosis and treatment of your injuries. Biomechanics is the “study of the mechanical laws relating to the movement of living organisms.” Our therapists apply this when working with their clients.
What is biomechanical approach?
The biomechanical approach is a remediation or restora- tion approach, and the intervention is designed to restore or establish client-level factors of structural stability, tissue integrity, range of motion (ROM), strength, and endurance.
What are the 4 most common frames of reference used?
Occupational Therapy Frames of ReferenceOccupational Therapy professionals use “theory” to guide their practice. ... Developmental Frame of Reference.Rehabilitation Frame of Reference.Model Of Human Occupation (MOHO)Psychodynamic Frame of Reference.
Who developed the biomechanical frame of reference occupational therapy?
James, A. B. (2003). Biomechanical frame of reference. In: Crepeau, E. B., Cohn, E. S., & Schell, B. A. B. (Eds.), Willard and Spackman's Occupational Therapy (10th ed., pp.
What is the difference between a model and a frame of reference?
A model of practice helps organize one's thinking, where-as a frame of reference is a tool to guide one's intervention. A frame of reference tells you what to do and how to evaluate and intervene with clients.
Is the PEO model a frame of reference?
Although the PEO model is a holistic and transactive approach that is applicable to a variety of intervention situations, it is often necessary to combine the model with a frame of reference to best meet the needs of a client.
What are the occupational therapy models of practice?
Top 5 Occupational Therapy Models To KnowAllen's Cognitive Disabilities Model (CDM)Canadian Model of Occupational Performance and Engagement (CMOP-E)Dunn's Model of Sensory Processing.Model of Human Occupations (MOHO)Person-Environment-Occupation-Performance Model (PEOP Model)
What is Moho frame of reference?
