- Painkiller pills. Acetaminophen and NSAIDs like ibuprofen can ease pain.
- Immobilizing devices. A splint, brace, or sleeve can hold your hand in a stable position to lessen pain.
- Hand therapy. ...
- Cortisone shots.
What are the best natural remedies for osteoarthritis?
Treatments for Osteoarthritis in Hands Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) Research suggests Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) may be useful in treating knee osteoarthritis 2 and rheumatoid arthritis in the hand. 3 Occasionally, TENS may be recommended to decrease hand pain caused by osteoarthritis.
What is the best OTC medicine for osteoarthritis?
the standard pharmacological treatment includes agents for control of pain and inflammation (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics including opioids, intraarticular corticosteroids) and the group of the symptomatic slow acting drugs for oa such as glucosamine sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, diacerein, unsaponifiables extract of soybean …
How to prevent and treat osteoarthritis in the hands?
Nov 01, 2019 · Splints and braces. Hand braces and splints found in drugstores immobilize your hand and fingers and keep them in a less painful position. They also can be worn at night, if flare-ups disturb your sleep. "But don't wear splints or braces all the time, as this can make the affected joints stiffer," says Dr. Shmerling.
What are the best natural supplements for osteoarthritis?
Hand therapists can teach joint protection exercises and activity modification to help protect joints. Anti-inflammatory medication or a steroid injection into the joint can decrease pain, but neither cures osteoarthritis. Surgery is considered when the …

Can osteoarthritis in hands be reversed?
A physical exam and x-ray often is enough to confirm hand osteoarthritis. Unfortunately, you cannot reverse osteoarthritis or even slow its progression in most cases.Nov 1, 2019
How do you stop osteoarthritis from progressing in fingers?
Moving your hands and fingers can help keep your ligaments and tendons flexible and increase the function of synovial fluid. Try regular hand exercises to strengthen muscles and relieve stiffness and pain.
What are the 4 stages of osteoarthritis in the hands?
Stage 1 (early or doubtful) Stage 2 (mild or minimal) Stage 3 (moderate) Stage 4 (severe)Apr 6, 2021
What is best treatment for arthritis in hands?
Oral pain medications most frequently recommended to treat hand arthritis include acetaminophen and/or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen.
Can you get rid of arthritis bumps on fingers?
You can treat pain and swelling with rest, splints, ice, physical therapy, and pain medicines like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In rare cases, your doctor might suggest surgery to remove the nodes, or replace or fuse one of the joints in your fingers.Aug 20, 2020
What can you soak your hands in for arthritis?
Many people with hand OA report that soaking their hands in warm water in the morning assists in decreasing the stiffness. Begin by filling a clean sink or large basin with warm (not hot) water. If swelling is also noted, add approximately ¼ cup of Epsom salt to the water to assist in decreasing the swelling.Jul 15, 2013
What does osteoarthritis look like in the hands?
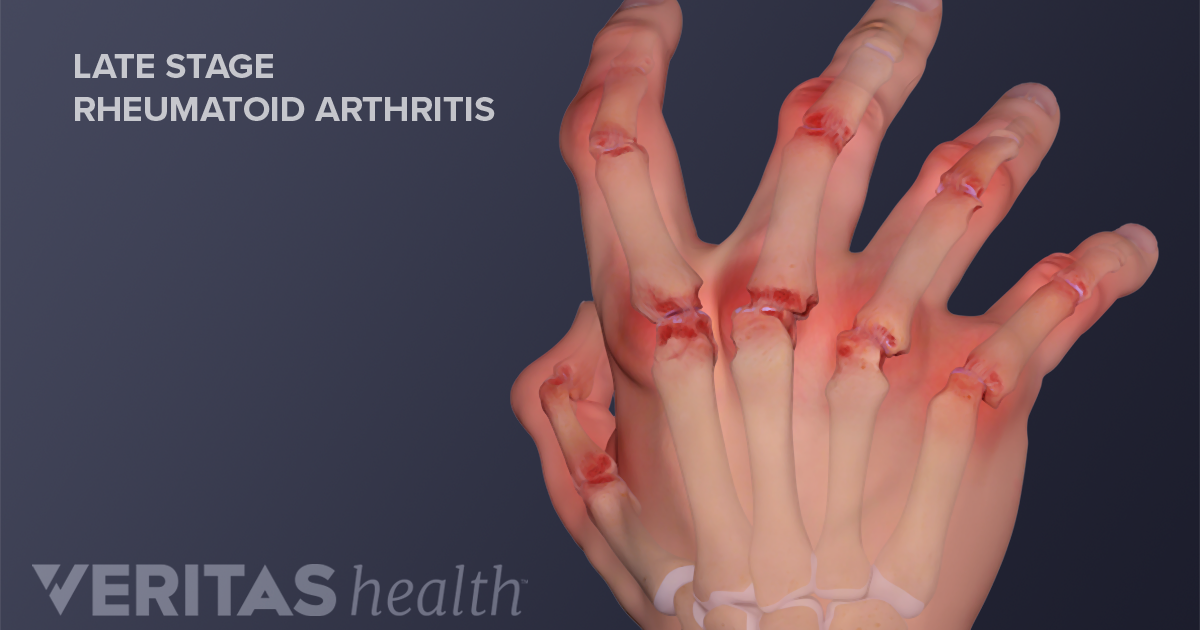
Nodules: Bony lumps may form on the middle joint of the finger (Bouchard's nodes) or at the joint near the fingertip (Heberden's nodes). Joint deformity: Bone changes, loss of cartilage, unstable or loose ligaments and swelling can make your finger joints large and misshapen.
