
Medication
View all physicians • All Locations
- Atkinson, John L. M.D.
- Bancos, Irina M.D.
- Chang, Alice Y. M.D.
- Erickson, Bradley J. M.D., Ph.D.
- Erickson, Dana M.D.
- Farley, David R. M.D.
- Grebe, Stefan K. M.D., Ph.D.
- Lyden, Melanie L. M.D.
- McKenzie, Travis J. M.D.
- Meyer, Fredric B. M.D.
Procedures
The purpose of homeopathic treatment is not only to cure Cushing’s disease, but to improve your dog’s health in general. Cushing’s disease is not something that can be cured in a day or two. It needs long term treatment and relying on chemical’s for too long can be dangerous for your dog.
Therapy
How do You Diagnose Cushing Syndrome? The diagnosis of Cushing Syndrome requires blood and urine hormone measurements, x-rays of the adrenal gland, and a thoughtful and experienced doctor. The diagnostic process follows a three-step approach: Screening for the disease, Confirming the disease, and Performing subtype diagnosis.
Self-care
Cushings syndrome is a symptom that affects many parts of the body. Unfortunately, the worst part of it is the part that everyone can see – the changes in physical appearance. When a person has this syndrome, there is nothing they can do to hide it. One good thing about the syndrome is that it’s reversible.
Nutrition
What type of doctors treat Cushings disease?
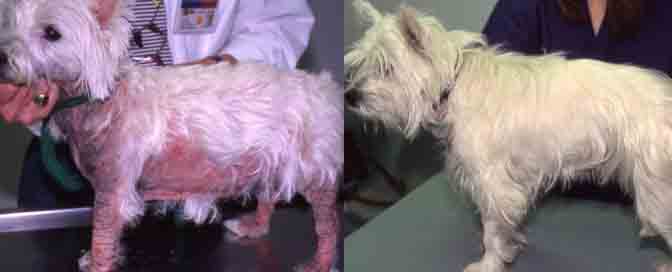
Is homeopathic treatment good for Cushings?
How do you check for Cushings disease?
Can Cushings disease be reversed?
What is the treatment of choice for Cushing's disease?
Treatment of choice for classic Cushing disease is transsphenoidal surgery by an experienced neurosurgeon. The goal of surgery is to remove the adenoma, preserving as much pituitary function as possible. The more extensive the mass and the resulting resection, the greater the risk for loss of pituitary function.
How long should a patient be treated for Cushing's disease?
If treatment removes the source of excess cortisol, most of the symptoms of Cushing's syndrome disappear within 12 months.
Does Cushings Syndrome go away?
Most cases of Cushing's syndrome can be cured, though it may take some time for your symptoms to ease up. The condition is more common in women than in men. It's most often seen in people ages 25-40.
Can Cushings be cured without surgery?
Osilodrostat (Isturisa) is the first FDA approved drug who either can't undergo pituitary gland surgery or have undergone the surgery but still have the disease. The oral tablet functions by blocking the enzyme responsible for cortisol synthesis, 11-beta-hydroxylase.
What is the main cause of Cushing disease?
The most common cause of Cushing's syndrome is the long-term, high-dose use of the cortisol-like glucocorticoids. These medicines are used to treat other medical conditions, such as asthma link, rheumatoid arthritis link, and lupus link. Glucocorticoids are often injected into a joint to treat pain.
What are the 4 underlying causes of Cushing's syndrome?
Your body's own overproduction (endogenous Cushing syndrome)A pituitary gland tumor (pituitary adenoma). ... An ACTH -secreting tumor. ... A primary adrenal gland disease. ... Familial Cushing syndrome.
How does Cushings make you feel?
People with Cushing's syndrome may see their face get round ("moon face"), they gain weight in unusual ways, bruise easily or feel weak, tired and sad. Women and men may also notice fertility and other problems. CS is most often found in adults between the ages of 20 and 50.
Is there a medication to reduce cortisol?
Cortisol blockers can be effective in treating high cortisol level disorders, such as Cushing's syndrome. However, they're also marketed as a dietary supplement that can help you curb your appetite, lose weight, and build muscle.
How do I get rid of cortisol?
Stressed? 10 Ways To Lower Your Cortisol LevelsEat a whole-food, plant-based diet. ... If needed, add supplements. ... Take deep breaths. ... Reduce your caffeine intake. ... Get adequate sleep. ... Exercise regularly. ... Write in a journal. ... Indulge in hobbies.More items...•
What Is Cushing's Syndrome?
Cushing's syndrome is the result of the excessive production of corticosteroids by the adrenal glands. An overproduction of corticotropin — the hor...
What Are The Symptoms of Cushing's Syndrome?
The following are the most common symptoms of Cushing's syndrome. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may includ...