The Model of Human Occupation (or MOHO) is a very important occupation-based framework and is woven into the fabric of occupational therapy. It utilizes a top-down holistic approach to looking at the individual, their meaningful activities or occupations, and relationship with their environment.
What is biomechanical model?
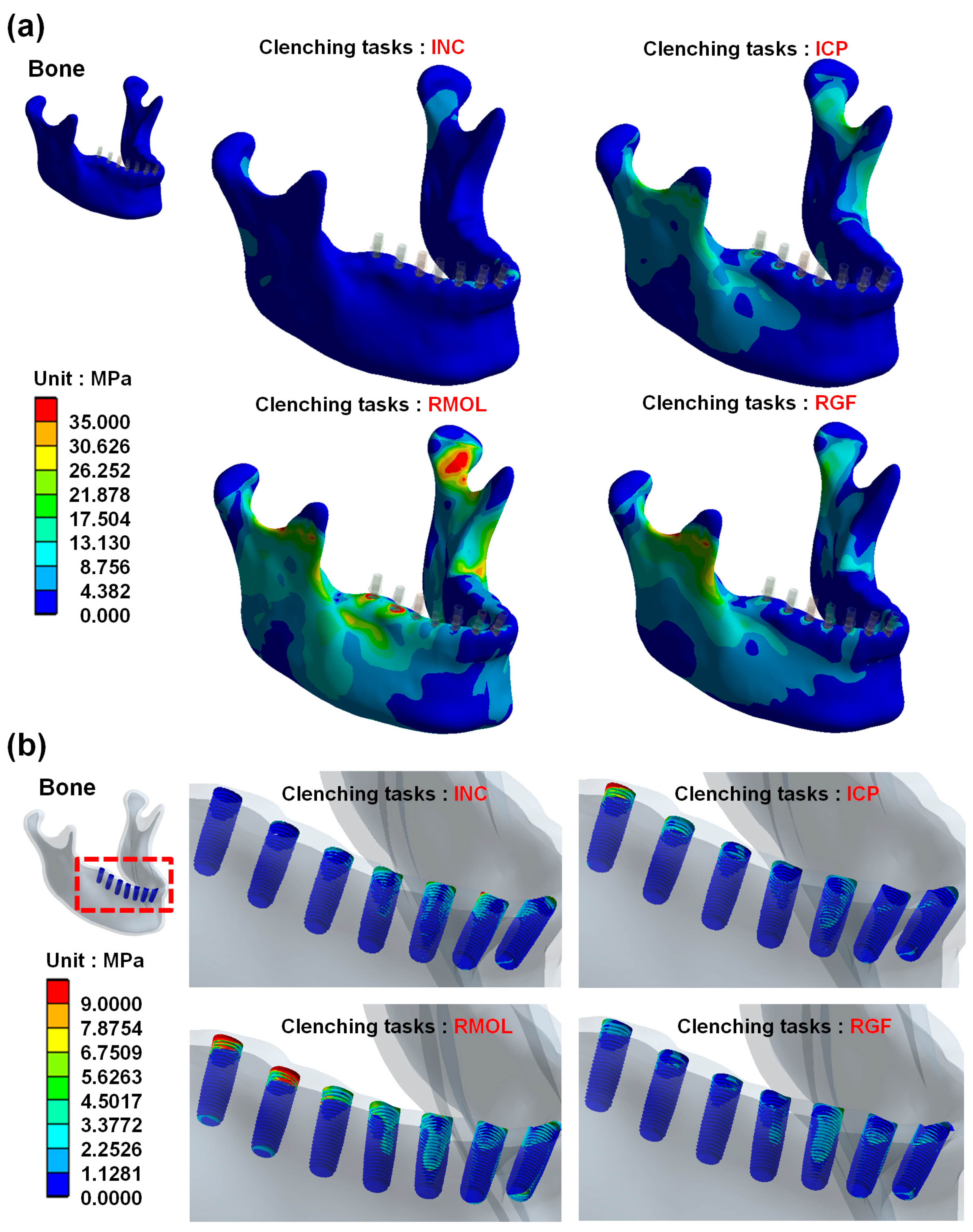
A biomechanical model of the artery requires the prescription of conditions at its boundary, such as flow, pressure, and stiffness. For some applications, it is possible to use in vivo measured information directly for CFD studies.
What is the principle of biomechanical models?
Biomechanical models use computer programs for the realization of multibody mechanics, which in turn either on the d'Alambert principle (realization of balance of power taking into account static and dynamic forces) or on the Lagrange function (a system is completely described by the energy of movement and the potential energy).
What is computational modeling of pelvic floor?
Computational modeling involves a complex integration of the anatomical, mechanical, and physiological properties of the pelvic floor muscles (PFMs ). Defining the geometry of the muscles is relatively straightforward, and has been carried out using magnetic resonance images (MRIs) of the region of interest [1–5 ]. Most MRI scanners now provide high-quality images whereby the muscles, organs, and bones can be readily identified and segmented. Anatomically accurate models are now possible to produce. However, incorporating the functionality of the muscles and other structures remains challenging.
What are the components of a heel model?
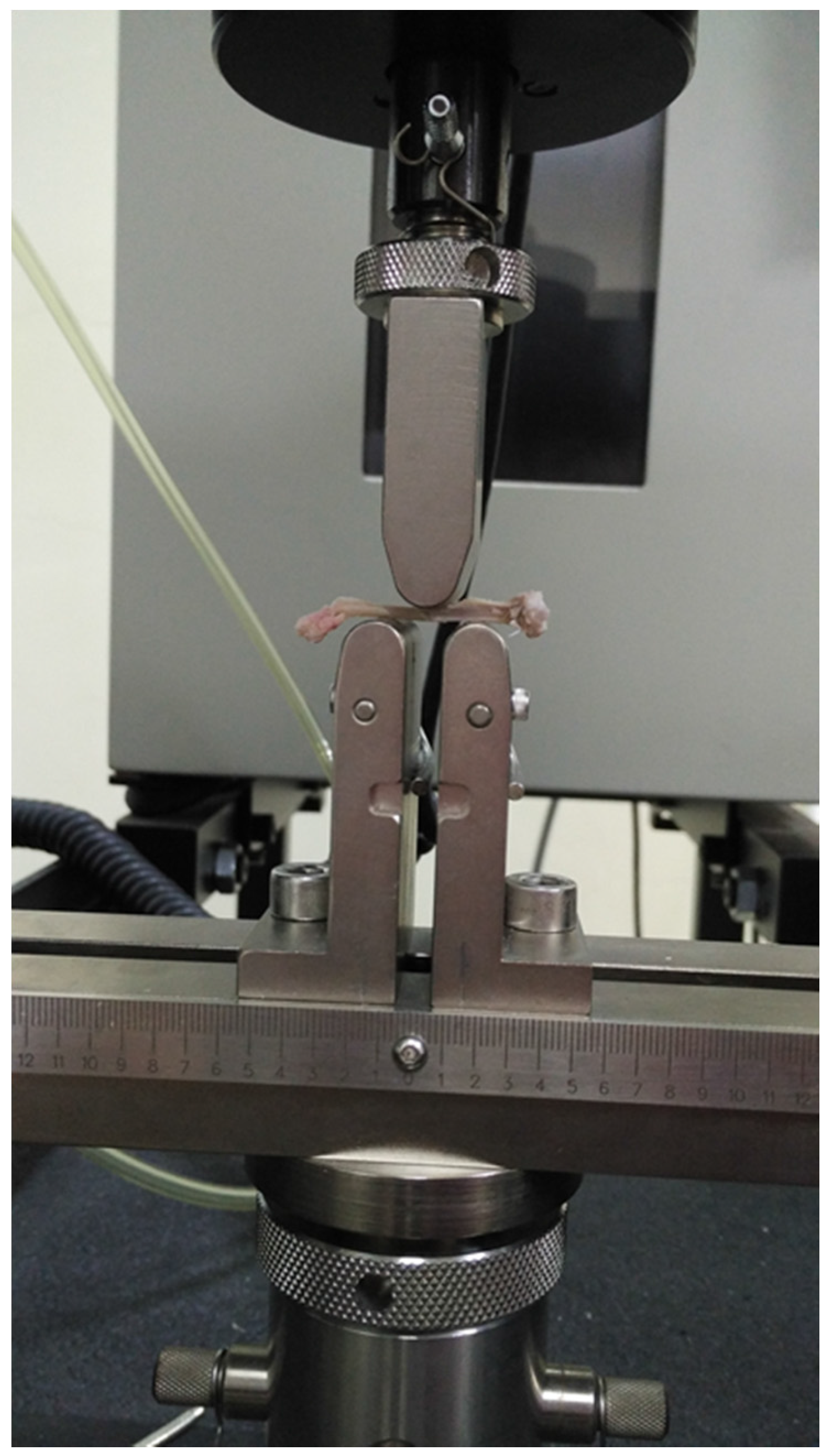
The heel model consists of three large components: a rigid bone, a merged set of nonbone layers (fats, tendon, muscle , and skin; in the model without, the PC will have fats replaced by the muscle layer), and a rigid support surface below. Stress behavior was computed using a biomechanical simulation of the heel on a flat base using the Abaqus software suite.
What is a biomechanical frame of reference?