What is the life expectancy of a person with osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis reduces the quality and quantity of life. By using Quality adjusted life Years (a measure of disease burden taking life quality into account) it can be said that the average, 50-84 year old, non-obese person with knee OA will lose 1.9 years.May 8, 2015
What happens if osteoarthritis is left untreated?
If left untreated, it'll get worse with time. Although death from OA is rare, it's a significant cause of disability among adults. It's important to talk to your doctor if OA is impacting your quality of life. Surgery to replace joints may be an option, as well as pain medication and lifestyle changes.
What causes arthritis in hands to flare up?
The most common triggers of an OA flare are overdoing an activity or trauma to the joint. Other triggers can include bone spurs, stress, repetitive motions, cold weather, a change in barometric pressure, an infection or weight gain. Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is an inflammatory disease that affects the skin and joints.
How do I get rid of arthritis in my knuckles?
Ice: Applying ice to the fingers can help relieve pain and inflammation within the knuckle joints, especially if swelling is present. Medication: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help manage symptoms and reduce pain.Oct 15, 2021
How can I reduce inflammation in my hands?
Use a warm, moist compress (or towel or heating pad) on your fingers and hands for 15 minutes before you exercise. To reduce swelling, use ice packs. Put an ice pack on the painful joint for 10 to 15 minutes at a time. You may want to switch between moist heat and ice packs.Jun 16, 2020
What is the treatment for arthritis in the hand?
They sometimes are referred to as cortisone shots. Surgery used to treat hand arthritis may be either arthroplasty (removing a damaged joint and replacing it with an artificial one) or arthrodesis (fusing the bones of an affected joint together).
What is the best treatment for osteoarthritis?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): In studies, CBT has been found to help people with osteoarthritis to deal with fatigue, disability, low mood, and pain, and to improve overall quality of life. 3.
Why are my fingers crooked?
Osteoarthritis (OA) of the hand can be painful and debilitating, making everyday tasks difficult and causing fingers to become swollen and crooked. The recommended treatments for hand osteoarthritis, as laid out by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and the Arthritis Foundation (AF), include multiple strategies.
Who is Carol Eustice?
Carol Eustice is a writer covering arthritis and chronic illness, who herself has been diagnosed with both rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. David Ozeri, MD, is a board-certified rheumatologist from Tel Aviv, Israel specializing in arthritis, autoimmune diseases, and biologic therapies. Osteoarthritis (OA) of the hand can be painful ...
What is the best medication for arthritis?
Oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): The most common of these are ibuprofen (Advil and other brands) and naproxen (Aleve). Topical NSAIDs: Creams, ointments, gels, and medicated patches can provide symptom relief directly to the affected joints, such as Voltaren Gel (diclofenac, 1%).
Where is the CMC joint?
The ACR/AF guidelines recommend kinesiotaping specifically for the first carpometacarpal (CMC) joint of the hand, which is at the base of the thumb. Orthoses: These braces can stabilize and protect the joints, and are especially useful for the CMC joint.
