Medication
The patients, a 32-year-old man with paroxysmal AF and a 60-year-old man with persistent AF underwent successful pulmonary vein and posterior wall isolation using a dedicated PFCA catheter powered by the proprietary Adagio iCLAS™ cryoablation and pulsed field ablation (PFA) consoles.
Procedures
- Attempt vagal maneuvers.
- If unsuccessful, administer adenosine 6 mg IV bolus followed by a rapid normal saline flush.
- If unsuccessful, administer adenosine 12 mg IV bolus followed by a rapid normal saline flush.
Nutrition
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation are treated with unsynchronized shocks, also referred to as defibrillation. If a patient develops ventricular fibrillation during synchronized cardioversion with a monophasic defibrillator, pulselessness should be verified.
How do you treat ventricular fibrillation?
Ventricular fib: Vf is worse; it usually causes cardiac arrest which is often fatal. Atrial fibrillation, while not as severe, also has significant health risks. It ... Read More why is ventricular fibrillation worse than atrial fibrillation?
How do you treat V tach with a pulse?
How is pulseless V fib treated?
What is worse an or B fibrillation?
What is the drug of choice for ventricular fibrillation?
Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes. If epinephrine is not effective, the next medication in the algorithm is amiodarone 300 mg. Defibrillation and medication are given in an alternating fashion between cycles of 2 minutes of high-quality CPR.
How do you fix ventricular fibrillation?
Treatment for ventricular fibrillation includes medications, medical devices and surgery....Surgery or other proceduresImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). ... Cardiac ablation. ... Coronary angioplasty and stent placement. ... Coronary bypass surgery.
How long can you live with ventricular fibrillation?
Survival: Overall survival to 1 month was only 1.6% for patients with non-shockable rhythms and 9.5% for patients found in VF. With increasing time to defibrillation, the survival rate fell rapidly from approximately 50% with a minimal delay to 5% at 15 min.
What is ventricular fibrillation and how it can be treated?
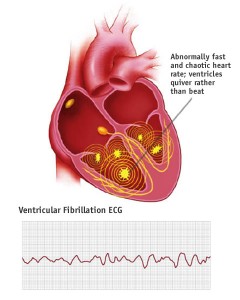
Ventricular fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, that affects your heart's ventricles. Ventricular fibrillation is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. CPR and defibrillation can restore your heart to its normal rhythm and may be life saving.
Which is more serious atrial fibrillation or ventricular fibrillation?
Ventricular fibrillation is more serious than atrial fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation frequently results in loss of consciousness and death, because ventricular arrhythmias are more likely to interrupt the pumping of blood, or undermine the heart's ability to supply the body with oxygen-rich blood.
Can ventricular fibrillation stop on its own?
Ventricular fibrillation seldom terminates spontaneously, since several re-entrant wavefronts, independent from each other, coexist, and the simultaneous extinction of all the circuits is unlikely.
Can ventricular fibrillation cause permanent damage?
The longer the body lacks blood, the greater the risk of damage to your brain and other organs. Ventricular fibrillation is the most frequent cause of sudden cardiac death. The risk of other long-term complications depends on how fast you receive treatment.
What is the heart rate for ventricular fibrillation?
If you're having an episode of ventricular fibrillation, the ECG usually shows a heartbeat of about 300 to 400 beats a minute.
What drugs can cause ventricular fibrillation?
The following drug classes may cause monomorphic ventricular tachycardia: anesthetics, antiarrhythmics, anticancer drugs, anticonvulsants, antidepressants, anti-manic medications, antiplatelet, antipsychotic, beta agonists, ergot derivatives, herbs, cocaine, inotropes, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, sympathomimetics, ...
What is the most common cause of ventricular fibrillation?
Ventricular fibrillation is most commonly caused by the following: Heart disease. Heart attack or chest pain (angina). Diseases that change the structure of the heart by making its walls thicker or weaker.
What causes sudden ventricular fibrillation?
Ventricular fibrillation happens when the electrical signals in your heart go haywire. This causes a ventricle to quiver (fibrillate) instead of pumping blood through your body. Without medical treatment right away, V-fib can be deadly. In fact, it's the most common cause of sudden cardiac death.