The theoretical base of biomechanical frame of reference (FOR) is considered as a remedial approach focusing on impairments that limit occupational performance. This FOR assumes clients are able to acquire the voluntary motor skills necessary to perform the desired human occupation, meaning that the underlying impairment is amenable to remediation. It also assumes that engaging in occupation and therapeutic activities has the potential to remediate the underlying impairment, and results in improvement in occupational performance. The goals are to prevent deterioration and maintain existing movements for occupational performance, to restore movements for occupational performance, and to compensate/adapt for loss of movements in occupational performance. Individuals who have limitations in performing occupations due to limitations in movements, inadequate muscle strength, loss of endurance, or other biomedical conditions are suitable to use this FOR. The goals are to prevent limitation of range of motion, to move the target body part through full range of motion, either passively or actively appropriately, and to position the body to prevent contractures and edema. Assessment includes assessing the performance components on movements, strength and endurance. Some assessments associated with this FOR include standardized objective tests of occupational performance, pain scales, examination of skin/wounds, sensory testing, etc. Interventions associated with this FOR include ADL retraining, work hardening, static and dynamic orthoses, active, active assistive, passive range of motion exercises, nerve gliding, etc. The variety of interventions aims to amend underlying impairment and result in enhanced occupational performance in desired occupations.
What are the goals of biomedical limitations?
The goals are to prevent limitation of range of motion, to move the target body part through full range of motion, ...
How Do Biomechanics Work?
Biomechanical analysis takes a basic human movement—like walking or throwing a ball—and breaks it down into precise details in order to identify patterns or areas of deficiency that may be improved upon.
