
Medication
What to know about internal hemangiomas
- Types. Hemangiomas can develop in many internal organs, including the liver and brain. ...
- Treatment. Most internal hemangiomas do not need treatment. ...
- Causes and risk factors. Researchers do not yet know what causes internal hemangiomas. ...
- Diagnosis. While they are uncommon, internal hemangiomas most often occur in the liver and brain. ...
- Takeaway. ...
Procedures
What to do:
- Avoid processed meats like hotdogs, lunch meat, sausages, brats and similar meats.
- Avoid canned and frozen fruits and vegetables and opt for whole foods.
- Rule of thumb: shop the outside of the store and stay out of the center aisles.
Nutrition
People who have a liver hemangioma rarely experience signs and symptoms and typically don't need treatment. It may be unsettling to know you have a mass in your liver, even if it's a benign mass. However, there's no evidence that an untreated liver hemangioma can lead to liver cancer. The liver is your largest internal organ.
See more
To remove a hemangioma through a surgical procedure, an incision must be made to access the mass of blood vessels. The hemangioma tissue is removed through the incision made on the skin surface, then the surgeon stitches up the healthy skin left behind.
What are the different types of treatment for hemangioma?
What are the home remedies for liver haemangioma?
Does hemangioma lead to cancer?
Can you remove a hemangioma?

What is the most common treatment for hemangiomas?
Most hemangiomas that need medical treatment are treated with medicines called beta blockers. Propranolol is a beta blocker (part of a class of drugs used to manage problems in the heart) that is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat infantile hemangioma.
How do you shrink a hemangioma?
Treatments options include:Steroids. These medicines are used to shrink the blood vessels in a hemangioma. ... Propanolol. This treatment works similar to steroids but has fewer side effects. ... Beta blockers. These medicines are sometimes prescribed to help reduce the size of a hemangioma.Laser treatments. ... Surgery.
Do hemangiomas need to be removed?
Because hemangiomas very rarely become cancerous, most do not require any medical treatment. However, some hemangiomas can be disfiguring, and many people seek a doctor's care for cosmetic reasons. In most cases of hemangioma, treatment does not involve surgery.
Can hemangiomas be cured?
Treatments can shrink or remove the growth. Laser surgery can remove a large hemangioma of the skin that's uncomfortable or is causing problems. Laser treatments can also reduce remaining discoloration after a hemangioma has healed.
How do you remove a hemangioma at home?
There is currently no scientific evidence to suggest that home remedies are effective at removing cherry angiomas. People should not try to remove them by cutting them off the skin. They should contact a doctor instead.
Can a dermatologist treat a hemangioma?
While most hemangiomas are harmless, some may require treatment. If a hemangioma interferes with vision, feeding, breathing, or other body functions, or grows exceptionally large or causes pain, it will likely require treatment by a dermatologist.
What kind of doctor removes hemangioma?
The team approach to hemangioma should, at the least, include pediatric dermatology and plastic surgery specialists.
When should I be worried about a hemangioma?
Contact your child's doctor if the hemangioma bleeds, forms a sore or looks infected. Seek medical care if the condition interferes with your child's vision, breathing, hearing or elimination.
What causes hemangiomas to grow?
The female hormone estrogen, which increases during pregnancy, is believed to cause some liver hemangiomas to grow larger. Very rarely, a growing hemangioma can cause signs and symptoms that may require treatment, including pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, abdominal bloating or nausea.
Is hemangioma serious?
These conditions can be life-threatening if they're large or affect your child's airway or another organ. A hemangioma can also be serious if it has uncontrollable bleeding. Depending on where your child's growth is located, it may cause physical problems.
When does a hemangioma stop growing?
About 80 percent of hemangiomas stop growing by about 5 months, Dr. Antaya says. After hitting this plateau phase, they stay unchanged for several months, and then begin to slowly disappear over time (called involution). By the time children reach 10 years of age, hemangiomas are usually gone.
What are the two types of hemangiomas?
The two main types of infantile hemangiomas are:Superficial hemangiomas, or cutaneous ("in-the-skin") hemangiomas, grow on the skin surface. ... Deep hemangiomas grow under the skin, making it bulge, often with a blue or purple tint.
