
Explore
Treatment
- Medications. Doctors usually treat heart failure with a combination of medications. ...
- Surgery and medical devices. In some cases, doctors recommend surgery to treat the underlying problem that led to heart failure.
- Palliative care and end-of-life care. Your doctor may recommend including palliative care in your treatment plan. ...
How can you treat diastolic heart failure with medication?
Treatment and Prevention
- Lifestyle. Quit smoking: If you need nicotine patches to succeed, make it temporary, and slowly taper down the dosage to zero.
- Medications. Medications for conditions that put you at risk for diastolic dysfunction include those to control diabetes, blood pressure, LDL and HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and obesity.
- A Word From Verywell. ...
What is the best medication for diastolic dysfunction?
a. Patients with diastolic dysfunction do not tolerate AF and fast ventricular response. Aim for a resting HR between 60-70bpm to increase diastolic filling time and thus potentially symptoms. Use either cardio-selective beta-blockers (e.g. Bisoprolol) or non-dihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers (e.g. Diltiazem). b.
How to treat Grade 1 diastolic dysfunction?
The 10-year survival rate for those with isolated diastolic HF was 57%. In univariate Cox regression analysis, significant associations were found for overall HF, isolated systolic HF, combined HF, and all-cause mortality, but not for isolated diastolic HF (Table 3).
What is the mortality rate for diastolic heart failure?

Can you improve diastolic heart failure?
In addition to dietary changes, high blood pressure can be treated with medications called diuretics. These drugs have been shown to effectively help manage diastolic heart failure by removing excess sodium and fluid from the body.
What medication is used for diastolic heart failure?
Treatments for diastolic failure have included diuretics, ACEIs, ARBs, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, and statins. ACE inhibitors, propranolol, and statins reduce mortality in patients with diastolic heart failure.
What is the most common cause of diastolic heart failure?
HYPERTENSION. Chronic hypertension is the most common cause of diastolic dysfunction and failure. It leads to left ventricular hypertrophy and increased connective tissue content, both of which decrease cardiac compliance.
How do you reverse diastolic dysfunction?
Exercise training, initiated at an advanced age, reverses age-related diastolic and microvascular dysfunction; these data suggest that late-life exercise training can be implemented to improve coronary perfusion and diastolic function in the elderly.
Can diastolic dysfunction get better?
Although diastolic heart failure can't be cured, treatment can help ease symptoms and improve the way your heart pumps.
What is the life expectancy with diastolic dysfunction?
Conclusions: Our study results indicate that diastolic dysfunction with a normal EF, in the absence of CAD and systolic dysfunction, has an excellent prognosis over a long period (5-6 years).
How long can you live with diastolic CHF?
In general, about half of all people diagnosed with congestive heart failure will survive five years. About 30% will survive for 10 years. In patients who receive a heart transplant, about 21% of patients are alive 20 years later.
Is diastolic heart failure a death sentence?
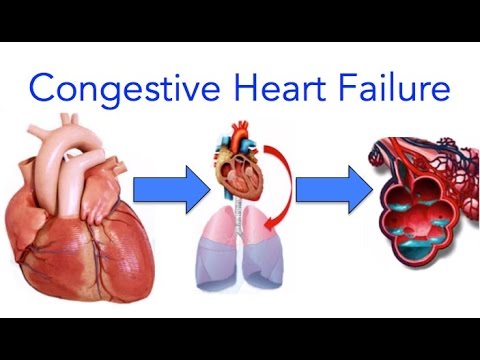
Although it can be a severe disease, heart failure is not a death sentence, and treatment is now better than ever. When this happens, blood and fluid may back up into the lungs (congestive heart failure), and some parts of the body don't get enough oxygen-rich blood to work normally.
Should I be worried about diastolic dysfunction?
When your heart isn't able to relax fast enough, it's called diastolic dysfunction (DD). DD is dangerous and is believed to be associated with congestive heart failure symptoms in patients who have what's called preserved left ventricular ejection fraction, according to cardiologist Wael Jaber, MD.
What medications treat diastolic hypertension?
What medications treat diastolic hypertension?Calcium channel blockers. Norvasc (amlodipine) ... Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Prinivil, Zestril (lisinopril) ... Water pills or diuretics. Chlorthalidone. ... Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) Atacand (candesartan) ... Beta-blockers. Tenormin (Atenolol)
How do beta blockers help diastolic heart failure?
Beta-blockers are drugs that can slow your heart rate and keep it from overworking. They also can stop your heart from responding to stress hormones, such as adrenaline. Over time, beta-blockers may help your heart pump better.
What is the procedure to open a blocked diastolic artery?
If a blocked blood vessel is contributing to your diastolic heart failure, you may benefit from angioplasty. This is a procedure in which a small balloon is inflated in the blocked portion of the artery, opening it wider for improved blood flow. In some cases, a flexible mesh tube called a stent is left in place to help keep the artery open.
What is heart failure?
Heart failure is a broad term that describes several conditions when the heart has weakened and is no longer efficiently pumping blood to the rest of the body.
What is the ejection fraction of a heart?
A healthy heart usually has an ejection fraction of between 50 and 70 percent. HFpEF may be diagnosed with an ejection fraction of 40 to 49 percent. The ejection fraction could be higher in some cases of diastolic heart failure, but in those cases, the left ventricle isn’t filling with as much blood as it normally should.
What happens when the left ventricle doesn't relax enough?
Diastolic heart failure occurs when the left ventricle can’t relax enough to fill with a sufficient amount of blood, or does so at higher pressures. So when the heart beats, a smaller-than-normal amount of blood is pumped out to the body. Over time, organs can suffer from a reduced flow of oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood and higher filling pressures.
How long do people with heart failure live?
Some estimates suggest that about half of the people with heart failure will live for at least 5 years after diagnosis, while about 30 percent live at least 10 years.
Is diastolic heart failure a cure?
Recognizing the early symptoms of diastolic heart failure is critical in starting treatment before the heart weakens further. Although heart failure is a serious condition with no current cure, improvements in medications and medical technology have improved the outlook for many people facing this condition.
Does spironolactone help with heart failure?
A 2020 journal article reported that the diuretic spironolactone, when added to other blood pressure-lowering drugs, improved outcomes for people with diastolic heart failure and resistant hypertension.
What are the best treatments for diastolic heart failure?
As researchers search for the best treatments for diastolic heart failure, controlling blood pressure and fluid in the body are key strategies; heart-protecting drugs may be helpful.
How to tell if you have diastolic or systolic heart failure?
The main way to distinguish one type from the other is with an echocardiogram. It can show the size and shape of the left ventricle and gauge how it is functioning. It can also determine ejection fraction — the percentage of blood in the filled left ventricle that is pumped out during a contraction.
What does diastolic heart failure feel like?
Diastolic heart failure looks and feels just like systolic heart failure. Its hallmarks are shortness of breath with exertion or when lying down; swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen; unexplained fatigue; or a bulging jugular vein. The main way to distinguish one type from the other is with an echocardiogram.
Why is the ventricle restricted?
Open space inside the ventricles can be restricted by heart muscle that "bulks up" due to overwork or other causes, or that stiffens and loses its flexibility.
Which heart failure is weak and flabby?
Diastolic heart failure, in which the left ventricle stiffens and bulks up, is different from systolic heart failure, in which the left ventricle becomes weak and flabby.
How to treat a clogged heart?
Treatments the heart groups suggest might work include angioplasty or bypass surgery when blood flow through cholesterol-clogged coronary arteries hampers heart function, and the use of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, or calcium-channel blockers to help ease symptoms. Watching salt and fluid intake, as well as regular exercise, may also help.
What are the two phases of heartbeat?
Every heartbeat has two distinct phases. During systole (SIS-tuh-lee), cardiac muscle fibers contract in unison. This makes the heart twist a bit and close in on itself, propelling blood to the lungs and the body. During diastole (die-AS-tuh-lee), the muscle fibers relax and stretch.
How can doctors correct heart failure?
Doctors sometimes can correct heart failure by treating the underlying cause. For example, repairing a heart valve or controlling a fast heart rhythm may reverse heart failure. But for most people, treatment of heart failure involves a balance of the right medications and, sometimes, use of devices that help the heart beat and contract properly.
What does a doctor do if you have a heart failure?
The doctor may examine the veins in your neck and check for fluid buildup in your abdomen and legs.
What is the purpose of an echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram can be used to measure ejection fraction, which shows how well the heart is pumping and helps classify heart failure and guides treatment. Stress test.
How to make your heart beat faster?
Stop smoking. Smoking damages your blood vessels, raises blood pressure, reduces the amount of oxygen in your blood and makes your heart beat faster.
How to diagnose heart failure?
To diagnose heart failure, your doctor will take a careful medical history, review your symptoms and perform a physical examination. Your doctor will also check for the presence of risk factors, such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease or diabetes.
What is a stress test for a heart?
Sometimes a stress test is done while wearing a mask that measures how well the heart and lungs get oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan. In a cardiac CT scan, you lie on a table inside a doughnut-shaped machine.
Is heart failure a chronic disease?
Heart failure is a chronic disease needing lifelong management. However, with treatment, signs and symptoms of heart failure can improve, and the heart sometimes becomes stronger. Treatment may help you live longer and reduce your chance of dying suddenly.
What happens when you have diastolic heart failure?
Rehabilitation by Stage . If you have diastolic heart failure, your left ventricle has become stiffer than normal. Because of that, your heartcan't relax the way it should. When it pumps, it can't fill up with bloodas it's supposed to. Because there's less blood in the ventricle, less blood is pumped out to your body.
Why is diastolic heart failure more common as you get older?
So diastolic heart failure is more common as people get older. Other than normal aging, the most common causes are: High blood pressure : If you have it, your heart has to work harder to pump more blood through your body.
Why is my left ventricle stiff?
Because of that, your heart can't relax the way it should. When it pumps, it can't fill up with blood as it's supposed to. Because there's less blood in the ventricle, less blood is pumped out to your body.
What is the term for the amount of blood flowing to your heart muscle that is blocked or less than normal?
Coronary artery disease: The amount of blood flowing to your heart muscle is blocked or less than normal. Find out more about the different types of cardiovascular diseases.
What causes the wall of the heart to thicken?
Diabetes: The disease can cause the wall of your heart to thicken. That makes it stiffen. Read more on how diabetes affects your heart. Coronary artery disease: The amount of blood flowing to your heart muscle is blocked or less than normal.
Can diastolic heart failure be cured?
Although diastolic heart failure can't be cured, treatment can help ease symptoms and improve the way your heart pumps.
What can you do about heart failure?
Heart failure caused by damage to the heart that has developed over time can’t be cured. But it can be treated, quite often with strategies to improve symptoms.
Clinical trials
Clinical trials are scientific studies that determine if a possible new medical advance can help people and whether it has harmful side effects.
Lifestyle Management
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
- Diastolic dysfunction that does respond to lifestyle changes and medication may require more aggressive—and sometimes invasive—treatment. Cardioversion Atrial fibrillation (AFib)—an abnormally fast and irregular heartbeat—is a common characteristic of diastolic dysfunction,21 and one that can cause heart palpitations, shortness of breath, and a tendency to become easil…
A Word from Verywell
- Diastolic dysfunction is a potentially serious diagnosis, but there are many ways in which you can prevent the condition from progressing or causing symptoms that affect your ability to function. Tweaks to your diet, an increase in your activity level, quitting smoking (if you use tobacco), and cutting back on alcohol if your intake is beyond moderate are all straightforward and effective c…
Causes
Pathophysiology
- Aging takes some of the spring out of the muscles in the heart. High blood pressure, cholesterol-clogged coronary arteries, muscle damage from a heart attack, a malfunctioning heart valve, diabetes, anemia, an overactive thyroid gland, and other problems can also stiffen heart muscle and bulk up the muscle inside the left ventricle.
Symptoms
- Diastolic heart failure looks and feels just like systolic heart failure. Its hallmarks are shortness of breath with exertion or when lying down; swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen; unexplained fatigue; or a bulging jugular vein. The main way to distinguish one type from the other is with an echocardiogram. It can show the size and shape of the left ventricle and gauge how it is functio…
Terminology
- A low ejection fraction (under 35% or so) with symptoms equals systolic heart failure; a normal ejection fraction with symptoms equals diastolic heart failure.
Treatment
- The big problem with diastolic heart failure is that doctors don't yet know the best way to treat it. Therapies proven to work for systolic heart failure (characterized by a thin, flabby left ventricle) don't necessarily work for diastolic heart failure (characterized by a thick, stiff left ventricle). Scores of clinical trials investigating possib...
Contraindications
- In the meantime, the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology recommend controlling:
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Heart failure is a chronic disease needing lifelong management. However, with treatment, signs and symptoms of heart failure can improve, and the heart sometimes becomes stronger. Doctors sometimes can correct heart failure by treating the underlying cause. For example, repairing a heart valve or controlling a fast heart rhythm may reverse heart failure. But for most people, trea…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Making lifestyle changes can often help relieve signs and symptoms of heart failure and prevent the disease from worsening. These changes may be among the most important and beneficial you can make: 1. Stop smoking. Smoking damages your blood vessels, raises blood pressure, reduces the amount of oxygen in your blood and makes your heart beat faster...
Coping and Support
- Proper heart failure treatment can sometimes improve symptoms and help you live longer. You and your doctor can work together to help make you most comfortable. Pay attention to your body and how you feel, and tell your doctor when you're feeling better or worse. This way, your doctor will know what treatment works best for you. These steps may help you manage heart failure: 1. …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you think you may have heart failure or you are worried about your heart failure risk because of other underlying conditions, make an appointment with your family doctor. If heart failure is found early, your treatment may be easier and more effective. Because appointments can be brief and there's often a lot to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared for your appointment. Here's some i…