Is chondroitin good for arthritis?
Choindroitin is a substance that occurs naturally in cartilage. A manufactured form of chondroitin, chondroitin sulfate, made from animal cartilage, has been touted as useful for treating arthritis. 7 Although not recommended for hip or knee arthritis, it is conditionally recommended for hand OA.
How to help osteoarthritis in hands?
A cane or walker take weight off your knee or hip as you walk. Hold the cane in the hand opposite the leg that hurts. Tools for gripping and grabbing may make it easier to work in the kitchen if you have osteoarthritis in your fingers.
What is the best medicine for osteoarthritis?
Medications that can help relieve osteoarthritis symptoms, primarily pain, include: Acetaminophen. Acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) has been shown to help some people with osteoarthritis who have mild to moderate pain. Taking more than the recommended dose of acetaminophen can cause liver damage.
Why do we need an MRI?
An MRI isn't commonly needed to diagnose osteoarthritis but can help provide more information in complex cases.
How to reduce pain in a joint?
Physical therapy. A physical therapist can show you exercises to strengthen the muscles around your joint, increase your flexibility and reduce pain. Regular gentle exercise that you do on your own, such as swimming or walking, can be equally effective.
Why does my knee bow outward?
Knee osteotomy. For some people, arthritis damages one side of the knee more than the other side . This can cause your knee to bow inward or outward. Removing or adding a wedge of bone in your shinbone or thighbone can help straighten this bowing and shift your weight to the undamaged part of your knee joint.
What is hip prosthesis?
Hip prostheses are designed to mimic the ball-and-socket action of your hip joint. During hip replacement surgery, your surgeon removes the diseased or damaged parts of your hip joint and inserts the artificial joint. Knee comparisons. Open pop-up dialog box.
How to relieve pain from a swollen joint?
Avoid moves that cause pain in your joints. Heat and cold. Both heat and cold can relieve pain and swelling in your joint. Heat, especially moist heat, can help muscles relax and ease pain.
What is the best treatment for arthritis pain?
Another drug option for severe pain is corticosteroid injections into the joints. These can provide weeks or even months of relief, but they can be painful, cause tendon damage, and worsen the breakdown of cartilage if overused. (Talk with your doctor about whether this is an option for you.) Splints and braces.
How to improve hand strength?
Hand exercises and physical therapy may help strengthen hand muscles and increase finger range of motion. "Ask your doctor about seeing an occupational therapist," says Dr. Shmerling. "He or she can create specialized exercises that can best help maintain hand function.". Image: SelectStock/Getty Images.
What is the most common joint disorder?
Osteoarthritis, the most common joint disorder, is known as "wear and tear" arthritis. It causes the protective cartilage on the ends of your bones to break down and wear away. Over time, the bones in the joint rub together and trigger pain, swelling, and inflammation. Osteoarthritis most commonly affects three parts of the hand:
Can you reverse osteoarthritis?
A physical exam and x-ray often is enough to confirm hand osteoarthritis. Unfortunately, you cannot reverse osteoarthritis or even slow its progression in most cases. But that doesn't mean you're defenseless. The following strategies may help manage flare-ups. Medication.
What is the best medication for a flare up?
Mild inflammation and pain can be treated with over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like naproxen (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil) or pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol).
Can you wear splints at night?
They also can be worn at night, if flare-ups disturb your sleep. "But don't wear splints or braces all the time, as this can make the affected joints stiffer," says Dr. Shmerling. Heat and cold therapy. Icing sore fingers can reduce swelling and inflammation and numb the pain until it subsides.
Can osteoarthritis cause sore fingers?
Everyone experiences the occasional painful hands and sore fingers, but when osteoarthritis strikes, it can put a hold on many aspects of your life. "As osteoarthritis progresses, you may lose some hand mobility, like the ability to grasp and hold objects," says Dr. Robert Shmerling, clinical chief of rheumatology at Harvard-affiliated Beth Israel ...
What causes arthritis in the hand?
If the smooth surfaces wear out, then they no longer fit together and arthritis develops. Injury, infection, gout, psoriasis, and other conditions can also cause arthritis of the hand.
How to tell if arthritis is in your hand?