How Is Cushing's Syndrome Diagnosed?
In addition to a complete medical history and medical examination, diagnostic procedures for Cushing's syndrome may include: 1. X-rays to locate an...
Treatment For Cushing's Syndrome
Treatment for Cushing's syndrome depends on its cause. Surgery may be needed to remove the tumor or the pituitary or adrenal glands. Other treatmen...
How to help cushing syndrome?
Gently soothe aches and pains. Hot baths, massages and low-impact exercises, such as water aerobics and tai chi, can help alleviate some of the muscle and joint pain that accompanies Cushing syndrome recovery.
Why do we need meds for Cushing syndrome?
Medications might also be used before surgery in people who have become very sick with Cushing syndrome to improve signs and symptoms and minimize surgical risk.
How long does it take for cortisol to be replaced?
However, this process can take up to a year or longer . In some instances, people with Cushing syndrome never return to normal adrenal function. They then need lifelong replacement therapy.
What is the most common cause of Cushing syndrome?
Taking glucocorticoid medications is the most common cause of Cushing syndrome. Your doctor can review all your medications — pills, injections, creams and inhalers — to determine if you're taking medications that can cause the disorder. If you are, you probably won't need other tests.
What is the root of Cushing's syndrome?
If the ACTH levels are similar between the sinuses and forearm, the root of the problem lies outside of the pituitary gland. These tests help your doctor diagnose Cushing syndrome, and they may help rule out other medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome — a hormone disorder in women with enlarged ovaries.
How to remove Cushing's tumor?
For a tumor in the adrenal glands, lungs or pancreas, the surgeon can remove it through a standard operation or by using minimally invasive surgical techniques, with smaller incisions.
How to lose weight after Cushing syndrome?
You'll improve little by little, and your persistence will be rewarded. Eat sensibly. Nutritious foods provide a good source of fuel for your recovering body and can help you lose pounds you gained from Cushing syndrome.
What are the treatments for cushing?
If a tumor is the cause of Cushing, treatments may include medication, surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a combination of these treatments. The treatment depends on the tumor’s location and type. Pituitary tumors. The most common treatments for pituitary tumors are: Surgery.
How to treat Cushing syndrome?
For cases of Cushing syndrome caused by taking medicine to treat another disorder, your healthcare provider will, if possible, decrease the dose slowly and carefully and then give another medication so the body can go back to making its own cortisol.
What to do after adrenal surgery?
After surgery to remove both adrenal glands, you will need to take medications to replace adrenal function for the rest of your life and take additional precautions during illness or surgery . If your healthcare provider cannot remove the tumor, medications can help block the release of cortisol.
How to treat pituitary tumors?
The most common treatments for pituitary tumors are: Surgery. In most cases, a surgeon removes the tumor through a cut under the upper lip or at the bottom of the nose, between the nostrils. In rare cases, the surgeon may cut through the skull to reach the pituitary tumor. Radiation therapy.
Can radiation therapy be used for adrenal tumors?
If your healthcare provider cannot remove the tumor, medications can help block the release of cortisol. Radiation therapy usually is not used for adrenal tumors.
What is the best treatment for Cushing's disease?
The first thing your doctor may suggest to treat your Cushing's disease is a pituitary surgery. This is called t rans s phenoidal s urgery (TSS). It allows surgeons to remove the tumor on the pituitary gland. This is a very specialized brain surgery, so it is best performed by an experienced neurosurgeon who has done many of these specific procedures.
How to bring cortisol levels back to normal?
Treatment Goal: Bring cortisol back to normal. When treating Cushing's disease, surgery is the recommended first choice of treatment to bring cortisol levels back to normal. This is a specific surgery to remove the pituitary gland tumor. However, if you are unable to have surgery or choose not to, there are medications to help lower cortisol levels.
What is the target of a drug that doesn't reduce ACTH?
Target: Cortisol receptors. There is another class of medicines that doesn't actually reduce ACTH or cortisol levels. These medications bind to cortisol receptors found throughout the body. The cortisol that is made in the adrenal glands is then not able to attach to these receptors.
Can you cure Cushing's disease?
Well, there isn't a medication to cure Cushing's disease. But there are medications that may bring cortisol levels back to normal. This can help reduce your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Talk to your healthcare team about the best treatment option for you.
Can cortisol be lower after surgery?
Or maybe your symptoms returned after a period of time following surgery. Medications may be able to help lower cortisol in these instances as well.
How to treat Cushing's syndrome?
Treatment of Cushing's syndrome is essential to reduce mortality and associated comorbidities. Effective treatment includes the normalization of cortisol levels or action. It also includes the normalization of comorbidities via directly treating the cause of Cushing's syndrome and by adjunctive treatments (eg, antihypertensives). Surgical resection of the causal lesion(s) is generally the first-line approach. The choice of second-line treatments, including medication, bilateral adrenalectomy, and radiation therapy (for corticotrope tumors), must be individualized to each patient.