How can you prevent ventricular fibrillation?
How can ventricular fibrillation be prevented?You should eat a heart-healthy diet.You should stay active, such as by walking 30 minutes per day.If you smoke, start thinking about ways to help you quit. ... Avoid drinking excess alcohol, which can put extra stress on your heart.More items...•
What is ventricular fibrillation?
Key points about ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, that affects your heart’s ventricles. Ventricular fibrillation is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. CPR and defibrillation can restore your heart to its normal rhythm and may be life saving.
What is the procedure to eliminate electrical triggers of V-FIB?
Catheter ablation. This procedure uses energy to destroy small areas of your heart affected by the irregular heartbeat. This rarely used procedure for V-fib looks to eliminate electrical triggers of V-fib.
What is it called when your heart beats in and out of the heart?
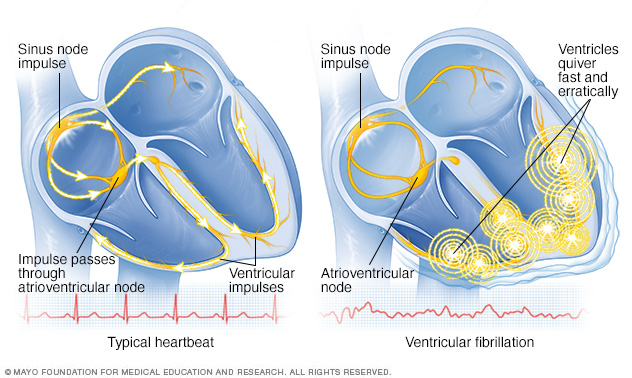
This keeps blood flowing throughout your body. An arrhythmia that starts in your ventricle is called ventricular fibrillation. This occurs when the electrical signals that tell your heart muscle to pump cause your ventricles to quiver (fibrillate) instead.
What is an implantable cardiac defibrillator?
Implantable cardiac defibrillators are devices that are implanted within the body that can shock the heart back to normal rhythm within seconds if V-fib is present. Although this device does not necessarily prevent V-fib, it can rapidly and automatically diagnose and treat this potentially fatal heart rhythm.
What is a V-fib?
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) is a dangerous type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat. It affects your heart’s ventricles. Your heart is a muscle system that contains 4 chambers; the 2 bottom chambers are the ventricles. In a healthy heart, your blood pumps evenly in and out of these chambers. This keeps blood flowing throughout your body.
What does it mean when your heart is quivering?
The quivering means that your heart is not pumping blood out to your body. In some people, V-fib may happen several times a day. This is called an “electrical storm.”. Because sustained V-fib can lead to cardiac arrest and death, it requires immediate medical attention.
What causes V-FIB in the heart?
Other causes include electrolyte abnormalities such as low potassium, certain medicines, and certain genetic diseases that affect the heart's ion channels or electrical conduction.
How to cure atrial flutter?
Currently, atrial flutter is successfully "cured" by radiofrequency catheter ablation; but treatment to restore atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm has been the traditional use of medications and external cardioversion.
What is a biventricular pacemaker?
Biventricular Pace Maker. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the first of a new type of pacemaker that paces both ventricles of the heart to coordinate their contractions and improve their pumping ability.
What is radiofrequency ablation?
A technique pioneered at UCSF, radiofrequency catheter ablation destroys or disrupts parts of the electrical pathways causing the arrhythmias, providing relief for patients who may not have responded well to medications, or who would rather not or can't take medications.
How many joules does external cardioversion have?
External cardioversion is delivery of high energy shocks of 50 to 300 joules through two defibrillator pads attached to the chest. In some cases, external cardioversion has failed because the electrical current has to first travel through chest muscle and skeletal structures before reaching the heart.
When was internal cardioversion developed?
Internal cardioversion for conversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter to a normal sinus rhythm was developed here at UCSF Medical Center in 1991. Internal cardioversion is low energy electrical shock (1 to 10 joules) delivered internally in the heart through two catheters inserted in a vein in the groin and a small electrode pad applied to the chest. This procedure is performed in the electrophysiology lab by our electrophysiologist.
What is an implantable cardioverter?