Benefits of Biomechanics in Physical Therapy
In recent years, biomechanical evaluations are becoming more and more prevalent in physical therapy. In fact, one study estimated that 75% of sports medicine physical therapists use video motion analysis regularly in their practice. 1
Exercises and Examples
The information that a physical therapist gathers from a biomechanical assessment can be used to improve any problems or deficiencies through specific exercises.
A Word From Verywell
Many different types of people can benefit from a biomechanical evaluation. If you are interested in this type of service, it’s best to speak with your physician first. They can help locate a physical therapist who specializes in this type of assessment and identify how it may help in your particular situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Biomechanics are used by physical therapists to study a person’s movements. Quick and complex motions—like those that take place when running or jumping—are slowed down and evaluated in order to identify components that can be changed or improved upon.
Why is biomechanical research less funded?
There is less funding for biomechanical studies aimed at improving performance compared to studies focused on preventing and treating injuries. Students looking for biomechanical research on improving sports technique often will have fewer sources than students researching the biomechanics of injury.
How does biomechanics improve performance?
Another way biomechanics research improves performance is advances in exercise and conditioning programs. Bio-mechanical studies of exercise movements and training devices serve to determine the most effective training to improve performance (Figure 1.5). Biomechanical research on exercises is often compared to research on ...
How is biomechanics used in kinesiology?
Biomechanics provides information for a variety of kinesiology professions to analyze human movement to improve effectiveness or decrease the risk of injury. How the movement is analyzed falls on a continuum between a qualitative analysis and a quantitative analysis. Quantitative analysis involves the measurement of biome-chanical variables and usually requires a computer to do the voluminous numerical calculations performed. Even short movements will have thousands of samples of data to be collected, scaled, and numerically processed. In contrast, qualitative analysis has been defined as the "systematic observation and introspective judgment of the quality of human movement for the purpose of providing the most appropriate intervention to improve performance" (Knudson & Morrison, 2002, p. 4). Analysis in both quantitative and qualitative contexts means identification of the factors that affect human movement performance, which is then interpreted using other higher levels of thinking (synthesis, evaluation) in applying the information to the movement of interest. Solving problems in human movement involves high levels of critical thinking and an interdisciplinary approach, integrating the many kinesiology sciences.
How does biomechanical research help in sports medicine?
Biomechanical research is a powerful ally in the sports medicine quest to prevent and treat injury. Biomechanical studies help prevent injuries by providing information on the mechanical properties of tissues, mechanical loadings during movement, and preventative or rehabilitative therapies. Biomechanical studies provide important data to confirm potential injury mechanisms hypothesized by sports medicine physicians and epidemiological studies. The increased participation of girls and women in sports has made it clear that females are at a higher risk for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries than males due to several biomechanical factors (Boden, Griffin, & Garrett, 2000). Continued biomechanical and sports medicine studies may help unravel the mystery of this high risk and develop prevention strategies.
Why is qualitative analysis of gait important?
Qualitative analysis of gait (walking) is of importance in physical therapy and the treatment of many musculoskeletal conditions. Dramatic increases in computer memory and power have opened up new areas of application for biomechanists. Many of these areas are related to treating and preventing human injury.
How does the coach use biomechanics?
The coach uses his knowledge of biomechanics to help in the qualitative analysis of this situation. Since the coach knows that a better arch affects the force the gymnast creates against the mat and affects the angle of takeoff of the gymnast, he decides to help the gymnast work on her "arch" following the round off.
What are the two areas of biomechanics?
The applications of biomechanics to human movement can be classified into two main areas: the improvement of performance and the reduction or treatment of injury.
Why is it important to use a biomechanical frame of reference?
In the biomechanical frames of reference, it ’s easy to develop measurable biomechanical goals because this frame of reference uses quantitative evaluation data such as degree of range of motion. Other frames of reference may be used along with the biomechanical frame of reference for the better result, it depends upon the condition and need ...
What is the third assumption of the biomechanical frame of reference?
The third assumption is the principle of Rest and stress. First, the body must rest to heal itself. Then, the peripheral structure must be stressed to regain range, strength, and endurance. The fourth assumption is the belief that the biomechanical frame of reference is best suited for patients with an intact central nervous system.
What is OT in a treatment plan?
OT develops the method to integrate purposeful activities and their treatment goals. Analysis of joints and muscles during an activity is the base of the Biomechanical frame of reference. This analysis helps OT to plan and check the progress, whether goals are achieved or not.