When to measure cortisol?
6.3c We recommend measuring serum cortisol or urine free cortisol (UFC) off-medication at 6- to 12-month intervals to assess the effect of RT and also if patients develop new adrenal insufficiency symptoms while on stable medical therapy. (1|⊕⊕⊕○)
How long after transsphenoidal surgery should you measure sodium?
3.1ci We recommend measuring serum sodium several times during the first 5–14 days after transsphenoidal surgery. (1|⊕⊕○○)
Can transsphenoidal surgery be repeated?
6.2 We suggest repeat transsphenoidal surgery, particularly in patients with evidence of incomplete resection, or a pituitary lesion on imaging. (2|⊕⊕○○)
What are the treatments for Cushing's disease?
What are the Treatment Options for Cushing’s Disease? The only effective treatments for Cushing’s disease are to remove the tumor, to reduce its ability to make ACTH, or to remove the adrenal glands. There are other complementary approaches that may be used to treat some of the symptoms.
What is the treatment for pituitary tumors?
Radiosurgery. Other options for treatment include radiation therapy to the entire pituitary gland or targeted radiation therapy (called radiosurgery ), when the tumor is seen on MRI. This may be used as the only treatment or it may be given if pituitary surgery is not completely successful.
How to get a tumor out of the pituitary?
This is usually carried out by going via the nose or upper lip and through the sphenoid sinus to reach the tumor. This is known as transsphenoidal surgery and avoids having to get to the pituitary via the upper skull. This route is less traumatic for the patient and allows quicker recovery.
What hormones are removed from the adrenal glands?
Removal of both adrenal glands also removes the ability of the body to produce cortisol. Since adrenal hormones are necessary for life, patients must then take a cortisol-like hormone and the hormone florinef, which controls salt and water balance, every day for the rest of their life.
Can cortisol be used as a long term treatment?
While some promising drugs are being tested in clinical studies, currently available medications to reduce cortisol levels, when given alone, do not work well as a long-term treatment. These medicines are most often used in conjunction with radiation therapy. Transsphenoidal Surgical Approach.
What is the FDA approved drug for Cushing's disease?
Cushing’s disease is a rare disease in which the adrenal glands make too much of the cortisol hormone. Isturisa is the first FDA-approved drug to directly address this cortisol overproduction by blocking the enzyme known as 11-beta-hydroxylase and preventing cortisol synthesis.
What are the health problems associated with Cushing's disease?
Cushing’s disease can cause significant health issues, such as high blood pressure, obesity, type 2 diabetes, blood clots in the legs and lungs, bone loss and fractures, a weakened immune system and depression. Patients may have thin arms and legs, a round red full face, increased fat around the neck, easy bruising, ...
What is the cause of Cushing's disease?
Cushing’s disease is caused by a pituitary tumor that releases too much of a hormone called adrenocorticotropin, which stimulates the adrenal gland to produce an excessive amount of cortisol. The disease is most common among adults between the ages of 30 to 50, and it affects women three times more often than men.
Who approved Isturisa?
The FDA granted the approval of Isturisa to Novartis. The FDA, an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, protects the public health by assuring the safety, effectiveness, and security of human and veterinary drugs, vaccines and other biological products for human use, and medical devices.
How much isturisa for 24 weeks?
In the 24-week, single-arm, open-label period, all patients received a starting dose of 2 milligrams ( mg) of Isturisa twice a day that could be increased every two weeks up to 30 mg twice a day. At the end of this 24-week period, about half of patients had cortisol levels within normal limits.
What is the treatment for Cushing's disease?
The goals of treatment include normalization of hormone excess, long-term disease control and the reversal of comorbidities caused by the underlying pathology. The treatment of choice is neurosurgical tumour removal of the pituitary adenoma. Second-line treatments include medical therapy, bilateral adrenalectomy and radiation therapy. Drug treatment modalities target at the hypothalamic/pituitary level, the adrenal gland and at the glucocorticoid receptor level and are commonly used in patients in whom surgery has failed. Bilateral adrenalectomy is the second-line treatment for persistent hypercortisolism that offers immediate control of hypercortisolism. However, this treatment option requires a careful individualized evaluation, since it has the disadvantage of permanent hypoadrenalism which requires lifelong glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid replacement therapy and bears the risk of developing Nelson’s syndrome. Although there are some very promising medical therapy options it clearly remains a second-line treatment option. However, there are numerous circumstances where medical management of CD is indicated. Medical therapy is frequently used in cases with severe hypercortisolism before surgery in order to control the metabolic effects and help reduce the anestesiological risk. Additionally, it can help to bridge the time gap until radiotherapy takes effect. The aim of this review is to analyze and present current treatment options in Cushing’s disease.