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator is a device for people who are prone to life-threatening rapid heart rhythms. It is slightly larger than a pacemaker and usually is implanted beneath the skin below the collarbone. It is connected to a defibrillation/pace wire (s) positioned inside the heart via a vein. It has the capability of delivering an electric shock to the heart when it determines the heart rate is too fast. It also is capable of pacing or stimulating the heart when it is going too slow.
Can you convert atrial fibrillation to normal?
The less time a patient is in atrial fibrillation, the easier it is to cardiovert back to a normal rhythm, but even patients with long-standing chronic atrial fibrillation can be converted successfully to a normal rhythm through internal cardioversion.
What is VF in cardiac arrest?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF or V-fib) is the most common initial heart rhythm in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), and the most salvageable one . 5 In VF, the etiology of arrest is often attributed to either acute ischemia or non-ischemic arrhythmia. 8
How many joules should a defibrillator be?
If the defibrillator is biphasic, the manufacturer recommended joules should be selected (usually 120 to 200 joules). If the amount is unknown, use the maximum available and subsequent doses should be equivalent, and possibly higher. 1.
What is the most important intervention for cardiac arrest?
Irrespective of the cause of cardiac arrest, the most important interventions are early recognition and calling for help—including appropriate management of the deteriorating patient—early defibrillation, high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) with minimal interruption of chest compressions, and treatment of reversible causes. 6
What are the causes of VF?
The easiest way to remember the most common causes of VF are to review the reversible “Hs and Ts” in cardiac arrest. The Hs include hypoxia, hypovolemia, hypothermia, hyper/hypokalemia, and hydrogen ions (acidosis). The Ts are tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, toxins, and thrombosis (pulmonary or coronary).
What is the most important algorithm for resuscitation?
Ventricular fibrillation falls under the ACLS Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm and is the most important algorithm to know for adult resuscitation. 1 Ventricular fibrillation treatment starts with early and effective CPR with the application of oxygen and monitor/defibrillator placement. Keeping the brain, heart, ...
What to do if you have a V-fib?
Step 2: Defibrillation to fix your heart rhythm. Step 3: Medication to make the rhythm stable again. Defibrillators for V-fib.
Why do doctors not know what causes ventricular fibrillation?
For instance, it happens most often during or right after a heart attack. That may be because the heart’s electrical signals can become unstable when there isn’t enough blood flow.
What is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death?
Ventricular fibrillation happens when the electrical signals in your heart go haywire. This causes a ventricle to quiver (fibrillate) instead of pumping blood through your body. Without medical treatment right away, V-fib can be deadly. In fact, it’s the most common cause of sudden cardiac death.
What are the symptoms of ventricular fibrillation?
The main symptom is fainting. You may also have symptoms of ventricular tachycardia (VT). This is when the lower chambers of your heart beat too fast. It can lead to V-fib. Signs and symptoms of VT include: Chest pain. Pounding or fast heartbeat.
What are the complications of V-FIB?
V-fib can lead to serious complications including: Injuries from CPR. Skin burns from defibrillation. Brain injury from a lack of oxygen. Injury to your heart muscle. Death. Ventricular Fibrillation Prevention. You can’t completely prevent an episode of ventricular fibrillation.
What tests are used to check for heart damage?
Tests of how well your heart works, such as an EKG. Blood tests to look for heart damage. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI exams, and echocardiograms. Ventricular Fibrillation Treatment. V-fib comes on quickly and needs treatment just as fast.
What is the heart muscle called that keeps your heart from pumping blood the way it should?
Ventricular fibrillation, or V-fib, is a dangerous problem with your heart rhythm (called an arrhythmia) that keeps your heart from pumping blood the way it should. It is a medical emergency. Your heart muscle has four main sections, called chambers. The bottom two chambers are the ventricles.
Drugs used to treat Ventricular Fibrillation
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Diagnosis and Tests
Ventricular fibrillation is usually confirmed by an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), especially after a person has been resuscitated from cardiac arrest. This is also useful to determine the heart’s ability to function going forward.
Management and Treatment
The condition is a life-threatening medical emergency and every minute counts. The following actions can help save the life of someone who has gone into sudden cardiac arrest because of ventricular fibrillation:
Frequently Asked Questions
Atrial fibrillation is similar to ventricular fibrillation, but it’s happening in the upper chambers of the heart, called the atria. When the atria fibrillate, they beat very fast (sometimes several hundred times per minute). This can cause blood to collect in the atria and over time, this can cause the atria to stretch and enlarge.
What is the best medication for atrial fibrillation?
These medications include dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban. They are shorter acting than warfarin and usually don't require regular blood tests or monitoring by your doctor.
What to do if you think you have atrial fibrillation?
If you think you may have atrial fibrillation, it is critical that you make an appointment with your family doctor. If atrial fibrillation is found early, your treatment may be easier and more effective. However, you may be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist).
How does catheter ablation help with atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is often caused by rapidly discharging triggers, or "hot spots." In catheter ablation to treat atrial fibrillation, a doctor inserts long, thin tubes (catheters) into your groin and guides them through blood vessels to your heart. The electrodes at the tips of the catheters help your doctor determine where these triggers are located. Electrodes at the catheter tips can use radiofrequency energy, extreme cold (cryotherapy) or heat to destroy these triggers, scarring the tissue so that the erratic signals are normalized.
What is the procedure called when a catheter is placed in the left atrium?
Left atrial appendage closure. Your doctor may also consider a procedure called left atrial appendage closure. In this procedure, doctors insert a catheter through a vein in the leg and eventually guide it to the upper left heart chamber (left atrium).
How to diagnose atrial fibrillation?
To diagnose atrial fibrillation, your doctor may review your signs and symptoms, review your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition, including:
What is an ECG test?
Electrocardiogram (ECG). An ECG uses small sensors (electrodes) attached to your chest and arms to sense and record electrical signals as they travel through your heart. This test is a primary tool for diagnosing atrial fibrillation. Holter monitor.
How does cardioversion work?
In this brief procedure, an electrical shock is delivered to your heart through paddles or patches placed on your chest. The shock stops your heart's electrical activity for a short moment. The goal is to reset your heart's normal rhythm.
Ethan Deckert, MD, examines treatment options for refractory ventricular fibrillation
Tones ring out and dispatch announces a 9-Echo call in your district: an approximately 35-year-old male was found lying on the sidewalk, with bystanders currently receiving instructions to start CPR. You arrive on scene to find a sweaty 35-year-old male in running clothes, unresponsive and pulseless.
In Summary
Magnesium sulfate lacks substantial supporting evidence for its use in shock-refractory Vfib/Vtach and is not recommended for routine use at this time.
What is the best medicine for AFIB?
Heart rate controlling medicines, such as beta-blockers that include Coreg ( Carvedilol) and Lopressor and Toprol ( Metoprolol ), is the best way to treat AFib.
What is the name of the medication that is used to treat ventricular arrhythmias?
Sotylize ( sotalol hydrochloride) Sotylize (fluorouracil) is a prescription medication used to treat life-threatening heart rhythm problems called ventricular arrhythmias and to increase the amount of time between having symptoms of heart rhythm disorders called atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
How do you know if you have AFIB?
Symptoms of AFib are confusion, anxiety, fatigue, a fluttering in the chest, and the feeling that you may pass out or faint. Atrial fibrillation is treated with medications, cardioversion therapy, and surgery.
What is the name of the heart condition that causes heart palpitations?
Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is an abnormality in the heart rhythm, which involves irregular and often rapid beating of the heart. Symptoms may include heart palpitations, dizziness, fainting, fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Atrial fibrillation treatment may include medication or procedures like cardioversion or ablation ...
What is the name of the condition where blood clots form inside the heart and travel to the brain?
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) occurs when the two smaller, upper chambers of the heart (the atria) beat irregularly instead of rhythmically. This abnormal condition can allow blood clots to form inside the heart and later travel to the brain and cause a stroke.
Why is my heart rate so high?
Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, is a type of heart disorder that can cause an abnormally high heart rate. AFib occurs due to problems with an individual’s heart’s electrical activity. It results in poor pumping of blood by the heart because of which an individual is at a risk of blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other problems.
What are the symptoms of AFIB?
Early warning signs and symptoms of atrial fibrillation include chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, and lightheadedness. Treatment for atrial fibrillation includes medical procedures, surgery, and medication.

Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support