How to tell if you have hemangioma?
Hemangiomas inside the body present with symptoms specific to the organ that’s affected. For example, a hemangioma affecting the gastrointestinal tract or liver may present with symptoms such as: 1 nausea 2 vomiting 3 abdominal discomfort 4 loss of appetite 5 a feeling of fullness in the abdomen
Where do hemangiomas form?
Hemangiomas of the liver (hepatic hemangiomas) form in and on the liver’s surface. These can be related to infantile hemangiomas, or they can be unrelated. The non-infantile hemangiomas of the liver are thought to be sensitive to estrogen.
Does hemangioma go away on its own?
A single, small hemangioma usually requires no treatment. It’ll likely go away on its own. However, some cases may require treatment, such as skin hemangiomas that develop ulcerations or sores, or are in specific areas on the face such as the lip.
Is hemangioma a medical condition?
More often than not, a hemangioma is more of a cosmetic concern than a medical one. Still, you should talk to a healthcare provider if you have any concerns or want to discuss removal.
Can hemangiomas cause symptoms?
Depending on the location and size, hemangiomas don’ t normally cause symptoms during or after their formation. However, they may cause some symptoms if they grow large or in a sensitive area or if there are multiple hemangiomas.
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are one of the most popular medications used for hemangiomas treatment since 2008. Two common types of beta-blocker medicines used are:
Corticosteroid Medication
This medication can be used to reduce the pain and growth of hemangiomas. Corticosteroid is injected into the hemangiomas with the help of a syringe. Patients who do not respond to beta-blockers can opt for corticosteroid injections. Nowadays, they are less frequently used but are highly effective during the first six months of life.
Laser Treatment
Laser treatment can also be used to remove hemangiomas from the surface of the skin. The laser is effective in healing ulcerated hemangiomas and eliminating small blood vessels from the surface of hemangiomas. This option is normally safe and does not have any long-term or significant side effects.
Medicated Gel
This option costs more than all other options because the medicated gel (e.g., Regranex) used in this procedure is expensive. Chronically ulcerated hemangiomas can be treated using medicated gel. Before you try it, you should discuss its side effects with your doctor.
Surgery
A surgical removal is a suitable option when hemangiomas have permanently damaged the tissues, and you are experiencing recurrent bleeding. General anesthesia is used to perform the surgery.
What is the best treatment for hemangioma?
Topical medicine (on the skin rubbed onto the hemangioma). Topical beta blockers: These may help lighten the hemangioma and slow its growth. This works best on smaller, superficial hemangiomas. Topical antibiotic: These are applied when there are open sores with concern for infection. Oral medicine (taken by mouth).
What is a hemangioma?
A hemangioma (hee man jee OH mah) is a common vascular birthmark, made of extra blood vessels in the skin. It is a benign (non-cancerous) growth. The exact cause is not known. Hemangiomas are typically not inherited, but others in the family may also have had them.
How long does it take for hemangioma to fade?
At around 1 year of age, the hemangioma begins to slowly shrink and fade in color. This happens over the next 1 to 10 years. Many go away completely during this time. By the time a child is 5 years old, half of all hemangiomas will be flat and lighter in color. By age 10, many are gone or only faintly visible.
What temperature does hemangioma fever go to?
Fever over 101 degrees Fahrenheit (taken under the arm) Skin looks open or oozes. Skin breaks down (ulcerates) Call your child’s doctor if you have concerns about a hemangioma medicine, such as: You run out of the prescribed oral medicine. Your child refuses to take the medicine.
How to tell if a child has hemangioma?
The doctor can usually look at your child’s skin and tell if there is a hemangioma. If the diagnosis is not clear, an ultrasound scan or MRI test may be needed.
Is hemangioma more common in girls than boys?
The Hemangioma and Vascular Malformations Clinic expertly cares for children with hemangioma. Request an Appointment. Hemangiomas are more common in girls than in boys. They are more common in premature infants, twins and Caucasian children. Most hemangiomas go through several phases of growth.
Where do hemangiomas occur?
Hemangiomas may occur anywhere on the body. Some children may have more than one. There are three main types: Superficia l (on the surface of the skin): These look flat at first, and then become bright red with a raised, uneven surface.
How to treat hemangioma?
At UPMC, we use a combination of stopping blood flow to the tumor (embolization), surgical removal of the tumor, and radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is effective in the treatment of pain caused by hemangiomas.
How common are hemangiomas?
Hemangiomas most often appear in adults between the ages of 30 and 50. They are very common and occur in approximately 10 percent of the world’s population. Most cases show no symptoms. Symptomatic hemangiomas represent less than one percent of all hemangiomas, and are more common in women than in men.
What is the best treatment for pain in the spine?
Ethanol injections with fluoroscopic guidance have also proven effective in treating pain. Another treatment option is embolization followed by removal of the small bones that make up a vertebra ( laminectomy) or removal of the vertebra (vertebrectomy).
Where do hemangiomas occur?
Spinal Hemangioma. Spinal hemangiomas are the most common primary tumor of the spine. These mostly occur in the mid-back and lower-back.
Can MRI show hemangioma?
Hemangioma symptoms. Most hemangiomas are symptom-free, but symptoms may include: Back pain. Pain that radiates along a nerve due to inflammation or irritation of the nerve root. Spinal cord compression. Treatment.
Can hemangioma be left untreated?
If left untreated, symptomatic hemangiomas can cause serious neurological effects. At UPMC, we treat hemangiomas with surgical removal (resection) of the tumor or the affected vertebra, and radiation therapy to treat pain. Ethanol injections and laminectomy may also be performed. Symptoms & Diagnosis. Hemangioma Symptoms and Diagnosis.
What is the treatment for hemangioma?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses powerful energy beams, such as X-rays, to damage the cells of the hemangioma. This treatment is rarely used because of the availability of safer and more effective treatments.
How to treat liver hemangioma?
Treatment options may include: Surgery to remove the liver hemangioma. If the hemangioma can be easily separated from the liver, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the mass.
What doctor can diagnose liver hemangioma?
If it's thought that you have a liver mass, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in the digestive system (gastroenterologist) or one who specializes in the liver (hepatologist).
How to stop blood flow in liver?
Two ways to stop the blood flow are tying off the main artery (hepatic artery ligation) or injecting medication into the artery to block it (arterial embolization). Healthy liver tissue is unharmed because it can draw blood from other nearby vessels. Liver transplant surgery.
Can hemangioma cause liver problems?
In most cases a liver hemangioma will never grow and will never cause problems. Your doctor may schedule follow-up exams to check your liver hemangioma periodically for growth if the hemangioma is large. Liver hemangioma treatment depends on the location and size of the hemangioma, whether you have more than one hemangioma, your overall health, ...
Can you have liver hemangiomas before an appointment?
Write down any symptoms you're experiencing. Most people with liver hemangiomas don't have any signs or symptoms.
Can you leave hemangiomas alone?
Leave alone: Small hemangiomas are best left alone. If they are in an area that is dangerous, like near the eye, we can inject them with steroids, use high potency topical steroids, topical Aldara ( imiquimod) cream or propranalol with some relief.
Can hemangioma be treated with steroids?
A treatable problem: Hemangioma 's prior treatment often involved doing nothing or taking steroids. Small ones not causing functional or cosmetic impairment need nothing . Oral Propranolol is now a fantastic option that works in many cases- it's been revolutionary in managing this problem. This can be given to infants and the earlier it is started, the greater chance the hemangioma won't reach it's maximal growth.
Can hemangioma cause problems?
Usually nothing: Most hemangiomas are an incidental finding and do not cause problems. Usually they remain stable in size and do not grow. It depends on where they may be located, as some may grow or be in a sensitive location. Some rarely will grow large enough to trap platelets. Most of the time a hemangioma can be left alone without consequences.
What are the complications of hemangioma?
Complications depend on the size and location of the hemangioma, and include: Compression (pushing) against surrounding organs such as the stomach (leading to feelings of fullness soon after beginning a meal); bile ducts (leading to jaundice ); or the liver capsule (which causes pain)
How small is a hemangioma?
Small (a few millimeters to 2 centimeters in diameter ) and medium (2 to 5 centimeters) hemangiomas usually do not cause symptoms, but should be followed regularly by a doctor. Such monitoring is needed because about 10% of hemangiomas increase in size over time, for unknown reasons.
How common is liver hemangioma?
How common are liver hemangiomas? Liver hemangioma is the most common benign (non-cancerous) liver tumor, affecting up to 5% of adults in the United States.
What imaging technique can be used to detect liver hemangioma?
The imaging techniques that can single out liver hemangioma from other types of tumors include: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (high-frequency sound waves are sent through body tissues and the echoes are recorded and transformed into video or photos)
Can hemangioma spread to other areas of the body?
Usually, a patient has only one hemangioma, but in some cases there may be more than one. Hemangiomas do not develop into cancer and do not spread to other areas of the body. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
Do hemangiomas need surgery?
Smaller hemangiomas do not need to be treated, but larger hemangiomas may need surgery. Appointments & Access. Contact Us. Overview. Symptoms and Causes. Diagnosis and Tests. Management and Treatment. Prevention. Liver Hemangioma.
What is the most common type of hemangioma?
Types of hemangiomas include: Capillary hemangiomas: The most common type made up of small capillaries normal in size but high in number. Typically bright red. Cavernous hemangiomas: Made up of larger, dilated blood vessels. May appear as a bluish swelling under the skin.
What is a bruise-like hemangioma?
Deep hemangioma. These appear bruise-like or bluish in color and are usually only diagnosed once swelling becomes apparent. Combination hemangioma: These are located under the skin but have a superficial or cutaneous stain on the skin’s surface. Some children have multiple hemangiomas (up to several hundred).
What is the name of the hemangioma that is made up of blood vessels?
Other names: Birth mark; Cavernous hemangioma; Infant hemangioma; Strawberry mark; Strawberry nevus. Hemangiomas are noncancerous growths (tumors) that are made up of blood vessels. There are many different types of hemangiomas and they can occur on the skin, muscle, bone, or internal organs.
What percentage of babies have hemangioma?
Infantile hemangiomas are common, appearing in 4-10% of Caucasian infants. Premature infants and girl babies are more likely than males or Asian infants to develop one. They are rare in African-American babies. Superficial hemangioma: Often referred to as a “strawberry mark”, these are the most common type.
When do infantile hemangiomas appear?
Infantile Hemangiomas. These typically appear on or just under the skin within one to three weeks after birth. They may start off as a faint birthmark on the skin that over a baby’s first two to four months brightens in color and increases in size. This is called the proliferative phase.
Do hemangiomas need to be treated?
Most hemangiomas do not require any treatment because they rarely become cancerous; however, some people may seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Some children’s hospitals specialize in the management of infantile hemangiomas and arguably offer the best advice about treatment.
Can hemangiomas be treated with surgery?
Treatment does not involve surgery in most circumstances, although surgery may be considered for hemangiomas that are deep in the muscle or bone, or if growths on the skin cause problems with vision, breathing or eating.
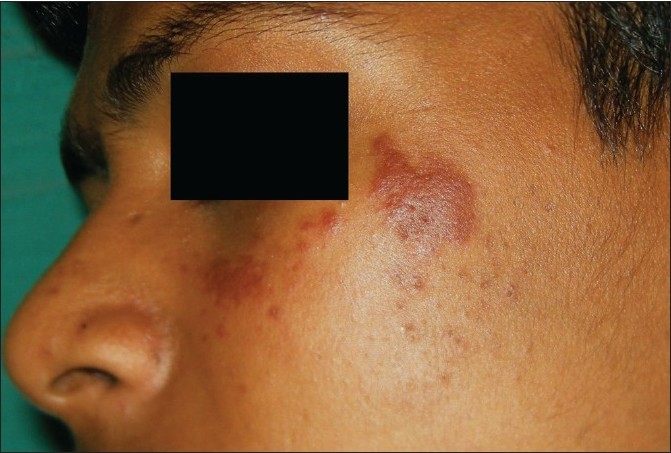
Types of Hemangiomas
Diagnosis
When Treatment Is Needed
Treatment
Specialist to consult
When to Call The Doctor
More Information
- The doctor can usually look at your child’s skin and tell if there is a hemangioma. If the diagnosis is not clear, an ultrasound scan or MRI test may be needed.