The three most common sites where arthritis happens in the hand are (see Figure 1): 1 At the base of the thumb, where the thumb and wrist come together (the trapeziometacarpal or basilar joint) 2 At the joint closest to the fingertip (the distal interphalangeal or DIP joint) 3 At the middle joint of a finger (the proximal interphalangeal or PIP joint)
What causes a swollen finger?
At the base of the thumb, where the thumb and wrist come together (the trapeziometacarpal or basilar joint) At the joint closest to the fingertip (the distal interphalangeal or DIP joint) All forms of hand arthritis can cause stiffness, swelling, pain, and deformity. Osteoarthritis sometimes causes bony nodules at the middle joint of the finger ...
How to diagnose osteoarthritis?
When diagnosing osteoarthritis, your doctor will ask you about your hands and other joints. Explain how your symptoms affect what you do. Your doctor will check how your hands look and function. X-rays of joints with osteoarthritis can show loss of normal joint space, “bone spurs,” or other changes.
Does steroid injection help with osteoarthritis?
Hand therapists can teach joint protection exercises and activity modification to help protect joints. Anti-inflammatory medication or a steroid injection into the joint can decrease pain, but neither cures osteoarthritis.
What is joint fusion surgery?
One type of surgery is joint fusion. The worn cartilage is removed and the bones on each side of the joint are fused together, which means that the joint will not move but it will not hurt.
Can arthritis hurt your hand?
Arthritis of the hand can hurt and keep you from being able to do what you want or need to do. The most common forms of arthri tis in the hand are osteoarthritis, post-traumatic arthritis (after an injury), and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease in which the smooth cartilage that covers the bone surfaces at ...
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
Over-The-Counter Therapies
- Pain and swelling are hallmarks of all types of osteoarthritis. Among the first-line treatments for these symptoms of OA are products that don't require a healthcare provider's prescription and can be purchased at pharmacies, supermarkets, big box stores, and other venues. 1. Oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): The most common of these areibuprofen (Advil an…
Prescriptions
- When self-treatment and OTC medications don't work well enough, it may take stronger medication to relieve hand osteoarthritis symptoms. In addition to prescription-strength NSAIDs or acetaminophen, these may include: 1. Tramadol, an opioid that's sold as ConZipor Qdolo 2. Cymbalta (duloxetine), a type of antidepressant known as a selective serotonin and norepinephri…
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
- These treatments typically are not considered unless the damage caused to the joints in the hands by OA is severe and less aggressive measures haven't worked. 1. Intra-articular corticosteroid injection involves injecting a steroid medication, which works by relieving inflammation, between the bones of the affected joint. They sometimes are referred to as cortis…
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Included in the ACR/AF recommendations for treating hand osteoarthritis are a couple of CAM options.1 1. Choindroitin is a substance that occurs naturally in cartilage. A manufactured form of chondroitin, chondroitin sulfate, made from animal cartilage, has been touted as useful for treating arthritis.7Although not recommended for hip or knee arthritis, it is conditionally recomm…
A Word from Verywell
- Losing ability and flexibility in your hands due to osteoarthritis is nothing short of frustrating. It can mean you aren't able to do simple and necessary tasks such as opening jars or squeezing lemons; it also can make it difficult to do things you enjoy, like playing the piano or knitting. Therefore, it's vital to see a healthcare provider, preferably a rheumatologist who specializes in a…
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Learn all you can about your condition and how to manage it, especially about how lifestyle changes can affect your symptoms. Exercising and losing weight if you're overweight are important ways to lessen the joint pain and stiffness of osteoarthritis. 1. Exercise. Low-impact exercise can increase your endurance and strengthen the muscles around your joint, making you…
Alternative Medicine
- Complementary and alternative medicine treatments that have shown promise for osteoarthritis include: 1. Acupuncture.Some studies indicate that acupuncture can relieve pain and improve function in people who have knee osteoarthritis. During acupuncture, hair-thin needles are inserted into your skin at precise spots on your body. 2. Glucosamine and chondroitin.Studies ha…
Coping and Support
- Your ability to cope despite pain and disability caused by osteoarthritis often determines how much of an impact osteoarthritis will have on your life. Talk to your doctor if you're feeling frustrated, because he or she may have ideas to help you cope or be able to refer you to someone who can help.
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You might start by seeing your primary care doctor, who might refer you to a doctor who specializes in joint disorders (rheumatologist) or orthopedic surgery.