What is the effect of Cushing's disease on the body?
In Cushing’s disease (CD), the elevated ACTH secretion leads to an excess of adrenal gland cortisol secretion. The autonomous ACTH-secretion by the adenoma and the disturbance of the normal cortisol feedback mechanism with the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis leads to a loss of the circadian rhythm of cortisol production, excessive cortisol production and hypercortisolism. The clinical consequences for the patients are grave and include high blood pressure, diabetes, loss of libido, menstrual disorders, weight gain, hirsutism, acne, easy bruising, purplish skin striae, osteoporosis, muscle weakness, depression and cognitive impairment.1,3,4Although externally visible clinical signs of the pathology are often strikingly obvious, the rare incidence and low prevalence5of the disease leads to a considerable delay between the onset of symptoms and the establishment of diagnosis.6,7One has to consider that patients often present with obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and depression in the early stage of their disease which are wide spread diseases. This can hinder the early detection of CD and complicate the diagnosis. On the other hand, untreated CD is accompanied by a significantly higher mortality compared to the general population due to vascular and metabolic comorbidities so that early disease detection is of paramount importance.1,5,8–13
How to treat CD?
The first treatment of choice is the neurosurgical tumor removal, most cases being operated via a transsphenoidal approach. In cases where the surgical procedure alone cannot achieve disease control, second-line treatment options have to be considered. These consist of medical therapy, radiotherapy and bilateral adrenalectomy. Treatment results with somatostatin- analogues directed to the receptor subtype 5 are promising and might offer an option for long-term medical therapy. SR radiotherapy is increasingly used for circumscribed residual adenomas within the cavernous sinus. Therefore, the search for new and effective medical tools is still open. All these aspects emphasize the need of effective treatment of CD itself as well as long-term follow-up of these patients in order to control its complications and detect recurrence in a timely fashion.
What is the best treatment for adenoma in the pituitary gland?
Transsphenoidal microsurgical removal of ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma is the first-line treatment in CD.14Although endoscopic surgery has gained increasing recognition as an alternative to the classical microscopic technique,17robust data about outcome with this treatment modality are still scarce; a recent review of endoscopic surgery showed an overall remission rate of 74% in CD,18while the reported overall success rates of transsphenoidal microsurgery for CD vary from 68.5% to 94%.19–23Despite an ongoing competitive discussion whether microscopy or endoscopy is the superior technique for transsphenoidal surgery, one has to keep in mind that the most important determinant of surgical outcome is the experience of the neurosurgeon, since both, endoscope and microscope, are only visualising devices.
What is the treatment for CD?
The goals of treatment in CD are the normalization of cortisol excess, long-term disease control, avoidance of recurrence and reversal of clinical features.14The initial therapy of first choice is transsphenoidal surgery (TS) for tumour removal. Survival rates of patients cured by TS do not differ from those in the general population.15,16In the event of failure after initial or repeat pituitary surgery, second-line treatment options include medical therapy, radiotherapy or bilateral adrenalectomy.
How often do adenomas recur?
Recurrence occurs more likely and earlier in patients with macroadenomas compared to those with microadenomas (mean of 16 vs . 49 months). 26,33In recurrent CD, repeat transsphenoidal surgery has been shown to be effective in 46% to 71% of patients.28,35–40Because of significant scar tissue and altered normal anatomy, repeat surgery for recurrent pituitary adenomas is in general more challenging than an initial operation or an immediate re-operation for persistent disease. Ikeda et al (2011) found that the use of MET-PET was extremely helpful in the detection of adenoma in recurrent CD in one 45 year old female patient.41Surgical navigation and the Doppler probe are highly recommended for localizing the portion of the internal carotid artery (ICA) within the cavernous sinus and for confirming regional anatomy.39,42
Is Cushing's disease endogenous?
Endogenous Cushing’s syndrome is a grave and devastating condition. Eighty percent of the patients harbour an adrenocorticotropin-hormone (ACTH) secreting pituitary adenoma (Cushing’s disease), while extrapituitary tumour (ectopic ACTH syndrome) and ectopic CRH-secreting tumours are very rare findings. The remaining 20% of ACTH-independent Cushing’s syndrome are (in most instances) due to an adrenal tumour or, more rarely, macronodular adrenal hyperplasia, primary pigmented nodular disease (either as isolated disease or as part of the Carney complex), or the McCune-Albright syndrome.1,2

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Treatments for Cushing syndrome are designed to lower the high level of cortisol in your body. The best treatment for you depends on the cause of the syndrome. Options include: