
Medication
This is typically in the form of levothyroxine, which is synthetic T4 ( Levothroid, Levoxyl, Synthroid ). Oral medications can restore hormone levels and reverse the symptoms of hypothyroidism, but they must be taken regularly and over the long term. Dosing is adjusted based on blood levels.
Procedures
Jul 17, 2017 · The most common Hashimoto’s treatment is synthetic T4 hormone medication, usually prescribed as the drug Synthroid® or Levoxyl®. Synthroid® is actually the most commonly prescribed drug in America, with 21.6 million prescriptions a month. 1
Nutrition
If Hashimoto’s disease does progress to hypothyroidism, usual treatment is a synthetic (man-made) form of thyroid hormone called levothyroxine (Synthroid®, Tirosint®, Levoxyl®, Levothroid®, Unithroid®).
How I reversed my Hashimoto's disease naturally?
Mar 02, 2018 · Alternative, Integrative and Functional Approach #1. Diet. Diet is perhaps one of the best ways to potentially address immune function and treat Hashimoto's. Not many... #2. Supplements. Certain supplements can also be used to potentially improve thyroid disease and bolster the immune... #3. LDN. ...
Are there any natural treatment for Hashimotos disease?
May 14, 2019 · Building back your gut microbiome with the correct probiotics is a common natural treatment for Hashimoto’s disease. 3. Take Natural Supplements. Your adrenal hormones and thyroid hormones are connected, and most people who suffer from Hashimoto’s disease often experience adrenal fatigue.
How to heal Hashimoto's naturally?
Jan 15, 2022 · Although anyone can develop Hashimoto's disease, it's most common among middle-aged women. The primary treatment is thyroid hormone replacement. Hashimoto's disease is also known as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and chronic autoimmune thyroiditis.
Does Hashimoto's disease go away on its own?
Aug 06, 2021 · For those wishing to overcome their Hashimoto’s symptoms, I always suggest that going gluten, dairy and soy free is the best place to start. Those three foods tend to be the most problematic for people with thyroid conditions, and removing them can often lead to a significant reduction in symptoms.
See more
What is the life expectancy of someone with Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
With early diagnosis, timely institution of levothyroxine replacement therapy, informed patient follow-up care, and attention to other attendant complications, the prognosis in Hashimoto thyroiditis is excellent, with patients leading a normal life.
What makes Hashimoto's disease worse?
Sugar and processed foods can lead to increased inflammation in the body. Inflammation can slow down the conversion of T4 to triiodothyronine, or T3, another thyroid hormone. This can make your symptoms and thyroid disease worsen.Jul 23, 2020
Can Hashimoto's disease be cured?
Treatments for Hashimoto's Thyroiditis. There is no cure for Hashimoto's, but replacing hormones with medication can regulate hormone levels and restore your normal metabolism.Nov 11, 2020
How serious is Hashimoto's disease?
If Hashimoto's is left untreated, complications can be life-threatening. Because the hormones produced by the thyroid are so vital to the body's functions, untreated Hashimoto's can lead to serious and even life-threatening complications.Feb 23, 2018
What foods should you avoid with Hashimoto's?
On the autoimmune protocol diet, you remove all grains, legumes, nightshades (such as eggplant and peppers), dairy, eggs, coffee, alcohol, sugar, oil and food additives from your diet.
What are the stages of Hashimoto's disease?
There are three phases to thyroiditis:Thyrotoxic phase. Thyrotoxicosis means that the thyroid is inflamed and releases too many hormones.Hypothyroid phase. Following the excessive release of thyroid hormones for a few weeks or months, the thyroid will not have enough thyroid hormones to release. ... Euthyroid phase.Oct 26, 2018
What triggers Hashimoto's?
Too much iodine in the diet may function as a trigger among people already at risk for Hashimoto's disease. Radiation exposure. People exposed to excessive levels of environmental radiation are more prone to Hashimoto's disease.Jan 15, 2022
Does Hashimoto's go away if thyroid is removed?
Hashimoto's disease is a thyroid condition that causes the formation of antibodies that attack the thyroid gland. Thyroidectomy reduces thyroid antibody titers by an average of 92 percent, so the symptoms of Hashimoto's go away without a thyroid gland.Mar 2, 2018
Does Hashimoto's shorten life expectancy?
Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT), an inflammatory disorder of the thyroid, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism, but a study has suggested that even when thyroid function is normal, HT may increase symptoms and decrease quality of life.Feb 27, 2011
How does Hashimoto's affect the brain?
Additionally, an unmanaged autoimmune condition causes chronic inflammation. The chronic inflammation that so many Hashimoto's patients struggle with inflames the brain too. This slows down the speed at which the brain operates, makes it function less efficiently and causes it to degenerate more quickly.Jan 5, 2021
What happens if you don't treat Hashimoto's disease?
If left untreated, hypothyroidism caused by Hashimoto disease can lead to serious complications: Goiter, which can interfere with swallowing or breathing. Heart problems such as enlarged heart or heart failure. Mental health issues such as depression, decreased sexual desire, slowed mental functioning.Jan 23, 2022
Can u lose weight with Hashimoto's?
Yes, it is possible to lose weight when you have hypothyroidism, but only if you're willing to change up your diet. Avoid inflammatory foods for weight loss when you have an underactive thyroid, contributing to weight gain.Feb 3, 2020
Ask a Doctor
My mother-in-law was recently diagnosed with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. She started a course of long-term hormone replacement therapy, but I want to make sure she has the best care and is taking the best medicine. What is the best treatment for Hashimoto’s disease?
Doctor's Response
If there is no evidence of hormone deficiency and only antibodies tests are positive, the use of medications is one that must be discussed in detail by the patient and doctor. Other medical conditions, patient preference, and the presence of symptoms are all taken into consideration in determining a treatment plan.
What is the most common medication for Hashimoto's?
The most common Hashimoto’s treatment is synthetic T4 hormone medication, usually prescribed as the drug Synthroid® or Levoxyl®. Synthroid® is actually the most commonly prescribed drug in America, with 21.6 million prescriptions a month. 1
What is the best thyroid medication for hypothyroidism?
Desiccated thyroid medications, such as Amour®, WP Thyroid®, and Nature-Throid®, provide the full range of thyroid hormones, including T4, T3, T2, and T1. This is particularly beneficial for those patients who have difficulty converting T4 to T3. It may also be helpful for hypothyroid patients trying to lose weight.
Why is the T4 to T3 ratio lower?
This is because pigs produce thyroid hormones at different ratios than humans do.
What are the downsides of synthetic medications?
Another downside of synthetic medications is the inactive ingredients used . Thyroid hormones are prescribed in micrograms, so the amount of T4 in each pill is incredibly small. The rest of the pill is composed of inactive ingredients, synthetic colors, and fillers that vary by brand.
What is a T4 tirosint?
Synthroid®, for example, contains lactose and cornstarch. 2 Tirosint is a T4 medication that includes only three inactive ingredients (gelatin, glycerin, and water). It is also produced in a dedicated facility to eliminate the risk of cross-exposure.
What is T3 medication?
There are several types of T3 medication, including preformed, synthetic T3 (frequently prescribed as Cytomel®), and compounded T3 medications, which are custom-prepared at the exact strength and dose requirements of the patient, as specified by their doctor.
Is thyroid medicine the same as immunosuppressant?
I first want to clarify that thyroid medications are not in the same family as harsh drugs and immunosuppressants used to treat other autoimmune conditions. Thyroid medications are a supplemental dose or replacement for a hormone that is necessary for you to live.
How does diet affect Hashimoto's disease?
What you eat and how you eat it can have a big impact on the success of your Hashimoto's disease treatment plan. Dietary changes can potentially improve the overall quality of life for people living with Hashimoto's disease. 2. Numerous studies have investigated the benefits of diet for autoimmune diseases.
What happens when you have Hashimoto's disease?
In Hashimoto's disease, your body makes antibodies to your thyroid hormones and attacks them. This impairs your thyroid's ability to produce hormones, leading to a gradual decline in function and eventually an underactive thyroid.
Why do we avoid eating certain foods?
Certain foods are incorporated or avoided to help reduce autoimmune activity in the body that triggers dysfunction of your thyroid gland. Like autoimmune diets, these diets may require a lot of trial and error, and specific food requirements may vary from person to person. 2.
What vegetables can help with thyroid issues?
Vegetables that fall into this category include broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and kale. The effect that these vegetables can have on your thyroid function is limited. Consuming a lot of these foods is not recommended, but eating them in moderation should not be a problem. 9.
Does iodine affect thyroid?
The thyroid uses iodine, a mineral in some foods, to make thyroid hormones. However, people with Hashimoto’s disease or other types of autoimmune thyroid disorders may be sensitive to the harmful side effects of iodine. Eating foods that have large amounts of iodine, such as kelp, dulse, or other kinds of seaweed, ...
Is Hashimoto's disease an autoimmune disease?
Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes an underactive thyroid, or hypothyroidism. Researchers have started to link the foods we eat to the cause of autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto's and how to treat them. There isn't a specific diet that can help prevent or treat Hashimoto's disease specifically, ...
Does eating a diet help with autoimmune disease?
Numerous studies have investigated the benefits of diet for autoimmune diseases. 3 The focus is usually on eating or avoiding foods that can contribute to inflammation. When there is inflammation in your body, more antibodies are produced, leading to increased autoimmune disease activity.
What is the immune system in Hashimoto's disease?
Hashimoto’s disease is an autoimmune disease, which means the body’s immune system is attacking its own cells and organs. Normally, the immune system protects the body against infections caused by bacteria, viruses and other harmful substances. In Hashimoto’s disease, the immune system makes antibodies that attack and damage the thyroid tissue.
Why does Hashimoto's cause hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto’s hypothyroidism happens when the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough thyroid hormones to meet the body’s needs because its immune system has damaged it . Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, which is how you turn food into energy.
What does a high TSH mean?
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) test: A high TSH level most commonly means the thyroid gland is not producing enough T4 hormone. This lab is usually most consistent with a diagnosis of hypothyroidism or subclinical hypothyroidism. Free T4 test: A low T4 level suggests that the person has hypothyroidism.
What is the name of the condition where the thyroid gland is enlarged?
Some people may not have any symptoms at first. As the disease slowly progresses, the thyroid gland becomes enlarged (a condition called a goiter ). A goiter is a common first sign of Hashimoto’s disease. A goiter is painless, but can create a feeling of fullness in the throat, and can make the front of your neck look swollen.
What is the name of the thyroid gland that controls the body's metabolism?
It’s also called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis or autoimmune thyroiditis. The thyroid gland makes hormones that control virtually all of the body’s metabolic functions (how the body turns food into energy) and keep it working normally. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a type of autoimmune disease — your immune system doesn’t ...
What is the Cleveland Clinic?
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Where is the thyroid gland located?
Overview. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland produces two hormones that control metabolism (how the body turns food into energy) and keep the body working properly.
What is the best treatment for Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
One of the most common recommendations used by integrative physicians to treat Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the use of specific diets such as the AIP diet . The conventional physician would say that this therapy has little to no value because it's "untested".
How to diagnose Hashimoto's?
Other ways to diagnose Hashimoto's include: Presence of thyroid antibodies + Thyroid Symptoms - This is perhaps the most common way to diagnose Hashimoto's.
What is the autoimmune disease of the thyroid gland?
An autoimmune disease is characterized by a dysfunction in your immune system in which it accidentally targets, attacks and destroys your own body tissues . In the case of Hashimoto's this autoimmune target is directed right at the thyroid gland.
Why does EBV cause Hashimoto's?
Certain bacteria and viruses may look similar to existing structures which may be why EBV tends to lead to Hashimoto's more than other viruses. Environmental triggers - Environmental exposure to endocrine disruptions may also increase your risk of developing Hashimoto's thyroiditis (17).
Why is Hashimoto's disease so difficult to diagnose?
Hashimoto's is notoriously difficult to diagnose because the symptoms associated with this disease tend to fluctuate over time and tend to change in severity. This has to do with the progression of the disease and how autoimmunity impacts not only your thyroid but also other tissues in the body.
What does it mean if you have a family history of Hashimoto's?
So if you have a family history of Hashimoto's or thyroid disease it doesn't mean that you will necessarily present with that condition, but it does mean that you are at increased risk. Your risk is then determined by how many environmental factors you are exposed to throughout your life (9).
What diets help with immune system?
Other diets that may be effective for altering immune function include the AIP diet, the ketogenic diet and Whole 30 . Basically, any diet that removes highly processed foods, gluten, sugar, and potential inflammatory fats may reduce your symptoms and help drop your antibodies.
Why is it important to test your gut for Hashimoto's?
Testing your gastrointestinal function is a crucial step to ensure your gut is healthy and not contributing to your Hashimoto’s disease. “It’s important to ensure patients have the right probiotics onboard and that they are not harboring any infections they didn’t previously know about,” says Dr. Gore.
How do you know if you have Hashimoto's disease?
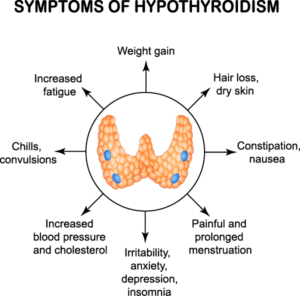
Have you noticed your hair is thinning, you’re perpetually exhausted, your face is puffy, and you can’t stand going out in the cold? These are all signs that you might be experiencing hypothyroidism, specifically Hashimoto’s disease.#N#Hashimoto’s disease is an autoimmune disorder, also called chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, in which your antibodies attack healthy thyroid tissue and hamper the function of your thyroid gland. When your thyroid gland isn’t producing an adequate amount of certain hormones, you can start experiencing a host of unwanted symptoms, including:
What happens if your thyroid isn't producing enough hormones?
When your thyroid gland isn’t producing an adequate amount of certain hormones, you can start experiencing a host of unwanted symptoms, including: Fatigue. Weight gain. Sensitivity to cold. Brain fog. Constipation and bloating. Dry skin. Depression and/or anxiety.
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto’s disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism, responsible for approximately 90 to 95% of cases in the United States. Luckily, when you work with one of our functional medicine or holistic practitioners, you can implement several changes to your diet and lifestyle to naturally improve your thyroid function and combat ...
Where does T3 take place?
Most of it must be converted to T3, a more biologically active form of the hormone, for proper thyroid health, and 20% of this conversion takes place in your gut. If your gut microbiome has been damaged, this process may be disrupted.
Does gluten help with Hashimoto's?
Going gluten- and dairy-free has also been shown to improve the lives of people with Hashimoto’s disease. The connection between gluten and thyroid disorders is well established. The protein portion of gluten, called gliadin, has a molecular structure that is almost identical to that of the thyroid gland, and the same reaction ...
Does Hashimoto's cause adrenal fatigue?
Your adrenal hormones and thyroid hormones are connected, and most people who suffer from Hashimoto’s disease often experience adrenal fatigue.#N #If you come into the Center with Hashimoto’s disease, you will be tested for vitamin and mineral deficiencies, which can detect naturally low levels of vitamins, such as the B vitamins, magnesium and vitamin C in your body that help support your adrenals.#N#Then, once your levels are determined, your doctor may recommend you take supplements to get your adrenal hormones and thyroid hormones working properly. “For people with Hashimoto’s, zinc and selenium and iodine are really important supplements,” Dr. Gore says.
When does Hashimoto's disease occur?
Hashimoto's disease can occur at any age but more commonly occurs during middle age. Heredity. You're at higher risk for Hashimoto's disease if others in your family have thyroid or other autoimmune diseases. Other autoimmune disease.
How does Hashimoto's disease affect thyroid?
Hashimoto's disease typically progresses slowly over years and causes chronic thyroid damage, leading to a drop in thyroid hormone levels in your blood. The signs and symptoms are mainly those of an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism). Signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism include: Fatigue and sluggishness. Increased sensitivity to cold.
Why do I get goiters?
Goiter. Constant stimulation of your thyroid to release more hormones may cause the gland to become enlarged, a condition known as a goiter. Hypothyroidism is one of the most common causes of goiters. It's generally not uncomfortable, but a large goiter can affect your appearance and may interfere with swallowing or breathing.
What causes a virus to attack the thyroid gland?
Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disorder in which your immune system creates antibodies that damage your thyroid gland. Doctors don't know what causes your immune system to attack your thyroid gland. Some scientists think a virus or bacterium might trigger the response, while others believe a genetic flaw may be involved.
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism?
The thyroid gland is part of your endocrine system, which produces hormones that coordinate many of your body's functions. Inflammation from Hashimoto's disease , also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, often leads to an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism). Hashimoto's disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism.
What are the symptoms of a coma?
Its signs and symptoms include drowsiness followed by profound lethargy and unconsciousness. A myxedema coma may be triggered by exposure to cold, sedatives, infection or other stress on your body. Myxedema requires immediate emergency medical treatment. Birth defects.
Where is the thyroid gland located?
Thyroid gland. Your thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck, just below the Adam's apple. Hashimoto's disease is a condition in which your immune system attacks your thyroid, a small gland at the base of your neck below your Adam's apple. The thyroid gland is part of your endocrine system, which produces hormones that coordinate many ...
What are the causes of Hashimoto's disease?
Look for infections, periods of severe stress, the use of medications (especially antibiotics, antacids, and oral contraceptives), accidents, and exposure to toxins. These are events that may have contributed to Hashimoto’s.
What foods can prevent a leaky gut?
Prevent the gut from healing: Non-meat protein sources such as legumes (beans), dairy, grains, soy, nuts, and sometimes seeds, may prevent the healing of a leaky gut, as these foods are often found to be reactive in Hashimoto’s and can perpetuate intestinal permeability.
What are the benefits of being vegan?
Reported health benefits of a vegan diet include weight loss, improved kidney function, possible protection against cancer, and a reduced risk of heart disease.
What is fermented food?
Fermented foods – Fermentation is a process of food preservation that produces probiotics, or “good bacteria,” that can balance intestinal flora. I recommend that you buy fermented foods, like sauerkraut, that require refrigeration, as probiotic bacteria can only survive a couple of weeks at room temperature.
Does iodine cause Hashimoto's?
While iodine is essential for thyroid function, excessive amounts can exacerbate Hashimoto’s. Today, with iodized salt being prevalent in most countries, iodine excess is recognized as a risk factor for developing Hashimoto’s! (Read more about the iodine and Hashimoto’s controversy and foods high in iodine.)
Can carbs cause weight gain?
Not only are carbs not required, they’re also the greatest contributor to blood sugar imbalances — which up to 50 percent of those with Hashimoto’s may have! These imbalances can contribute to anxiety, weight gain, hair loss, irritability, weakened adrenals, fatigue, and increased thyroid antibodies.
Is the root cause diet one size fits all?
The Root Cause Intro (eliminating dairy/soy/gluten), Paleo, Autoimmune Paleo, and Root Cause Autoimmune diets have all been successful for many people with Hashimoto’s, but no diet is one-size-fits-all. You will need to tailor your diet to your own needs by removing any personally reactive foods.

Benefits
How It Works
Considerations
Hashimoto's vs. Other Diets
Specialist to consult
A Word from Verywell
- Treatment for Hashimoto's disease may include observation and use of medications. If there's no evidence of hormone deficiency, and your thyroid is functioning normally, your doctor may suggest a wait-and-see approach. If you need medication, chances are you'll need it for the rest …