Which assumption is the belief that the biomechanical frame of reference is best suited for patients with an intact central nervous system
The fourth assumption is the belief that the biomechanical frame of reference is best suited for patients with an intact central nervous system. Patients may have limited range, strength, and endurance, but have the ability to perform smooth, isolated movements.
What is an occupational therapist?
Occupational therapist (OT) uses purposeful activities to treat their clients, purposeful activities have some purpose and meaning to the life. OT develops the method to integrate purposeful activities and their treatment goals. Analysis of joints and muscles ...
What is the biomedical model?
The biomedical model views health as binary terms of simply healthy, and not healthy. While this is generally a good way of looking at healthcare in general, the biomedical model is criticised for its broad and almost universally applicable definition of unhealthy, and extremely narrow, nearly unobtainable small definition of healthy.
What is Western medicine?
Traditionally, western medicine has been centred around the biomedical model and its underpinning philosophi es to best determine a person’s health status. The biomedical model.
Why is biomechanical frame of reference important in occupational therapy?
Occupational therapists are concerned with the relationship between people’s occupations and their health, and assess people’s disengagement from their occupations, provide ways for them to re-engage in their occupations, or suggest alternatives so that people’s quality of life may improve. Core values and beliefs about the importance of occupation to humans constitute a paradigm of occupation. In daily practice, occupational role issues that individuals may experience can be appreciated by referring to conceptual models of practice using a ‘top-down’ approach. Examples of such models of practice are the Canadian Model of Occupational Performance (CMOP) (see Chapter 7 for further information) and the Model of Human Occupation (MOHO) (see Chapter 6 for further information). Such models provide the knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary to understand how we can analyse, intervene and evaluate individuals in relation to their roles and efficacy of occupational performances, e.g. in self-care, work and leisure. However, in order to understand the individual’s specific occupational performance problems, it is also necessary to analyse and understand their ‘performance capacities’ in more detail. Performance capacities refer to cognition, behaviour, neural development, personal interactions and, most importantly for this chapter, movement. The biomechanical frame of reference deals exclusively with the capacity for motion, whilst other frames of reference deal with other capacities, e.g. the cognitive behavioural frame of reference deals with cognition and behaviour. A biomechanical frame of reference may be useful in assessment, intervention and evaluation with people who have occupational performance problems, created primarily by some disease, injury or event that impinges on their voluntary movement, muscle strength, endurance or usually a combination of all three. The loss of one or more of these capacities will interfere to some degree with an individual’s ability to perform their occupations to their satisfaction. The biomechanical frame of reference assists in understanding the assessment, intervention and evaluation strategies associated with changing physical performance capacities in order to help individuals re-engage in their occupations.
What is biomechanical frame of reference?
The biomechanical frame of reference in occupational therapy is primarily concerned with an individual’s motion during occupations. Motion in this context can be understood in more detail as the capacity for movement, muscle strength and endurance (the ability to resist fatigue). An individual’s quality of motion may be compromised as they carry ...
What is occupational therapy?
Occupational therapists are concerned with the relationship between people’s occupations and their health, and assess people’s disengagement from their occupations, provide ways for them to re-engage in their occupations, or suggest alternatives so that people’s quality of life may improve.
What is the purpose of assessment in occupational therapy?
Occupational therapists ought to be concerned with the principles of assessment and measurement in their practice to facilitate collaborative goals, build intervention plans and document measures of outcomes. This process of assessment can be undertaken through client-driven assessment, therapist observation and the use of standardized and non-standardized instruments.
What are the biomechanical factors of movement?
Understanding the biomechanical basis of movement includes knowing the locomotor system (how bones and joints perform together, especially in relation to the appendicular skeleton), active and passive joint range of movement (a.ROM and p.ROM), the function of skeletal muscle, types of muscle work (concentric and eccentric, isotonic and isometric contraction), muscle architecture and role, the peripheral nervous system (motor, sensory and autonomic) and the relationship between the peripheral nervous system (synaptic transmission and innervation) and muscles (sliding filament theory).
Do occupational therapists use biomechanical frames?
However, it is also apparent that occupa tional therapists do use the technology of the biomechanical frame of reference at certain times with selected individuals who do have CNS damage in the form of stroke, multiple sclerosis and so on.